源码环境 : idea + spring 4.3.4 +tomcat7 + gradle
附 : 基于 java 注解的 配置元数据 的 web.xml 配置做参考(spring 3.0 后支持)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
com.ycit.config.DataSourceConfig,
com.ycit.config.AppConfig
</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>solutionServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>com.ycit.config.MvcConfig</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>solutionServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- 开启 druid 监控-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/druid/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
1. ContextLoaderListener 简介
★ 位置 : Spring-web 的 jar 包中 ,包路径 : org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
★ UML 关系图如下 :
介绍:
引导性 监听器,用于启动 和 关闭 Spring 的 根 WebApplicationContext,委托(delegate)给 ContextLoader 和 ContextCleanupListener 执行。
如果配置 了 org.Springframework.web.util.Log4jConfigListener(已过时) ,则 应该 配置在 Log4jConfigListener 的后面;Spring 3.1 之后,ContextLoaderListener支持 通过构造函数 直接注入 根 WebApplicationContext ,因此允许 编程式 的 配置 Servlet 3.0+ 的 环境。
该类继承了 ServletContextListener,ServletContextListener 是 servlet 中 八个 分门别类的监听器之一 ,负责监听 Servlet Context 的生命周期 (该生命周期其实就对应着应用的生命周期)。所以 ContextLoaderListener 就负责 监听 Spring 的初始化和 Spring 的 消亡 。当 启动服务器发布项目时,spring 初始化,触发 ContextInitialized()方法,初始化 WebApplicationContext 对象;当关闭服务器时,触发 contextDestroyed ( ) 方法,销毁 WebApplicationContext 对象 。
而主要的操作业务从 ContextLoader 类继承而来;
2. 流程分析
初始化大致流程如下图所示(有所省略,其中省略了 配置并且 刷新 WebApplicationContext 方法)。
分析:
加载 web.xml 中的配置,和 spring 相关的启动配置包括 : ContextLoaderListener 监听器的配置;contextClass ( 配置Spring使用的 ApplicationContext 实现类,可省略,原因见下文)以及 contextConfigLocation(配置文件的位置,可省略,见下) 参数的配置;
静态代码块 :应用启动,ContextLoaderListener 及其父类 ContextLoader 开始工作 。 这里有必要提及一下关于子父类静态代码块,构造函数的执行顺序的问题 。正常的顺序是 。 父类的静态代码块 → 子类的静态代码块 → 父类代码块(非静态) → 父类构造函数 → 子类代码块 (非静态) → 子类构造函数 。 所以首先执行 ContextLoader 的静态代码块 :此代码块的功能是读取 Spring 的配置文件 ContextLoader.properties ,而该配置文件的内容只有如下一行,为 Spring 的字段 defaultStrategies(java.util.Properties 类型) 赋如下的键值对 。
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContextinitWebApplicationContext : 通过 给定的 ServletContext 初始化 Spring 的 web 应用上下文(WebApplicationContext),分别保存在如下两个私有字段中:
/**
* The 'current' WebApplicationContext, if the ContextLoader class is
* deployed in the web app ClassLoader itself.
* volatile 为 多线程中用到的 关键字 ,作用是 保持被修饰的字段在被读取的时候返回的都是当前最新的,
*/
private static volatile WebApplicationContext currentContext;
/**
* The root WebApplicationContext instance that this loader manages.
