写在前面
这是我在电赛飞控备赛期间写的一个小函数,功能是寻找目标点所在方格的中心。这样四旋翼在方格地图上移动一定距离之后就可以使用openmv将四旋翼辅助定位至目前所在方格的中心。今年G题刚出来的时候本来以为能用上这个函数进行辅助定位,但是后面补充说明中方格的线太细,无法使用,就没能用上这个方案,把这个分享给大家。

详述
整体思路是先使用openmv中寻找直线的函数,找到所有横线和竖线,并筛选出离目标点最近的两条横线和竖线,从而锁定方格中心。
寻找直线的函数如下

该函数使用霍夫变换返回所有直线对象,我们调用该函数,通过限制寻找直线的角度来找到图像中所有的横线和竖线
min_degree = 80
max_degree = 100
for l in img.find_lines(roi=(50,30,220,180),threshold = 900, theta_margin = 25, rho_margin = 25):
if (min_degree <= l.theta()) and (l.theta() <= max_degree):
img.draw_line(l.line(), color = (255, 0, 0))
heng.append(l)
for l in img.find_lines(roi=(50,30,220,180),threshold = 1000,theta_margin = 35, rho_margin = 25):
if (30 >= l.theta()) or (l.theta() >= 150):
img.draw_line(l.line(), color = (255, 0, 0))
shu.append(l)
对于找到的每条直线,我们可以获得其角度theta值和视野左上角到直线的垂直距离rho值,示意图如下,对于openmv来说,图中的原点就是openmv视野的左上角。
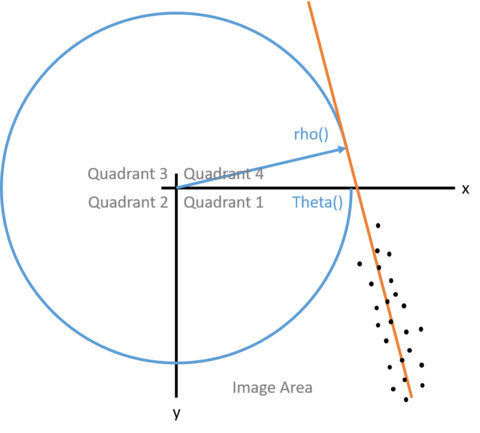
由于我们寻找的都是横线和竖线,可以把rho值近似认为是横线的纵坐标值和竖线的横坐标值,并以此筛选出离目标点最近的两条横线和两条竖线。
if len(heng)>=2:
heng1 = heng[0]
for l in heng:
if abs(l.rho()-my_place[0])<abs(heng1.rho()-my_place[0]):
heng1 = l
heng.pop(heng.index(heng1))
#print(heng)
heng2 = heng[0]
for l in heng:
if abs(l.rho()-my_place[0])<abs(heng2.rho()-my_place[0]):
heng2 = l
count.append(1)
if len(shu)>=2:
shu1 = shu[0]
for l in shu:
if abs(abs(l.rho())-my_place[1])<abs(abs(shu1.rho())-my_place[1]):
shu1 = l
shu.pop(shu.index(shu1))
# print(shu)
shu2 = shu[0]
for l in shu:
if abs(abs(l.rho(</







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








