分析
dfs 回溯可解。为什么不剪枝?因为暂时没有什么剪枝的思路。
代码
#include <cstdio>
int G[5][5], startx, starty, min;
int A[5][5] = {1,1,1,1,1, 0,1,1,1,1, 0,0,-1,1,1, 0,0,0,0,1, 0,0,0,0,0};
int next[8][2] = {-2,-1, -2,1, -1,-2, -1,2, 1,-2, 1,2, 2,-1, 2,1};
void dfs(int x, int y, int s)
{
if (s >= min) return;
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if (G[i][j] != A[i][j]) n++;
if (n == 0) { min = s < min ? s: min; return; }
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int nx = x + next[k][0];
int ny = y + next[k][1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < 5 && ny >=0 && ny < 5) {
int t = G[x][y];
G[x][y] = G[nx][ny]; G[nx][ny] = t;
dfs(nx, ny, s + 1);
G[nx][ny] = G[x][y]; G[x][y] = t;
}
}
}
void solve()
{
min = 11;
dfs(startx, starty, 0);
if (min == 11) printf("Unsolvable in less than 11 move(s).\n");
else printf("Solvable in %d move(s).\n", min);
}
int main()
{
int N;
char c;
scanf("%d\n", &N);
while (N--) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if ((c = getchar()) == ' ') {
startx = i;
starty = j;
c = '0' - 1;
}
G[i][j] = c - '0';
}
getchar();
}
solve();
}
return 0;
}题目
Description
There are black and white knights on a 5 by 5 chessboard. There are twelve of each color, and there is one square that is empty. At any time, a knight can move into an empty square as long as it moves like a knight in normal chess (what else did you expect?).
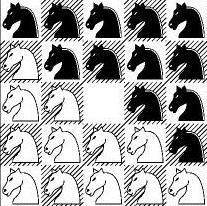
Given an initial position of the board, the question is: what is the minimum number of moves in which we can reach the final position which is:
Input
First line of the input file contains an integer N (N < 14) that indicates how many sets of inputs are there. The description of each set is given below:
Each set consists of five lines; each line represents one row of a chessboard. The positions occupied by white knights are marked by 0 and the positions occupied by black knights are marked by 1. The space corresponds to the empty square on board.
There is no blank line between the two sets of input.
Note: The first set of the sample input below corresponds to this configuration:
Output
For each set your task is to find the minimum number of moves leading from the starting input configuration to the final one. If that number is bigger than 10, then output one line stating
Unsolvable in less than 11 move(s).
otherwise output one line stating
Solvable in n move(s).
where n ≤ 10.
The output for each set is produced in a single line as shown in the sample output.
Sample Input
2 01011 110 1 01110 01010 00100 10110 01 11 10111 01001 00000
Sample Output
Unsolvable in less than 11 move(s). Solvable in 7 move(s).























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








