- 环境:python3 + unittest + requests
- Excel管理测试用例,
- HTMLTestRunner生成测试报告
- 测试完成后邮件发送测试报告
- jsonpath方式做预期结果数据处理,后期多样化处理
- 后期扩展,CI持续集成
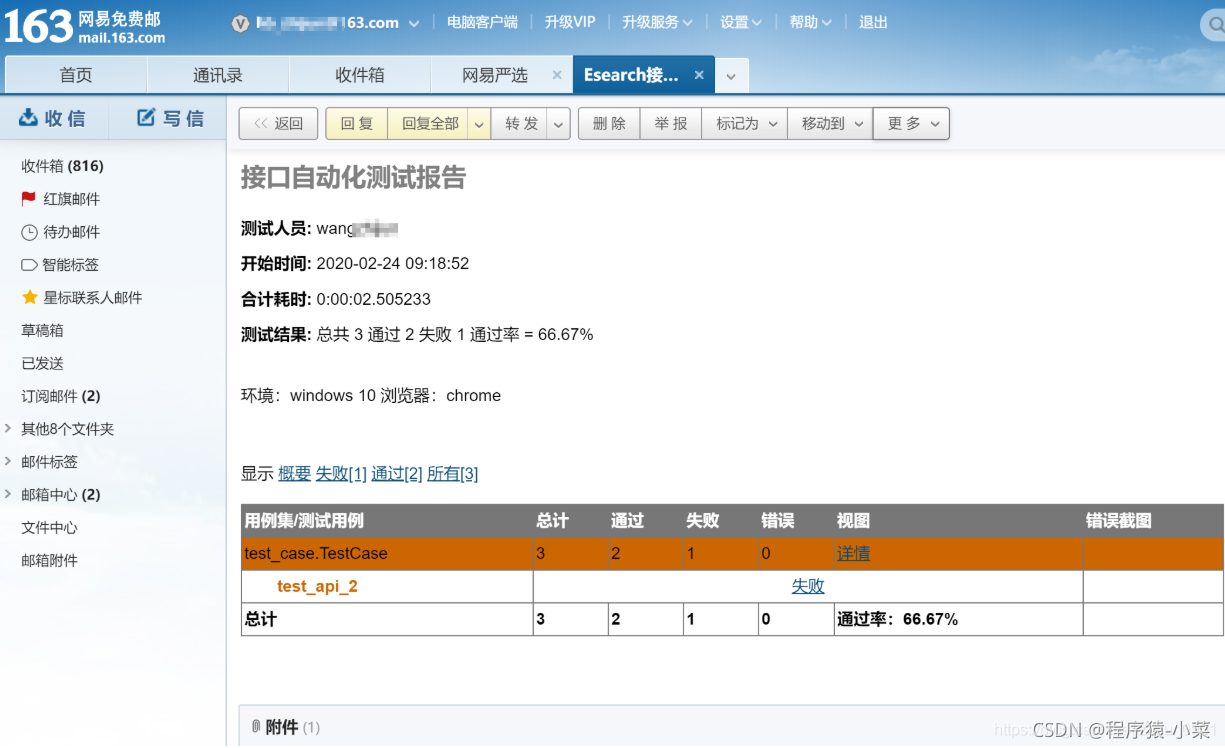
发送邮件效果:
项目整体结构: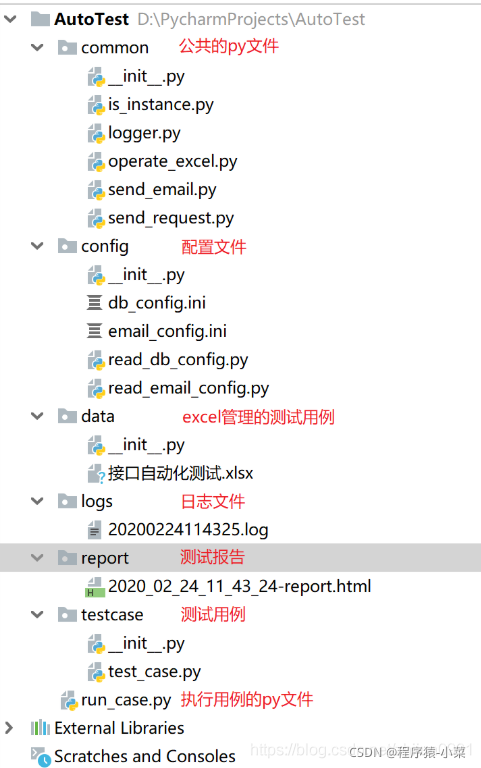
common模块代码
class IsInstance:
def get_instance(self, value, check):
flag = None
if isinstance(value, str):
if check == value:
flag = True
else:
flag = False
elif isinstance(value, float):
if value - float(check) == 0:
flag = True
else:
flag = False
elif isinstance(value, int):
if value - int(check) == 0:
flag = True
else:
flag = False
return flag
# logger.py
import logging
import time
import os
class MyLogging:
def __init__(self):
timestr = time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S', time.localtime(time.time()))
lib_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../logs'))
filename = lib_path + '/' + timestr + '.log' # 日志文件的地址
self.logger = logging.getLogger() # 定义对应的程序模块名name,默认为root
self.logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) # 必须设置,这里如果不显示设置,默认过滤掉warning之前的所有级别的信息
sh = logging.StreamHandler() # 日志输出到屏幕控制台
sh.setLevel(logging.INFO) # 设置日志等级
fh = logging.FileHandler(filename=filename) # 向文件filename输出日志信息
fh.setLevel(logging.INFO) # 设置日志等级
# 设置格式对象
formatter = logging.Formatter(
"%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d]%(levelname)s - %(message)s") # 定义日志输出格式
# 设置handler的格式对象
sh.setFormatter(formatter)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
# 将handler增加到logger中
self.logger.addHandler(sh)
self.logger.addHandler(fh)
if __name__ == "__main__":
log = MyLogging().logger
log.debug("debug")
log.info("info")
log.warning("warning")
log.error("error")
log.critical("critical")
# operate_excel.py
import xlrd
from xlrd import xldate_as_tuple
import openpyxl
import datetime
class ExcelData():
def __init__(self, file_path, sheet_name):
self.file_path = file_path
self.sheet_name = sheet_name
self.workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(self.file_path)
# 获取工作表的内容
self.table = self.workbook.sheet_by_name(self.sheet_name)
# 获取第一行内容
self.keys = self.table.row_values(0)
# 获取行数
self.rowNum = self.table.nrows
# 获取列数
self.colNum = self.table.ncols
def readExcel(self):
datas = []
for i in range(1, self.rowNum):
sheet_data = []
