学习书籍:Netty权威指南
多种IO方式的比较:
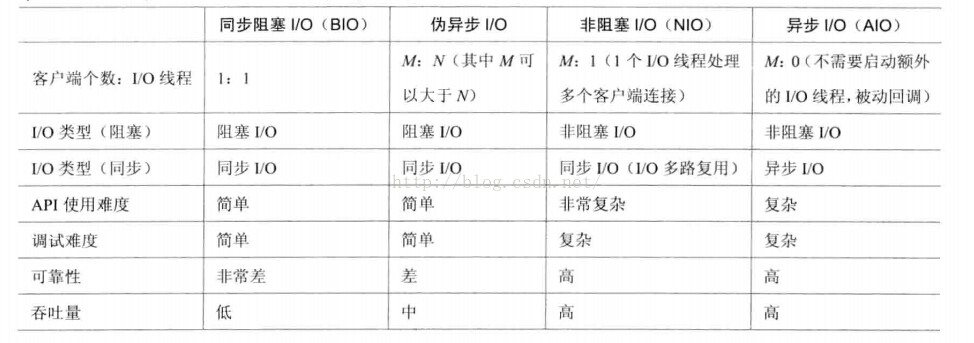
1、BIO(同步阻塞IO)
使用ServerSocket绑定IP地址和监听端口,客户端发起连接,通过三次握手建立连接,用socket来进行通信,通过输入输出流的方式来进行同步阻塞的通信
每次客户端发起连接请求,都会启动一个线程
线程数量:客户端并发访问数为1:1,由于线程是JAVA虚拟机中非常宝贵的资源,一旦线程数急剧增加,系统性能会急剧下降,导致线程栈溢出,创建新的线程失败,并最终导致宕机
所以在JDK1.4之前,人们想到了一种方法,即PIO方式
2、PIO(伪异步阻塞IO)
使用线程池来处理客户端的请求
客户端个数:线程池最大线程数=M:N,其中M远大于N
在read和write的时候,还是IO阻塞的,只是把每个线程交由线程池来控制管理
3、NIO(异步阻塞IO)
用NIO方式处理IO
使用多路复用器Selector来轮询每个通道Channel,当通道中有事件时就通知处理,不会阻塞
使用相当复杂
4、AIO(真正的异步非阻塞IO)
NIO2.0引入了新的异步通道的概念,不需要使用多路复用器(Selector)对注册通道进行轮询即可实现异步读写,从而简化了NIO编程模型
使用Netty框架进行编程步骤
1、构建事件处理池
2、使用引导程序关联事件处理池、通道、事件处理器
3、绑定端口服务
4、等待操作完成
5、关闭事件处理池
几种IO的功能和特性对比
按照书上的例子码了一遍:
服务端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class NettyServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// 等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandle());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
new NettyServer().bind(port);
}
}
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
public class NettyServerHandle extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order:" + body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
ctx.close();
}
}客户端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class NettyClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
// 1、创建线程池
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 2、使用引导器关联线程池、通道、通达处理器、设置执行参数
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandle());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作 3、绑定端口同步操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// 4、监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 5、释放资源
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
new NettyClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
}客户端处理器:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class NettyClientHandle extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger
.getLogger(NettyClientHandle.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
public NettyClientHandle() {
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
}
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is:" + body);
}
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpected exception from downstream:"
+ cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








