遍历算法:
for_each
//普通函数
void print01(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
//仿函数
class print02 {
public:
void operator()(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
};
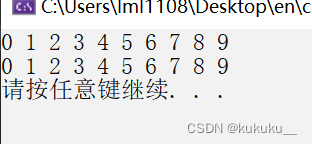
void test01() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);
cout << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());
cout << endl;
}
Transform
class Transform {
public:
int operator()(int v) {
return v;
}
};
class Myprint {
public:
void operator()(int v) {
cout << v << " ";
}
};
void test02() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int> v1;//目标容器
v1.resize(v.size());//为目标容器开辟空间
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v1.begin(), Transform());
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), Myprint());
cout << endl;
}

查找算法:
Find
//内置数据类型的查找
void test03() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
if (it == v.end()) {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到" << *it << endl;
}
}

//自定义类型查找
class Person {
public:
string name;
int age;
Person(string n, int a) :name(n), age(a) {
}
//重载== 让find底层知道如何判等
bool operator==(const Person& p) {
if (this->name == p.name && this->age == p.age) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
};
void test04() {
vector<Person> v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 30);
Person p3("ccc", 20);
Person p4("ddd", 50);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
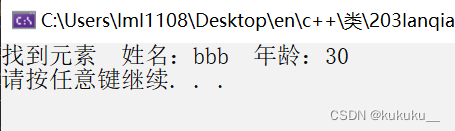
vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p2);
if (it == v.end()) {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到元素 姓名:" << it->name << " 年龄:" << it->age << endl;
}
}
Find_if
//仿函数
class Greater5 {
public:
bool operator()(int val) {
return val > 5;
}
};
//内置数据类型查找条件函数
void test05() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater5());
if (it == v.end()) {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到大于5的数据:" << *it << endl;
}
}

class Person {
public:
string name;
int age;
Person(string n, int a) :name(n), age(a) {
}
//重载== 让find底层知道如何判等
bool operator==(const Person& p) {
if (this->name == p.name && this->age == p.age) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
};
//查找大于30岁的人
class Greater30 {
public:
bool operator()(Person& p) {
return p.age > 30;
}
};
//自定义类型的查找条件函数
void test06() {
vector<Person> v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 30);
Person p3("ccc", 20);
Person p4("ddd", 50);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater30());
if (it == v.end()) {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到大于30岁的人 姓名:" << it->name << " 年龄:" << it->age << endl;
}
}

Adjacent_find
//查找相邻两个相同的数
void test07() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(3);
vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it == v.end()) {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到相邻相同的数据:" << *it << endl;
}
}

Binary_search
//查找指定元素是否存在
//容器必须有序
void test08() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
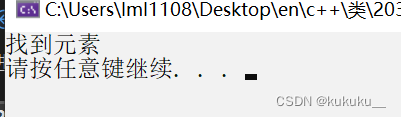
if (binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9)) {
cout << "找到元素" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "未找到元素" << endl;
}
}
Count
//查找统计内置数据
void test09() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(50);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 30);
cout << "30的元素个数是:" << num << endl;
}

//查找统计自定义类型
class Per {
public:
string name;
int age;
Per(string n, int a) :name(n), age(a) {
}
bool operator==(const Per& p) {
return this->age == p.age;
}
};
void test10() {
vector<Per> v;
Per p1("aaa", 10);
Per p2("bbb", 30);
Per p3("ccc", 40);
Per p4("ddd", 20);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
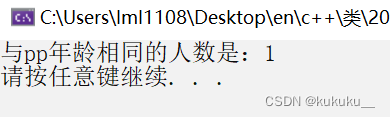
Per pp("ddd", 20);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
cout << "与pp年龄相同的人数是:" << num << endl;
}
Count_if
//统计查找内置数据类型
void test11() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(60);
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());
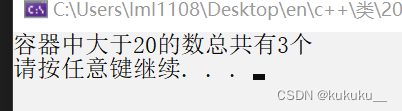
cout << "容器中大于20的数总共有" << num << "个" << endl;
}
//查找统计自定义类型
class Per {
public:
string name;
int age;
Per(string n, int a) :name(n), age(a) {
}
bool operator==(const Per& p) {
return this->age == p.age;
}
};
class Grater30 {
public:
bool operator()(const Per&p) {
return p.age > 30;
}
};
void test12() {
vector<Per> v;
Per p1("aaa", 10);
Per p2("bbb", 30);
Per p3("ccc", 40);
Per p4("ddd", 20);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Grater30());
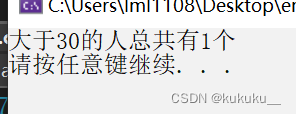
cout << "大于30的人总共有" << num << "个" << endl;
}
排序算法:
Sort
void test14() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(70);
//升序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//降序
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}

