1.结构体解决闰年问题
![]()
代码:
#include "stdio.h"
struct Date
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
int is_leap(struct Date *date);
int get_day(struct Date *date);
int DAY[12] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
void main() {
struct Date *date = (struct Date *) malloc (sizeof(struct Date));
printf("Please input date(like 1990,3,14):");
scanf("%d,%d,%d", &date->year, &date->month, &date->day);
printf("The day is %d", get_day(date));
}
int is_leap(struct Date *date) {
if(date->year%4== 0 && date->year%100 != 0 || date->year%400 == 0) {
return 1;
} else return 0;
}
int get_day(struct Date *date) {
int result = 0;
if(is_leap(date)) {
DAY[1] = 29;
}
for(int i = 0; i < date->month - 1; i++) {
result = result + DAY[i];
}
result = result + date->day;
return result;
}
输出结果:

3.打印学生成绩
代码:
#include "stdio.h"
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[10];
int score;
};
void print(struct Student *student);
void main() {
struct Student *student = (struct Student *) malloc (5 * sizeof(struct Student));
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Please input student info(like 001,jin,100):");
scanf("%d,%s,%d", &(student + i)->num, (student + i)->name, &(student + i)->score);
//(student + i)->num=1; (student + i)->name="jin"; (student + i)->score=100;
}
print(student);
}
void print(struct Student *student) {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("The student info is %d, %s, %d\n", student->num, student->name, student->score);
student++;
}
}
输出结果:

4.在3题基础上增加input函数。
![]()
代码:
#include "stdio.h"
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[10];
int score;
};
void print(struct Student *student);
void input(struct Student *student);
void main() {
struct Student *student = (struct Student *) malloc (5 * sizeof(struct Student));
input(student);
print(student);
}
void print(struct Student *student) {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("The student info is %d, %s, %d\n", student->num, student->name, student->score);
student++;
}
}
void input(struct Student *student) {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Please input student info(like 001,jin,100):");
scanf("%d,%s,%d", &(student + i)->num, (student + i)->name, &(student + i)->score);
//(student + i)->num=1; (student + i)->name="jin"; (student + i)->score=100;
}
}
输出结果:

5.求学生成绩的最大值和平均值
代码:
#include "stdio.h"
struct Student
{
int num;
char name[10];
int score[3];
};
void print(struct Student *student, int count);
void input(struct Student *student, int count);
int get_mean(struct Student *student, int count);
struct Student *get_max(struct Student *student, int count);
void main() {
int count = 10;
struct Student *student = (struct Student *) malloc (count * sizeof(struct Student));
input(student, count);
print(student, count);
printf("The mean score is: %d\n", get_mean(student, count));
struct Student *p = get_max(student, count);
printf("The max score student info is: %d, %s, %d, %d, %d\n", p->num, p->name, p->score[0], p->score[1], p->score[2]);
}
void print(struct Student *student, int count) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("The student info is %d, %s, %d, %d, %d\n", student->num, student->name, student->score[0], student->score[1], student->score[2]);
student++;
}
}
void input(struct Student *student, int count) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("Please input student info(like 001,jin,100):");
scanf("%d %s %d %d %d", &(student + i)->num, (student + i)->name, (student + i)->score, (student + i)->score + 1, (student + i)->score + 2);
//(student + i)->num=1; (student + i)->name="jin"; (student + i)->score=100;
}
}
int get_mean(struct Student *student,int count) {
int mean = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//printf("get_mean:%d", student->score[0]);
mean = mean + student->score[0] + student->score[1] + student->score[2];
student++;
}
return mean/(count*3);
}
struct Student *get_max(struct Student *student, int count) {
int max_score = 0;
int sum = 0;
struct Student *max_score_stu = student;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
sum = student->score[0] + student->score[1] + student->score[2];
if(max_score < sum){
max_score = sum;
max_score_stu = student;
}
student++;
}
return max_score_stu;
}
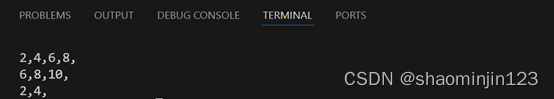
6. 报数问题
![]()
代码:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct List
{
int id;
struct List *next;
};
struct List *init(int n);
struct List *deal(struct List *list, int n);
void print(struct List *list, int n);
void release(struct List *list);
void main() {
int n = 13;
struct List *list = init(n);
struct List *result = deal(list, n);
print(list, n);
printf("The result is:%d", result->id);
release(list);
//print(list, n);
}
struct List *init(int n) {
struct List * list = (struct List *) malloc (n * sizeof(struct List));
struct List *head_node = list;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list->id = i;
list->next = list + 1;
list++;
}
list--;
list->next = head_node;
return head_node;
}
struct List *deal(struct List *list, int n) {
int count = 0;
struct List *node = list;
while(node->next != node) {
count++;
if(count == 2) {
node->next = node->next->next;
count = 0;
}
node = node->next;
}
return node;
}
void print(struct List *list, int n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d,", list->id);
list = list->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void release(struct List *list) {
free(list);
}
输出结果:

