| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 9977 | Accepted: 4243 |
Description
A robot crashes with a wall if it attempts to move outside the area of the warehouse, and two robots crash with each other if they ever try to occupy the same spot.
Input
The second line contains two integers, 1 <= N, M <= 100, denoting the numbers of robots and instructions respectively.
Then follow N lines with two integers, 1 <= Xi <= A, 1 <= Yi <= B and one letter (N, S, E or W), giving the starting position and direction of each robot, in order from 1 through N. No two robots start at the same position.
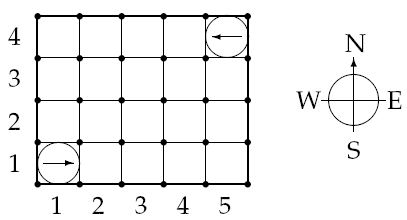
Figure 1: The starting positions of the robots in the sample warehouse
Finally there are M lines, giving the instructions in sequential order.
An instruction has the following format:
< robot #> < action> < repeat>
Where is one of
- L: turn left 90 degrees,
- R: turn right 90 degrees, or
- F: move forward one meter,
and 1 <= < repeat> <= 100 is the number of times the robot should perform this single move.
Output
- Robot i crashes into the wall, if robot i crashes into a wall. (A robot crashes into a wall if Xi = 0, Xi = A + 1, Yi = 0 or Yi = B + 1.)
- Robot i crashes into robot j, if robots i and j crash, and i is the moving robot.
- OK, if no crashing occurs.
Only the first crash is to be reported.
这题就是纯模拟,当然由于我初始化的习惯问题还是WA了一发。
开一个dir数组记录走不同方向的单位坐标变化量,0,1,2,3对于N,E, S, W四个方向, 变化方向时只需要改变将方向值控制在0,1,2,3就行。
用一个book数组记录这个点上是否存在机器人,如果存在机器人,记录编号,用以判断两个机器人是否会撞上。
由于我之前初始化是用for循环每次初始化到边境a,b。如果下一次循环的ab小于上一次的话,可能导致当判断机器人出界时,因为先判断是否撞上机器人,再判断墙,所以上一次超过本次边界而没被初始化的点可能有book值残余,导致判断为与机器人相撞了,而实际应该是撞墙。
所以能用memset还是用memset啊。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2]={{0,1}, {1,0}, {0,-1}, {-1,0} };
int book[105][105];
struct p
{
int x;
int y;
int d;
}c[105];
int main()
{
int a,b;
int n,m;
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
int j,i;
memset(book, 0, sizeof(book));
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
char x,q;
scanf("%d%d%c%c", &c[i].x, &c[i].y,&q, &x);
book[c[i].x][c[i].y]=i;
if(x=='N')c[i].d=0;
if(x=='E')c[i].d=1;
if(x=='S')c[i].d=2;
if(x=='W')c[i].d=3;
}
int flag=1, w=0,o,p;
for(i=0; i<m; i++)
{
int k, time;
char x,r;
scanf("%d%c%c%d", &k, &r, &x, &time);
if(flag)
{
if(x=='L')
{
time%=4;
c[k].d-=time;
c[k].d+=4;
c[k].d%=4;
}
if(x=='R')
{
time%=4;
c[k].d+=time;
c[k].d%=4;
}
if(x=='F')
{
for(j=0; j<time; j++)
{
book[c[k].x][c[k].y]=0;
c[k].x+=dir[c[k].d][0];
c[k].y+=dir[c[k].d][1];
if(book[c[k].x][c[k].y]>0)
{
flag=0;
w=2;
o=k;
p=book[c[k].x][c[k].y];
break;
}
book[c[k].x][c[k].y]=k;
if(c[k].y>b || c[k].y<1 || c[k].x>a || c[k].x<1)
{
flag=0;
w=1;
o=k;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
if(flag)printf("OK\n");
else if(w==1)printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall\n", o);
else if(w==2)printf("Robot %d crashes into robot %d\n", o, p);
}
return 0;
}
























 489
489











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