for j in range(self.colNum):
# 获取单元格类型
c_type = self.table.cell(i, j).ctype
# 获取单元格数据
c_cell = self.table.cell_value(i, j)
if c_type == 2 and c_cell % 1 == 0:
c_cell = int(c_cell)
elif c_type == 3:
date = datetime.datetime(*xldate_as_tuple(c_cell, 0))
c_cell = date.strftime('%Y/%d/%m %H:%M:%S')
elif c_type == 4:
c_cell = True if c_cell == 1 else False
# sheet_data[self.keys[j]] = c_cell # 字典
sheet_data.append(c_cell)
datas.append(sheet_data)
return datas
def write(self, rowNum, colNum, result):
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.file_path)
table = workbook.get_sheet_by_name(self.sheet_name)
table = workbook.active
# rows = table.max_row
# cols = table.max_column
# values = ['E','X','C','E','L']
# for value in values:
# table.cell(rows + 1, 1).value = value
# rows = rows + 1
# 指定单元格中写入数据
table.cell(rowNum, colNum, result)
workbook.save(self.file_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
file_path = "D:\python_data\接口自动化测试.xlsx"
sheet_name = "测试用例"
data = ExcelData(file_path, sheet_name)
datas = data.readExcel()
print(datas)
print(type(datas))
for i in datas:
print(i)
# data.write(2,12,"哈哈")
# send_email.py
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.header import Header
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from config import read_email_config
import smtplib
def send_email(subject, mail_body, file_names=list()):
# 获取邮件相关信息
smtp_server = read_email_config.smtp_server
port = read_email_config.port
user_name = read_email_config.user_name
password = read_email_config.password
sender = read_email_config.sender
receiver = read_email_config.receiver
# 定义邮件内容
msg = MIMEMultipart()
body = MIMEText(mail_body, _subtype="html", _charset="utf-8")
msg["Subject"] = Header(subject, "utf-8")
msg["From"] = user_name
msg["To"] = receiver
msg.attach(body)
# 附件:附件名称用英文
for file_name in file_names:
att = MIMEText(open(file_name, "rb").read(), "base64", "utf-8")
att["Content-Type"] = "application/octet-stream"
att["Content-Disposition"] = "attachment;filename='%s'" % (file_name)
msg.attach(att)
# 登录并发送邮件
try:
smtp = smtplib.SMTP()
smtp.connect(smtp_server)
smtp.login(user_name, password)
smtp.sendmail(sender, receiver.split(','), msg.as_string())
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("邮件发送失败!")
