1.从示例开始
自定义一个View,显示"HelloWorld"
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class CustomView1 extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private String str = "Hello World!";
public CustomView1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
// 实例化一个画笔工具
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
// 设置字体大小
mPaint.setTextSize(50);
// 设置画笔颜色
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
}
// 重写onMeasure方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
// 重写onDraw方法
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
/**
* getWidth() / 2 - mPaint.measureText(str) / 2让文字在水平方向居中
*/
canvas.drawText(str, getWidth() / 2 - mPaint.measureText(str) / 2,
getHeight()/2, mPaint);
}
}
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<com.example.customviewpractice.CustomView1
android:id="@+id/cus_textview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/darker_gray" />
</LinearLayout>
假如我要求你去画一个空心的圆,你会怎么做,首先你要拿张白纸,然后你会问我圆的半径多大?圆的位置在哪?圆的线条颜色是什么?圆的线条粗细是多少?等我把这些问题都告诉你之后,你就会明白要求,并按照这个要求去画一个圆。我们自定义控件呢,也是这样需要下面三个步骤:
①重写onMeasure(获得半径的大小)
②重写onLayout(获得圆的位置)
③重写onDraw(用实例化的画笔包括:颜色,粗细等去绘画)
待这三个方法都重写完后我们的自定义控件就完成了,为了讲的能够详细我们这一篇专门来讲解onMeasure以及和其相关的方法,首先我们需要明白的是Android给我提供了可以操纵控件测量的方法是onMeasure()方法,在上面的自定义控件中我们采用了其默认的实现
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
} public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
}
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
} 然后调用LayoutInflater将我们的布局文件加载进来并添加到mContentParent视图中。跟上节奏我们来看看installDecor()方法的源码
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
//mDecor为空,则创建一个Decor对象
mDecor = generateDecor();
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
//generateLayout()方法会根据窗口的风格修饰,选择对应的修饰布局文件
//并且将id为content(android:id="@+id/content")的FrameLayout赋值给mContentParent
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
。。。省略部分代码。。。
}
}
protected DecorView generateDecor() {
return new DecorView(getContext(), -1);
}
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
。。。省略部分代码。。。
View in = mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
decor.addView(in, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(FILL_PARENT, FILL_PARENT));
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
。。。省略部分代码。。。
return contentParent;
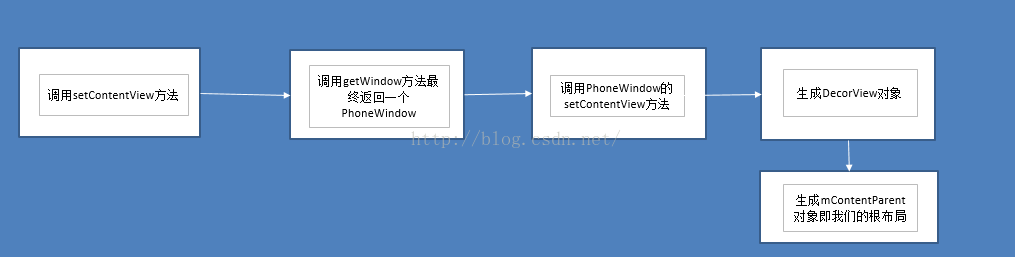
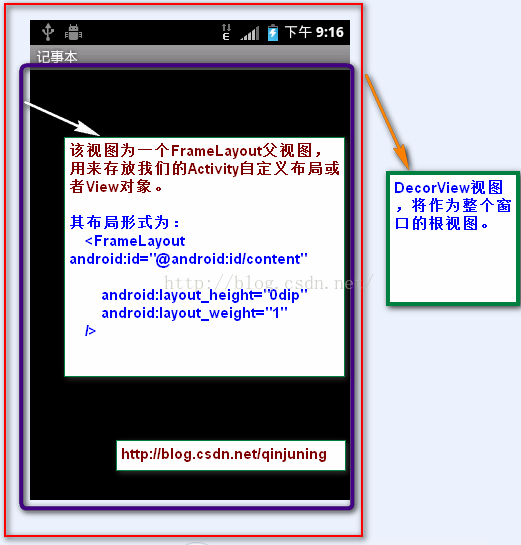
} 根据窗口的风格修饰类型为该窗口选择不同的窗口布局文件(根视图),这些窗口修饰布局文件指定一个用来存放Activity自定义布局文件的ViewGroup视图,一般为FrameLayout 其id 为: android:id="@android:id/content",并将其赋给mContentParent,到这里mContentParent和mDecor均已生成,而我们xml布局文件中的布局则会被添加至mContentParent。接着对上面的过程做一个简单的总结如下图
所以说实际上我们在写xml布局文件的时候我们的根布局并不是我们能在xml文件中能看到的最上面的那个,而是FrameLayout,我们再用谷歌给我提供的hierarchyviewer这个工具来看看我们最开始的那个小例子的布局情况,看完你就明白了
到这里我们回到最初我们提出的问题widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec是从哪来?我们在上面提到是从其父View传递过来的,那么它的父View的这两个参数又是从哪来,这样一步一步我们就需要知道View绘制的时候是从儿开始的,其实担任此重任的是ViewRootImpl,绘制开始是从ViewRootImpl中的performTraversals()这个方法开始的,我们来看看源码,可能有的人会说又看源码,只有看源码才能学的更透彻,这里我们只看主要的代码,理解其流程即可,其实performTraversals()方法的代码很多,我们省略后如下
private void performTraversals() {
int desiredWindowWidth;
int desiredWindowHeight;
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
。。。省略部分代码。。。
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
。。。省略部分代码。。。
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
。。。省略部分代码。。。
host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
。。。省略部分代码。。。
} /**
* Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's
* layout params.