Random_shuffle
void Myprint(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
//洗牌随机数打乱
void test15() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
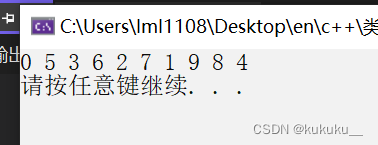
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Myprint);
cout << endl;
}
Merge
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
//将两个有序容器合并到一个容器且这个目标容器也是有序的
void test16() {
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 1);
}
vector<int> v;
v.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v.begin());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
}
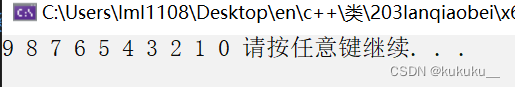
Reverse
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
void test17() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
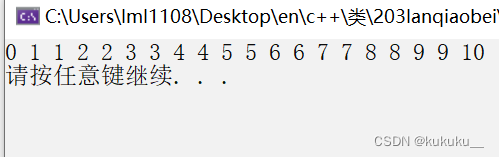
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
}
拷贝和替换的函数:
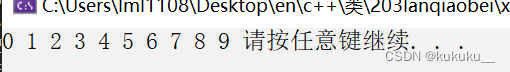
Copy
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
void test18() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int> v1;
v1.resize(v.size());
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v1.begin());
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print02);
}
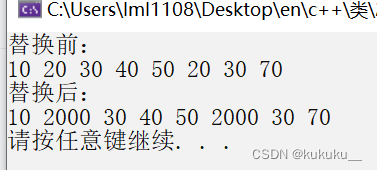
Replace
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}void test19() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(70);
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 2000);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
}
Replace_if
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
class Greater300 {
public:
bool operator()(int val) {
return val >= 30;
}
};
void test20() {
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(70);
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater300(), 3000);
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
}

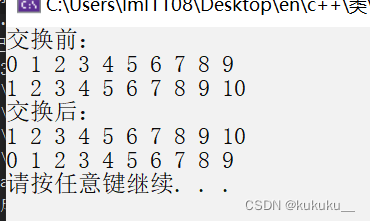
Swap
void print02(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
void test21() {
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 1);
}
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
swap(v1, v2);
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print02);
cout << endl;
}
生成算法
Accumulate
//accumulat 累加算法
void test22() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
cout << total << endl;
}

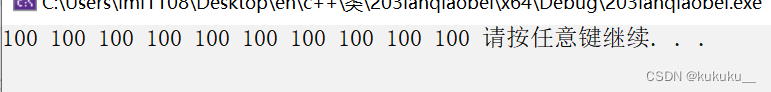
Fill
void test23() {
vector<int> v;
v.resize(10);
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02);
}
集合常用算法
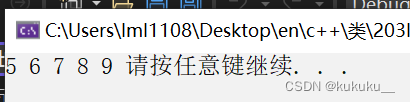
Set_intersection 交集 有序
//交集
void test24() {
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
vector<int> v3;
v3.resize(min(v1.size(),v2.size()));
vector<int>::iterator pos = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), pos, print02);
}
Set_union 并集 容器必须有序
//并集
void test25() {
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
vector<int> v3;
v3.resize(v1.size()+ v2.size());
vector<int>::iterator pos = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), pos, print02);
}

Set_difference 差集 两个容器必须有序
void test26() {
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
vector<int> v3;
v3.resize(max(v1.size() , v2.size()));
vector<int>::iterator pos = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "v1和v2的差集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), pos, print02);
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator itpos = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.begin());
cout << "v2和v1的差集:" << endl;
for_each(v3.begin(), itpos, print02);
cout << endl;
}






















 60
60











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








