题目:
1.
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
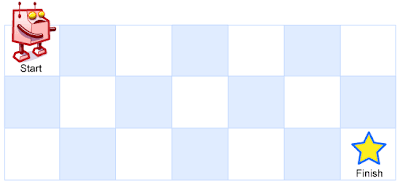
Above is a 3 x 7 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
» Solve this problem
2.
Follow up for "Unique Paths":
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as 1 and 0 respectively in the grid.
For example,
There is one obstacle in the middle of a 3x3 grid as illustrated below.
[ [0,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,0] ]
The total number of unique paths is 2.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
» Solve this problem
3.
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
» Solve this problem
分析:
三道题目如出一辙,分别可以用递归,二维DP,一维DP的解法,先放代码。
代码:
1. Unique Path I
//一维DP法
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j-1];
return dp[n-1];
}
}
//二维DP法
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
int[][] matrix = new int[m][n];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) matrix[i][0] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) matrix[0][i] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j] + matrix[i][j-1];
return matrix[m-1][n-1];
}
}
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
dp[i][0] = 1;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
dp[0][j] = 1;
if(i>0 && j>0)
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
2. Unique Path II
//一维DP法
public class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
if(obstacleGrid[0][0] == 0) dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
dp[j+1] = obstacleGrid[i][j]==1?0:dp[j]+dp[j+1];
return dp[n];
}
}
//二维DP法
public class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
if(obstacleGrid==null || obstacleGrid.length==0 || obstacleGrid[0][0]==1) return 0;
int m = obstacleGrid.length, n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1) dp[i][0] = 0;
else dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0];
}
for(int j=1; j<n; j++){
if(obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1) dp[0][j] = 0;
else dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1];
}
for(int i=1; i<m; i++){
for(int j=1; j<n; j++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][j]==1) dp[i][j] = 0;
else dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
//递归法
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
if(m==1 && n==1) return 1;
if(m==1 || n==1) return 1;
return uniquePaths(m-1, n) + uniquePaths(m, n-1);
}
}3. Minimum Sum Path
//一维DP
public class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
if(i==0 && j==0) dp[0] = grid[0][0];
else if(i == 0) dp[j] = grid[0][j] + dp[j-1];
else if(j == 0) dp[j] = grid[i][0] + dp[0];
else dp[j] = grid[i][j] + Math.min(dp[j], dp[j-1]);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
//二维DP
public class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
// Start typing your Java solution below
// DO NOT write main() function
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i=1; i<m; i++) dp[i][0] = grid[i][0] + dp[i-1][0];
for(int j=1; j<n; j++) dp[0][j] = grid[0][j] + dp[0][j-1];
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}小结:
二维数组的DP算法简单明了,从左上到右下的遍历,选择最优元素并带到下层遍历,最后结束遍历,返回最终值,即最优解。
一维数组DP算法可以看做二维,就想n-queen问题中的board[i]=j的思路一样。具体的解释是,在一个二层循环遍历里,当前的dp[j]表示当前的i,j位置,同时又表示(i-1, j)的位置,而dp[j-1]表示(i, j-1)的位置。
这就是滚动数组的核心思路,剩下的东西就是选择最优解的DP算法了,比较简单。
滚动算法比二维DP有效的节省了空间。























 3147
3147

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








