本篇是自己调了源码后,有些地方没看懂,然后搜索并且参考了
https://www.cnblogs.com/chiangchou/p/ribbon-1.html#_label3_4
https://www.cnblogs.com/chiangchou/p/ribbon-2.html
目录
下面介绍@LoadBalanced注解如何让RestTemplate具备负载均衡能力的
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer 选择 Server
4.从 DiscoveryClient 获取Server列表
一、简介及核心原理
其他原理介绍在另一篇已写https://blog.csdn.net/jy02268879/article/details/107224106
原理图解
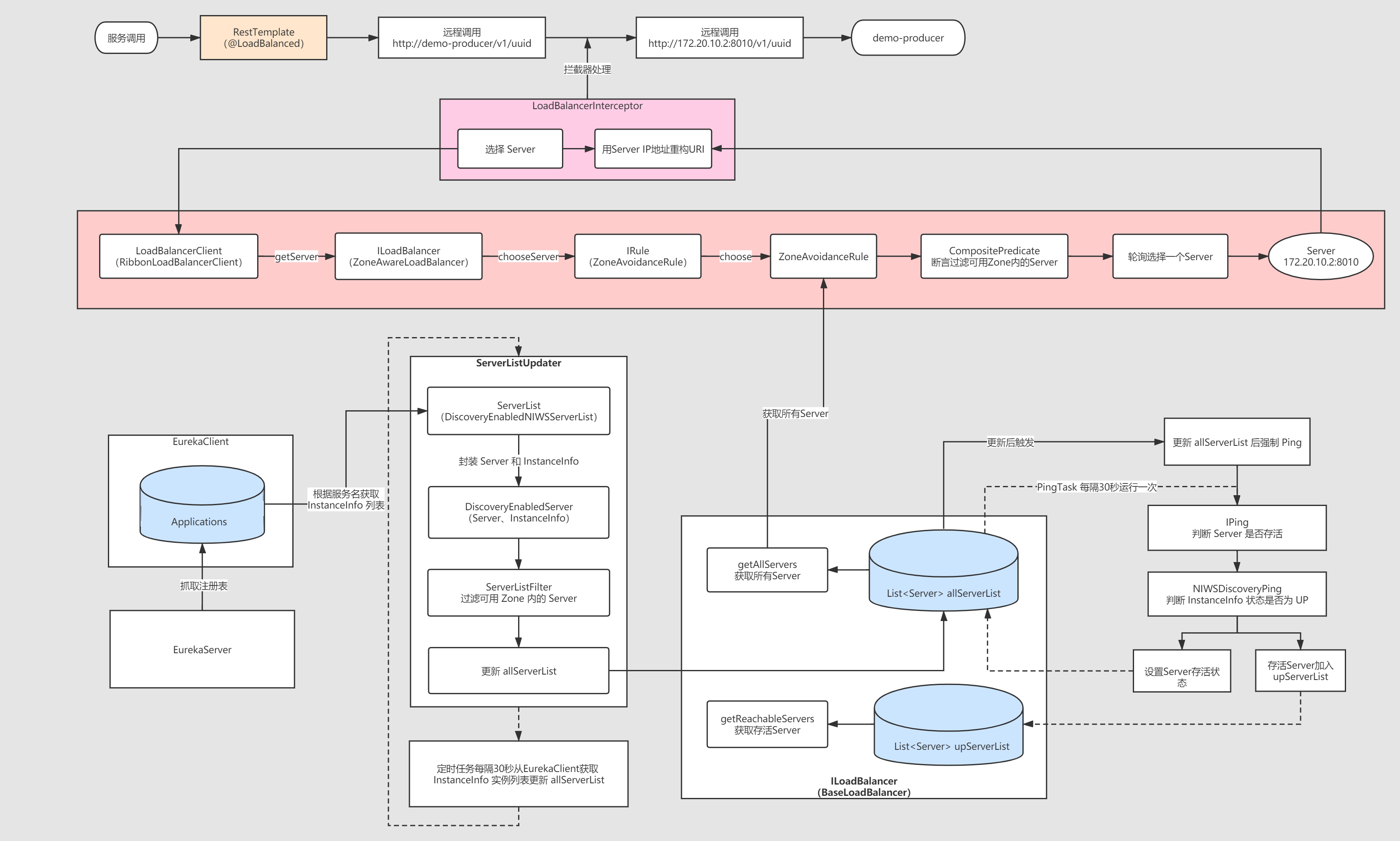
二、结合SpringBoot怎么自动装配的源码分析
服务调用者的启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableHystrix
public class OrderApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApp.class, args);
}
/**
* 向Spring容器中定义RestTemplate对象
* @return
*/
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate(new OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory());
}
}
这个@LoadBalanced表示feign中用于RPC调用的resttemplate需要使用LoadBalancerClient
@LoadBalanced 注解让 RestTemplate 具备负载均衡的能力了
下面介绍@LoadBalanced注解如何让RestTemplate具备负载均衡能力的
真正的自动装配入口在这个地方:
spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon的jar包里面有个spring.factories,里面的内容表示启动时需要springboot自动装配RibbonAutoConfiguration

RibbonAutoConfiguration
源码:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ IClient.class, RestTemplate.class, AsyncRestTemplate.class, Ribbon.class})
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class, AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class, ServerIntrospectorProperties.class})
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
//获取ioc中RibbonClientSpecification(每个RibbonClient都会有一个)
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
//饥饿加载模式配置
@Autowired
private RibbonEagerLoadProperties ribbonEagerLoadProperties;
@Bean
public HasFeatures ribbonFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Ribbon", Ribbon.class);
}
//子容器管理器
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
//负载均衡客户端(LoadBalancerInterceptor需要)
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(springClientFactory());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory(final SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {
return new RibbonLoadBalancedRetryFactory(clientFactory);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory() {
return new PropertiesFactory();
}
//饥饿加载模式
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "ribbon.eager-load.enabled")
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer ribbonApplicationContextInitializer() {
return new RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(springClientFactory(),
ribbonEagerLoadProperties.getClients());
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(HttpRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient
protected static class RibbonClientHttpRequestFactoryConfiguration {
@Autowired
private SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;
@Bean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory) {
return restTemplate -> restTemplate.setRequestFactory(ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory);
}
@Bean
public RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory() {
return new RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory(this.springClientFactory);
}
}
//TODO: support for autoconfiguring restemplate to use apache http client or okhttp
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnRibbonRestClientCondition.class)
@interface ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient { }
