<?xml ="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayoutxmlns:android
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android=""
apk=""
res=""
schemas.android.com=""
http:="" >
<!-- 添加一个ListView控件 -->
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
<LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>一个 ListView通常有两个职责。
(1)将数据填充到布局。
(2)处理用户的选择点击等操作。
第一点很好理解,ListView就是实现这个功能的。第二点也不难做到,在后面的学习中读者会发现,这非常简单。
一个ListView的创建需要3个元素。
(1)ListView中的每一列的View。
(2)填入View的数据或者图片等。
(3)连接数据与ListView的适配器。
也就是说,要使用ListView,首先要了解什么是适配器。适配器是一个连接数据和AdapterView(ListView就是一个典型的AdapterView,后面还会学习其他的)的桥梁,通过它能有效地实现数据与AdapterView的分离设置,使AdapterView与数据的绑定更加简便,修改更加方便
Android中提供了很多的Adapter,表4-5列出了常用的几个。
表4-5 常用适配器
| Adapter | 含义 |
| ArrayAdapter<T> | 用来绑定一个数组,支持泛型操作 |
| SimpleAdapter | 用来绑定在xml中定义的控件对应的数据 |
| SimpleCursorAdapter | 用来绑定游标得到的数据 |
| BaseAdapter | 通用的基础适配器 |
其实适配器还有很多,要注意的是,各种Adapter只不过是转换的方式和能力不一样而已。下面就通过使用不同的Adapter来为ListView绑定数据(SimpleCursorAdapter暂且不讲,后面讲SQLite时会介绍)。
4.12.1 ListView使用ArrayAdapter
用ArrayAdapter可以实现简单的ListView的数据绑定。默认情况下,ArrayAdapter绑定每个对象的toString值到layout中预先定义的TextView控件上。ArrayAdapter的使用非常简单。
实例:
工程目录:EX_04_12
在布局文件中加入一个ListView控件。
<?xml ="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayoutxmlns:android
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android=""
apk=""
res=""
schemas.android.com=""
http:="" >
<!-- 添加一个ListView控件 -->
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
<LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
然后在Activity中初始化。
publicclass MyListView extends Activity { privatestaticfinal String[] strs = new String[] { "first", "second", "third", "fourth", "fifth" };//定义一个String数组用来显示ListView的内容private ListView lv;/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv);//得到ListView对象的引用 /*为ListView设置Adapter来绑定数据*/
lv.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, strs)); } }
▲图4-29 ListView使用ArrayAdapter运行效果
代码非常的简单,运行效果如图4-29所示。
分析一下使用的步骤。
(1)定义一个数组来存放ListView中item的内容。
(2)通过实现ArrayAdapter的构造函数来创建一个ArrayAdapter的对象。
(3)通过ListView的setAdapter()方法绑定ArrayAdapter。
其中第二步有必要说一下的是,ArrayAdapter有多个构造函数,例子中实现的是最常用的一种。第一个参数为上下文,第二个参数为一个包含TextView,用来填充ListView的每一行的布局资源ID。第三个参数为ListView的内容。其中第二个参数可以自定义一个layout,但是这个layout必须要有TextView控件。通常我们使用Android提供的资源,除了例子中所用的,常用的还有如下几种,可实现带RadioButton和CheckBox的ListView。
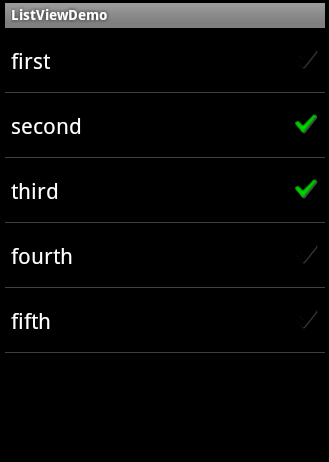
(1)通过指定android.R.layout.simple_list_item_checked这个资源,实现带选择框的ListView。需要用setChoiceMode()方法设定选择为多选还是单选,否则将不能实现选择效果,运行效果如图4-30所示。
实现代码如下:
lv.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_checked, strs)); lv.setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_MULTIPLE);
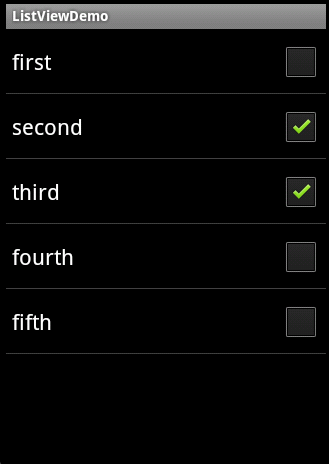
(2)通过指定android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice这个资源实现带CheckBox的ListView。同样的,需要用setChoiceMode()方法来设置单选或者多选,运行效果如图4-31所示。
实现代码如下:
lv.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_multiple_choice, strs)); lv.setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_MULTIPLE);
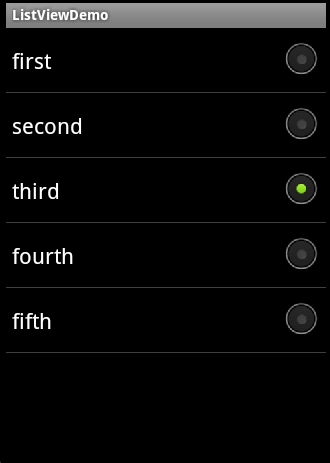
(3)通过指定android.R.layout.simple_list_item_single_choice这个资源实现带RadioButton的ListView。这里要注意的是,这里并不是指定了单选。是多选还是单选要通过setChoiceMode()方法来指定,运行效果如图4-32所示。
