56.机器人的运动范围
题目内容:
代码及思路:
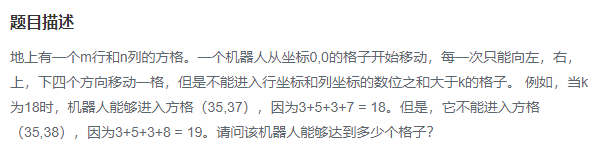
关于运动坐标范围如图所示

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols)
{
if (threshold< 0 || rows <= 0 || cols<=0)
return 0;
bool* visit = new bool[rows*cols];//用来存放每个节点处是否可以进入
memset(visit, 0, rows*cols);
int count = movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, 0, 0, visit);
delete[] visit;
return count;
}
int movingCountCore(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, bool* visit)
{
int num=0;
if (check(threshold, rows, cols, row, col, visit)) //如果满足进入条件
{
visit[row*cols + col] = true;
//判断当前位置的上下左右
num = 1 + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col + 1, visit)
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col - 1, visit)
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row - 1, col, visit)
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row + 1, col, visit);
}
return num;
}
//用来判断行坐标与列坐标的数位之和是否大于k
bool check(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, bool*visit)
{
//如果和小于等于k则可以返回true
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0 && row < rows&&col < cols&&((GetSum(col) + GetSum(row) )<= threshold) && !visit[row*cols + col])
return true;
return false;
}
//计算当前行坐标/列坐标的数位之和
int GetSum(int number)
{
int sum = 0;
while (number >0)
{
sum +=(number%10 );
number /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
};
void main()
{
Solution* object = new Solution();
int threshold;
int rows, cols;
cin >> threshold >> rows >> cols;
int count = object->movingCount(threshold, rows, cols);
cout << count << endl;
}






















 101
101











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








