前言
本文基于 jdk 1.8 分析 HashMap 源码,主要内容有
- 基础知识简介
- HashMap 的底层存储详解
在 jdk1.8 中,HashMap 使用了红黑树来优化,若要彻底理解 HashMap 的相关知识,可以先了解红黑树的相关内容,然后再阅读本文。
主要参数
本小节主要介绍 HashMap 的核心参数及其值设定原理。
-
loadFactor
loadFactor 负载系数(也称负载因子),默认值为 0.75。该值决定了一个 HashMap 实例对象的存储容量将在何时进行扩容。举个简单但不是那么恰当的例子,如图 1 将 hash 表看成是一个装水的桶,在往桶中加入水,当水的体积到达桶的容量的 75% 时则需要更换更大的桶来装水。更换桶后需将小桶的水加入到大桶中。
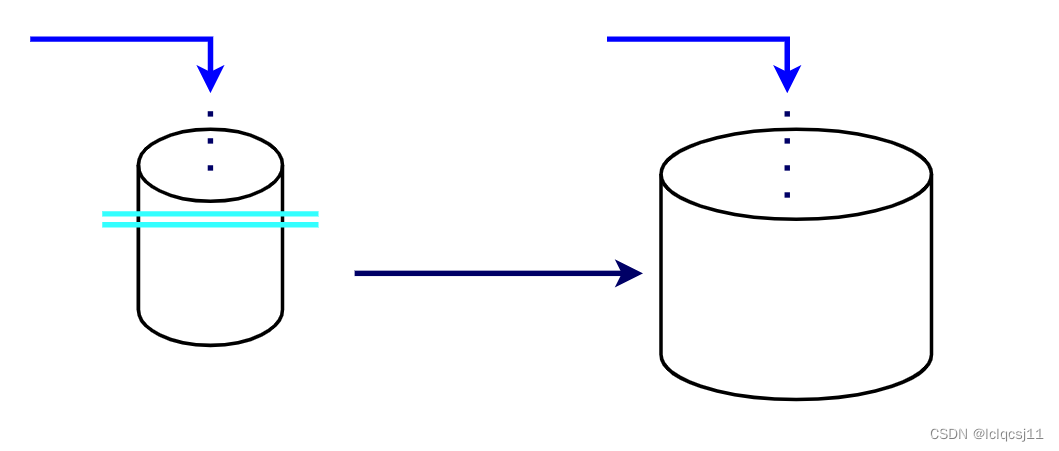
图 1 那么 0.75 值是否是固定不可变?
0.75 是 jdk 设定的默认值,定义该值是权衡时间复杂度和空间复杂度的平衡点而考虑的,该值可在创建 HashMap 实例时通过传入参数改变,其取值范围为 0 ~ 1。
/** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;若实例化 HashMap 时未指定负载系数,将使用默认的值 0.75。负载因子越大,hash 表中可装的元素越多,空间利用率高,但带来的问题是 hash 冲突增加,由于 HashMap 中采用的是拉链法解决 hash 冲突,当冲突增加时,桶中的链表将增加,导致查询性能降低。负载因子越小,hash 表中可装的元素越少,虽减少了 hash 冲突,但需要频繁扩容导致空间利用率不高浪费资源。
实际使用过程中,可依据业务需求适当更改,不过大部分情况下,使用默认值即可。
为何一定是 0.75?
注意看源码中给出的很关键的一个词——
Poisson distribution(泊松分布)。* Because TreeNodes are about twice the size of regular nodes, we * use them only when bins contain enough nodes to warrant use * (see TREEIFY_THRESHOLD). And when they become too small (due to * removal or resizing) they are converted back to plain bins. In * usages with well-distributed user hashCodes, tree bins are * rarely used. Ideally, under random hashCodes, the frequency of * nodes in bins follows a **Poisson distribution** * (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution) with a * parameter of about 0.5 on average for the default resizing * threshold of 0.75, although with a large variance because of * resizing granularity. Ignoring variance, the expected * occurrences of list size k are (exp(-0.5) * pow(0.5, k) / * factorial(k)). The first values are: * * 0: 0.60653066 * 1: 0.30326533 * 2: 0.07581633 * 3: 0.01263606 * 4: 0.00157952 * 5: 0.00015795 * 6: 0.00001316 * 7: 0.00000094 * 8: 0.00000006在理想情况下,使用随机哈希码,节点出现的频率在hash桶中遵循泊松分布,同时给出了桶中元素个数和概率的对照表。从表中可以看到当桶中元素到达8个的时候,概率已经变得非常小,也就是说用 0.75 作为负载因子,每个碰撞位置的链表长度超过8个是几乎不可能的。
-
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD & MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY
这两个参数定义了 hash 表的桶的链表转红黑树的阈值,取值分别为 8,64。只有当桶中的链表长度 >= 8 且 hash 表中元素的数量 > 64 时,才会将链表转化为红黑树。if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 链表长度大于 8 后,尝试转化为红黑树final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; // 再次 hash 表的元素是否大于等于最小元素转化数量 64,不满足则继续扩容 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize();为何是 8、64 的取值?