private static class OnRibbonRestClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OnRibbonRestClientCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
@Deprecated //remove in Edgware"
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.http.client.enabled")
static class ZuulProperty {}
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.restclient.enabled")
static class RibbonProperty {}
}
}
注意开头的这个 @AutoConfigureBefore({LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class, AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class})
表示该类实例化完成后会去实例化 LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类
这个配置类实例化了几个重要的东西:
SpringClientFactory
它为每个@RibbonClient(服务提供者)创建一个子容器,并通过serviceId获取子容器中的IClient、ILoadBalancer、IClientConfig、RibbonLoadBalancerContext、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
每个子容器中都会注入RibbonClientConfiguration,它定义了单个ribbon client需要的各个组件(ILoadBalancer、IClientConfig、IRule、IPing、ServerList、ServerListUpdater、ServerListFilter、RetryHandler、ServerIntrospector、RibbonLoadBalancerContext)
Ribbon实现了子容器的隔离。
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
负载均衡客户端底层要根据服务名获取某个实例,肯定又需要一个实例库,比如从配置文件、注册中心获取。
默认RibbonLoadBalancerClient 会从 Eureka 注册中心获取实例。
RibbonLoadBalancedRetryFactory
有重试功能
RibbonApplicationContextInitializer
本质是一个ioc的事件监听器,主要的作用是根据定义的每个Ribbon Client初始化响应的子容器。比如定义为饥饿加载模式
饥饿加载模式其实就是提前加载(ioc容器初始化后加载)
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration
实例化了几个类
SmartInitializingSingleton、LoadBalancerRequestFactory、LoadBalancerInterceptor、RestTemplateCustomizer
做了几件事:
1.使用定制器RestTemplateCustomizer定制restTemplate,让它具备负载均衡的功能。
2.实际上定制器里面是加入了LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器
LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器实现了接口ClientHttpRequestInterceptor,所以如果我们想定制化 RestTemplate,就可以实现这个接口来定制化,然后还可以用 @Order 标记拦截器的先后顺序)
所有的请求都要经过LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法。
是否真的所有的请求都会经过LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法,由该拦截器来做负载均衡?
不是的!
调试源码的时候发现,只有单独用ribbon的时候走了LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法的。
spring cloud全套上去,feign+ribbon,http客户端用OKHttp,这样的话没有走LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法的。
三、单独使用rinbbon时的调用流程
流程图
图片来自 https://www.cnblogs.com/chiangchou/p/ribbon-2.html
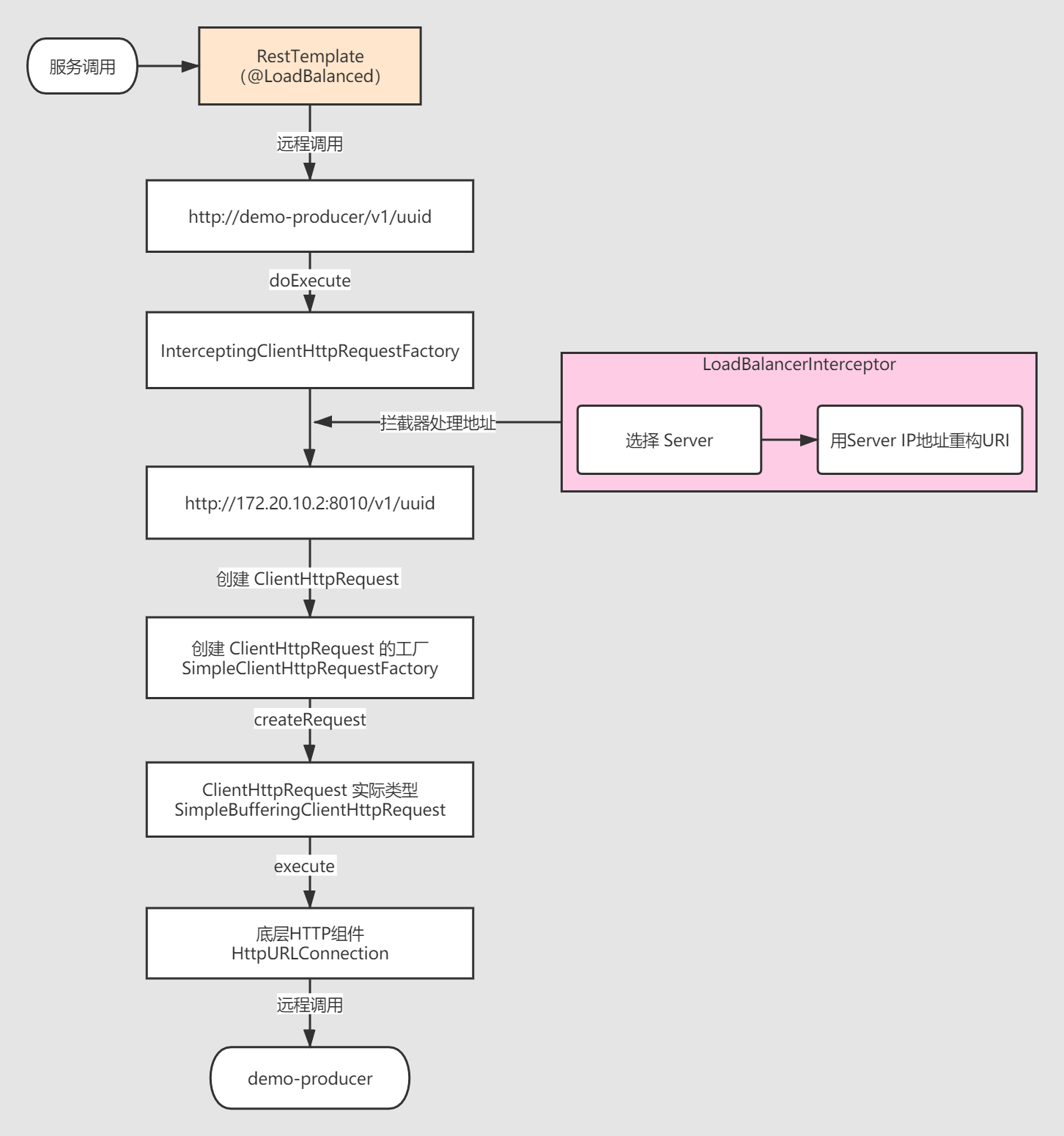
以restTemplate.getForEntity("http://demo-producer/v1/uuid", String.class) 这个GET请求为例
LoadBalancerInterceptor
LoadBalancerInterceptor.intercept()该方法被调用的调用链
RestTemplate.getForEntity()--------> RestTemplate.execute()-------->RestTemplate.doExecute()-------->AbstractClientHttpRequest.execute()
-------->AbstractBufferingClientHttpRequest.executeInternal()-------->InterceptingClientHttpRequest.executeInternal()-------->InterceptingRequestExecution.execute()
RestTemplate.doExecute方法
首先根据 url、method 创建一个 ClientHttpRequest,然后利用 ClientHttpRequest 来发起请求。
RestTemplate 的 doExecute 中调用 request.execute() 其实是调用了 InterceptingClientHttpRequest 父类 AbstractClientHttpRequest 中的 execute 方法。
一步步进去可以发现最终其实是调用了 InterceptingClientHttpRequest 的 executeInternal 方法。
InterceptingClientHttpRequest.executeInternal方法
创建了 InterceptingRequestExecution 来执行请求。
InterceptingRequestExecution.execute方法
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse execute(HttpRequest request, byte[] body) throws IOException {
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
ClientHttpRequestInterceptor nextInterceptor = this.iterator.next();
