一场爆零的比赛,反思一下
E - Diagonal
首先这种yy题一定要写个爆搜看看规律(代码很挫,n = 7就不动了)
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n;
int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}; //UDLR
int vis[1010][1010], mat[1010][1010], res[1010][1010];
int ans;
bool check(int i, int j) {
if (i >= 1 && i <= n && j >= 1 && j <= n && !vis[i][j]) return true;
return false;
}
void dfs(int x, int y, int k) {
if (k == 1) {
int num = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) num += mat[i][i];
//cout << num << endl;
if (num > ans) {
ans = num;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j) {
res[i][j] = mat[i][j];
}
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++ i) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if (check(nx, ny)) {
vis[nx][ny] = 1; mat[nx][ny] = k - 1;
dfs(nx, ny, k - 1);
vis[nx][ny] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
//freopen("input.in", "r", stdin);
//freopen("output.out", "w", stdout);
while (cin >> n) {
ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j) {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
vis[i][j] = 1; mat[i][j] = n * n;
dfs(i, j, n * n);
}
cout << ans << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j)
printf("%04d ", res[i][j]);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
然后应该能看出一个规律:

代码很简单了
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
while (cin >> n) {
int ans = 0, num = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++ i) {
num = n * n - 2 * i;
ans += num;
}
ans = ans + num / 2;
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
F - The Three Guys
这个是个暴力枚举题,情况并不多。时间复杂度为
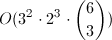 ,可以承受。比较坑的地方是,可以把人倒过来。
,可以承受。比较坑的地方是,可以把人倒过来。
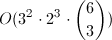 ,可以承受。比较坑的地方是,可以把人倒过来。
,可以承受。比较坑的地方是,可以把人倒过来。
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
double s[20], _s[20];
double work(double* a) {
double res = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; ++ i)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 6; ++ j)
for (int k = j + 1; k <= 6; ++ k) {
double l1, l2, l3;
l1 = l2 = l3 = 0.0;
for (int x = k; x % 6 != i; ++ x) l1 += a[x];
for (int x = i; x < j; ++ x) l2 += a[x];
for (int x = j; x < k; ++ x) l3 += a[x];
//cout << i << " " << j << " " << k << endl;
//cout << l1 << " " << l2 << " " << l3 << endl;
double temp;
double p = l1 + l2 + l3;
p /= 2.0;
if (p * (p - l1) * (p - l2) *(p - l3) >= -1e-10) {
temp = sqrt(p * (p - l1) * (p - l2) *(p - l3));
//res = max(temp, res);
if (temp > res) res = temp;
//cout << temp << endl;
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
//freopen("input.in", "r", stdin);
//freopen("2.out", "w", stdout);
double t;
while (scanf("%lf", &t) != EOF) {
s[0] = t;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; ++ i) {
scanf("%lf", &s[i]);
}
for (int i = 6; i < 12; ++ i) {
s[i] = s[i - 6];
}
memcpy(_s, s, 12 * sizeof(double));
double res = 0.0;
//for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++ i) cout << _s[i] << " "; cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 3); ++ i) {
int g = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++ j) {
if ((g & i) == g) {
swap(_s[2 * j], _s[2 * j + 1]); swap(_s[2 * j + 6], _s[2 * j + 7]);
}
g <<= 1;
}
double temp = work(_s); res = max(res, temp);
memcpy(_s, s, 12 * sizeof(double));
}
printf("%.10lf\n", res);
}
}
I - Mines
TODO
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int mat[15][25], temp[15][25], vis[15][25];
int dy[] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1}, dx[] = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};//UDLR
int N, M;
int res, ans;
bool check(int x, int y) {
if (x >= 1 && x <= N && y >= 1 && y <= (2 * M + 1))
return true;
return false;
}
void dfs(int x, int y, int cnt) {
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
puts("ok1");
if (cnt == (N * (2 * M + 1))) {
puts("ok4");
res = min(ans, res);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++ i) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = x + dy[i];
if (check(nx, ny) && !vis[nx][ny]) {
puts("ok2");
if (mat[nx][ny] >= 0) {
vis[nx][ny] = 1;
dfs(nx, ny, cnt++);
vis[nx][ny] = 0;
}
int flag = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++ j) {
int nnx = nx + dx[j], nny = ny + dy[j];
if (check(nnx, nny)) {
if (mat[nnx][nny] == 0) {
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag) {
puts("ok3");
vis[nx][ny] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++ j) {
int nnx = nx + dx[j], nny = ny + dy[j];
if (check(nnx, nny) && mat[nnx][nny]) mat[nnx][nny] --;
}
ans ++;
dfs(nx, ny, cnt++);
ans --;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++ j) {
int nnx = nx + dx[j], nny = ny + dy[j];
if (check(nnx, nny) && mat[nnx][nny]) mat[nnx][nny] ++;
}
vis[nx][ny] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
freopen("input.in", "r", stdin);
while (scanf("%d%d", &N, &M) != EOF) {
memset(mat, -1, sizeof(mat));
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
res = (~0U >> 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++ i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; ++ j) {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
mat[i][2 * j] = temp[i][2 * j] = t;
}
}
vis[1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < 8; ++ i) {
int nx = 1 + dx[i], ny = 1 + dy[i];
mat[nx][ny] --;
}
ans = 0;
dfs(1, 1, 1);
cout << res << endl;
}
}






















 398
398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








