在linux的网络设备里,其中一个最关键的结构体应该要算net_device了,它由对应的网络设备驱动进行创建和初始化,服务于内核网络子系统。
1. struct net_device 注释分析
struct net_device这个结构体比较大,在了解它之前,我们先看一下它的注释:
1433 /**
1434 * struct net_device - The DEVICE structure.
1435 * Actually, this whole structure is a big mistake. It mixes I/O //这个结构体的设计是一个很大的失误,它并没有对IO数据和高级别的数据进行区分,也就是说这个结构
1436 * data with strictly "high-level" data, and it has to know about //体并没有对数据的来源是普通内存还是高速缓存进行辨别,因此在INET模型里面,它不得不处理各种
1437 * almost every data structure used in the INET module. //不同的数据类型
1438 *
1439 * @name: This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure //它代表一个接口的名字,在设备注册的时候,我们可以指定接口名字,如果没指定,他会自动申请
1440 * (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name //一个自加1的名字,比如eth0,eth1,eth2...
1441 * of the interface.
1442 *
1443 * @name_hlist: Device name hash chain, please keep it close to name[] //以名字为索引的哈希表
1444 * @ifalias: SNMP alias // snmp的别名
1445 * @mem_end: Shared memory end //每一个设备都会分配一块内存区域,start和end指定了这块区域
1446 * @mem_start: Shared memory start
1447 * @base_addr: Device I/O address //网络硬件设备的基地址,内存管理系统将每一个外部设备都看作一块连续的地址,然后将它与内存中的一块地址进行映射,这样操作内存地址就相当于操作这块网络硬件设备的地址,而这里的基地址就是这个网络硬件设备的起始地址。他会在probe的时候初始化
1448 * @irq: Device IRQ number //该设备对应的中断号
1449 *
1450 * @carrier_changes: Stats to monitor carrier on<->off transitions
1451 *
1452 * @state: Generic network queuing layer state, see netdev_state_t //表示设备的状态,它很重要
1453 * @dev_list: The global list of network devices //所有net_device对象组成的一个链表,可以说系统中所有的网络设备都可以通过它查到
1454 * @napi_list: List entry used for polling NAPI devices //如果该支持NAPI,会将它挂到这个链表上,CPU就可以更快的找到NAPI poll的设备
1455 * @unreg_list: List entry when we are unregistering the //正在被卸载的设备会加到这个链表
1456 * device; see the function unregister_netdev
1457 * @close_list: List entry used when we are closing the device //正在被关闭的设备会加到这个链表
1458 * @ptype_all: Device-specific packet handlers for all protocols //某些特定协议的处理函数会挂接在这里,但是未必是需要的
1459 * @ptype_specific: Device-specific, protocol-specific packet handlers
1460 *
1461 * @adj_list: Directly linked devices, like slaves for bonding
1462 * @features: Currently active device features //用来标识接口的各种能力和特性
1463 * @hw_features: User-changeable features //一些硬件相关的特性,这些是可以在用户空间修改的
1464 *
1465 * @wanted_features: User-requested features
1466 * @vlan_features: Mask of features inheritable by VLAN devices //是否支持vlan功能
1467 *
1468 * @hw_enc_features: Mask of features inherited by encapsulating devices //是否支持硬件封装功能
1469 * This field indicates what encapsulation
1470 * offloads the hardware is capable of doing,
1471 * and drivers will need to set them appropriately.
1472 *
1473 * @mpls_features: Mask of features inheritable by MPLS
1474 *
1475 * @ifindex: interface index //内核指定的索引号,比如第一个,第二个设备等等
1476 * @group: The group the device belongs to //这个设备属于哪个组
1477 *
1478 * @stats: Statistics struct, which was left as a legacy, use //一些接口的信息,用于提供给旧接口的用户空间获取
1479 * rtnl_link_stats64 instead
1480 *
1481 * @rx_dropped: Dropped packets by core network, //被内核丢掉的包,注意不是被driver丢的
1482 * do not use this in drivers
1483 * @tx_dropped: Dropped packets by core network,
1484 * do not use this in drivers
1485 * @rx_nohandler: nohandler dropped packets by core network on
1486 * inactive devices, do not use this in drivers
1487 *
1488 * @wireless_handlers: List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions, //无线子系统的一些接口
1489 * instead of ioctl,
1490 * see <net/iw_handler.h> for details.
