在C语言阶段已经了解过文件的相关操作,在这里对C语言中的文件操作就不赘述了:
需要了解C语言文件相关操作的请戳这里👇C语言文件相关操作。
在Linux系统里文件操作又是怎么一回事呢?
跟着我的节奏,我们一起来了解一下。
Linux文件
一、系统文件I/O
一、什么是系统文件I/O
操作文件的方式,除了之前了解过的C语言文件操作接口之外,我们还可以采用系统接口来进行文件访问。
(当然C++和其他语言也都有各自的操作文件的方法,不过语言操作文件的方法其实都是对系统调用接口的封装)
如何以系统调用的方式来操作文件?(直接上代码)
1、写文件
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <sys/types.h>
3 #include <sys/stat.h>
4 #include <fcntl.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6 #include <string.h>
7
8 int main()
9 {
10 umask(0);
11 int fd = open("myfile",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0644);
12 if(fd < 0)
13 {
14 perror("open");
15 return 1;
16 }
17
18 int count = 5;
19 const char *msg = "hello world!\n";
20 int len = strlen(msg);
21
22 while(count--)
23 {
24 write(fd,msg,len);
25 //msg 为缓冲区首地址,len 为本次读取多少字节的数据,返回值 为实际写了多少字节数据
26 }
27
28 close(fd);
29 return 0;
30 } 运行代码,在myfile 这个文件里可以看到:

说明写操作已经完成。
2、读文件
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <sys/types.h>
3 #include <sys/stat.h>
4 #include <fcntl.h>
5 #include <unistd.h>
6 #include <string.h>
7
8 int main()
9 {
10 int fd = open("myfile",O_RDONLY);
11 if(fd < 0)
12 {
13 perror("open");
14 return 1;
15 }
16
17 const char *msg = "hello world!\n";
18 char buf[1024];
19
20 while(1)
21 {
22 ssize_t s = read(fd ,buf ,strlen(msg));
23 if(s > 0)
24 {
25 printf("%s",buf);
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 break;
30 }
31 }
32
33 close(fd);
34 return 0;
35 }
运行代码,可以看到运行结果:
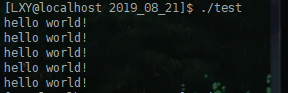
说明读操作也已经完成。
通过上述两个代码可见,直接使用系统调用,也能对文件进行操作。
二、文件操作接口介绍
- open (打开文件)
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);参数:
1、pathname : 要打开或者创建的目标文








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 387
387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