*/
private WebApplicationContext context; // 保存初始化的ApplicationContext 实现类,可用于 ServletContext 消亡时 ApplicationContext关闭并释放资源currentContext 是指 当前 的 WebApplicationContext;
context 是指 每个 ServletContext 对应的那个 WebApplicationContext;
Java支持volatile关键字,但它被用于其他不同的用途。当volatile用于一个作用域时,Java保证如下:
1.(适用于Java所有版本)读和写一个volatile变量有全局的排序。也就是说每个线程访问一个volatile作用域时会在继续执行之前读取它的当前值,而不是(可能)使用一个缓存的值。(但是并不保证经常读写volatile作用域时读和写的相对顺序,也就是说通常这并不是有用的线程构建)。
2.(适用于Java5及其之后的版本)volatile的读和写建立了一个happens-before关系,类似于申请和释放一个互斥锁。
使用volatile会比使用锁更快,但是在一些情况下它不能工作。volatile使用范围在Java5中得到了扩展,特别是双重检查锁定现在能够正确工作。3 . 源码分析
初始化源码分析
ContextLoader . initWebApplicationContext ()主代码:最终返回 一个 WebApplicationContext 的相关实现类;
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
/**创建相应的 WebApplicationContext 实例 begin**/
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
/**创建相应的 WebApplicationContext 实例 end**/
/**设置 parent context属性,对于多个 root WebApplicationContext 可以共享,对于单个的不需要关心parent context**/
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
/**设置 parent context 属性 end**/
// 配置 并且刷新 WebApplicationContext,此处比较复杂
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//注册 context
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
/**保存当前的应用上下文 begin**/
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
/**保存当前的应用上下文 end**/
return this.context;相关类介绍:
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 接口: WebApplicationContext 和 ConfigurableApplicationContext 的 子接口
WebApplicationConext 接口:ApplicationContext 的子接口,为 web 应用 提供 配置(获取 ServletContext)的接口;当应用正在运行时,是只读的,但是如果实现类支持的话,可以重新加载;相对于其父接口的 ApplicationContext , 该接口提供了 获取 ServletContext 对象的方法;
ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口:ApplicationContext 的子接口,提供 配置 一个 应用上下文的 属性,如设置 environment,BeanFactoryPostProcessor,ApplicationListener,ProtocolResolver 等;
附录1: AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 和 XmlWebApplicationContext 的 顶层中 和 BeanFactory 相关的UML 类图;
以上源代码主要做了三件事:
① 实例化 WebApplicationContext 相关 实现类
② 加载并 设置父 上下文 (此处略 ,一般的 web 应用 无 父上下文,返回 null)
③ 配置 并 刷新 WebApplicationContext
3.1 ContextLoader . createWebApplicationContext (ServletContext sc):实例化 WebApplicationContext 实现类
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);//实例化
} ContextLoader . determineContextClass(ServletContext sc) 方法: 决定contextClass,该 contextClass 决定了 WebApplicationContext 的 实现类的类型;这里创建的 实现类为 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ;
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
//获取 web.xml 中 初始化参数 contextClass,本文设置了该参数
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); //使用指定的 class 反射出 Class 对象
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// 否则使用默认策略,即获得 XMLWebApplicationContext 对应的bean 的名称
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}3.2 加载并 设置父 上下文
略
3.3 ContextLoader . configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext):配置并且刷新 WebApplicationContext
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
//获取 web.xml 中定义的 contextId 初始化值,未定义
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);//配置了 servletContext 属性
//获取 web.xml 中定义的 contextConfiLocation 初始化参数值 ,已定义,
//配置了除 mvc 配置文件的其他配置文件路径如 数据库连接配置 和 spring 配置文件
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);//配置了 configLocation 字段属性
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
/** 初始化 应用上下文 中 和 Servlet 相关的 占位符 属性资源 begin **/
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
/** 初始化 应用上下文 中 和 Servlet 相关的 占位符 属性资源 end**/
// 加载web.xml 中 自定义的 其他初始化内容,这里都没有定义
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//WebApplicationContext 的刷新
wac.refresh();
}---------------------------- environment 获取 begin---------------------------------------------------
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext . getEnvironment 方法为抽象方法;
AbstractApplicationContext . getEnvironment 为方法的实现:
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = createEnvironment();//调用 StandardEnvironment的构造函数
}
return this.environment;
}AbstractEnvironment 构造函数 及 customizePropertySources方法:
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(String.format(
"Initialized %s with PropertySources %s", getClass().getSimpleName(), this.propertySources));
}
}
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}Note:父类 中调用 被子类重写(override)的自身方法时,会执行子类的重写方法,而不会执行父类中的方法;如果想要执行父类中的方法,需要明确调用 super.methodName();
所以这里调用 StandardServletEnvironment 中的重写方法:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
//添加 key 为 servletConfigInitParams ,value 为 Object 占位符
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
