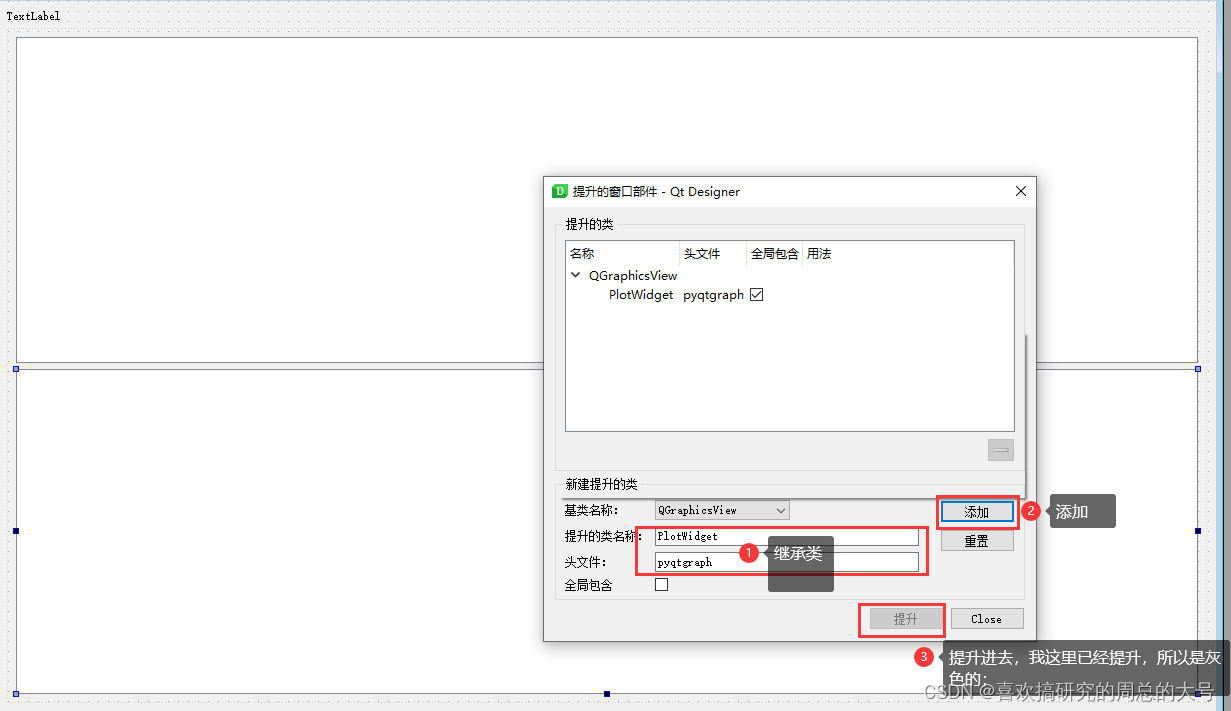
pyqt显示波形的控件为graphicsView,在ui界面中新建一个graphicsView控件,然后如图所示提升类,然后ui转为py文件,就可以在主py文件中调用
以下是初始化
y_min = 0
y_max = 1950
self.graphicsView.plotItem.clear() # 清空绘图部件中的项
self.graphicsView.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 设置绘图部件显示网格线
self.graphicsView.setYRange(y_min, y_max)
self.graphicsView.setXRange(0, 100)
self.graphicsView.setLabel(axis='left', text='数据') # 设置Y轴标签
self.graphicsView.setLabel(axis='bottom', text='时间') # 设置X轴标签
self.label = pg.TextItem() # 创建一个文本项
self.graphicsView.addItem(self.label) # 在图形部件中添加文本项
self.vLine = pg.InfiniteLine(angle=90, movable=False, ) # 创建一个垂直线条
self.hLine = pg.InfiniteLine(angle=0, movable=False, ) # 创建一个水平线条
self.graphicsView.addItem(self.vLine, ignoreBounds=True) # 在图形部件中添加垂直线条
self.graphicsView.addItem(self.hLine, ignoreBounds=True) # 在图形部件中添加水平线条
self.move_slot = pg.SignalProxy(self.graphicsView.scene().sigMouseMoved, rateLimit=60, slot=self.print_slot)
self.graphicsView.getAxis("bottom").setTicks([[(1, 'A'), (2, 'B'), (3, 'C'), (4, 'D')]]) # 设置y轴显示坐标;
self.canvasZ = self.graphicsView.plot(pen="g", name="y2")
self.canvasZ.setData([1,2,3,4]) # 显示数据;
# 显示数据的另外方法;
hour = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] # X轴坐标
temperature = [30,32,34,32,33,31,29,32,35,45] # Y轴坐标
self.graphicsView.setBackground('w') # 设置背景颜色为白色
pen = pg.mkPen(color = (255 , 0 , 0) , width = 15) # 设置曲线颜色为红色,宽度设置为15个像素点
styles ={'color':'r' , 'font-size':'30px'} # 设置标签的颜色和大小
self.graphicsView.setLabel('bottom' , '温度' , **styles) # 设置底部X的标签名字为温度
self.graphicsView.setLabel('left' , '功率' , **styles) # 设置左边Y的标签名字为功率
self.graphicsView.plot(hour , temperature ,pen = pen)如果不用ui提升方式,也可以直接定义,这里的self.k_plt_2就等于self.graphicsView;但是注意的是要将self.k_plt_2添加到对应的显示控件中
self.k_layout_volume = QtWidgets.QGridLayout() # 实例化一个网格布局层
self.widget_3.setLayout(self.k_layout_volume)
self.k_plt_2 = pg.PlotWidget()
self.k_layout_volume.addWidget(self.k_plt_2) 这里是csdn其他人搞得pyqt串口波形显示数据,我测试过,是跑的起来的,但是显示ui中需要提升pyqtgraph才行
import sys
import numpy as np
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import serial
import serial.tools.list_ports
from ui_main import Ui_MainWindow
import pyqtgraph as pg
class AppMainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_MainWindow):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(AppMainWindow, self).__init__(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
self.setWindowTitle("串口数据波形显示工具")
self.PosX = 0
self.dataIndex = 0 # 数据列表当前索引
self.dataMaxLength = 10000 # 数据列表最大长度
self.dataheader = b'$$:' # 数据帧开头
self.dataX = np.zeros(self.dataMaxLength, dtype=float)
self.dataY = np.zeros(self.dataMaxLength, dtype=float)
self.dataZ = np.zeros(self.dataMaxLength, dtype=float)
self.dataH = np.zeros(self.dataMaxLength, dtype=float)
self.mSerial = serial.Serial()
self.ScanComPort()
self.SelectComPort()
self.btnScanPort.clicked.connect(self.ScanComPort)
self.btnOpenPort.clicked.connect(self.OpenComPort)
self.btnClosePort.clicked.connect(self.CloseComPort)
self.cmbComPort.currentIndexChanged.connect(self.SelectComPort)
self.mTimer = QTimer()
self.mTimer.timeout.connect(self.ReceiverPortData)
self.plotM.setAntialiasing(True)
# self.plotM.setBackground()
self.canvasX = self.plotM.plot(self.dataX, pen=pg.mkPen(color='r', width=1))
