1. Java回调机制
回调是一种双向调用模式,即被调用方在被调用时也会调用对方,这就叫回调。通过一个图来理解回调的过程:
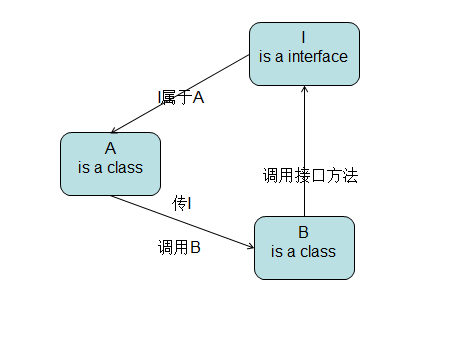
1) A实现I的接口的方法
2) A持有B实例对象的引用
3) A传递I接口对象给B
4) A调用B的方法解决问题
5) B解决问题后,调用I接口的方法,因为A实现了I接口,也就相当于调用了A的方法。
代码示例:
接口I:
public interface I {
public void Imathod(String result);
}类A:
public class A implements I{
@Override
public void Imathod(String result) {
//对返回的结果进行处理
if (result.endsWith("I do it,return result to you")) {
System.out.println("I get it!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
B b = new B(a);
b.Bmethod();
}
}类B:
public class B {
I i ;
public B(I i) {
this.i = i;
}
public void Bmethod()
{
//这里做的事是固定的
System.out.println("solve the problem");
i.Imathod("I do it,return result to you");
}
}B类主要是定义了解决问题的方法,A调用B的方法来解决问题,B处理完问题后就会返回处理结果或者提示给A,提示A问题已解决,A可以根据B的处理结果再做相应的处理。
2. Java反射机制
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
在类对象没有实例化之前,我们就可以通过完整的类名获取这个类的信息(如类的成员变量名,类的方法名等),同时,也可以通过反射来实例化对象,调用实例对象的方法和设置实例对象的属性值等。
1) 获取类的信息
Class<?> class1 = Class.forName("com.lgy.testreflect.Person");
//取得父类名称
Class<?> superclass = class1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println("Person类的父类名:" + superclass.getName());
Field[] fields = class1.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
System.out.println("类中的成员" + i + ": " + fields[i]);
}
//取得类方法
Method[] methods = class1.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
System.out.println("取得Person类的方法" + i + ":");
System.out.println("函数名:" + methods[i].getName());
System.out.println("函数返回类型:" + methods[i].getReturnType());
System.out.println("函数访问修饰符:" + Modifier.toString(methods[i].getModifiers()));
System.out.println("函数代码写法: " + methods[i]);
}
//取得类实现的接口,因为接口类也属于Class,所以得到接口中的方法也是一样的方法得到
Class<?> interfaces[] = class1.getInterfaces();
for (int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; i++) {
System.out.println("实现的接口类名: " + interfaces[i].getName());
}2) 通过反射实例化对象后的操作
try {
Class newoneClass = Class.forName("com.lgy.testreflect.Person");
Object obj = newoneClass.newInstance();
Field personNameField = newoneClass.getDeclaredField("name");
personNameField.setAccessible(true); //取消访问检查
personNameField.set(obj, "小xiao");
System.out.println("修改属性之后得到属性变量的值:" + personNameField.get(obj));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//调用方法
try {
Class<?> newoneClass = Class.forName("com.lgy.testreflect.Person");
System.out.println("调用无参方法say:");
Method method = newoneClass.getMethod("say");
method.invoke(newoneClass.newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}





















 867
867

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