链表转化为红黑树是一个复杂的过程,且红黑树的数据结构 TreeNode 所需内存是链表 Node 的两倍,费时且费空间。深层次的原因还是基于泊松分布的概率计算而来,而不是拍脑门子决定。
-
UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD
该属性定义了有红黑树转化为列表的值,默认为 6。即当红黑树的节点数为 6 是,将桶的数据结构将由红黑树转化为链表。为何取值为 6?

存储详解
存储结构
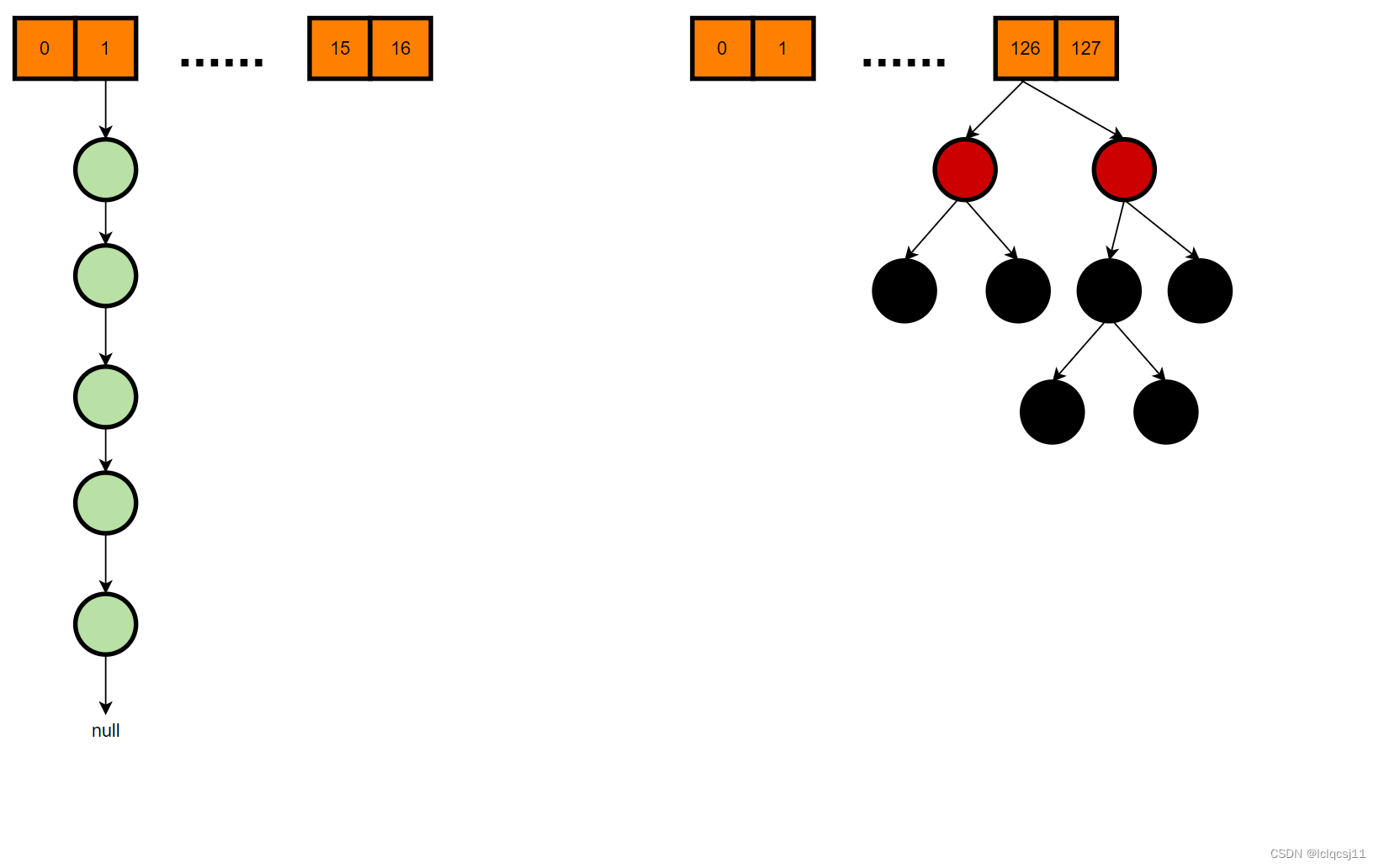
在 jdk1.8 中,HashMap 存储数据使用的数据结构是数组 + 链表 / 红黑树。
- 链表节点数据结构为
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; // hash 值 final K key; // map 中的 key V value; // map 中的 value Node<K,V> next; // 下一个 node } - 红黑树节点数据结构为
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red;
HashMap 的底层数据存储示例可参考图 2。
添加键值对
Map 定义了多种添加键值对方式,常用方式有以下两种
-
put
public V put(K key, V value) { // } -
putAll
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { // }
无论通过哪种方式添加,最后都是调用方法 putVal 将数据添加到 HashMap 实例中。我们通过 putVal 方法的源码,详细分析数据添加过程及数据存储结构随着存储数量的增加发生变化过程。putVal 源码如下。
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 先判断存储的数组是否为空或者长度为 0
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length; // 通过 resize 方法新建一个默认大小的数组
// 判断数组的 i 位置是否已经有元素
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// 不存在元素,则直接将键值对的 node 值放入该位置,结束添加
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
// 数组的 i 位置已经存在元素了
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 如果 hash 值相同且 key 值也相同,说明是更新该 key 对应的值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 如果 p 是 nodeTree 类型,这个下文再详细分析