else:
print("邮件发送成功!")
finally:
smtp.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
subject = "测试标题"
mail_body = "测试本文"
receiver = "780156051@qq.com,hb_zhijun@163.com" # 接收人邮件地址 用逗号分隔
file_names = [r'D:\PycharmProjects\AutoTest\result\2020-02-23 13_38_41report.html']
send_email(subject, mail_body, receiver, file_names)
# send_request.py
import requests
import json
class RunMethod:
# post请求
def do_post(self, url, data, headers=None):
res = None
if headers != None:
res = requests.post(url=url, json=data, headers=headers)
else:
res = requests.post(url=url, json=data)
return res.json()
# get请求
def do_get(self, url, data=None, headers=None):
res = None
if headers != None:
res = requests.get(url=url, data=data, headers=headers)
else:
res = requests.get(url=url, data=data)
return res.json()
def run_method(self, method, url, data=None, headers=None):
res = None
if method == "POST" or method == "post":
res = self.do_post(url, data, headers)
else:
res = self.do_get(url, data, headers)
return res
config模块
# coding:utf-8
# 邮件配置信息
[mysqlconf]
host = 127.0.0.1
port = 3306
user = root
password = root
db = test
# coding:utf-8
# 邮箱配置信息
# email_config.ini
[email]
smtp_server = smtp.qq.com
port = 465
sender = 780***51@qq.com
password = hrpk******baf
user_name = 780***51@qq.com
receiver = 780***51@qq.com,h***n@163.com
# coding:utf-8
from pymysql import connect, cursors
from pymysql.err import OperationalError
import os
import configparser
# read_db_config.py
# 读取DB配数据
# os.path.realpath(__file__):返回当前文件的绝对路径
# os.path.dirname(): 返回()所在目录
cur_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
configPath = os.path.join(cur_path, "db_config.ini") # 路径拼接:/config/db_config.ini
conf = configparser.ConfigParser()