实现代码如下:
lv.setAdapter(newArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_single_choice,strs));
lv.setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_SINGLE);
▲图4-30 带选择框的ListView ▲图4-31 带CheckBox的ListView ▲图4-32 带RadioButton的ListView
在前面讲到过,ListView的职责除了填充数据外,还要处理用户的操作。通过如下的代码就可以为ListView绑定一个点击监听器,点击后在标题栏显示点击的行数。
lv.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() { @Override publicvoid onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2, long arg3) { //点击后在标题上显示点击了第几行 setTitle("你点击了第"+arg2+"行"); } });
4.12.2 ListView使用SimpleAdapter
很多时候需要在列表中展示一些除了文字以外的东西,比如图片等。这时候可以使用SimpleAdapter。SimpleAdapter的使用也非常简单,同时它的功能也非常强大。可以通过它自定义ListView中的item的内容,比如图片、多选框等。看一个例子,实现一个每一行都有一个ImageView和TextView的ListView。先看一下运行效果,如图4-34所示。
▲图4-34 带图标的ListView
首先在布局文件中增加一个ListView控件。
还需要定义一个ListView中每一行的布局,用RelativeLayout来实现一个带两行字和一个图片的布局。
item.xml:
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayoutxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_width="fill_parent">
<ImageViewandroid:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/ItemImage"/>
<TextViewandroid:id="@+id/ItemTitle" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:textSize="20sp"/>
<TextViewandroid:id="@+id/ItemText" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_below="@+id/ItemTitle"/> </RelativeLayout>
配置完毕,就可以在Java代码中为ListView绑定数据。
publicclass MyListViewSimple extends Activity { private ListView lv; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv);/*定义一个动态数组*/
ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> listItem = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>();/*在数组中存放数据*/
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("ItemImage", R.drawable.icon);//加入图片 map.put("ItemTitle", "第"+i+"行"); map.put("ItemText", "这是第"+i+"行"); listItem.add(map); } SimpleAdapter mSimpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this,listItem,//需要绑定的数据
R.layout.item,//每一行的布局//动态数组中的数据源的键对应到定义布局的View中new String[] {"ItemImage"
,"ItemTitle", "ItemText"},
newint[] {R.id.ItemImage,R.id.ItemTitle,R.id.ItemText}
);
lv.setAdapter(mSimpleAdapter);//为ListView绑定适配器 lv.setOnItemClickListener(new
OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
publicvoid onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2,
long arg3) {
setTitle("你点击了第"+arg2+"行");//设置标题栏显示点击的行
}
});
}
}
使用simpleAdapter的数据一般都是用HashMap构成的列表,列表的每一节对应ListView的每一行。通过SimpleAdapter的构造函数,将HashMap的每个键的数据映射到布局文件中对应控件上。这个布局文件一般根据自己的需要来自己定义。梳理一下使用SimpleAdapter的步骤。
(1)根据需要定义ListView每行所实现的布局。
(2)定义一个HashMap构成的列表,将数据以键值对的方式存放在里面。
(3)构造SimpleAdapter对象。
(4)将LsitView绑定到SimpleAdapter上。
4.12.3 ListView使用BaseAdapter与ListView的优化
在ListView的使用中,有时候还需要在里面加入按钮等控件,实现单独的操作。也就是说,这个ListView不再只是展示数据,也不仅仅是这一行要来处理用户的操作,而是里面的控件要获得用户的焦点。读者可以试试用SimpleAdapter添加一个按钮到ListView的条目中,会发现可以添加,但是却无法获得焦点,点击操作被ListView的Item所覆盖。这时候最方便的方法就是使用灵活的适配器BaseAdapter了。
▲图4-35 BaseAdapter中的方法
使用BaseAdapter必须写一个类继承它,同时BaseAdapter是一个抽象类,继承它必须实现它的方法。BaseAdapter的灵活性就在于它要重写很多方法,看一下有哪些方法,如图4-35所示为继承自BaseAdapter的SpeechListAdapter所实现的方法,其中最重要的即为getView()方法。这些方法都有什么作用呢?我们通过分析ListView的原理来为读者解答。