*
* @param windowSize
* The available width or height of the window
*
* @param rootDimension
* The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the
* window.
*
* @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
*/
private int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
} ①UNSPECIFIED:父View没有对子View施加任何约束。它可以是任何它想要的大小。
②EXACTLY:父View已经确定了子View的确切尺寸。子View将被限制在给定的界限内,而忽略其本身的大小。
③AT_MOST:子View的大小不能超过指定的大小
它有三个主要的方法:
①getMode(imeasureSpec)它的作用就是根据规格提取出mode,这里的mode是上面的三种模式之一
②getSize(int measureSpec)它的作用就是根据规格提取出size,这里的size就是我们所说的大小
③makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode)根据size和mode,创建一个测量要求。
说了这些可能大家仍然是一头雾水接下来我们看看它的源码,MeasureSpec是View的内部类,它的源码如下
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
//转化为二进制就是11向左移30位,其结果为:11 0000...(11后跟30个0)
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* 下面就是MeasureSpec的三种模式
*/
//0左移30位变为 :00 0000...(00后跟30个0)
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
//01左移30位变为:01 0000...(01后跟30个0)
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
//10左移30位变为:10 0000...(10后跟30个0)
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
//创建一个测量的规格其高位的前两位代表mode,后面30为代表size,即measureSpec=size+mode;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
return size + mode;
}
//与运算获得mode,这里为什么可以得到mode?因为从measureSpec=size+mode,而MODE_MASK=11 0000...(11后跟30个0)
//我们都知道 & 运算的规则是"遇0为0,遇1不变",而MODE_MASK的前两位为11后面30为全为0,这样进行运算后就可以得到measureSpec的前两位,而刚好
//这前两位就代表了mode。
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
//这里的思想跟getMode方法是一样的,首先对MODE_MASK进行取反,得到的结果为00 1111...(00后跟30个1)& 运算的规则是"遇0为0,遇1不变",而此时~MODE_MASK
//的前两位为0后面30为全为1,所以measureSpec&~MODE_MASK得到的结果去后面30位,这后面的30位就是我们的size
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
public static String toString(int measureSpec) {
。。。内容省略。。。
}
} MeasureSpec这个类的设计是非常巧妙的,用int类型占有32位,它将其高2位作为mode,后30为作为size这样用32位就解决了size和mode的问题
看完的它的源码大家可能似懂非懂,那么我们就举个例子画个图,让你彻底理解它的设计思想。
假如现在我们的mode是EXACTLY,而size=101(5)那么size+mode的值为:
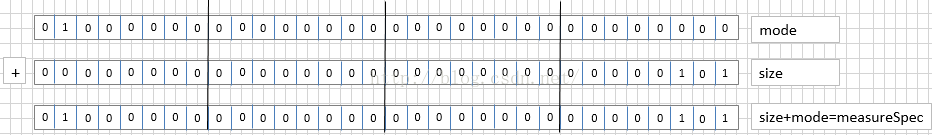
这时候通过size+mode构造除了MeasureSpec对象及测量要求,当需要获得Mode的时候只需要用measureSpec与MODE_TASK相与即可如下图:
我们看到得到的值就是上面的mode,而如果想获得size的话只需要只需要measureSpec与~MODE_TASK相与即可如下图
好了到这里我们应该对MeasureSpec有了一定的理解。这时返回去看看我们的getRootMeasureSpec方法,你是不是能看懂了?看懂后回到performTraversals方法,通过getRootMeasureSpec方法得到childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec后,我们看到在performTraversals方法中会调用host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec,childHeightMeasureSpec),这样childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec这两个测量要求就一步一步的传下去并由当前View与其父容器共同决定其测量大小,在这里View与ViewGroup中的递归调用过程中有几个重要的方法,而对于View是measure方法,接着我们看看host.measure也就是View的measure方法的源码吧
public class View implements ... {
。。。省略了部分代码。。。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//判断是否为强制布局,即带有“FORCE_LAYOUT”标记 以及 widthMeasureSpec或heightMeasureSpec发生了改变
if ((mPrivateFlags & FORCE_LAYOUT) == FORCE_LAYOUT ||
widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec ||
heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) {
//清除MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET标记 ,该标记会在onMeasure()方法后被设置
mPrivateFlags &= ~MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) {
ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.ON_MEASURE);
}
// 1、 测量该View本身的大小
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if ((mPrivateFlags & MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
//下一步是layout了,添加LAYOUT_REQUIRED标记
mPrivateFlags |= LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;//保存值
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;//保存值
}
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
//获得android:minHeight这个属性的值,一般不设置此属性如果没有设置的话mMinWidth=0
int suggestedMinWidth = mMinWidth;
if (mBGDrawable != null) {
//获得背景的宽度
final int bgMinWidth = mBGDrawable.getMinimumWidth();
//从背景的宽度和minHeight属性中选出一个最大的值作为返回值
if (suggestedMinWidth < bgMinWidth) {
suggestedMinWidth = bgMinWidth;
}
}
return suggestedMinWidth;
}
//在这里这里size是getSuggestedMinimumWidth方法的返回值,这也是默认的大小
//measureSpec是父View传过来的measureSpec,测量要求
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