1491 * @wireless_data: Instance data managed by the core of wireless extensions
1492 *
1493 * @netdev_ops: Includes several pointers to callbacks, //很重要!操作网络设备的函数都聚集在这里了,在网络初始化的时候被初始化,具体支持哪些操作函数,
1494 * if one wants to override the ndo_*() functions //请看这个函数struct net_device_ops()
1495 * @ethtool_ops: Management operations //ethtool的操作接口
1496 * @ndisc_ops: Includes callbacks for different IPv6 neighbour
1497 * discovery handling. Necessary for e.g. 6LoWPAN.
1498 * @header_ops: Includes callbacks for creating,parsing,caching,etc //对L2头部处理的函数
1499 * of Layer 2 headers.
1500 *
1501 * @flags: Interface flags (a la BSD) //标识接口的状态,比如UP/down等,可以通过用户空间修改
1502 * @priv_flags: Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace, //和flags类似,但是用户空间不能修改
1503 * see if.h for the definitions
1504 * @gflags: Global flags ( kept as legacy ) //全局标识,和flags配合使用
1505 * @padded: How much padding added by alloc_netdev() //对齐时使用的字节数,在申请net_device的时候,需要进行对齐,它表示填充的字节数
1506 * @operstate: RFC2863 operstate
1507 * @link_mode: Mapping policy to operstate
1508 * @if_port: Selectable AUI, TP, ... 目前较少用,对于支持多介质的网络设备时,用来指定哪种设备的接口
1509 * @dma: DMA channel //为该设备分配的DMA通道,如果支持的话,目前来说应该都支持了
1510 * @mtu: Interface MTU value //这个不用说了,一般1500
1511 * @min_mtu: Interface Minimum MTU value
1512 * @max_mtu: Interface Maximum MTU value
1513 * @type: Interface hardware type //接口的硬件类型,目前来说主要都是以太网
1514 * @hard_header_len: Maximum hardware header length.
1515 * @min_header_len: Minimum hardware header length
1516 *
1517 * @needed_headroom: Extra headroom the hardware may need, but not in all //需要头部空间吗
1518 * cases can this be guaranteed
1519 * @needed_tailroom: Extra tailroom the hardware may need, but not in all
1520 * cases can this be guaranteed. Some cases also use
1521 * LL_MAX_HEADER instead to allocate the skb
1522 *
1523 * interface address info:
1524 *
1525 * @perm_addr: Permanent hw address //烧写在硬件中的地址,初始化的时候读取到这里
1526 * @addr_assign_type: Hw address assignment type //硬件地址分配类型,目前来说都是支持用户空间对硬件地址进行设置了
1527 * @addr_len: Hardware address length //这个不用说了,14B
1528 * @neigh_priv_len: Used in neigh_alloc()
1529 * @dev_id: Used to differentiate devices that share //这个应该很少用了,如果有多个设备共用一个mac地址,就会有它的作用了,目前见过这样的产品,虽然mac
1530 * the same link layer address //地址一样,但是硬件设备不一样,工作是没有问题的
1531 * @dev_port: Used to differentiate devices that share //如果有多个网络接口实现相同的功能就会用到
1532 * the same function
1533 * @addr_list_lock: XXX: need comments on this one
1534 * @uc_promisc: Counter that indicates promiscuous mode //我们知道,如果不是在混杂模式下,网卡只会接收发往自己的单播地址, 但是如果同时想接收发往其他
1535 * has been enabled due to the need to listen to //mac的单播地址,就需要添加到这里让驱动不要过滤掉
1536 * additional unicast addresses in a device that
1537 * does not implement ndo_set_rx_mode()
1538 * @uc: unicast mac addresses //自己的单播地址
1539 * @mc: multicast mac addresses //自己的广播地址
1540 * @dev_addrs: list of device hw addresses //现在的设备可能同时使用多个mac地址,那么将会保留在这个链表里面
1541 * @queues_kset: Group of all Kobjects in the Tx and RX queues //Tx和Rx链的对象
1542 * @promiscuity: Number of times the NIC is told to work in //是否工作在混杂模式
1543 * promiscuous mode; if it becomes 0 the NIC will
1544 * exit promiscuous mode
1545 * @allmulti: Counter, enables or disables allmulticast mode //开启或关闭allmulti功能,可以通过ifconfig命令设置
1546 *
1547 * @vlan_info: VLAN info //顾名思义
1548 * @dsa_ptr: dsa specific data //下面是各种不同类型包
1549 * @tipc_ptr: TIPC specific data
1550 * @atalk_ptr: AppleTalk link
1552 * @dn_ptr: DECnet specific data
1553 * @ip6_ptr: IPv6 specific data //
1554 * @ax25_ptr: AX.25 specific data
1555 * @ieee80211_ptr: IEEE 802.11 specific data, assign before registering
1556 *
1557 * @dev_addr: Hw address (before bcast, //设备的mac地址
1558 * because most packets are unicast)
1559 *
1560 * @_rx: Array of RX queues //与发包相关的一些设置
1561 * @num_rx_queues: Number of RX queues
1562 * allocated at register_netdev() time
1563 * @real_num_rx_queues: Number of RX queues currently active in device
1564 *
1565 * @rx_handler: handler for received packets //收包处理函数
1566 * @rx_handler_data: XXX: need comments on this one
1567 * @ingress_queue: XXX: need comments on this one
1568 * @broadcast: hw bcast address //广播地址
1569 *
1570 * @rx_cpu_rmap: CPU reverse-mapping for RX completion interrupts,
1571 * indexed by RX queue number. Assigned by driver.