当系统开始绘制ListView的时候,首先调用getCount()方法。得到它的返回值,即ListView的长度。然后系统调用getView()方法,根据这个长度逐一绘制ListView的每一行。也就是说,如果让getCount()返回1,那么只显示一行。而getItem()和getItemId()则在需要处理和取得Adapter中的数据时调用。那么getView如何使用呢?如果有10000行数据,就绘制10000次?这肯定会极大的消耗资源,导致ListView滑动非常的慢,那应该怎么做呢?通过一个例子来讲解如何在使用BaseAdapter的时候优化ListView的显示。例子中将上一节中的ImageView换成Button,并且处理Button的点击事件,其中对ListView的显示做了优化。
布局文件和上一例类同,读者可以在光盘的工程目录中查看,这里只给出Activity类。
publicclass MyListViewBase extends Activity { private ListView lv; /*定义一个动态数组*/ ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>listItem;/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv);
MyAdapter mAdapter = new MyAdapter(this);//得到一个MyAdapter对象lv.setAdapter(mAdapter);//为ListView绑定Adapter /*为ListView添加点击事件*/
lv.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() { @Override publicvoid onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2, long arg3) { Log.v("MyListViewBase", "你点击了ListView条目" + arg2);//在LogCat中输出信息 } }); }/*添加一个得到数据的方法,方便使用*/ private ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> getDate(){ ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> listItem = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>(); /*为动态数组添加数据*/ for(int i=0;i<30;i++) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("ItemTitle", "第"+i+"行"); map.put("ItemText", "这是第"+i+"行"); listItem.add(map); } return listItem; }/* * 新建一个类继承BaseAdapter,实现视图与数据的绑定 */ privateclass MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter { private LayoutInflater mInflater;//得到一个LayoutInfalter对象用来导入布局 /*构造函数*/
public MyAdapter(Context context) { this.mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context); } @Override publicint getCount() { return getDate().size();//返回数组的长度 } @Override public Object getItem(int position) { returnnull; } @Override publiclong getItemId(int position) { return 0; } /*书中详细解释该方法*/ @Override public View getView(finalint position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder holder; //观察convertView随ListView滚动情况
Log.v("MyListViewBase", "getView " + position + " " + convertView);
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item,
null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
/*得到各个控件的对象*/
holder.title = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.ItemTitle);
holder.text = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.ItemText);
holder.bt = (Button) convertView.findViewById(R.id.ItemButton);
convertView.setTag(holder);//绑定ViewHolder对象 }
else{
holder = (ViewHolder)convertView.getTag();//取出ViewHolder对象 }
/*设置TextView显示的内容,即我们存放在动态数组中的数据*/
holder.title.setText(getDate().get(position).get("ItemTitle").toString());
holder.text.setText(getDate().get(position).get("ItemText").toString());
/*为Button添加点击事件*/ holder.bt.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
publicvoid onClick(View v) {
Log.v("MyListViewBase", "你点击了按钮" + position); //打印Button的点击信息
}
});
return convertView;
}
}/*存放控件*/ publicfinalclass ViewHolder{
public TextView title;
public TextView text;
public Button bt;
}
}
运行效果如图4-36所示。还需要注意的是,Button会抢夺ListView的焦点,需要将Button设置为没有焦点。设置非常简单,只需要在xml的Button标签下加入一行:android:focusable=“false”代码就可以了。在LogCat观察点击后输出的信息,如图4-37所示。