//添加 key 为 servletContextInitParams,value 为 Object 占位符
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
//添加 key 为 jndiProperties,value 为 Object 占位符
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);//执行父类 StandardEnvironment 中方法,添加了2 个
}StandardEnvironment 中的重写方法:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
//key 为 systemProperties
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
//key 为 systemEnvironment
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}getEnvironment 方法 最终返回 StandardServletEnvironment 实现类,其中的 propertySource 字段(MutablePropertySources 类)中初始化了 5 个 PropertySource(目前前 3 个 source 都是 占位符 object,后期会进行填充和替换);即完成了 Environment 相关实现类的 初始化;
附录2 :StandardEnvironment 顶层父类 UML 图
相关类介绍:
PropertySources 接口 :包含 一个 或者 多个 PropertySource 的对象;即用于 保存;提供了 是否包含 | 获取 property source 的 抽象方法;
MutablePropertySources 类:PropertySources 接口 的实现类,用于 操作 属性资源,并且 提供了可以拷贝 已存在 的 PropertySources 的 构造函数;
PropertySource 抽象类:代表一个 资源 的抽象基类,使用键值对表示;
MapPropertySource:PropertySource 的 实现类,从 Map 对象中读取 键 和 值,即可以通过 Map 对象 构造 PropertySource ;
SystemEnvironmentPopertySource: MapPropertySource 的子类,特殊的 MapPropertySource,用于处理 使用 AbstractEnvironment . getSystemEnvironment 方法 获取到的 系统环境变量;
ServletContextPropertySource:从 一个 ServletContext 对象中 读取 初始化参数,即 通过 ServletContext 对象构造 PropertySource;
ServletConfigPropertySource:类同上;
ConfigurableEnvironment:Environment 类型的 配置接口,提供设置 active profiles 和 default profiles (用于不同的环境开发的不同配置)以及 操作底层属性资源 的 设施;
StandardEnvironment:Environment 的实现类,适合于在标准的场景下使用(如 非 web 场景);
------------------------------------ environment 获取 end---------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------ 初始化 PropertySources begin---------------------------------------------------
ConfigurableWebEnvironment . initPropertySources 为抽象方法;
StandardServletEnvironment . initPropertySources 为方法的实现:
public void initPropertySources(ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}WebApplicationContextUtils . initServletPropertySources 方法:使用给定的 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig 对象的实例 替换 StubPropertySource 中的相关占位符
public static void initServletPropertySources(
MutablePropertySources propertySources, ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
Assert.notNull(propertySources, "'propertySources' must not be null");
// 替换 key 为 servletContextInitParams 的 source 值
if (servletContext != null && propertySources.contains(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME) &&
propertySources.get(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
propertySources.replace(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new ServletContextPropertySource(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, servletContext));
}
// 替换 key 为 servletConfigInitParams的 source 值
if (servletConfig != null && propertySources.contains(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME) &&
propertySources.get(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
propertySources.replace(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new ServletConfigPropertySource(StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, servletConfig));
}
} initPropertySources() 方法 在 下面 的 refresh() 方法 中也会调用到 ,这里提前加载 是为了 确保 在 任何 的 后处理 (post-processing)或者 初始化 发生在 refresh() 之前 这两种情况下,Servlet 属性资源 仍然可用;
主要是将 MutablePropertySources 对象中 propertySourceList 列表中保存的和 ServletConfig 和 ServletContext 相关的属性 替换成 当前 环境下 的 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig(此时的 ServletConfig 为 null) ,这样就 顺利的 将 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig 中 保存的 各种资源信息 转移到了 当前 应用上下文中,即 保存在AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 对象下的 ConfigurableEnvironment 参数 中;
综上,initPropertySources 方法的目的就是 将 当前的 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig 资源 加载到 WebApplicationContext 的 相关实现类的 environment 属性中;
------------------------------------ 初始化 PropertySources end---------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ConfigurableApplicationContext . refresh 方法为抽象方法;
AbstractApplicationContext . refresh : 所有的 ApplicationContext 的唯一实现方法,采用了 模版方法设计模式;
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 刷新前的准备 工作:涉及属性的设置以及属性资源的 初始化
prepareRefresh();
// 通知子类刷新 内置的 bean 工厂,获得一个新的 bean factory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 配置 工厂的 标准上下文特性,例如 上下文的 ClassLoader 和 post-processors
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//在 应用上下文 子类中 增加 后处理(post-processing) 的 bean 工厂
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 在应用上下文中调用所有 已注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcesser 作为 bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册具有拦截功能的 bean processors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 为应用上下文 初始化 消息 源
