题目描述:给你两个数组,可以是数字的,也可以是字符串,我们假设是数字的!举个例子:
X = 1, 5, 6, 4, 1, 3, 7
Y = 1, 1, 6, 8, 3, 4, 7
求一个新的数组S,该数组中的每个数均是X和Y数组中的公共数,并满足原数组中数字的前后关系,这样的数组有很多个,比如说 (1,1),(1,1,3,7),(1,6,7)等。同时S数组要是长度最长的那个,像上面的(1,1,3,7),长度是4,那么即为所求解!
做DP题目最重要的一点是能正确的构造出DP函数,如果能很好的构造出来,就成功一半了。
dp[i][j] 表示X数组的前i位和Y数组的前j位之前的LCS,那么它可以由前面三个状态推出来。
0 if(i=0 || j=0) --初始化,不难理解,不管是X还是Y数组,只要有一个长度是0,那么S数组就是0
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1] if(i,j>0 && X[i] != Y[j]) --S数组没有添加数字,那么只能从前面继承来,一个从X,一个从Y,看那个大
dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 if(i,j>0 && X[i] == Y[j]) --如果是两个相同,当然是把S数组加1,可以看成X和Y都继承了
代码很简单,两个for循环就可以了。
这样我们可以总结出该问题的递归形式表达:
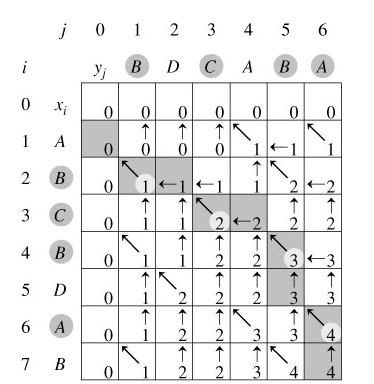
按照动态规划的思想,对问题的求解,其实就是对子问题自底向上的计算过程。这里,计算c[i][j]时,c[i-1][j-1]、c[i-1][j]、c[i][j-1]已经计算出来了,这样,我们可以根据X[i]与Y[j]的取值,按照上面的递推,求出c[i][j],同时把路径记录在b[i][j]中(路径只有3中方向:左上、左、上,如下图)。
计算c[][]矩阵的时间复杂度是O(m*n);根据b[][]矩阵寻找最长公共子序列的过程,由于每次调用至少向上或向左移动一步,这样最多需要(m+n)次就会i = 0或j = 0,也就是算法时间复杂度为O(m+n)。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
void LCS_Print(int **LCS_Direction, char *str, int row, int column)
{
if(str == NULL)
return;
int nLen1 = strlen(str);
if(nLen1 == 0 || row < 0 || column < 0)
return;
if(LCS_Direction[row][column] == 1)
{
if(row > 0 && column > 0)
LCS_Print(LCS_Direction, str, row - 1, column - 1);
printf("%c ", str[row]);
}
else if(LCS_Direction[row][column] == 2)
{
if(row > 0)
LCS_Print(LCS_Direction, str, row - 1, column);
}
else if(LCS_Direction[row][column] == 3)
{
if(column > 0)
LCS_Print(LCS_Direction, str, row, column - 1);
}
}
int LCS(char *str1, char *str2)
{
if(str1 == NULL || str2 == NULL)
return 0;
int nLen1 = strlen(str1);
int nLen2 = strlen(str2);
if(nLen1 <= 0 || nLen2 <= 0)
return 0;
// 申请一个二维数组,保存不同位置的LCS值
int **LCS_Length = new int*[nLen1];
// 申请一个二维数组,保存公共序列的位置
int **LCS_Direction = new int*[nLen1];
for(int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
LCS_Length[i] = new int[nLen2];
LCS_Direction[i] = new int[nLen2];
}
for(int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
LCS_Length[i][0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nLen2; i++)
LCS_Length[0][i] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nLen2; j++)
{
LCS_Direction[i][j] = 0;
}
}
cout<<"Init OK!"<<endl;
for(int i = 0; i <nLen1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nLen2; j++)
{
if(i == 0 || j == 0)
{
if(str1[i] == str2[j])
{
LCS_Length[i][j] = 1;
LCS_Direction[i][j] = 1;
}
else
LCS_Length[i][j] = 0;
}
else if(str1[i] == str2[j])
{
LCS_Length[i][j] = LCS_Length[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
LCS_Direction[i][j] = 1;
}
else if(LCS_Length[i - 1][j] > LCS_Length[i][j - 1])
{
LCS_Length[i][j] = LCS_Length[i - 1][j];
LCS_Direction[i][j] = 2;
}
else
{
LCS_Length[i][j] = LCS_Length[i][j - 1];
LCS_Direction[i][j] = 3;
}
}
}
LCS_Print(LCS_Direction, str1, nLen1 - 1, nLen2 - 1);
cout<<endl;
int nLCS = LCS_Length[nLen1 - 1][nLen2 - 1];
for(int i = 0; i < nLen1; i++)
{
delete[] LCS_Length[i];
delete[] LCS_Direction[i];
}
delete [] LCS_Length;
delete [] LCS_Direction;
return nLCS;
}
int main()
{
cout<<LCS("ABCBDAB", "BDCABA")<<endl;
return 0;
}








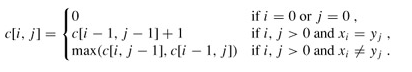


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