return nextInterceptor.intercept(request, body, this);
}
else {
HttpMethod method = request.getMethod();
Assert.state(method != null, "No standard HTTP method");
ClientHttpRequest delegate = requestFactory.createRequest(request.getURI(), method);
request.getHeaders().forEach((key, value) -> delegate.getHeaders().addAll(key, value));
if (body.length > 0) {
if (delegate instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) {
StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) delegate;
streamingOutputMessage.setBody(outputStream -> StreamUtils.copy(body, outputStream));
}
else {
StreamUtils.copy(body, delegate.getBody());
}
}
return delegate.execute();
}
}先遍历执行所有拦截器,然后通过 ClientHttpRequest 发起真正的 http 请求。
遍历拦截器的时候就会调用到LoadBalancerInterceptor.intercept方法
LoadBalancerInterceptor.intercept 源码
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
final URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost();
Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}从请求的原始地址中获取了服务名称,然后调用了 loadBalancer 的 execute 方法,也就是 RibbonLoadBalancerClient.execute()方法
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
负载均衡客户端底层要根据服务名获取某个实例,肯定又需要一个实例库,比如从配置文件、注册中心获取。
默认RibbonLoadBalancerClient 会从 Eureka 注册中心获取实例。
它实现了LoadBalancerClient接口,该接口有几个方法
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser {
// 从 LoadBalancer 找一个 Server 来发送请求
<T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
// 从传入的 ServiceInstance 取 Server 来发送请求
<T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
// 对原始 URI 重构
URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original);
}
RibbonLoadBalancerClient.execute()源码
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
// 根据服务名获取一个负载均衡器 ILoadBalancer
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
// 利用负载均衡器获取实例 Server
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer);
if (server == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
// 封装实例信息:RibbonServer 的父类是 ServiceInstance
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server,
serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}做了几件事
1.根据服务名获取服务对应的负载均衡器 ILoadBalancer。
2.从 ILoadBalancer 中根据一定策略选出一个实例 Server。
3.将 server、serviceId 等信息封装到 RibbonServer 中,也就是一个服务实例 ServiceInstance。
4.调用了 LoadBalancerRequest.apply()方法,并传入 ServiceInstance,将地址中的服务名替换为真实的IP地址。
这个 LoadBalancerRequest 其实就是 LoadBalancerRequestFactory.createRequest中
创建的一个匿名类,在它的函数式接口内,主要是用装饰器 ServiceRequestWrapper 将 request 包了一层。
public class LoadBalancerRequestFactory {
public LoadBalancerRequest<ClientHttpResponse> createRequest(final HttpRequest request,
final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) {
return instance -> {
// 封装 HttpRequest,ServiceRequestWrapper 重载了 getURI 方法。
HttpRequest serviceRequest = new ServiceRequestWrapper(request, instance, loadBalancer);
if (transformers != null) {
for (LoadBalancerRequestTransformer transformer : transformers) {
serviceRequest = transformer.transformRequest(serviceRequest, instance);
}
}
// 继续执行拦截器
return execution.execute(serviceRequest, body);
};
}
}
ServiceRequestWrapper 主要就是重写了 getURI 方法,在重写的 getURI 方法内,它用 loadBalancer 对 URI 进行了重构,进去可以发现,就是将原始地址中的服务名替换为 Server 的真实IP、端口地址。
四、ILoadBalancer获取Server
使 RestTemplate 具备负载均衡的能力,最重要的一个组件之一就是 ILoadBalancer,因为要用它来获取能调用的 Server,有了 Server 才能对原始带有服务名的 URI 进行重构。
ILoadBalancer 的默认实现类为 ZoneAwareLoadBalancer。
创建负载均衡器 ILoadBalancer
1.SpringClientFactory与上下文
怎么在运行时获取到每个服务的ILoadBalancer?
