STL算法部分主要是由三个头文件承担:<algorithm>、<numeric>、<functional>
1.<algorithm>:意思是算法,只要想使用STL库中的算法函数就得包含该头文件。
2.<numeric>:该头文件包含了一系列用于计算数值序列的算法,由于其具有一定的灵活性,它也能够适用于其它非数值序列的计算
3.<functional>:定义了一些模板,可以用来声明函数对象。
STL库中的算法大致可以分为四类:
1.非可变序列算法:算法不修改容器元素的值或顺序。如:for_each,先行查找,子序列匹配,元素个数,元素比较,最大与最小值。
2.可变序列算法:算法要修改容器元素的值或顺序。例如:复制、填充、交换、替换、生成等
3.排序算法:包括排序、二分查找、归并排序、堆排序、有序查找等。
4.数值算法:包括向量运算、复数运算、求和、内积等。
一、非可变序列算法及相关举例:
1.循环函数:
(1)for_each:对每一个元素执行相同的指针操作,并返回函数对象。
2.查询函数:
(1)find():返回 元素值=指定值 的首次出现的位置。
(2)find_of():找到符合指定谓词的首次出现的位置,并返回该位置。
(3)find_first_of():在序列中找出第一次出现 元素值=指定值之一 的位置。
(4)adjacent_find():找到第一次两个相邻元素相等的元素的位置,并返回该位置。
(5)find_end():返回指定子序列在该序列中最后出现的位置。
(6)search():返回指定子序列第一次出现的位置。
(7)search_n():返回 指定值连续出现指定次数 的第一个位置。
3.计数函数:
(1)count():返回 指定值在序列中出现的次数。
(2)count_if():返回在[first, last)范围内满足特定条件的元素的数目。
4.比较函数:
(1)equal():若两个序列的元素对应相等,则返回true,否则返回false。
(2)mismatch():返回两个序列开始出现不同的第一个位置。
(3)min_element():返回序列当中第一个最小值元素的位置。
(4)max_element():返回序列当中第一个最大值元素的位置。
一些举例:
1.find函数:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int num_to_find = 6;
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), num_to_find);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到匹配元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "匹配元素的索引值是:" << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
system("pause");
}运行结果:
1.find_if函数:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
bool func(int x) //找到能被5整除的数
{
if (x % 5 == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void main()
{
vector<int> v(20);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
v[i] = i+1;
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), func);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到匹配元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第一个能被5整除的数的索引值是:" << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
system("pause");
}
3.count函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v(20);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
v[i] = (i + 1)*(i + 3);
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
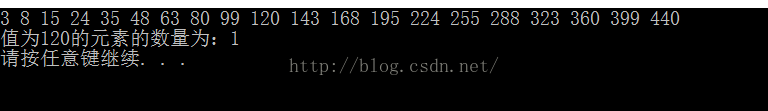
cout << "值为120的元素的数量为:" << count(v.begin(), v.end(), 120) << endl;
system("pause");
}4.count_if函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool func(int x)
{
if (x % 5 == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void main()
{
vector<int> v(20);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
v[i] = (i + 1)*(i + 3);
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
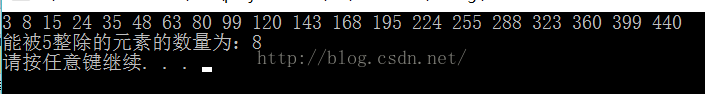
cout << "能被5整除的元素的数量为:" << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), func) << endl;
system("pause");
}运行结果:
4.search函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v1;
cout << "v1序列:";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 5);
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v2;
cout << "v2序列:";
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
v2.push_back(i + 7);
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = search(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end());
if (it != v1.end())
{
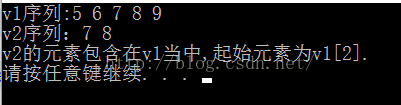
cout << "v2的元素包含在v1当中,起始元素为v1[" << it - v1.begin() << "]." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v2的元素不包含在v1当中" << endl;
}
system("pause");
}运行结果:
4.search_n
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(8);
v.push_back(8);
v.push_back(8);
v.push_back(7);
v.push_back(2);
cout << "v序列:";
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = search_n(v.begin(), v.end(), 3, 8);//找到连续出现3个8的第一个位置
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << "连续出现3个8的起始位置是:" << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有连续出现3个8" << endl;
}
system("pause");
}运行结果:
4.find_end
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(-5);
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(-6);
v1.push_back(-8);
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(-11);
cout << "v1序列:";
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.push_back(1);
v2.push_back(2);
cout << "v2序列:";
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++)
{
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = find_end(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end());
if (it != v1.end())
{
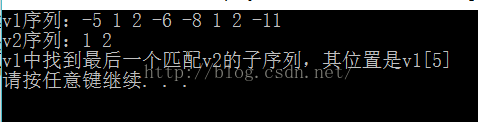
cout << "v1中找到最后一个匹配v2的子序列,其位置是v1[" << it - v1.begin() << "]" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有在v1中找到最后一个匹配v2的子序列" << endl;
}
system("pause");
}运行结果:
二、可变序列算法和举例
1.copy函数
函数原型:copy(v1.begin(),v1.end(),l.begin()):将v1当中的所有序列都复制进l当中
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(5);
list<int> l;
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(4);
l.push_back(6);
l.push_back(8);
l.push_back(10);
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), l.begin());
list<int>::iterator it;
for (it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}运行结果:
1.transform函数
函数原型:transform(v.begin(),v.end(),l.begin(),func):将v中的元素按照func所描述的方式转换到l中。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int func(int x)
{
return x*x;
}
void main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(5);
list<int> l;
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(4);
l.push_back(6);
l.push_back(8);
l.push_back(10);
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), l.begin(),func);
list<int>::iterator it;
for (it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}
3.replace函数
函数原型replace(v.begin(),v.end(),num1,num2):将序列v中的num1替换为num2.
4.replace_if函数
函数原型:replace(v.begin(),v.end(),func,num):将序列v中所有符合函数func所描述的数字全部替换成num。
5.fill_n函数
函数原型:fill_n(v.begin(),v.end(),num1,num2):从v.begin()这个位置开始,添加num1个数字num2(会覆盖原来的数据)。
6.generate_n函数:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
vector<int> v(10);
generate_n(v.begin(), 5, rand);
vector<int>::iterator it;
for (it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}运行结果:
7.remove_if函数:
函数原型:remove_if(v.begin(),v.end(),func):删除序列v中符合func条件的元素。
8.unique函数:
函数原型:unique(v.begin(),v.end()):将序列v中的元素去重。


























 1259
1259











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