1572 * This must only be set if the ndo_rx_flow_steer
1573 * operation is defined
1574 * @index_hlist: Device index hash chain
1575 *
1576 * @_tx: Array of TX queues //与收报相关的以下设置
1577 * @num_tx_queues: Number of TX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time
1578 * @real_num_tx_queues: Number of TX queues currently active in device
1579 * @qdisc: Root qdisc from userspace point of view
1580 * @tx_queue_len: Max frames per queue allowed
1581 * @tx_global_lock: XXX: need comments on this one
1582 *
1583 * @xps_maps: XXX: need comments on this one
1584 *
1585 * @watchdog_timeo: Represents the timeout that is used by //initial的时候该函数被初始化,网络层确定传输已经超时,将会调用driver中的tx_timeout处理时间
1586 * the watchdog (see dev_watchdog())
1587 * @watchdog_timer: List of timers
1588 *
1589 * @pcpu_refcnt: Number of references to this device //该设备被多少个CPU引用
1590 * @todo_list: Delayed register/unregister //下面是和卸载相关的一些设定
1591 * @link_watch_list: XXX: need comments on this one
1592 *
1593 * @reg_state: Register/unregister state machine
1594 * @dismantle: Device is going to be freed
1595 * @rtnl_link_state: This enum represents the phases of creating
1596 * a new link
1597 *
1598 * @needs_free_netdev: Should unregister perform free_netdev?
1599 * @priv_destructor: Called from unregister
1600 * @npinfo: XXX: need comments on this one
1601 * @nd_net: Network namespace this network device is inside
1602 *
1603 * @ml_priv: Mid-layer private //统计信息
1604 * @lstats: Loopback statistics
1605 * @tstats: Tunnel statistics
1606 * @dstats: Dummy statistics
1607 * @vstats: Virtual ethernet statistics
1608 *
1609 * @garp_port: GARP //免费ARP接口
1610 * @mrp_port: MRP //MAR接口
1611 *
1612 * @dev: Class/net/name entry //虽然是网络设备,它终究是普通设备,所以它也有普通设备该有的属性,也就是struct device结构体里面的属性
1613 * @sysfs_groups: Space for optional device, statistics and wireless
1614 * sysfs groups
1615 *
1616 * @sysfs_rx_queue_group: Space for optional per-rx queue attributes
1617 * @rtnl_link_ops: Rtnl_link_ops //netlink接口操作函数
1618 *
1619 * @gso_max_size: Maximum size of generic segmentation offload
1620 * @gso_max_segs: Maximum number of segments that can be passed to the
1621 * NIC for GSO
1622 *
1623 * @dcbnl_ops: Data Center Bridging netlink ops //桥接操作函数
1624 * @num_tc: Number of traffic classes in the net device
1625 * @tc_to_txq: XXX: need comments on this one
1626 * @prio_tc_map: XXX: need comments on this one
1627 *
1628 * @fcoe_ddp_xid: Max exchange id for FCoE LRO by ddp
1629 *
1630 * @priomap: XXX: need comments on this one
1631 * @phydev: Physical device may attach itself
1632 * for hardware timestamping
1633 *
1634 * @qdisc_tx_busylock: lockdep class annotating Qdisc->busylock spinlock
1635 * @qdisc_running_key: lockdep class annotating Qdisc->running seqcount
1636 *
1637 * @proto_down: protocol port state information can be sent to the
1638 * switch driver and used to set the phys state of the
1639 * switch port.
1640 *
1641 * FIXME: cleanup struct net_device such that network protocol info
1642 * moves out.
