文化袁探索专栏——Activity、Window和View三者间关系
<文化袁探索专栏——View三大流程#Measure
文化袁探索专栏——View三大流程#Layout
文化袁探索专栏——Handler消息分发机制
文化袁探索专栏——事件分发机制
文化袁探索专栏——Launcher进程启动流程’VS’APP进程启动流程
文化袁探索专栏——Activity|Application启动流程
文化袁探索专栏——自定义View实现细节
文化袁探索专栏——线程安全
文化袁探索专栏——React Native启动流程
关于Android相关的Activity、Window和View三者间关系,这里我有自己的一套探索认知。并且该认识是由安卓的应用层系统源码进行分析的。
一个Activity具有一个Window窗口,Window实现类是PhoneWindow;PhonWindow是在Activity.attach方法中创建。Window中有一个DecorView,DecorView是作为Activity视图的View容器,且View视图都通过setContentView添加到DecorView中。
View视图能显示到屏幕上是由WindowManager操作DecorView后交由ViewRootImpl,并最终由WMS.addWindow实现的。
Window对象是在Activity的attach方法中被创建,而attach方法是在Activity通过Instrumentation反射被创建后通过activity.attach执行到。
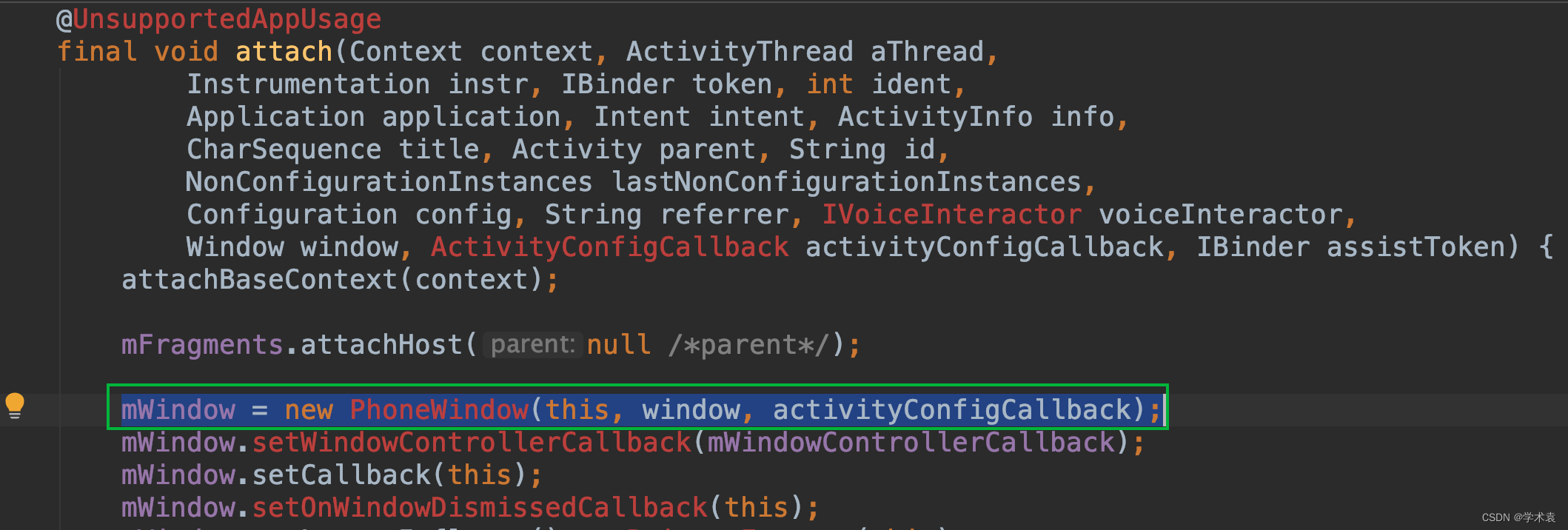
在App进程入口类ActivityThread.java的方法handleResumeActivity() 中且在A抽屉Activity生命周期onResume执行后:
... ...
///ActivityThread.java [Android API 30]
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
// Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity
// in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing
// the decor view we have to notify the view root that the
// callbacks may have changed.
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
... ....
截图中说明在Activity.attach方法中每次都会创建Window对象,且Window对象在同一Activity中全局唯一。再结合代码片段中的第4、5行表明了一个Activity对应一个Window(每个Activity都会创建自己的一个Window),一个Window对应一个DecorView。
在Activity的生命周期onCreate方法调用setContentView(R.layout.activity_demo)逻辑中的代码行第5、7、18、28行,又表明DecorView是作为Activity视图的View容器:
///AppCompatDelegate.java [Android API 30]
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
ViewGroup contentParent = mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);//contentParent本身是mSubDecor其中的ViewGroup
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);//将我们写的布局生成View,并添加到contentParent中
mAppCompatWindowCallback.getWrapped().onContentChanged();
}
//后面调用关系 :ensureSubDecor-->createSubDecor-->mWindow.setContentView(subDecor);
//然后调用执行,进入到PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();// 创建DecorView,mContentParent本身也是DecorView其中的一个ViewGroup
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final Scene newScene = new Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mContentParent.addView(view, params);//mSubDecor被添加到mContentParent中
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
之后在应用的进程入口类ActivityThread.java中handleResumeActivity方法中,执行wm.addView(decor, l);后将执行事件流转到WindowManager实现类 WindowManagerImpl的代理类 WindowManagerGlobal的 AddVieiw方法,然后创建ViewRootImpl对象并将View的绘制交给了ViewRootImpl。触发绘制在方法setView/requestLayout(); 绘制成功后在ViewRootImpl.java的setView中调用方法
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mTmpFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, inputChannel,
mTempInsets, mTempControls);
将窗口添加到屏幕。
表明View视图能显示到屏幕上是由WindowManager操作DecorView之后交由ViewRootImpl实现的。





















 402
402











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