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// hash 值相同,但 key 不同,且非 treeNode 类型,即出现了 hash 冲突
// 出现 hash 冲突后,HashMap 的处理方式是通过**拉链法**来解决。
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 判断 p 的 next 节点是否为空
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 下一个节点为空,将 当前 key-value 对应的 node 值挂在 p 的 next 下
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 判断哈希冲突生成的链表是否大于等于设定的阈值
// 若大于等于设定的阈值,则将数组 + 链表的存储结构转化为树
// 注意看,这里很重要,并不一定当到达阈值后就立马转变为红黑树,还需要判断桶的数量是否到达 64
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 转化为树
break;
}
// 若命中了链表中的某个节点,即链表中某个节点的 hash 值及 key 都与当前 key 一致
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
从上述代码片段看,有两个重要步骤,分别是
- resize
resize 方法用途就是对当前 HashMap 的存储容量进行扩充,做了两件事
- 容量扩充
- 数据迁移
扩容核心代码如下。
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
// 判断当前数组 tab 的元素数量是否大于等于 HashMap 允许的最大数量
// 当数组中元素数量大于等于最大数量时,将不在扩容
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 这里很重要,当且仅当旧的 tab 大小翻倍后依旧小于 HashMap 允许的最大值
// 且旧的 tab 大小大于等于默认的初始大小 16 时,才会更新 threshold
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
// 创建一个 newCap 大小的数组
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
// 如果旧 table 不为空,将数据迁移到新的 table 中
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
// 判断当前元素是否存在下一个节点,如果不存在,rehash 后放入新 table 的指定位置
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
// 如果是元素是 treeNode 类型,拆分树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