//获得测量的模式
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
//获得测量的大小
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
//模式为Unspecified及未指定大小
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
//将上面的size作为结果返回
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://模式为At_Most,此时使用默认的大小size
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://模式为Exactly,此时返回测量值
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
//为View设置宽和高
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
} 上面这些是对于一个View的测量,android中在进行测量时有两种情况,一种是一个View如Button,ImaeView这中,不能包含子View的对于这种测量一下就ok了,另外一种就是ViewGroup像LinearLayout,FrameLayout这种可以包含子View的,对于这种我们就需要循环遍历每一个子View并为其设置大小,在自定义的ViewGroup中重写onMeasure如下的伪代码
//某个ViewGroup类型的视图
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//必须调用super.ononMeasure()或者直接调用setMeasuredDimension()方法设置该View大小,否则会报异常。
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec , heightMeasureSpec)
//setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
// getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
//一、遍历每个子View
for(int i = 0 ; i < getChildCount() ; i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
//调用子View的onMeasure,设置他们的大小,
child.onMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
//二、直接调用ViewGroup中给我们提供好的measureChildren方法、
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} measureChildren方法的源码如下:
//widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec:父View传过来的测量要求
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
//遍历所有的View
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
//Gone掉的View排除
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
// 获取子元素的布局参数
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
//将父容器的测量规格以及上下和左右的边距还有子元素本身的布局参数传入getChildMeasureSpec方法计算最终测量要求
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 将计算好的宽高详细测量值传入measure方法,完成最后的测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//获取父View的测量模式
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
//获取父View的测量大小
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//父View计算出的子View的大小,子View不一定用这个值
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
//声明变量用来保存实际计算的到的子View的size和mode即大小和模式
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
//如果父容器的模式是Exactly即确定的大小
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
//子View的高度或宽度>0说明其实一个确切的值,因为match_parent和wrap_content的值是<0的
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
//子View的高度或宽度为match_parent
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;//将size即父View的大小减去边距值所得到的值赋值给resultSize
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;//指定子View的测量模式为EXACTLY
//子View的高度或宽度为wrap_content
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;//将size赋值给result
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;//指定子View的测量模式为AT_MOST
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
//如果父容器的测量模式是AT_MOST
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
// 因为父View的大小是受到限制值的限制,所以子View的大小也应该受到父容器的限制并且不能超过父View
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
//如果父容器的测量模式是UNSPECIFIED即父容器的大小未受限制
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
//如果自View的宽和高是一个精确的值
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
//子View的大小为精确值
resultSize = childDimension;
//测量的模式为EXACTLY
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
//子View的宽或高为match_parent
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
//resultSize=0;因为父View的大小是未定的,所以子View的大小也是未定的
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//根据resultSize和resultMode调用makeMeasureSpec方法得到测量要求,并将其作为返回值
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
} 我们经常说View的大小是由父View以及当前View共同决定的,这一点从上面这个方法也可以看出。但是这只是一个期望的大小,其大小的最终决定权由setMeasureDimenSion方法决定。
所以最终View的大小将受以下几个方面的影响(以下三点摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/8074262此博客,这是一个大神。。)
1、父View的MeasureSpec属性;
2、子View的LayoutParams属性;
3、setMeasuredDimension()或者其它类似设定 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight 值的方法。


























 7729
7729

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








