LeetCode 104 二叉树的最大深度
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
思路:
二叉树的高度相当于二叉树的最大深度。针对这一点,通过用后序遍历求高度的方法求出高度,即求出了最大深度。如果要直接求深度,理论上是使用前序遍历。
代码:
递归法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
int getHeight(TreeNode *node)
{
if(node==nullptr) return 0;
int leftheight = getHeight(node->left); // 左
int rightheight = getHeight(node->right); // 右
int height = 1+max(leftheight,rightheight); // 为什么加1---->因为上面求的是root的左右子树的高度,此时还需要加上它们到root的高度
return height;
}
};层序遍历法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
depth++;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};总结
层序遍历的方法昨天写过了,学习到了递归法。还学习到了高度和深度的区别。
LeetCode 111 二叉树的最小深度
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
思路:
二叉树的最小高度即二叉树的最小深度。所以还是可以采取后序遍历的方式去写代码。
代码:
递归法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getheight(root);
}
int getheight(TreeNode *node)
{
if(node==nullptr) return 0;
int leftheight = getheight(node->left); // 左
int rightheight = getheight(node->right); // 右
// 中
if(node->left&&!node->right)
return 1+leftheight;
else if(!node->left&&node->right)
return 1+rightheight;
int result = 1+min(leftheight,rightheight);
return result;
}
};层序遍历法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
depth++;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
que.push(node->right);
// 判断左右节点是否存在,不存在则说明已经到了最近叶节点处
if(!node->left&&!node->right)
return depth;
}
}
return depth;
}
};总结
加强递归的练习。
LeetCode 222 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/
思路:
1、普通二叉树
递归法类似求最大深度,依然用后序遍历的方法,只是在“中”的处理上有不同。层序遍历的话只要按部就班套层序遍历的模板就好,只是加了一个整型去记录节点数。
代码:
递归法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return count(root);
}
int count(TreeNode *node)
{
if(node==nullptr) return 0;
int leftnode = count(node->left); // 左
int rightnode = count(node->right); // 右
// 中
int sum = 1+leftnode+rightnode;
return sum;
}
};层序遍历法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
int sum = 0;
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
sum +=size;
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return sum;
}
};2、完全二叉树
满二叉树节点可以用深度来计算: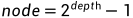 .而对于完全二叉树,除了最底层,上面的都是满二叉树,所以只要求到次底层的深度就可以求到除最底层外的节点数。所以关键在于确定是否是满二叉树。
.而对于完全二叉树,除了最底层,上面的都是满二叉树,所以只要求到次底层的深度就可以求到除最底层外的节点数。所以关键在于确定是否是满二叉树。
如何判断满二叉树?
答:通过对该子树的最左侧和最右侧进行遍历,看最左侧的深度和最右侧的深度是否相同。
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
// 终止条件
// 空节点
if(!root) return 0;
// 满二叉树
int leftheight = 0;
int rightheight = 0;
TreeNode *left = root->left;
TreeNode *right = root->right;
while(left)
{
left = left->left;
leftheight++;
}
while(right)
{
right = right->right;
rightheight++;
}
if(leftheight==rightheight)
return (2<<leftheight)-1;
// 左
int leftnode = countNodes(root->left);
// 右
int rightnode = countNodes(root->right);
// 中
int result = leftnode+rightnode+1;
return result;
}
};总结
想到了普通二叉树的递归法和层序遍历法。对于完全二叉树的性质还要加强学习。完全二叉树的递归法还要多加练习。
今日总结:
相对简单。利用完全二叉树的性质求节点还需要多加思考,看了视频可以理解,但是自己写的时候还是右问题。对于递归,现在按照卡哥给的三步走,简单的递归已经没有问题了。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