initMessageSource();
// 为应用上下文 初始化 事件 多路广播
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化其他特殊的 bean
onRefresh();
// 检查 监听器 相关的 bean ,并注册他们
registerListeners();
//实例化所有剩余的单例 bean (非 懒 初始化)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//最后一部:发布 相关的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}相关类介绍:
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 接口 :ListableBeanFactory,ConfigurableBeanFactory,AutowireCapableBeanFactory 的子接口,
ListableBeanFactory :提供了枚举所有 bean 实例的 方法,而不是提供名称去定向寻找;
ConfigurableBeanFactory:被大多数的 bean 工厂 实现的 配置接口,提供 了用于配置 bean 工厂 的 基础设施;
AutowireCapableBeanFactory: BeanFactory 的直接子接口,是 BeanFactory 的 扩展接口,能够实现自动装配;
刷新工作 所做的 工作比较多 ,下面一个一个分析 :
3.3.1 AbstractApplicationContext . prepareRefresh():为刷新 准备 context;
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);//context 是否 已经关闭,false 代表未关闭
this.active.set(true);// context 当前是否是活跃的,true 代表 活跃
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
initPropertySources();//上面有调用过
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();//验证资源
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>();
}AbstractApplicationContext . initPropertySources 方法:空方法,由不同的子类进行不同的实现;这里再次初始化 属性资源方法 ,但是此时 ServletContextPropertySource 已经 成功加入到了 MutablePropertySources 对象的 propertySourceList 列表中;
------------------------------------ property 验证 begin---------------------------------------------------
ConfigurableEnvironment . validateRequiredProperties 为抽象方法;
AbstractEnvironment . validateRequiredProperties 为实现方法:
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
public void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException {
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
}PopertySourcesPropertyReolver . validateRequiredProperties 方法:
public void validateRequiredProperties() {
MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();
for (String key : this.requiredProperties) {
if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {
ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {
throw ex;
}
}------------------------------------ property 验证 end---------------------------------------------------
综上,prepareRefresh()方法用于刷新前打开 AbstractApplicationContext 中的开关字段(close | active)、 environment 资源 的初始化和验证以及初始化 earlyApplicationEvents ;都是准备工作;
3.3.2 AbstractApplicationContext . obtainFreshBeanFactory():返回一个 新的 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bean 工厂类
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
/** template method 模式:不同的子类有不同的实现 begin**/
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); // 将上面得到的 bean 工厂返回
/** template method 模式:不同的子类有不同的实现 end**/
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}AbstractApplicationContext . refreshBeanFactory 为 抽象方法:使用了 模版方法设计模式,参看【design pattern】Template method(模板方法设计模式) 中的分析;
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext . refreshBeanFactory 实现:
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();//销毁 bean 工厂管理的所有 bean
closeBeanFactory(); //关闭 bean 工厂
}
/** 重新创建一个 新的 bean 工厂 begin **/
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory; //保存创建的 bean 工厂 对象
}
/** 重新创建一个 新的 bean 工厂 end **/
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}这里的刷新 bean 工厂 逻辑:如果 beanFactory 属性不为空,则先关闭,然后再构造一个新的 DefaultListableBeanFactory;
------------------------------------ createBeanFactory begin---------------------------------------------------
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext . createBeanFactory()方法:通过 调用 DefaultListableBeanFactory 构造函数实例化 beanFactory,在调用过程中会调用 其父类 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 的 无参构造函数,如下:这里配置了需要忽略的依赖接口,保存在其下的 ignoredDependencyInterfaces 字段中
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class); //忽略因为自动注入的 依赖接口
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) {
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc);
}创建 DefaultListableBeanFactory 过程中 配置了 ignoredDependencyInterfaces 属性(增加3个);
------------------------------------ createBeanFactory end---------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------ customizeBeanFactory begin---------------------------------------------------
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
}用于将 ApplicationContext 中的 部分属性信息 传递给 刚初始化的 beanFactory ;
------------------------------------ customizeBeanFactory end---------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------ loadBeanDefinitions begin---------------------------------------------------