1643 */
1644
2. struct net_device 结构体
上面这些是对struct net_device的基本介绍,下面将进一步介绍结构体的具体定义,需要说明的是,这个结构体很重要,所以了解越详细越好。
1645 struct net_device {
1646 char name[IFNAMSIZ];
1647 struct hlist_node name_hlist;
1648 char *ifalias;
1649 /*
1650 * I/O specific fields
1651 * FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one
1652 */
1653 unsigned long mem_end;
1654 unsigned long mem_start;
1655 unsigned long base_addr;
1656 int irq;
1657
1658 atomic_t carrier_changes;
1659
1660 /*
1661 * Some hardware also needs these fields (state,dev_list,
1662 * napi_list,unreg_list,close_list) but they are not
1663 * part of the usual set specified in Space.c.
1664 */
1665
1666 unsigned long state;
1667
1668 struct list_head dev_list;
1669 struct list_head napi_list;
1670 struct list_head unreg_list;
1671 struct list_head close_list;
1672 struct list_head ptype_all;
1673 struct list_head ptype_specific;
1674
1675 struct {
1676 struct list_head upper;
1677 struct list_head lower;
1678 } adj_list;
1679
1680 netdev_features_t features;
1681 netdev_features_t hw_features;
1682 netdev_features_t wanted_features;
1683 netdev_features_t vlan_features;
1684 netdev_features_t hw_enc_features;
1685 netdev_features_t mpls_features;
1686 netdev_features_t gso_partial_features;
1687
1688 int ifindex;
1689 int group;
1690
1691 struct net_device_stats stats;
1692
1693 atomic_long_t rx_dropped;
1694 atomic_long_t tx_dropped;
1695 atomic_long_t rx_nohandler;
1696
1697 #ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT
1698 const struct iw_handler_def *wireless_handlers;
1699 struct iw_public_data *wireless_data;
1700 #endif
1701 const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops;
1702 const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;
1703 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV
1704 const struct switchdev_ops *switchdev_ops;
1705 #endif
1706 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_L3_MASTER_DEV
1707 const struct l3mdev_ops *l3mdev_ops;
1708 #endif
1709 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
1710 const struct ndisc_ops *ndisc_ops;
1711 #endif
1712
1713 #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
1714 const struct xfrmdev_ops *xfrmdev_ops;
1715 #endif
1716
1717 const struct header_ops *header_ops;
1718
1719 unsigned int flags;
1720 unsigned int priv_flags;
1721
1722 unsigned short gflags;
1723 unsigned short padded;
1724
1725 unsigned char operstate;
1726 unsigned char link_mode;
1727
1728 unsigned char if_port;
1729 unsigned char dma;
1730
1731 unsigned int mtu;
1732 unsigned int min_mtu;
1733 unsigned int max_mtu;
1734 unsigned short type;
1735 unsigned short hard_header_len;
1736 unsigned char min_header_len;
1737
1738 unsigned short needed_headroom;
1739 unsigned short needed_tailroom;
1740
1741 /* Interface address info. */
1742 unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
1743 unsigned char addr_assign_type;
1744 unsigned char addr_len;
1745 unsigned short neigh_priv_len;
1746 unsigned short dev_id;
1747 unsigned short dev_port;
1748 spinlock_t addr_list_lock;
1749 unsigned char name_assign_type;
1750 bool uc_promisc;
1751 struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc;
1752 struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc;
1753 struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs;
1754
1755 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
1756 struct kset *queues_kset;
1757 #endif
1758 unsigned int promiscuity;
1759 unsigned int allmulti;
1760
1761
1762 /* Protocol-specific pointers */
1763
1764 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q)