conf.read(configPath, encoding="UTF-8")
host = conf.get("mysqlconf", "host")
port = conf.get("mysqlconf", "port ")
user = conf.get("mysqlconf", "user")
password = conf.get("mysqlconf", "password")
port = conf.get("mysqlconf", "port")
# coding:utf-8
import os
import configparser
# 读取邮件数据
# os.path.realpath(__file__):返回当前文件的绝对路径
# os.path.dirname(): 返回()所在目录
# read_email_config.py
cur_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)) # 当前文件的所在目录
configPath = os.path.join(cur_path, "email_config.ini") # 路径拼接:/config/email_config.ini
conf = configparser.ConfigParser()
conf.read(configPath, encoding='UTF-8') # 读取/config/email_config.ini 的内容
# get(section,option) 得到section中option的值,返回为string类型
smtp_server = conf.get("email", "smtp_server")
sender = conf.get("email", "sender")
user_name = conf.get("email","user_name")
password = conf.get("email", "password")
receiver = conf.get("email", "receiver")
port = conf.get("email", "port")
testcase模块
# test_case.py
from common.operate_excel import *
import unittest
from parameterized import parameterized
from common.send_request import RunMethod
import json
from common.logger import MyLogging
import jsonpath
from common.is_instance import IsInstance
from HTMLTestRunner import HTMLTestRunner
import os
import time
lib_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "../data"))
file_path = lib_path + "/" + "接口自动化测试.xlsx" # excel的地址
sheet_name = "测试用例"
log = MyLogging().logger
def getExcelData():
list = ExcelData(file_path, sheet_name).readExcel()
return list
class TestCase(unittest.TestCase):
@parameterized.expand(getExcelData())
def test_api(self, rowNumber, caseRowNumber, testCaseName, priority, apiName, url, method, parmsType, data,
checkPoint, isRun, result):
if isRun == "Y" or isRun == "y":