// 如果是链表,将链表的节点拆分并 rehash
// 本部分是链表拆分的核心逻辑
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
扩容逻辑比较简单,不详细展开说,这里着重讲解数据迁移的过程。数据迁移过程涉及到链表的拆分,放入高低位;以及链表转红黑树。
首先是链表的拆分,在遍历旧 hash 表的过程中,当遍历的某个元素的 next 节点不为空时,则要对该链表进行拆分。这里拆分逻辑并非将链表中的每个节点元素 rehash 后直接放入新表 table[hash] 的位置,链表拆分仅占用了新表的两个位置,分别是
newTab[j] = loHead;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
详细拆分过程可参见图 3。
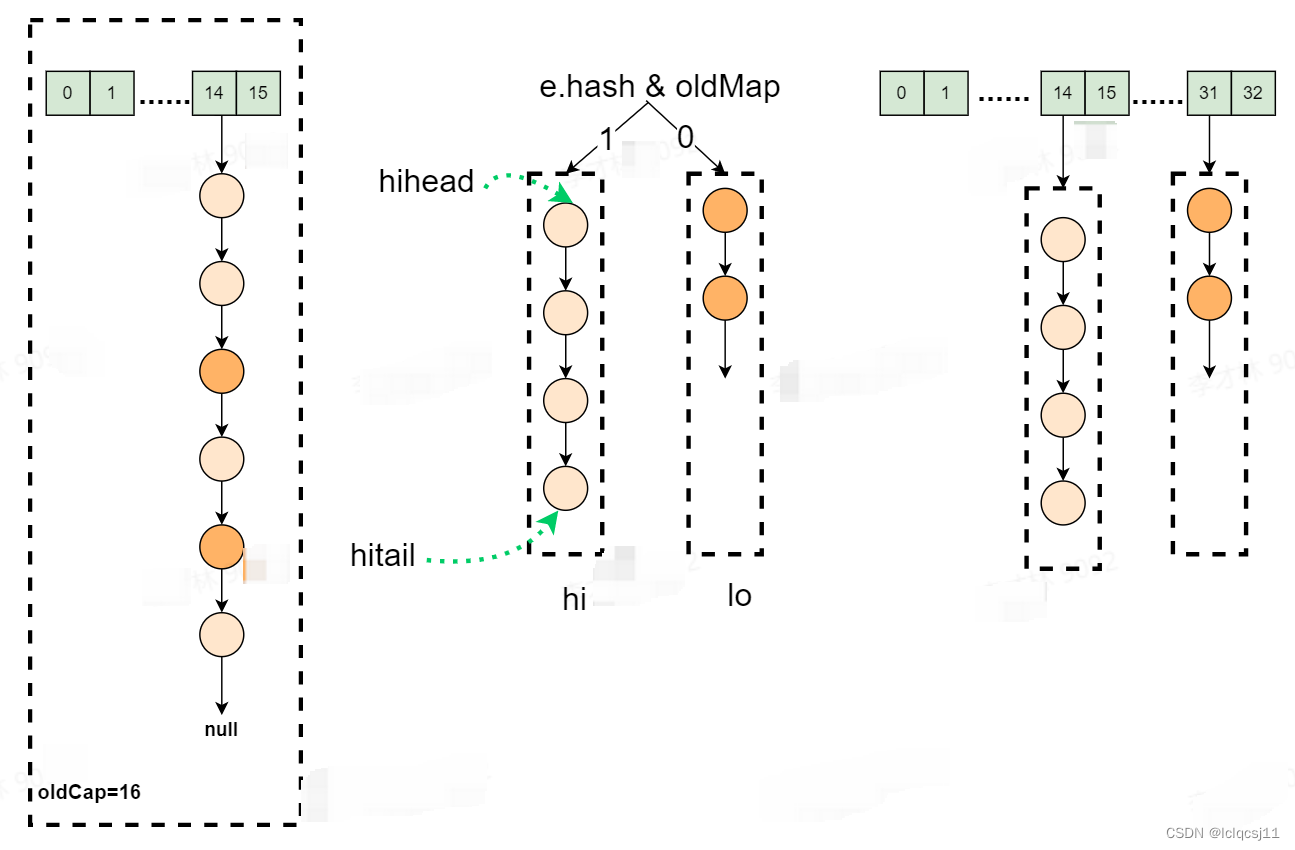
链表拆分核心代码如下
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
// 核心步骤,为啥要这样呢?
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
这里留个问题,为何要取 (e.hash & oldCap) == 0 以及 j+oldCap ?
其次红黑树的拆分,在 rehash 过程中,将遍历整颗红黑树,遍历时与链表相同,按高低位拆分红黑树,拆分后,将根据链表与红黑树转化阈值,当树的节点数小于阈值(UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6)时,红黑树将转化为链表存储,当大于阈值时,将继续使用红黑树,并调整红黑树每个节点的位置,使得拆分后的红黑树依旧保持平衡。关于红黑树的创建及平衡调整,可参考红黑树相关知识,这里不累述。
- treeifyBin
该方法用将数组中的链表转化为红黑树,核心代码如下。
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize(); // 扩容
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab); // 转化,这是核心
}
}
构建红黑树的核心源码
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
链表转红黑树受到两个参数的限制
- 当前桶的链表长度 >= 8
- 当前 hash 表元素数量 >= 64
需要说明的是,此处的元素不包括除链表 head 节点外的其余节点数以及数的 root 节点外的其他节点数。
在构建红黑树的过程中,会不断调整红黑树以满足红黑树达到平衡的条件,调整过程需要耗费时间,因此 HashMap 中的很多参数设定都是折中时间复杂度及空间复杂度来考虑得到的。
HashMap 存在扩容,那是否存在缩容呢?

























 708
708











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