1765 struct vlan_info __rcu *vlan_info;
1766 #endif
1767 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NET_DSA)
1768 struct dsa_switch_tree *dsa_ptr;
1769 #endif
1770 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TIPC)
1771 struct tipc_bearer __rcu *tipc_ptr;
1772 #endif
1773 void *atalk_ptr;
1774 struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr;
1775 struct dn_dev __rcu *dn_ptr;
1776 struct inet6_dev __rcu *ip6_ptr;
1777 void *ax25_ptr;
1778 struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr;
1779 struct wpan_dev *ieee802154_ptr;
1780 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MPLS_ROUTING)
1781 struct mpls_dev __rcu *mpls_ptr;
1782 #endif
1783
1784 /*
1785 * Cache lines mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans())
1786 */
1787 /* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */
1788 unsigned char *dev_addr;
1789
1790 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
1791 struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx;
1792
1793 unsigned int num_rx_queues;
1794 unsigned int real_num_rx_queues;
1795 #endif
1796
1797 struct bpf_prog __rcu *xdp_prog;
1798 unsigned long gro_flush_timeout;
1799 rx_handler_func_t __rcu *rx_handler;
1800 void __rcu *rx_handler_data;
1801
1802 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
1803 struct tcf_proto __rcu *ingress_cl_list;
1804 #endif
1805 struct netdev_queue __rcu *ingress_queue;
1806 #ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
1807 struct nf_hook_entry __rcu *nf_hooks_ingress;
1808 #endif
1809
1810 unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN];
1811 #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL
1812 struct cpu_rmap *rx_cpu_rmap;
1813 #endif
1814 struct hlist_node index_hlist;
1815
1816 /*
1817 * Cache lines mostly used on transmit path
1818 */
1819 struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
1820 unsigned int num_tx_queues;
1821 unsigned int real_num_tx_queues;
1822 struct Qdisc *qdisc;
1823 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
1824 DECLARE_HASHTABLE (qdisc_hash, 4);
1825 #endif
1826 unsigned long tx_queue_len;
1827 spinlock_t tx_global_lock;
1828 int watchdog_timeo;
1829
1830 #ifdef CONFIG_XPS
1831 struct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_maps;
1832 #endif
1833 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
1834 struct tcf_proto __rcu *egress_cl_list;
1835 #endif
1836
1837 /* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
1838 struct timer_list watchdog_timer;
1839
1840 int __percpu *pcpu_refcnt;
1841 struct list_head todo_list;
1842
1843 struct list_head link_watch_list;
1844
1845 enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,
1846 NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */
1847 NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */
1848 NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */
1849 NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */
1850 NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */
1851 } reg_state:8;
1852
1853 bool dismantle;
1854
1855 enum {
1856 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED,
1857 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING,
1858 } rtnl_link_state:16;
1859
1860 bool needs_free_netdev;
1861 void (*priv_destructor)(struct net_device *dev);
1862
1863 #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
1864 struct netpoll_info __rcu *npinfo;
1865 #endif
1866
1867 possible_net_t nd_net;
1868
1869 /* mid-layer private */
1870 union {
1871 void *ml_priv;
1872 struct pcpu_lstats __percpu *lstats;