用 SpringClientFactory.getLoadBalancer() 方法根据服务名获取的。
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String name) {
return getInstance(name, ILoadBalancer.class);
}从 getInstance 一步步进去可以发现,每个服务都会创建一个 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,也就是一个应用上下文 ApplicationContext。
相当于就是一个服务绑定一个 ILoadBalancer。
@Override
public <C> C getInstance(String name, Class<C> type) {
C instance = super.getInstance(name, type);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
}
IClientConfig config = getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
return instantiateWithConfig(getContext(name), type, config);
}NamedContextFactory
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
// 根据名称获取
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
if (BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context,
type).length > 0) {
return context.getBean(type);
}
return null;
}NamedContextFactory
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}这个 contexts => Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext>
而AnnotationConfigApplicationContext中放入了与这个服务绑定的 ILoadBalancer、IClientConfig、RibbonLoadBalancerContext 等。
这里为什么要每个服务都绑定一个 ApplicationContext 呢?
1.服务实例列表可以有多个来源,比如可以从 eureka 注册中心获取、可以通过代码配置、可以通过配置文件配置
2.每个服务还可以有很多个性化的配置,有默认的配置、定制的全局配置、个别服务的特定配置等,它这样做就便于用户定制每个服务的负载均衡策略
2.Ribbon的饥饿加载
这个Ribbon客户端的应用上下文默认是懒加载的,并不是在启动的时候就加载上下文,而是在第一次调用的时候才会去初始化。
如果想服务启动时就初始化,可以指定Ribbon客户端的具体名称,在启动的时候就加载配置项的上下文:
ribbon:
eager-load:
enabled: true
clients: demo-producer,demo-xxx在 RibbonAutoConfiguration 配置类中可以找到这个饥饿配置,如果开启了饥饿加载,就会创建 RibbonApplicationContextInitializer 来在启动时初始化上下文。
3.何时创建ILoadBalancer的实例?
我这里是饥饿加载,第一次调用得时候才去初始化,以下为步骤
第一次调用触发了RibbonClientConfiguration配置类中创建ILoadBalancer
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}然后在远程调用的时候触发了 SpringClientFactory.getLoadBalancer() 方法。调用链如下:

客户端 Ribbon 定制
从RibbonClientConfiguration可以看到,创建 IRule、IPing、ServerList<Server>、ServerListFilter<Server>、ILoadBalancer 时,都先通过 propertiesFactory.isSet 判断是否已配置了对应类型的实现类,没有才使用默认的实现类。
针对特定的服务,这几个类可以自行定制化,也可以通过配置指定其它的实现类。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}1.全局策略配置
如果想要全局更改配置,需要加一个配置类,比如像下面这样:
@Configuration
public class GlobalRibbonConfiguration {
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule() {
return new RandomRule();
}
@Bean
public IPing ribbonPing() {
return new NoOpPing();
}
}2.基于注解的配置
如果想针对某一个服务定制配置,可以通过 @RibbonClients 来配置特定服务的配置类。
需要先定义一个服务配置类:
@Configuration
public class ProducerRibbonConfiguration {
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule() {
return new RandomRule();
}
@Bean
public IPing ribbonPing() {
return new NoOpPing();
}
}用 @RibbonClients 注解为服务指定特定的配置类,并排除掉,不让 Spring 扫描,否则就变成了全局配置了。
@RibbonClients({
@RibbonClient(name = "demo-producer", configuration = ProducerRibbonConfiguration.class)
})
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = ProducerRibbonConfiguration.class)
})3.配置文件配置
通过配置文件的方式来配置,配置的格式就是 <服务名称>.ribbon.<属性>:
demo-producer:
ribbon:
# ILoadBalancer
NFLoadBalancerClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.NoOpLoadBalancer
# IRule
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
# IPing
NFLoadBalancerPingClassName:
# ServerList<Server>
NIWSServerListClassName:
# ServerListFilter<Server>
NIWSServerListFilterClassName:4.优先级顺序
这几种配置方式的优先级顺序是
配置文件配置 > @RibbonClients 配置 > 全局配置 > 默认配置。
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer 选择 Server
ILoadBalancer的默认实现类 ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.chooseServer 方法
@Override
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
// ENABLED => ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer.enabled 默认 true
// AvailableZones 配置的只有一个 defaultZone
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone");
// 走父类获取 Server 的逻辑
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
// 多 zone 逻辑....