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext . loadBeanDefinitions 为 抽象方法 ;
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext . loadBeanDefinitions 实现方法(不同的子类有不同的实现方法):
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 通过 bean 工厂实例化 bean 定义的 reader,并在bean 工厂中注册 相关 的 注解的 post processors
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//通过 bean 工厂实例化 bean 定义的扫描器
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
//返回当前类持有的 bean 名称生成器,此时为null
BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = getBeanNameGenerator();
if (beanNameGenerator != null) {
reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR, beanNameGenerator);
}
// 返回当前类持有的 bean 定义 范围解析器,此时为 null
ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = getScopeMetadataResolver();
if (scopeMetadataResolver != null) {
reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
}
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Registering annotated classes: [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.annotatedClasses) + "]");
}
reader.register(this.annotatedClasses.toArray(new Class<?>[this.annotatedClasses.size()]));
}
if (!this.basePackages.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Scanning base packages: [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.basePackages) + "]");
}
scanner.scan(this.basePackages.toArray(new String[this.basePackages.size()]));
}
// web.xml 中配置的配置文件路径,spring 配置文件和 数据库配置文件,编程式的配置
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
try {
//获取每个 java 文件的 Class 对象,并利用 reader 注册
Class<?> clazz = getClassLoader().loadClass(configLocation);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Successfully resolved class for [" + configLocation + "]");
}
reader.register(clazz);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not load class for config location [" + configLocation +
"] - trying package scan. " + ex);
}
int count = scanner.scan(configLocation);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
if (count == 0) {
logger.info("No annotated classes found for specified class/package [" + configLocation + "]");
}
else {
logger.info("Found " + count + " annotated classes in package [" + configLocation + "]");
}
}
}
}
}
}相关类介绍:
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader : 用于 编程式注册 已注解 bean 的 方便适配器,需要提供 BeanDefinitionRegistry 类 构造对象,注册的是 BeanDefinitionRegisty 中 的 beanDefinition;该类 是 ClassPathBeanDefininationScanner 的 一个替代品,使用 相同的 注解策略但是只显示的注册类;
ClassPathBeanDefininationScanner : 一个 bean 定义的 扫描器 ,用于检查 classpath 下 符合条件的bean ,使用给定的记录器 BeanFactory 或者 ApplicationContext 注册 相关的 bean 定义;符合条件的 类 是 通过 配置 类型过滤器来侦测的,默认的过滤器包括 注解了 Spring 的 Component,Repository,Service,Controller 的 类,而且也支持 Java EE 6 的 ManagedBean 注解 和 JSR-330 的 Named 注解;
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext . getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 方法:
protected AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
return new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory, getEnvironment());
}------------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
调用如下的构造函数:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry); //注册相关处理器
}相关类:
BeanDefinitionRegistry : 处理 BeanDefinition 的接口,包括注册,移除,获取,判断是否包含等操作,例如处理 RootBeanDefinition 和 ChildBeanDefinition; Spring 的 BeanDefinitionReader 需要 通过 该接口的 实现类 来构造,在 Spring core 中 已知的实现者 是 DefaultListableBeanFactory 和 GenericApplicationContext ;
------------------------- 第 3 层 --------------------------
AnnotationConfigUtils . registerAnnotationConfigProcessors() 方法:注册 registry 中 所有相关的 注解 后 处理器(post processors)
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}AnnotationConfigUtils . registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 重载(overload)方法:
public static final AnnotationAwareOrderComparator INSTANCE = new AnnotationAwareOrderComparator();
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
// DefaultListableBeanFacotry 为 BeanDefinitionRegistry 的子类,向下转型,转为 DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
// 设置bean 工厂的 dependencyComparator 属性,对依赖的列表和数组提供可选的排序
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
// 设置 bean 工厂的 autowireCandidateResolver 属性,用来检查 一个 bean 定义是否需要自动注入 的 解析器
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(4);
// bean 工厂的 beanDefinitionMap 字段中是否包含bean 定义:
//org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,不包含则注册
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor,不包含则注册