1873 struct pcpu_sw_netstats __percpu *tstats;
1874 struct pcpu_dstats __percpu *dstats;
1875 struct pcpu_vstats __percpu *vstats;
1876 };
1877
1878 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GARP)
1879 struct garp_port __rcu *garp_port;
1880 #endif
1881 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MRP)
1882 struct mrp_port __rcu *mrp_port;
1883 #endif
1884
1885 struct device dev;
1886 const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4];
1887 const struct attribute_group *sysfs_rx_queue_group;
1888
1889 const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops;
1890
1891 /* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */
1892 #define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536
1893 unsigned int gso_max_size;
1894 #define GSO_MAX_SEGS 65535
1895 u16 gso_max_segs;
1896
1897 #ifdef CONFIG_DCB
1898 const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops;
1899 #endif
1900 u8 num_tc;
1901 struct netdev_tc_txq tc_to_txq[TC_MAX_QUEUE];
1902 u8 prio_tc_map[TC_BITMASK + 1];
1903
1904 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE)
1905 unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid;
1906 #endif
1907 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CGROUP_NET_PRIO)
1908 struct netprio_map __rcu *priomap;
1909 #endif
1910 struct phy_device *phydev;
1911 struct lock_class_key *qdisc_tx_busylock;
1912 struct lock_class_key *qdisc_running_key;
1913 bool proto_down;
1914 };
1915 #define to_net_dev(d) container_of(d, struct net_device, dev)
3. 网络设备有关的结构组织
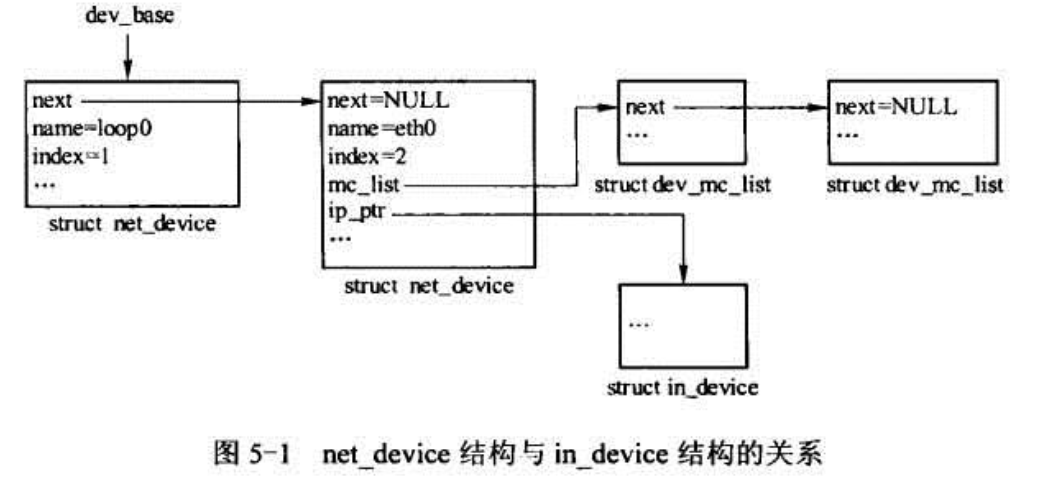
net_device结构包含了网络设备驱动相关的所有信息,按照信息的分类又把一些类型的信息组织到其他结构中,并嵌套在net_device 里面,比如与ipv4相关的配置嵌套在 in_device结构中,驱动的私有数据则嵌套在struct device中:
网络设备是通过多条链表串连在一起的,具体怎么串连稍后再讲。我们前面看到了,每一个net_device结构体都是由多个成员组成的,然而每个成员也有可能组成那么自己的链表,比如mc_list和ip_ptr,还有priv,虽然这个版本没有明确的定义priv这个指针,但是从alloc_netdev函数可以知道仍然为它保留着,只要传进去的sizeof_priv大于0.
下面我们看看其中一个很重要的成员ip_ptr (struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr)。它是一个头指针,指向struct in_device对象,那它表示什么意思呢?我们知道,每一个网络设备都可以设置IP地址,而且这些参数也可以通过应用层进行修改,这些信息是每一个接口独有的,虽然并不是每一个都需要设置这些信息,但设置的时候,它的存放位置就是在in_ptr指定链表里面。
下面我们来对比一下代码和实际输出:
root:/# ifconfig br-lan
br-lan Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 0A:02:8E:93:DD:3B
inet addr:192.168.1.129 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::802:8eff:fe93:dd3b/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:211672 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:120803 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:15794642 (15.0 MiB) TX bytes:24446287 (23.3 MiB)
23 struct in_device {
24 struct net_device *dev; //它绕回去指向net_device结构体头部
25 atomic_t refcnt; //这个对象被引用多少次
26 int dead;
27 struct in_ifaddr *ifa_list; /* IP ifaddr chain */
28 为什么是链表里面?一个结构体对象不久够了吗?事实是一个接口往往不仅可以设置多个mac地址,当然也可以设置多个IP地址,最常见的是IPv4地址和IPv6地址。
29 struct ip_mc_list __rcu *mc_list; /* IP multicast filter chain */
30 struct ip_mc_list __rcu * __rcu *mc_hash;
31
32 int mc_count; /* Number of installed mcasts */
33 spinlock_t mc_tomb_lock;
34 struct ip_mc_list *mc_tomb;
35 unsigned long mr_v1_seen;
36 unsigned long mr_v2_seen;
37 unsigned long mr_maxdelay;
38 unsigned char mr_qrv;
39 unsigned char mr_gq_running;
40 unsigned char mr_ifc_count;
41 struct timer_list mr_gq_timer; /* general query timer */
42 struct timer_list mr_ifc_timer; /* interface change timer */
43
44 struct neigh_parms *arp_parms;
45 struct ipv4_devconf cnf;
46 struct rcu_head rcu_head;
47 };
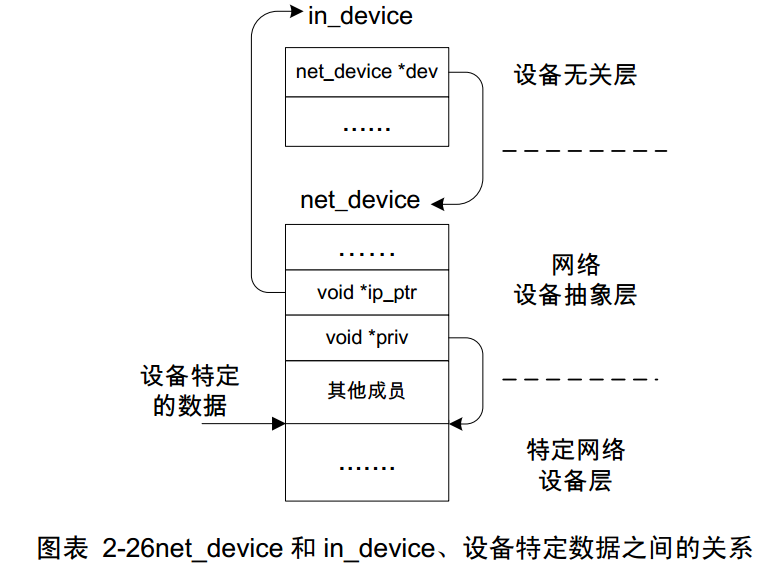
下面这个图是关于ip_ptr和priv两者的内存分配关系,这里需要注意的是,ip_ptr指向的链表是内存随机分配空间的,但是priv则不一样,他的空间是紧紧接在net_device结构体后面的!