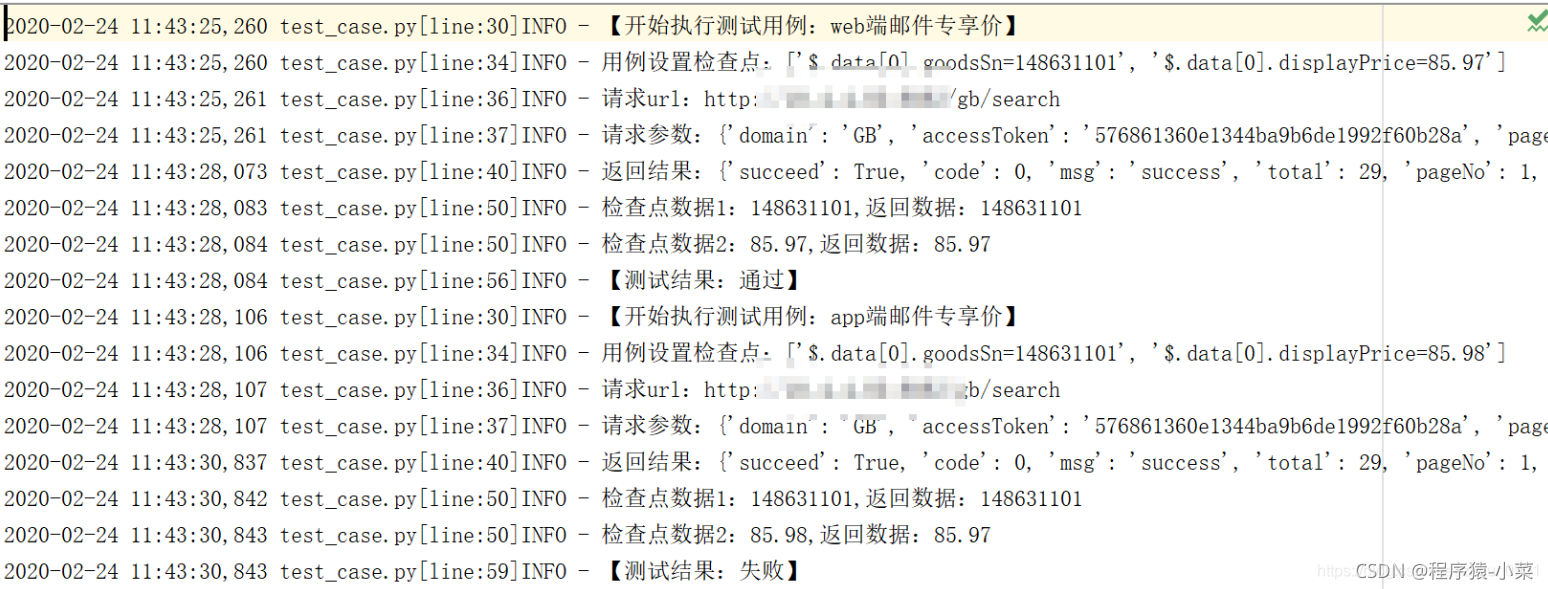
log.info("【开始执行测试用例:{}】".format(testCaseName))
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
data = json.loads(data) # 字典对象转换为json字符串
c = checkPoint.split(",")
log.info("用例设置检查点:%s" % c)
print("用例设置检查点:%s" % c)
log.info("请求url:%s" % url)
log.info("请求参数:%s" % data)
r = RunMethod()
res = r.run_method(method, url, data, headers)
log.info("返回结果:%s" % res)
flag = None
for i in range(0, len(c)):
checkPoint_dict = {}
checkPoint_dict[c[i].split('=')[0]] = c[i].split('=')[1]
# jsonpath方式获取检查点对应的返回数据
list = jsonpath.jsonpath(res, c[i].split('=')[0])
value = list[0]
check = checkPoint_dict[c[i].split('=')[0]]
log.info("检查点数据{}:{},返回数据:{}".format(i + 1, check, value))
print("检查点数据{}:{},返回数据:{}".format(i + 1, check, value))
# 判断检查点数据是否与返回的数据一致
flag = IsInstance().get_instance(value, check)
if flag:
log.info("【测试结果:通过】")
ExcelData(file_path, sheet_name).write(rowNumber + 1, 12, "Pass")
else:
log.info("【测试结果:失败】")
ExcelData(file_path, sheet_name).write(rowNumber + 1, 12, "Fail")
# 断言
self.assertTrue(flag, msg="检查点数据与实际返回数据不一致")
else:
unittest.skip("不执行")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# unittest.main()
# Alt+Shift+f10 执行生成报告
# 报告样式1
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTests(unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(TestCase))
now = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H_%M_%S')
report_path = r"D:\PycharmProjects\AutoTest\result\report.html"
with open(report_path, "wb") as f:
runner = HTMLTestRunner(stream=f, title="Esearch接口测试报告", description="测试用例执行情况", verbosity=2)
runner.run(suite)
用例执行文件
import os
import time
import unittest
from HTMLTestRunner import HTMLTestRunner
from common.send_email import send_email