Server server = null;
try {
LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats();
Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats);
logger.debug("Zone snapshots: {}", zoneSnapshot);
if (triggeringLoad == null) {
triggeringLoad = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".triggeringLoadPerServerThreshold", 0.2d);
}
if (triggeringBlackoutPercentage == null) {
triggeringBlackoutPercentage = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".avoidZoneWithBlackoutPercetage", 0.99999d);
}
Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get());
logger.debug("Available zones: {}", availableZones);
if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) {
String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones);
logger.debug("Zone chosen: {}", zone);
if (zone != null) {
BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone);
server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error choosing server using zone aware logic for load balancer={}", name, e);
}
if (server != null) {
return server;
} else {
logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked.");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
}做了几件事:
1.如果只配置了一个 zone,就走父类的 chooseServer
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer 调用父类的 chooseServer 方法是在 BaseLoadBalancer 中的
2.否则从多个 zone 中去选择实例
BaseLoadBalancer.chooseServer
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
//调用IRule的choose方法
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}做了几件事:
用 IRule 来选择实例,最终选择实例的策略就交给了 IRule 接口
IRule 的默认实现类是 ZoneAvoidanceRule
ZoneAvoidanceRule 的直接父类是 PredicateBasedRule。
rule.choose 的逻辑在 PredicateBasedRule 中
PredicateBasedRule.choose
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer();
// getPredicate() Server断言 => CompositePredicate
// RoundRobin 轮询方式获取实例
Optional<Server> server = getPredicate().chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(lb.getAllServers(), key);
if (server.isPresent()) {
return server.get();
} else {
return null;
}
}做了几件事
1. getPredicate() 返回的是 ZoneAvoidanceRule 创建的一个组合断言 CompositePredicate
在初始化 ZoneAvoidanceRule 配置时,ZoneAvoidanceRule.initWithNiwsConfig方法创建了 CompositePredicate,
可以看到这个组合断言主要有两个断言,
一个是zonePredicate 断言 Server 的 zone 是否可用,
一个是availabilityPredicate 断言 Server 本身是否可用,例如 Server 无法 ping 通。
2. 调用这个断言CompositePredicate的chooseRundRobinAfterFiltering方法来过滤出可用的 Server,并通过轮询的策略返回一个 Server
AbstractServerPredicate.chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering()
public Optional<Server> chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(List<Server> servers, Object loadBalancerKey) {
List<Server> eligible = getEligibleServers(servers, loadBalancerKey);
if (eligible.size() == 0) {
return Optional.absent();
}
return Optional.of(eligible.get(incrementAndGetModulo(eligible.size())));
}做了几件事
1.对所有实例通过断言过滤掉不可用的 Server
2.通过轮询的方式获取一个 Server 返回
这就是默认配置下 ILoadBalancer(ZoneAwareLoadBalancer) 通过 IRule(ZoneAvoidanceRule) 选择 Server 的流程了。
AbstractServerPredicate.getEligibleServers()
public List<Server> getEligibleServers(List<Server> servers, Object loadBalancerKey) {
if (loadBalancerKey == null) {
return ImmutableList.copyOf(Iterables.filter(servers, this.getServerOnlyPredicate()));
} else {
List<Server> results = Lists.newArrayList();
// 对每个 Server 断言
for (Server server: servers) {
if (this.apply(new PredicateKey(loadBalancerKey, server))) {
results.add(server);
}
}
return results;
}
}做了几件事:
1.遍历每个server,对每个 Server 断言,过滤调不可用的
2.返回所有可用的server
五、如何获取注册中心服务实例的源码分析
前面在通过 IRule 选择 Server 的时候,首先通过lb.getAllServers()获取了所有的 Server,那这些 Server 从哪里来的呢?
1.ILoadBalancer 初始化
ILoadBalancer 的默认实现类是 ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
实例化方法
public ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule,
IPing ping, ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping, serverList, filter, serverListUpdater);
}调用的super的构造方法
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping,
ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping);
this.serverListImpl = serverList;
this.filter = filter;
this.serverListUpdater = serverListUpdater;
if (filter instanceof AbstractServerListFilter) {
((AbstractServerListFilter) filter).setLoadBalancerStats(getLoadBalancerStats());
}
// 剩余的一些初始化
restOfInit(clientConfig);
}做了几件事
1.调用父类 BaseLoadBalancer 初始化
2.又做了一些剩余的初始化工作。
BaseLoadBalancer的构造方法
public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, IRule rule, IPing ping) {
initWithConfig(config, rule, ping);
}BaseLoadBalancer.initWithConfig()
void initWithConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping) {
this.config = clientConfig;
String clientName = clientConfig.getClientName();
this.name = clientName;
// ping 间隔时间,默认30秒
int pingIntervalTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingInterval,
Integer.parseInt("30")));
int maxTotalPingTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerMaxTotalPingTime,
Integer.parseInt("2")));
// 设置 ping 间隔时间,并重新设置了 ping 任务
setPingInterval(pingIntervalTime);
setMaxTotalPingTime(maxTotalPingTime);
// cross associate with each other
// i.e. Rule,Ping meet your container LB
// LB, these are your Ping and Rule guys ...
// 设置 IRule、IPing
setRule(rule);
//启动一个后台定时任务,然后每隔30秒运行一次 PingTask 任务
setPing(ping);
//设置了 ILoadBalancer 的 统计器 LoadBalancerStats,对 ILoadBalancer 的 Server 状态进行统计,比如连接失败、成功、熔断等信息。
setLoadBalancerStats(new LoadBalancerStats(clientName));
rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
if (ping instanceof AbstractLoadBalancerPing) {
((AbstractLoadBalancerPing) ping).setLoadBalancer(this);
}
logger.info("Client: {} instantiated a LoadBalancer: {}", name, this);
// PrimeConnections,请求预热,默认关闭
// 作用主要用于解决那些部署环境(如读EC2)在实际使用实时请求之前,从防火墙连接/路径进行预热(比如先加白名单、初始化等等动作比较耗时,可以用它先去打通)。
boolean enablePrimeConnections = clientConfig.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.EnablePrimeConnections, DefaultClientConfigImpl.DEFAULT_ENABLE_PRIME_CONNECTIONS);
if (enablePrimeConnections) {
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(true);
PrimeConnections primeConnections = new PrimeConnections(
this.getName(), clientConfig);
this.setPrimeConnections(primeConnections);
}
// 注册一些监控
init();
}做了几件事
1.设置 IPing 和 IRule,ping 的间隔时间是 30 秒,setPing 会启动一个后台定时任务,然后每隔30秒运行一次 PingTask 任务。