1.设备无关层采用 in_device{}数据结构保存 IP 地址和邻居信息——虽然是间接的
2.网络抽象层采用 net_device{}数据结构保存设备的名字、编号、地址等共性
3.设备特定层的数据则有设备驱动开发人员自己定义,一般有硬件发送、接收缓冲区、芯片寄存器的信息等等。 这片内存区一般是紧跟在 net_device{}后面,由驱动程序在创建 net_device{}的时候顺带把这块内存也创建了。当然还是用 priv指针指向,以方便访问。
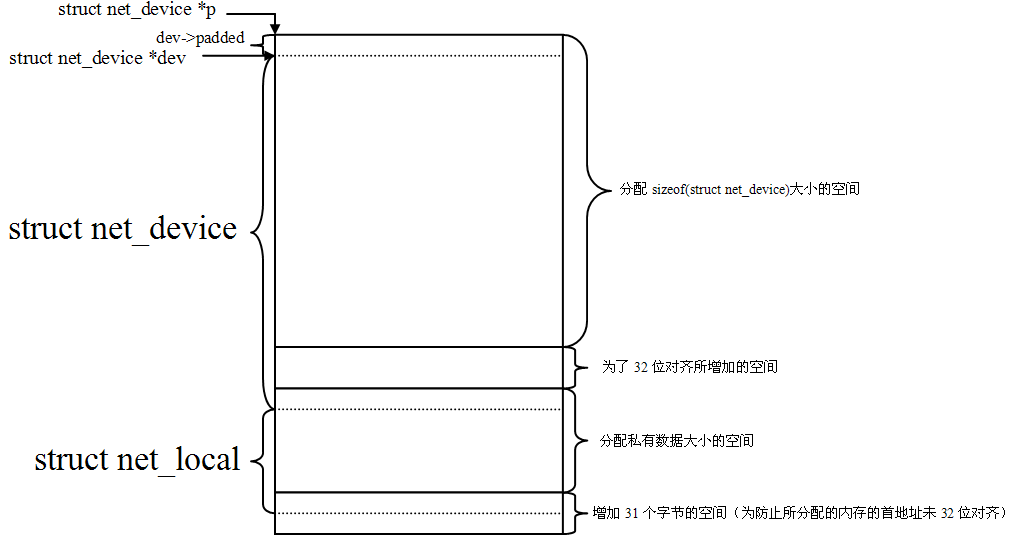
虽然说priv指向的私有数据空间是紧接在net_device后面,其实实际上更应该像这样添加了字节对齐:
为了更好的理解这一点,我们直接看代码:
7851 struct net_device *alloc_netdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, const char *name,
7852 unsigned char name_assign_type,
7853 void (*setup)(struct net_device *),
7854 unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs)
7855 {
7856 struct net_device *dev;
7857 size_t alloc_size;
7858 struct net_device *p;
7859
.......