# run_case.py
# 获取当前py文件绝对路径
cur_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
# 1: 加载测试用例
def all_test():
case_path = os.path.join(cur_path, "testcase")
suite = unittest.TestLoader().discover(start_dir=case_path, pattern="test_*.py", top_level_dir=None)
return suite
# 2: 执行测试用例
def run():
now = time.strftime("%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S")
# 测试报告路径
file_name = os.path.join(cur_path, "report") + "/" + now + "-report.html"
f = open(file_name, "wb")
runner = HTMLTestRunner(stream=f, title="接口自动化测试报告",
description="环境:windows 10 浏览器:chrome",
tester="wangzhijun")
runner.run(all_test())
f.close()
# 3: 获取最新的测试报告
def get_report(report_path):
list = os.listdir(report_path)
list.sort(key=lambda x: os.path.getmtime(os.path.join(report_path, x)))
print("测试报告:", list[-1])
report_file = os.path.join(report_path, list[-1])
return report_file
# 4: 发送邮件
def send_mail(subject, report_file, file_names):
# 读取测试报告内容,作为邮件的正文内容
with open(report_file, "rb") as f:
mail_body = f.read()
send_email(subject, mail_body, file_names)
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
report_path = os.path.join(cur_path, "report") # 测试报告路径
report_file = get_report(report_path) # 测试报告文件
subject = "Esearch接口测试报告" # 邮件主题
file_names = [report_file] # 邮件附件
# 发送邮件
send_mail(subject, report_file, file_names)
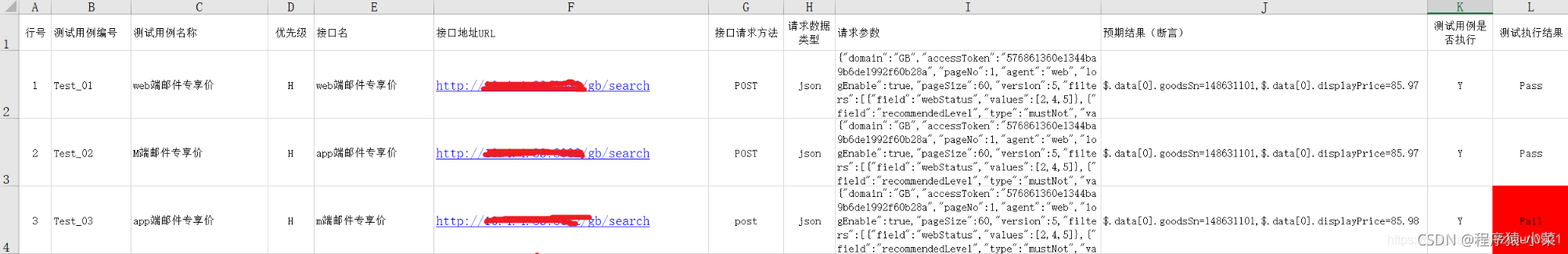
data:
report: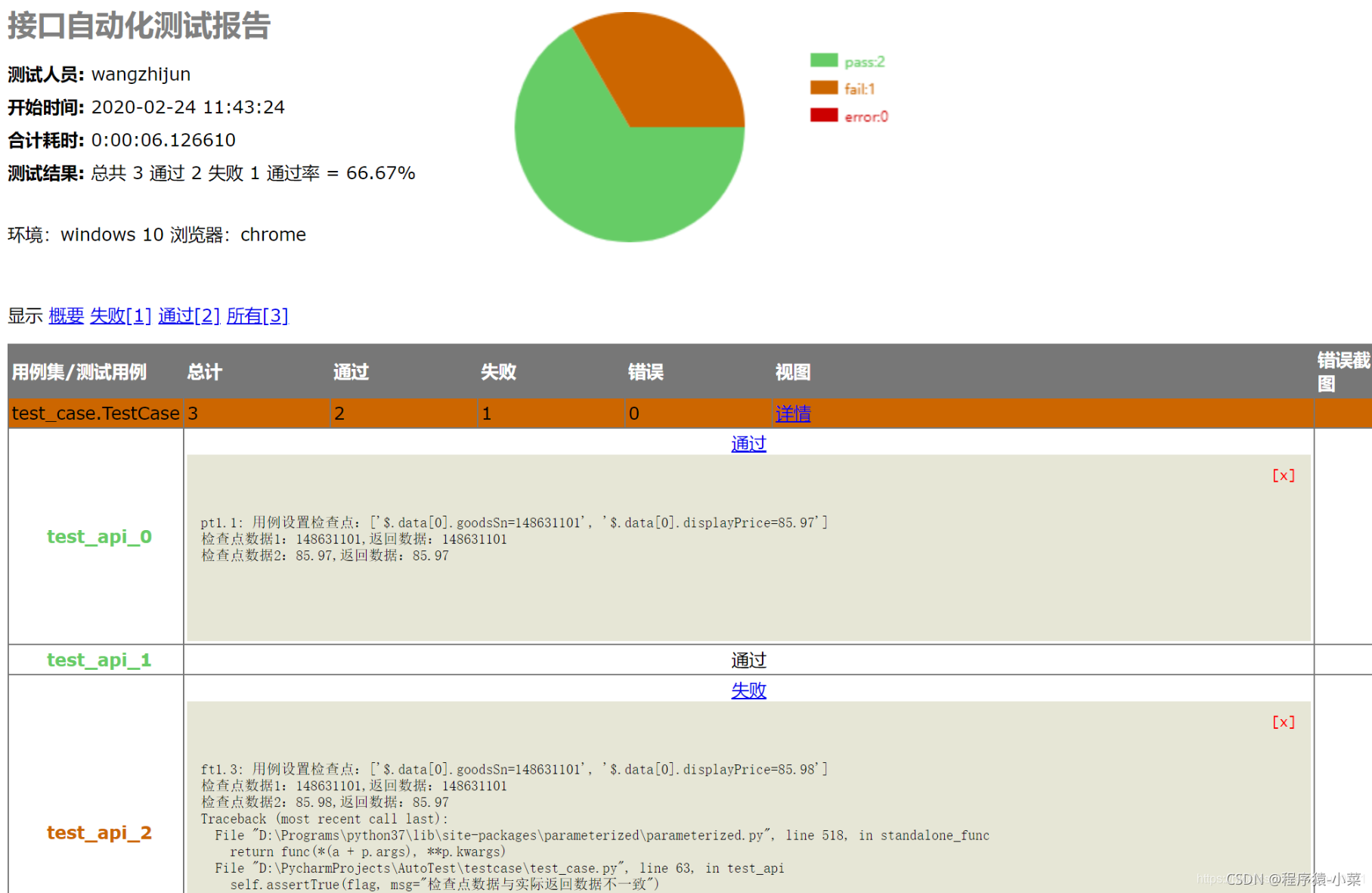
logs:
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:

这些资料,对于【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴上万个测试工程师们走过最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!有需要的小伙伴可以点击下方小卡片领取




















 773
773











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