7.8.9 单链表的删除,插入操作

代码:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct List
{
int id;
struct List *next;
};
struct List *create(int n);
void delete(struct List *list, int n);
void insert(struct List *list, struct List *node, int n);
void print(struct List *list);
void release(struct List *list);
void main() {
// int n = 13;
// struct List *list = create(n);
//7 delete node
// delete(list, 2);
// print(list);
//8 insert node
// struct List node;
// node.id = 14;
// node.next = NULL;
// int address = 2;
// insert(list, &node, address);
// print(list);
//9
int n = 13;
struct List *list = create(n);
print(list);
delete(list, 2);
print(list);
struct List node;
node.id = 14;
node.next = NULL;
int address = 3;
insert(list, &node, address);
print(list);
release(list);
}
struct List *create(int n) {
struct List *list = (struct List *) malloc (n * sizeof(struct List));
struct List *head_node = list;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list->id = i;
list->next = list + 1;
list++;
}
list--;
list->next = NULL;
return head_node;
}
void delete(struct List *list, int n) {
struct List *node = list;
while(node->next) {
if(node->id == n-1) {
node->next = node->next->next;
//free(node->next);
return;
}
node = node->next;
}
}
void print(struct List *list) {
for(int i = 0; list != NULL; i++) {
printf("%d,", list->id);
list = list->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void insert(struct List *list, struct List *insert_node, int n) {
struct List *node = list;
while(node) {
if(node->id == n) {
insert_node->next = node->next;
node->next = insert_node;
return;
}
node = node->next;
}
}
void release(struct List *list) {
free(list);
}
输出结果:

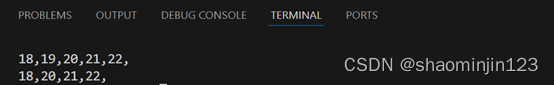
10.11.12 学生数据的管理

代码:
#include "stdio.h"
//10
struct Student1 {
int id;
int score;
struct Student1 *next;
};
struct Student1 *create(int m, int n);
struct Student1 *merge(struct Student1 *a, struct Student1 *b);
void sort(struct Student1 *c);
void print(struct Student1 *student);
void release(struct Student1 *list);
void swap(int *a, int *b);
//11
struct Student2 {
int id;
char *name;
struct Student2 *next;
};
struct Student2 *create2(int m, int n);
void delete(struct Student2 *a, struct Student2 *b);
void print2(struct Student2 *student);
//12
struct Student3 {
int id;
char *name;
int sex;
int age;
struct Student3 *next;
};
struct Student3 *create3(int m, int n);
void delete2(struct Student3 *a, int age);
void print3(struct Student3 *student);
void main() {
//10
struct Student1 *a = create(1, 5);
print(a);
struct Student1 *b = create(3, 6);
print(b);
struct Student1 *c = merge(a,b);
print(c);
sort(c);
print(c);
release(a);
release(b);
//11
// struct Student2 *a = create2(1, 5);
// print2(a);
// struct Student2 *b = create2(3, 6);
// print2(b);
// delete(a, b);
// print2(a);
//12
// struct Student3 *a = create3(0, 5);
// print3(a);
// delete2(a,19);
// print3(a);
}
struct Student1 *create(int m, int n) {
struct Student1 *list = (struct Student1 *) malloc ((n-m) * sizeof(struct Student1));
struct Student1 *head_node = list;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++) {
list->id = i*2;
list->score = 100;
list->next = list + 1;
list++;
}
list--;
list->next = NULL;
return head_node;
}
struct Student1 *merge(struct Student1 *a, struct Student1 *b) {
struct Student1 *tail_node = a;
while(tail_node->next) {
tail_node = tail_node->next;
}
tail_node->next = b;
return a;
}
void sort(struct Student1 *c) {
struct Student1 *head_node = c;
struct Student1 *node = c->next;
while (head_node->next)
{
while(node) {
if(head_node->id > node->id) {
swap(&head_node->id, &node->id);
swap(&head_node->score, &node->score);
}
node = node->next;
}
head_node = head_node->next;
node = head_node->next;
}
}
void print(struct Student1 *student) {
for(int i = 0; student != NULL; i++) {
printf("%d,", student->id);
student = student->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp;
temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
void release(struct Student1 *list) {
if(list)free(list);
}
//11
struct Student2 *create2(int m, int n) {
struct Student2 *list = (struct Student2 *) malloc ((n-m) * sizeof(struct Student2));
struct Student2 *head_node = list;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++) {
list->id = i*2;
list->name = "jin";
list->next = list + 1;
list++;
}
list--;
list->next = NULL;
return head_node;
}
void print2(struct Student2 *student) {
for(int i = 0; student != NULL; i++) {
printf("%d,", student->id);
student = student->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void delete(struct Student2 *a, struct Student2 *b) {
struct Student2 *a_node = (struct Student2 *) malloc (sizeof(struct Student2));
a_node->next = a;
struct Student2 *head = a_node;
int is_delete = 0;
struct Student2 *b_node = b;
while(a_node->next) {
while(b_node) {
if(a_node->next->id == b_node->id) {
if(a_node->next->id == b_node->id) {
a_node->next = a_node->next->next;
is_delete = 1;
break;
//free(a_node->next);
}
}
b_node = b_node->next;
}
if(!is_delete) {
a_node = a_node->next;
} else {
is_delete = 0;
}
b_node = b;
}
a = head->next;
//free(a_node);
}
struct Student3 *create3(int m, int n) {
struct Student3 *list = (struct Student3 *) malloc ((n-m) * sizeof(struct Student3));
struct Student3 *head_node = list;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++) {
list->id = i;
list->name = "jin";
list->sex = 1;
list->age = 18 + i;
list->next = list + 1;
list++;
}
list--;
list->next = NULL;
return head_node;
}
void delete2(struct Student3 *a, int age) {
struct Student3 *a_node = (struct Student3 *) malloc (sizeof(struct Student3));
a_node->next = a;
struct Student3 *head = a_node;
while(a_node->next) {
if(a_node->next->age == age) {
a_node->next = a_node->next->next;
break;
}
a_node = a_node->next;
}
}
void print3(struct Student3 *student) {
for(int i = 0; student != NULL; i++) {
printf("%d,", student->age);
student = student->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
输出结果:























 295
295











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