2.设置了 ILoadBalancer 的 统计器 LoadBalancerStats,对 ILoadBalancer 的 Server 状态进行统计,比如连接失败、成功、熔断等信息。
3.在启用 PrimeConnections 请求预热的情况下,创建 PrimeConnections 来预热客户端 与 Server 的链接。默认是关闭的。
4.最后是注册了一些监控、开启请求预热。
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.restOfInit ()
void restOfInit(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
boolean primeConnection = this.isEnablePrimingConnections();
// turn this off to avoid duplicated asynchronous priming done in BaseLoadBalancer.setServerList()
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(false);
// 开启动态更新 Server 的特性
enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature();
// 更新 Server 列表
updateListOfServers();
// 开启请求预热的情况下,对可用的 Server 进行预热
if (primeConnection && this.getPrimeConnections() != null) {
this.getPrimeConnections()
.primeConnections(getReachableServers());
}
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(primeConnection);
LOGGER.info("DynamicServerListLoadBalancer for client {} initialized: {}", clientConfig.getClientName(), this.toString());
}做了几件事
1.开启动态更新 Server 的特性,比如实例上线、下线、故障等,要能够更新 ILoadBalancer 的 Server 列表。
2.全量更新一次本地的 Server 列表。
2.全量更新Server列表
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.updateListOfServers()
@VisibleForTesting
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
// 从 ServerList 获取所有 Server 列表
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
// 用 ServerListFilter 过滤 Server
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
// 更新所有 Server 到本地缓存
updateAllServerList(servers);
}做了几件事
1.使用 ServerList 获取所有的 Server 列表。
在 RibbonClientConfiguration 中配置的是 ConfigurationBasedServerList,但和 eureka 集合和,就不是 ConfigurationBasedServerList 了。
2.使用 ServerListFilter 对 Server 列表过滤
其默认实现类是 ZonePreferenceServerListFilter,它主要是过滤出当前 Zone(defaultZone)下的 Server。
3.更新所有 Server 列表
先是设置 Server alive,然后调用父类(BaseLoadBalancer)的 setServersList 来更新Server列表,这说明 Server 是存储在 BaseLoadBalancer 里的。
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.updateAllServerList()
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
// 设置 Server alive
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
// 强制初始化 Ping
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}做了几件事
1.设置 Server alive
2.调用父类(BaseLoadBalancer)的 setServersList 来更新Server列表
这说明 Server 是存储在 BaseLoadBalancer 里的
3.强制初始化ping
3.Eureka+Ribbon 客户端配置
获取 Server 的组件是 ServerList,RibbonClientConfiguration 中配置的默认实现类是 ConfigurationBasedServerList。
ConfigurationBasedServerList 默认是从配置文件中获取,可以像下面这样配置服务实例地址,多个 Server 地址用逗号隔开。
demo-producer:
ribbon:
listOfServers: http://XX.XXX.X.XX:8010,http://XX.XXX.X.XX:8011但是和 eureka-client 结合后,也就是引入 spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client 的客户端依赖,它会帮我们引入 spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client 依赖,这个包中有一个 RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration 自动化配置类,它通过 @RibbonClients 注解定义了全局的 Ribbon 客户端配置类 为 EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration
RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration源码
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnRibbonAndEurekaEnabled
@AutoConfigureAfter(RibbonAutoConfiguration.class)
@RibbonClients(defaultConfiguration = EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration.class)
public class RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration {
}EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration 源码
@Configuration
public class EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration.class);
@Value("${ribbon.eureka.approximateZoneFromHostname:false}")
private boolean approximateZoneFromHostname = false;
@RibbonClientName
private String serviceId = "client";
@Autowired(required = false)
private EurekaClientConfig clientConfig;
@Autowired(required = false)
private EurekaInstanceConfig eurekaConfig;
@Autowired
private PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory;
public EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration() {
}
public EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig,
String serviceId, EurekaInstanceConfig eurekaConfig,
boolean approximateZoneFromHostname) {
this.clientConfig = clientConfig;
this.serviceId = serviceId;
this.eurekaConfig = eurekaConfig;
this.approximateZoneFromHostname = approximateZoneFromHostname;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, serviceId)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, serviceId);
}
NIWSDiscoveryPing ping = new NIWSDiscoveryPing();
ping.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return ping;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerList<?> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config, Provider<EurekaClient> eurekaClientProvider) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, serviceId)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, serviceId);
}
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList discoveryServerList = new DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList(
config, eurekaClientProvider);
DomainExtractingServerList serverList = new DomainExtractingServerList(
discoveryServerList, config, this.approximateZoneFromHostname);
return serverList;
}
@Bean
public ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector() {
return new EurekaServerIntrospector();
}
@PostConstruct
public void preprocess() {
String zone = ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext()
.getValue(ContextKey.zone);
if (this.clientConfig != null && StringUtils.isEmpty(zone)) {
if (this.approximateZoneFromHostname && this.eurekaConfig != null) {
String approxZone = ZoneUtils
.extractApproximateZone(this.eurekaConfig.getHostName(false));
log.debug("Setting Zone To " + approxZone);
ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext().setValue(ContextKey.zone,
approxZone);
}
else {
String availabilityZone = this.eurekaConfig == null ? null
: this.eurekaConfig.getMetadataMap().get("zone");
if (availabilityZone == null) {
String[] zones = this.clientConfig
.getAvailabilityZones(this.clientConfig.getRegion());
// Pick the first one from the regions we want to connect to
availabilityZone = zones != null && zones.length > 0 ? zones[0]
: null;
}
if (availabilityZone != null) {
// You can set this with archaius.deployment.* (maybe requires
// custom deployment context)?
ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext().setValue(ContextKey.zone,
availabilityZone);
}
}
}
RibbonUtils.initializeRibbonDefaults(serviceId);
}
}
可用看到:
IPing 的默认实现类为 NIWSDiscoveryPing。
ServerList 的默认实现类为 DomainExtractingServerList,
但是 DomainExtractingServerList 在构造时又传入了一个类型为 DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList 的 ServerList。
看名字大概也可以看出,DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList 就是从 EurekaClient 获取 Server 的组件。
4.从 DiscoveryClient 获取Server列表
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList.getUpdatedListOfServers()
@Override
public List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> getUpdatedListOfServers(){
return obtainServersViaDiscovery();
}
private List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> obtainServersViaDiscovery() {
List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> serverList = new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
if (eurekaClientProvider == null || eurekaClientProvider.get() == null) {
logger.warn("EurekaClient has not been initialized yet, returning an empty list");
return new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
}
// 得到 EurekaClient,实际类型是 CloudEurekaClient,其父类是 DiscoveryClient
EurekaClient eurekaClient = eurekaClientProvider.get();
if (vipAddresses!=null){
// 分割 vipAddresses,默认就是服务名称
for (String vipAddress : vipAddresses.split(",")) {
// if targetRegion is null, it will be interpreted as the same region of client
// 根据服务名称从 EurekaClient 获取实例信息
List<InstanceInfo> listOfInstanceInfo = eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(vipAddress, isSecure, targetRegion);
for (InstanceInfo ii : listOfInstanceInfo) {
if (ii.getStatus().equals(InstanceStatus.UP)) {
if(shouldUseOverridePort){
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Overriding port on client name: " + clientName + " to " + overridePort);
}
// copy is necessary since the InstanceInfo builder just uses the original reference,
// and we don't want to corrupt the global eureka copy of the object which may be
// used by other clients in our system
InstanceInfo copy = new InstanceInfo(ii);
if(isSecure){
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setSecurePort(overridePort).build();
}else{
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setPort(overridePort).build();
}
}
// 根据实例信息 InstanceInfo 创建 Server
DiscoveryEnabledServer des = new DiscoveryEnabledServer(ii, isSecure, shouldUseIpAddr);
des.setZone(DiscoveryClient.getZone(ii));
serverList.add(des);
}
}
if (serverList.size()>0 && prioritizeVipAddressBasedServers){
break; // if the current vipAddress has servers, we dont use subsequent vipAddress based servers
}
}
}
return serverList;
}做了几件事:
1.得到 EurekaClient,实际类型是 CloudEurekaClient,其父类是 DiscoveryClient
2.分割 vipAddresses,默认就是服务名称
3.getInstancesByVipAddress方法根据服务名称从 EurekaClient 获取实例信息
从 DiscoveryClient 的本地应用 Applications 中根据服务名取出所有的实例列表。
eureka-client 全量抓取注册表以及每隔30秒增量抓取注册表,都是合并到本地的 Applications 中。Ribbon 与 Eureka 结合后,Ribbon 获取 Server 就从 DiscoveryClient 的 Applications 中获取 Server 列表了
4.根据实例信息 InstanceInfo 创建 Server
它的核心逻辑就是根据服务名从 EurekaClient 获取 InstanceInfo 实例列表,然后封装 Server 信息返回。
5.定时更新Server列表
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer的初始化方法中有一个enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature方法
public void enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature() {
LOGGER.info("Using serverListUpdater {}", serverListUpdater.getClass().getSimpleName());
serverListUpdater.start(updateAction);
}做了几件事:
1.调用 ServerListUpdater 启动了一个 UpdateAction
ServerListUpdater 的默认实现类是 PollingServerListUpdater
PollingServerListUpdater.start()
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
// 执行一次 updateListOfServers
updateAction.doUpdate();
// 设置最后更新时间
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
};
// 固定频率调度
scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
wrapperRunnable,
initialDelayMs,
refreshIntervalMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}做了几件事
以固定的频率,每隔30秒调用一下 updateListOfServers 方法,将 DiscoveryClient 中 Applications 中缓存的实例同步到 ILoadBalancer 中的 allServerList 列表中。
UpdateAction只是调用了一下 DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.updateListOfServers() 方法,就是前面讲解过的全量更新 Server 的逻辑。
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers();
}
};六、非健康服务实例如何下线的源码分析
1.判断Server是否存活
在创建 ILoadBalancer 时,在初始化的时候BaseLoadBalancer.initWithConfig(),设置了当前的 ping,然后重新设置了一个调度任务,默认每隔30秒调度一次 PingTask 任务。
PingTask
class PingTask extends TimerTask {
public void run() {
try {
// pingStrategy => SerialPingStrategy
new Pinger(pingStrategy).runPinger();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error pinging", name, e);
