Linux Shell零基础案例实战(一)
本期内容:
1 Linux Shell的变量2 Linux Shell的控制结构3 Linux Shell的函数4 Linux Shell在大数据中的应用查看bash版本:查看当前时间:root@Master:/usr/local/spark/spark-1.6.0-bin-hadoop2.6/sbin# bash -version GNU bash, version 4.3.11(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu) Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html> This is free software; you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.首先创建文件(在其中输入如下内容) vim who.shroot@Master:/usr/local/spark/spark-1.6.0-bin-hadoop2.6/sbin# date 2016年 01月 30日 星期六 05:27:22 CST
#!/bin/bash date who ~1、 #!:表示shell脚本的起始符号(文本类型的特殊标记),#!后面是指定的目录,一般使用bash,#!/bin/bash 也可以简写为#!/bin/sh2、当执行shell文件的时候,需要执行权限 root@Master:~# chmod u+x who.sh3、执行who.sh (我们可以看到下面已经执行成功)root@Master:~# ./who.sh 2016年 01月 30日 星期六 05:33:42 CST root :0 2016-01-25 19:59 (:0) root pts/1 2016-01-30 05:07 (:0) root@Master:~#注:一般使用#进行注释,shell中一般是一些基本指令4、shell命令是一些基本的命令组合,在交互式命令终端中可以写入什么5、同一行有多条指令的时候,可以“;”进行分隔(下面将我们创建的who.sh修改为下面格式)#!/bin/bash date;who;ls -l1、vim是vi的加强版,提供了执行输入、输出、查找、删除、替换、快操作等众多的文本操作内容,更为强大的是用户可以根据自己的需要对vim进行定制。2、vim的几种工作模式:1)Normal Mode,如“:wq”保存并退出,“:q”直接退出,“:q!”退出不保存
# "who.sh" 2L, 27C 2L表示两行,27C表示27个字节数 (shell脚本的最后一行)2)Insert Mode ,使用“i”进行插入,修改内容后按下“ESC”退出到Normal Mode
使用gedit文本编辑器 gedit who.sh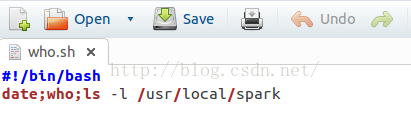






















 29万+
29万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