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含 org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//是否包含org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}注解处理器详情:
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor : 内部管理 Configuration 注解处理器 的 bean 的 名称;即ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类;
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor:内部管理 Autowired 注解处理器 的 bean 的名称;即AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 类;
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor:内部管理 Required 注解处理器 的 bean 的名称;即RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
类;
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor:内部管理 JSR-250 注解处理器 的 bean 的名称;即CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 类;
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor:内部管理 JPA 注解处理器 的 bean 的名称 , 没有使用 JPA类库,不会加载;即PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类;
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor:内部管理 @EventListener 注解 处理器 的 bean 的名称;即EventListenerMethodProcessor类;
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory:内部管理 EventListenerFactory 的 bean 的名称;即DefaultEventListenerFactory类;
相关类介绍:
DefualtListableBeanFactory: AbstractAutowireCapbleBeanFactory ,ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,BeanDefinitionRegistry 的实现类;一个 基于 bean 定义对象 的完全成熟的 bean 工厂;通常的使用方法是:首先 注册所有 的 beanDefinition(可能从 bean 定义 文件中 读取),
BeanDefinition 接口:一个 BeanDefinition 描述了一个 bean 的实例,包括 属性值,构造函数参数值,以及 更多的 信息
AnnotatedBeanDefinition:BeanDefinition 的抽象类;提供 AnnotationMetadata 类 的 获取方法,不需要保证类已经加载;
AbstractBeanDefinition:BeanDefinition 的抽象类
RootBeanDefinition 实现类: 支持通过 类的 Class 对象 创建 bean 定义,适用于注册 单独的 bean 定义;
GenericBeanDefinition 实现类:在 父 接口的基础上 增加 了 parentName 参数 ;通常情况下使用该类 注册 bean ,可以灵活的配置 父 名称;
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition:实现了 AnnotatedBeanDefinition ,继承了 GenericBeanDefinition,GenericBeanDefiniton 类的扩展,通过 AnnotatedBeanDefinition 接口 增加对 给定注解元数据的支持,通过 Class 数组 或者 AnnotationMetadata 或者 MethodMetadata 构造;
BeanDefinitionHolder 类: BeanMetadataElement 的实现类,持有 一个 包含了 名称 和 别名(aliases)的 BeanDefinition,可以注册为一个 内部 bean 的占位符;
AnnotationMetadata:定义 对指定类注解的 访问 ;可以在类未加载的时候访问;
Comparator:jdk 的 用于比较功能的类;
OrderComparator :spring 中 对 Comparator 的实现,用于对象的排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator:是 OrderComparator 的一个扩展,支持 Spring 的 Ordered 接口 以及 @Order 注解 和 @Priority 注解
AutowireCandidateResolver:决定 一个 bean 定义 是否需要 自动注入 的 策略接口;
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver:实现了 AutowireCandidateResolver,支持 注解 和 @Lazy 的 惰性 注解方法;------------------------- 第 5 层 --------------------------
AnnotationConfigUtils . registerPostProcessor()方法:注册 后处理器, 返回 BeanDefinitionHolder 对象
private static BeanDefinitionHolder registerPostProcessor(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, RootBeanDefinition definition, String beanName) {
definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definition);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(definition, beanName);
}------------------------- 第 6 层 --------------------------
BeanDefinitionRegistry . registerBeanDefinition()抽象方法
DefaultListableBeanFactory . registerBeanDefinition实现方法:向 bean 工厂中注册 bean 的 定义;实际上是以键值对的形式添加到 beanDefinitionMap 的字段中,同时维护 beanDefinitonName 字段 和 manualSinglethonNames;
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();//验证 bean 定义
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
// 检查该 beanDefinition 是否已经存在
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(oldBeanDefinition)) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 工厂的 bean创建阶段是否已经开始
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
//仍然处于 启动注册阶段
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
//重置所有 beanName 相关 bean definition 缓存
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}DefaultListableBeanFactory 中字段介绍:
beanDefinitionMap: bean 定义 对象的 Map 集合,通过 bean 名称 键入;
beanDefinitionNames:bean 定义 名称的 list 集合,
manualSingletonNames:手动注册的单例的名称的 list 集合;
附录3 :DefualtListableBeanFactory 上层关系图
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 实例化,其内部调用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 的构造器 ,同时调用了父类 ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider 的构造器,如下:
protected ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
return new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory, true, getEnvironment());
}------------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters, Environment environment) {
super(useDefaultFilters, environment);
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// Determine ResourceLoader to use.