}
}
}Pinger.runPinger
public void runPinger() throws Exception {
if (!pingInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return; // Ping in progress - nothing to do
}
// we are "in" - we get to Ping
Server[] allServers = null;
boolean[] results = null;
Lock allLock = null;
Lock upLock = null;
try {
/*
* The readLock should be free unless an addServer operation is
* going on...
*/
allLock = allServerLock.readLock();
allLock.lock();
// 加读锁,取出 allServerList 中的 Server
allServers = allServerList.toArray(new Server[allServerList.size()]);
allLock.unlock();
int numCandidates = allServers.length;
// 使用 IPingStrategy 和 IPing 对所有 Server 发起 ping 请求
results = pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers);
final List<Server> newUpList = new ArrayList<Server>();
final List<Server> changedServers = new ArrayList<Server>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
boolean isAlive = results[i];
Server svr = allServers[i];
boolean oldIsAlive = svr.isAlive();
// 设置 alive 是否存活
svr.setAlive(isAlive);
// 实例变更
if (oldIsAlive != isAlive) {
changedServers.add(svr);
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: Server [{}] status changed to {}",
name, svr.getId(), (isAlive ? "ALIVE" : "DEAD"));
}
// 添加存活的 Server
if (isAlive) {
newUpList.add(svr);
}
}
upLock = upServerLock.writeLock();
upLock.lock();
// 更新 upServerList,upServerList 只保存了存活的 Server
upServerList = newUpList;
upLock.unlock();
// 通知变更
notifyServerStatusChangeListener(changedServers);
} finally {
pingInProgress.set(false);
}
}主要做了几件事
核心逻辑就是遍历 allServers 列表,使用 IPingStrategy 和 IPing 来判断 Server 是否存活,并更新 Server 的状态,以及将所有存活的 Server 更新到 upServerList 中,upServerList 缓存了所有存活的 Server。
IPingStrategy的默认实现类是 SerialPingStrategy
private static class SerialPingStrategy implements IPingStrategy {
@Override
public boolean[] pingServers(IPing ping, Server[] servers) {
int numCandidates = servers.length;
boolean[] results = new boolean[numCandidates];
logger.debug("LoadBalancer: PingTask executing [{}] servers configured", numCandidates);
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
results[i] = false; /* Default answer is DEAD. */
try {
if (ping != null) {
// 使用 IPing 判断 Server 是否存活
results[i] = ping.isAlive(servers[i]);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Exception while pinging Server: '{}'", servers[i], e);
}
}
return results;
}
}做了几件事
它只是遍历所有 Server,然后用 IPing 判断 Server 是否存活
在集成 eureka-client 后,IPing默认实现类是 NIWSDiscoveryPing
NIWSDiscoveryPing.isAlive
public boolean isAlive(Server server) {
boolean isAlive = true;
if (server!=null && server instanceof DiscoveryEnabledServer){
DiscoveryEnabledServer dServer = (DiscoveryEnabledServer)server;
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = dServer.getInstanceInfo();
if (instanceInfo!=null){
InstanceStatus status = instanceInfo.getStatus();
if (status!=null){
// 判断Server对应的实例状态是否是 UP
isAlive = status.equals(InstanceStatus.UP);
}
}
}
return isAlive;
}做了几件事
其实就是判断对应 Server 的实例 InstanceInfo 的状态是否是 UP 状态,UP状态就表示 Server 存活。
七、结合Feign的调用流程的源码分析
调试源码的时候发现,只有单独用ribbon的时候走了LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法的。
spring cloud全套上去,feign+ribbon,http客户端用OKHttp,这样的话没有走LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器的intercept方法的。
调用链
SynchronousMethodHandler.executeAndDecode()-------->LoadBalancerFeignClient.execute()-------->
AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.executeWithLoadBalancer()-------->BlockingObservable.single()-------->
这里面进入了RXJAVA里面了-------->LoadBalancerCommand.selectServer()-------->LoadBalancerCommand.call()-------->
LoadBalancerContext.getServerFromLoadBalancer()-------->ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.chooseServer()-------->
BaseLoadBalancer.chooseServer()-------->PredicateBasedRule.choose()
源码
AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.executeWithLoadBalancer()
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
// 负载均衡命令
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = buildLoadBalancerCommand(request, requestConfig);
try {
// 发起负载均衡请求
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
// 重构 URI,将服务名用 Server 的 IP 和端口替换
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
// execute 发起调用,实际调用的是 RestClient 中的 execute
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof ClientException) {
throw (ClientException) t;
} else {
throw new ClientException(e);
}
}
}RestTemplate 基于 RestClient 的请求流程
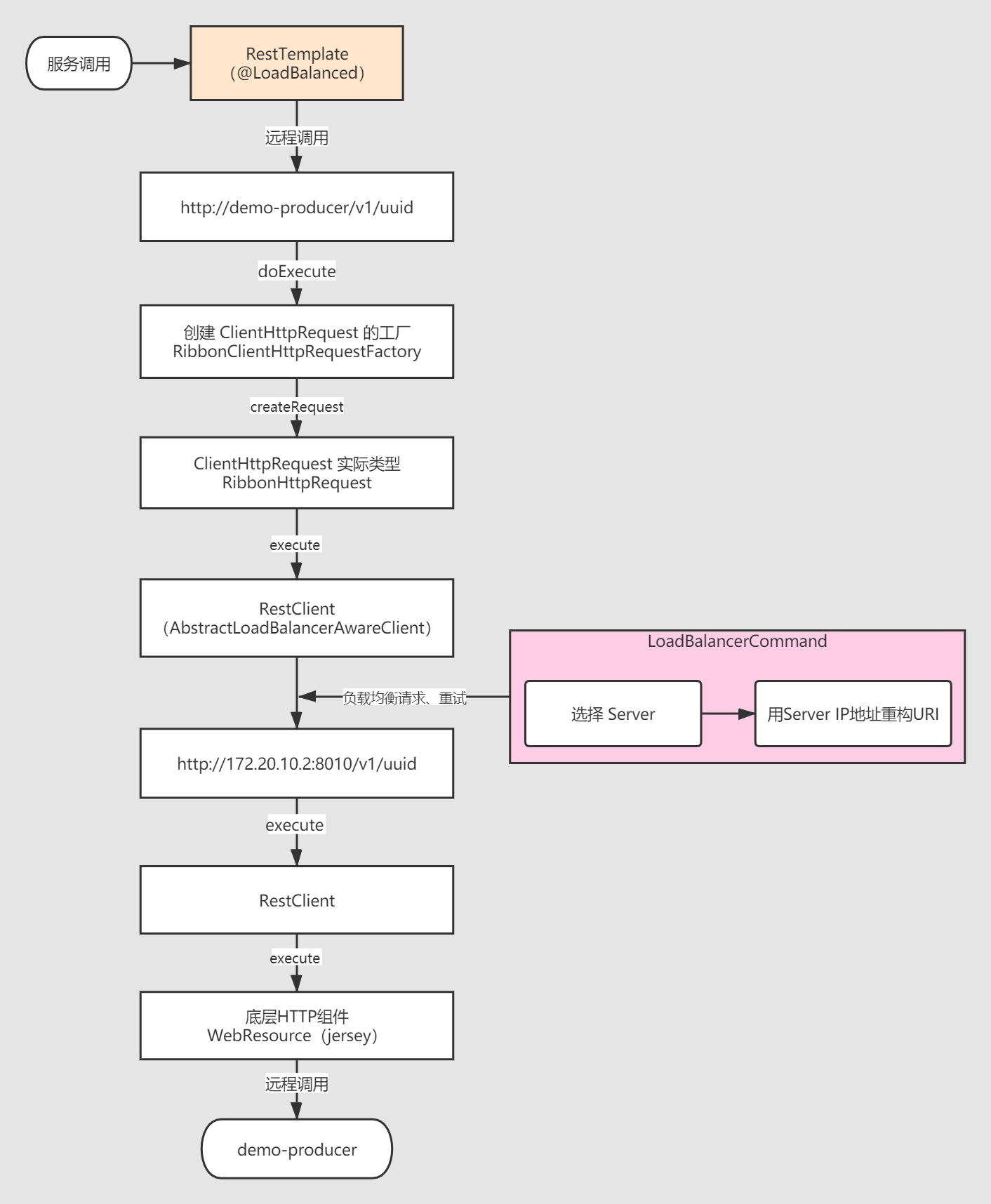
RestTemplate 基于 apache HttpClient 后的执行流程























 563
563











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