self.canvasY = self.plotM.plot(self.dataY, pen=pg.mkPen(color='g', width=1))
self.canvasZ = self.plotM.plot(self.dataZ, pen=pg.mkPen(color='b', width=1))
self.canvasH = self.plotM.plot(self.dataH, pen=pg.mkPen(color='y', width=1))
def ScanComPort(self):
self.cmbComPort.clear()
self.portDict = {}
portlist = list(serial.tools.list_ports.comports())
for port in portlist:
self.portDict["%s" % port[0]] = "%s" % port[1]
self.cmbComPort.addItem(port[0])
if len(self.portDict) == 0:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "警告", "未找到串口设备!", QMessageBox.Cancel, QMessageBox.Cancel)
pass
def SelectComPort(self):
if len(self.portDict) > 0 :
self.labComPortName.setText(self.portDict[self.cmbComPort.currentText()])
else:
self.labComPortName.setText("未检测到串口设备!")
pass
def OpenComPort(self):
self.mSerial.port = self.cmbComPort.currentText()
self.mSerial.baudrate = int(self.cmbBaudrate.currentText())
if self.mSerial.isOpen():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "串口已打开", QMessageBox.Cancel, QMessageBox.Cancel)
else:
try:
self.btnOpenPort.setEnabled(False)
self.mSerial.open()
self.mSerial.flushInput()
self.mSerial.flushOutput()
self.mTimer.start(1)
except:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "警告", "串口打开失败!", QMessageBox.Cancel, QMessageBox.Cancel)
self.btnOpenPort.setEnabled(True)
print(self.mSerial)
pass
def CloseComPort(self):
self.mTimer.stop()
if self.mSerial.isOpen():
self.btnOpenPort.setEnabled(True)
self.mSerial.flushInput()
self.mSerial.flushOutput()
self.mSerial.close()
pass
def ReceiverPortData(self):
'''
接收串口数据,并解析出每一个数据项更新到波形图
数据帧格式'$$:95.68,195.04,-184.0\r\n'
每个数据帧以b'$$:'开头,每个数据项以','分割
'''
try:
n = self.mSerial.inWaiting()
except:
self.CloseComPort()
if n > 0:
# 端口缓存内有数据
try:
self.recvdata = self.mSerial.readline(1024) # 读取一行数据最大长度1024字节
if self.recvdata.decode('UTF-8').startswith(self.dataheader.decode('UTF-8')):
rawdata = self.recvdata[len(self.dataheader) : len(self.recvdata) - 2]
data = rawdata.split(b',')
# print(rawdata)
if self.dataIndex < self.dataMaxLength:
# 接收到的数据长度小于最大数据缓存长度,直接按索引赋值,索引自增1
# print(rawdata, rawdata[0], rawdata[1], rawdata[2], self.dataX[self.dataIndex], self.dataY[self.dataIndex], self.dataZ[self.dataIndex])
self.dataX[self.dataIndex] = float(data[0])
self.dataY[self.dataIndex] = float(data[1])
self.dataZ[self.dataIndex] = float(data[2])
self.dataH[self.dataIndex] = float(data[3])
self.dataIndex = self.dataIndex + 1
else:
# 寄收到的数据长度大于或等于最大数据缓存长度,丢弃最前一个数据新数据添加到数据列尾
self.dataX[:-1] = self.dataX[1:]
self.dataY[:-1] = self.dataY[1:]
self.dataZ[:-1] = self.dataZ[1:]
self.dataH[:-1] = self.dataH[1:]
self.dataX[self.dataIndex - 1] = float(data[0])
self.dataY[self.dataIndex - 1] = float(data[1])
self.dataZ[self.dataIndex - 1] = float(data[2])
self.dataH[self.dataIndex - 1] = float(data[3])
# 更新波形数据
self.canvasX.setData(self.dataX)
self.canvasY.setData(self.dataY)
self.canvasZ.setData(self.dataZ)
self.canvasH.setData(self.dataH)
# self.canvasX.setPos(self.PosX, 0)
# self.canvasY.setPos(self.PosX, 0)
# self.canvasZ.setPos(self.PosX, 0)
except:
pass
pass
def SendPortData(self):
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
win = AppMainWindow()
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())





















 748
748











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