▲图4-36 使用BaseAdapter的ListVie
▲图4-37 点击ListView条目和Button得到的输出
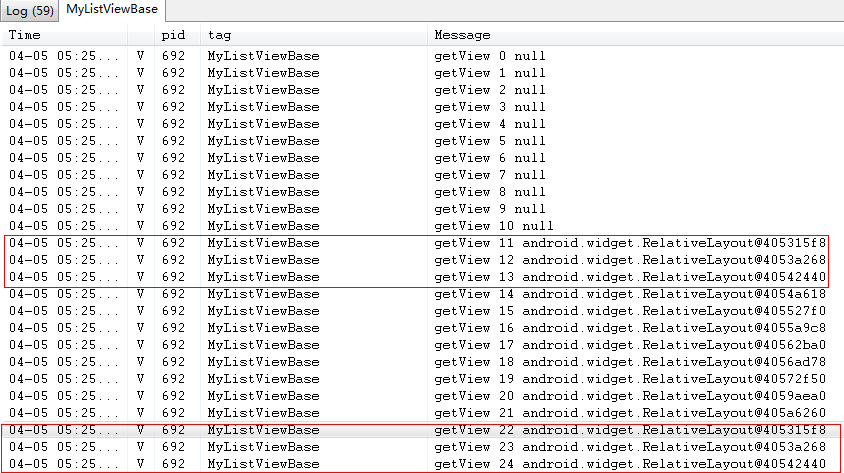
代码中getView()方法不容易理解。其实完全可以不用所谓的convertView和ViewHolder,直接导入布局并且设置控件显示的内容就可以了。但是这意味着有多少行数据就需要绘制多少行ListView,这显然是不可取的。这里采用了一种优化的方法。代码中,在getView()方法中加入了一行log输出convertView的内容。滚动ListView,输出信息如图4-38所示。
从图4-38中可以看出,当启动Activity呈现第一屏ListView的时候,convertView为零。当用户向下滚动ListView时,上面的条目变为不可见,下面出现新的条目。这时候convertView不再为空,而是创建了一系列的convertView的值。当又往下滚一屏的时候,发现第11行的容器用来容纳第22行,第12行的容器用来容纳第23行。也就是说convertView相当于一个缓存,开始为0,当有条目变为不可见,它缓存了它的数据,后面再出来的条目只需要更新数据就可以了,这样大大节省了系统资料的开销。
还可以继续优化。虽然重复利用了已经绘制的view,但是要得到其中的控件,需要在控件的容器中通过findViewById的方法来获得。如果这个容器非常复杂,这显然会增加系统资源的开销。在上面的例子中,引入了Tag的概念。或许不是最好的办法,但是它确实能使ListView变得更流畅。代码中,当convertView为空时,用setTag()方法为每个View绑定一个存放控件的ViewHolder对象。当convertView不为空,重复利用已经创建的view的时候,使用getTag()方法获取绑定的ViewHolder对象,这样就避免了findViewById对控件的层层查询,而是快速定位到控件。
▲图4-38 滚动ListView输出的convertView的值
总结一下,这节介绍了用BaseAdapter来绑定ListView的数据。因为BaseAdapter非常灵活,使用也相对较其他控件麻烦。同时ListView的优化问题也值得读者去研究,一个流畅的ListView会带来更好的用户体验。
Dialog
- AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
- builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
- builder.setTitle("你确定要离开吗?");
- builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑
- showDialog("你选择了确定");
- }
- });
- builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- //这里添加点击确定后的逻辑
- showDialog("你选择了取消");
- }
- });
- builder.create().show();
- private void showDialog(String str) {
- w AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this)
- .setMessage(str)
- .show();
- }
- AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
- builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
- builder.setTitle("投票");
- builder.setMessage("您认为什么样的内容能吸引您?");
- builder.setPositiveButton("有趣味的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- showDialog("你选择了有趣味的");
- }
- });
- builder.setNeutralButton("有思想的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- showDialog("你选择了有思想的");
- }
- });
- builder.setNegativeButton("主题强的", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- showDialog("你选择了主题强的");
- }
- });
- builder.create().show();
mSingleChoice 用于记录单选中的ID
- AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
- builder.setTitle("列表选择框");
- builder.setItems(mItems, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
- //点击后弹出窗口选择了第几项
- showDialog("你选择的id为" + which + " , " + mItems[which]);
- }
- });
- builder.create().show();
- int mSingleChoiceID = -1;
- AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
-
- mSingleChoiceID = -1;
- builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
- builder.setTitle("单项选择");
- builder.setSingleChoiceItems(mItems, 0, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- mSingleChoiceID = whichButton;
- showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]);
- }
- });
- builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- if(mSingleChoiceID > 0) {
- showDialog("你选择的是" + mSingleChoiceID);
- }
- }
- });
- builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
-
- }
- });
- builder.create().show();
- mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainDialog.this);
- mProgressDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
- mProgressDialog.setTitle("进度条窗口");
- mProgressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
- mProgressDialog.setMax(MAX_PROGRESS);
- mProgressDialog.setButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- //这里添加点击后的逻辑
- }
- });
- mProgressDialog.setButton2("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- //这里添加点击后的逻辑
- }
- });
- mProgressDialog.show();
- new Thread(this).start();
-
- ic void run() {
- int Progress = 0;
- while(Progress < MAX_PROGRESS) {
- try {
- Thread.sleep(100);
- Progress++;
- mProgressDialog.incrementProgressBy(1);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- // TODO Auto-generated catch block
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
-
- }
MultiChoiceID 用于记录多选选中的id号 存在ArrayList中
选中后 add 进ArrayList
取消选中后 remove 出ArrayList 。
- ArrayList <Integer>MultiChoiceID = new ArrayList <Integer>();
- AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainDialog.this);
-
- MultiChoiceID.clear();
- builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
- builder.setTitle("多项选择");
- builder.setMultiChoiceItems(mItems,
- new boolean[]{false, false, false, false, false, false, false},
- new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton,
- boolean isChecked) {
- if(isChecked) {
- MultiChoiceID.add(whichButton);
- showDialog("你选择的id为" + whichButton + " , " + mItems[whichButton]);
- }else {
- MultiChoiceID.remove(whichButton);
- }
-
- }
- });
- builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
- String str = "";
- int size = MultiChoiceID.size();
- for (int i = 0 ;i < size; i++) {
- str+= mItems[MultiChoiceID.get(i)] + ", ";
- }
- showDialog("你选择的是" + str);
- }
- });
- builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
- public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
-
- }
- });
- builder.create().show();
- <span style="color:#000000;"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:id="@+id/dialog">
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:id="@+id/dialogname">
- <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/tvUserName"
- android:text="姓名:" />
- <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/etUserName"
- android:minWidth="200dip"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:id="@+id/dialognum"
- android:layout_below="@+id/dialogname"
- >
- <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/tvPassWord"
- android:text="密码:" />
- <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/etPassWord"
- android:minWidth="200dip"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- </RelativeLayout></span>
- mProgressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this);
- mProgressDialog.setTitle("读取ing");
- mProgressDialog.setMessage("正在读取中请稍候");
- mProgressDialog.setIndeterminate(true);
- mProgressDialog.setCancelable(true);
- mProgressDialog.show();
//利用工厂方法构造一个简单的Toast,并链式结构的直接进行提示
2 Toast.makeText(this, "这是一个Toast提示", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();







































 554
554

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