7873
7874 alloc_size = sizeof(struct net_device); //这里获取到net_device的大小
7875 if (sizeof_priv) { //看一下传进来的希望申请的私有空间大小是多少
7876 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of private area */
7877 alloc_size = ALIGN(alloc_size, NETDEV_ALIGN); //对齐
7878 alloc_size += sizeof_priv;
7879 }
7880 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of whole construct */
7881 alloc_size += NETDEV_ALIGN - 1; //32-1=31
7882
7883 p = kvzalloc(alloc_size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_REPEAT); //这就是net_device和priv一起申请空间的地方
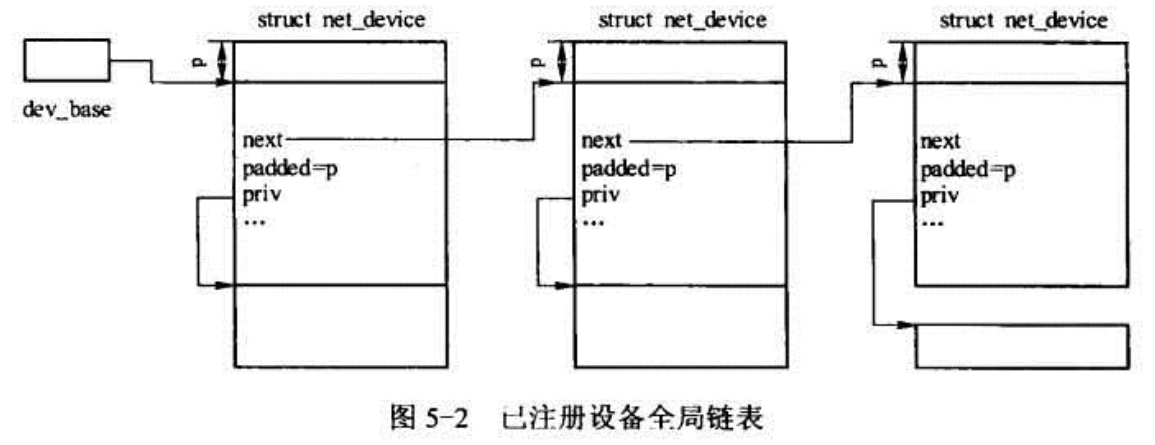
这样就组成了多个net_device结构:
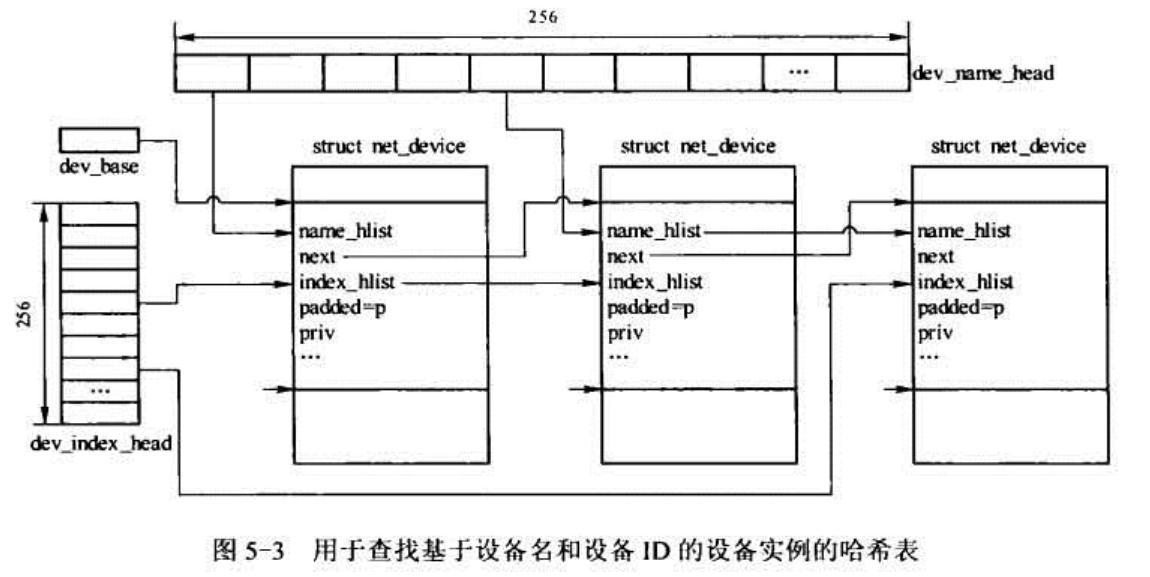
前面说过,net_device是由多种链表串连在一起的,那么是由哪些链表呢?我们来看看:
从图中可以知道,一共有三个链表:
dev_name_head: 基于接口名字的查找, dev->name,对应的函数是dev_get_by_name()
dev_index_head: 基于接口索引的查找,dev->ifindex, 对应的函数是dev_get_by_index()
dev_base: 基于其他参数的查找,比如设备类型,mac地址和标识等等
在了解了net_device后,我们后面讲继续了解 设备驱动模块的加载,设备的注册和设备的启动























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








