TITLE: Interpretable Convolutional Neural Networks
AUTHOR: Quanshi Zhang, Ying Nian Wu, Song-Chun Zhu
ASSOCIATION: UCLA
FROM: arXiv:1710.00935
CONTRIBUTION
- Slightly revised CNNs are propsed to improve their interpretability, which can be broadly applied to CNNs with different network structures.
- No annotations of object parts and/or textures are needed to ensure each high-layer filter to have a certain semantic meaning. Each filter automatically learns a meaningful object-part representation without any additional human supervision.
- When a traditional CNN is modified to an interpretable CNN, experimental settings need not to be changed for learning. I.e. the interpretable CNN does not change the previous loss function on the top layer and uses exactly the same training samples.
- The design for interpretability may decrease the discriminative power of the network a bit, but such a decrease is limited within a small range.
METHOD
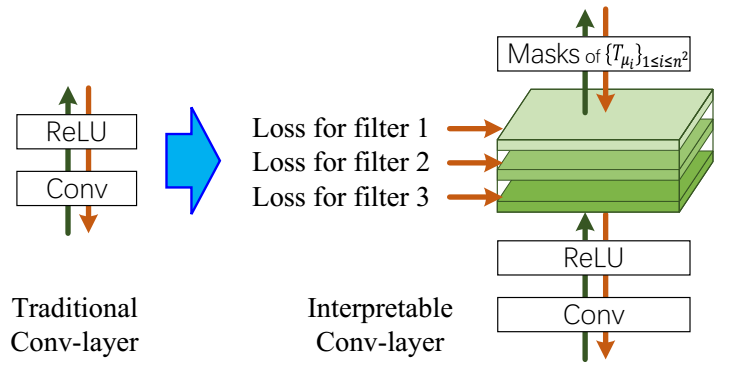
The loss for filter is illustrated in the following figure.
 {: .center-image .image-width-480}
{: .center-image .image-width-480}
A feature map is expected to be strongly activated in images of a certain category and keep silent on other images. Therefore, a number of templates are used to evaluate the fitness between the current feature map and the ideal distribution of activations w.r.t. its semantics. The template is an ideal distribution of activations according to space locations. The loss for layers is formulated as the mutual information between feature map X and templates T .
the loss can be re-written as
The first term is a constant denoting the piror entropy of T+ . The second term encourages a low conditional entropy of inter-category activations which means that a well-learned filter needs to be exclusively activated by a certain category and keep silent on other categories. The third term encorages a low conditional entropy of spatial distribution of activations. A well-learned filter should only be activated by a single region of the feature map, instead of repetitively appearing at different locations.
SOME THOUGHTS
This loss can reduce the redundancy among filters, which may be used to compress the model.

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