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
setResourceLoader((ResourceLoader) this.registry);
}
}------------------------- 第 3 层 --------------------------
public ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(boolean useDefaultFilters, Environment environment) {
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();//注册过滤器
}
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.environment = environment;
}------------------------- 第 4 层 --------------------------
其中的 registerDefaultFilters() 方法:注册默认的过滤器
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
// 为 @Component注解注册 默认过滤器 ,这将隐式的注解所有包含 Component 元注解的注解
//包括 Repository 注解, Service注解,Controller注解
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
//如果项目中加载了相关 jar 包,则会为 JSR-250 注册过滤器
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
//如果项目中加载了相关 jar 包,则会为 JSR-330 注册过滤器
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}AnnotationTypeFilter 类:TypeFilter 的间接实现类,作用是 使用 给定的注解 匹配 类 的 简单 过滤器,也会 检查 通过 继承得到的注解;通过 给定的注解的类型 实例化;
综上,ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 实例化的内部 一定会注册一个 过滤 @Component 注解的 AnnotationTypeFilter,尝试注册 过滤 JSR-250 注解(ManagedBean)的 AnnotationTypeFilter 和 JSR-330 注解(Named)的 AnnotationTypeFilter;说白了就是 配置 beanFactory 的 includeFilters 字段;返回的 scanner 内置了 registry 和 environment
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
BeanNameGenerator 实例化:返回自定义的 BeanNameGenerator,此处为 null;给 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 类 和 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 类 使用
protected BeanNameGenerator getBeanNameGenerator() {
return this.beanNameGenerator;
}BeanNameGenerator : 为 bean 定义 生成 bean 名称的 策略 接口,初始化时获取为空
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
DefaultListableBeanFactory . registerSingleton 方法:向 beanFactory 中 添加 手动注册的单例,维护 beanFactory 的 manualSingletonNames ,singletonObjects,singletonFactories,earlySingletonObjects,registeredSingletons 字段;
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException {
super.registerSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
if (!this.beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.manualSingletonNames.size() + 1);
updatedSingletons.addAll(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
if (!this.beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.manualSingletonNames.add(beanName);
}
}
clearByTypeCache();
}super . registerSingleton 方法 是 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry . registerSingleton 方法:
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (oldObject != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject +
"] under bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "] bound");
}
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
// 维护了 beanFactory 中的多个字段
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}------------------------- 第 1层 --------------------------
ScopeMetadataResolver 实例化:返回自定义的 ScopeMetadataResolver 类,此时为 null,给 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 类 和 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 类使用;
protected ScopeMetadataResolver getScopeMetadataResolver() {
return this.scopeMetadataResolver;
}ScopeMetadataResolver: 为 bean 定义 解析 范围 的 策略接口
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader . register 方法
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
for (Class<?> annotatedClass : annotatedClasses) {
registerBean(annotatedClass);
}
}
public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass) {
registerBean(annotatedClass, null, (Class<? extends Annotation>[]) null);
}
public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass, String name, Class<? extends Annotation>... qualifiers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}相关类介绍:
ScopeMetadata:描述 Spring 管理 的 bean 的 作用域,包括 作用域的 名称 和 代理作用域的行为,默认的作用域为 singleton,默认 的代理作用域是 不代理;
AnnotationMetadata:接口,定义 对指定类注解的 访问 ;可以在类未加载的时候访问;
StandardAnnotationMetadata:实现类,使用标准的反射反射一个 给定的类;
ScopeMetadataResolver:解析 bean 定义 的 作用域 的策略接口;
ScopedProxyMode:各种 代理作用域的值 的 枚举 :
default : default 通常 等于 no ,除非 配置了不同的 default
no : 不创建 作用域代理
interfaces:创建 JDK 动态代理
target_class:创建 基于 一个类的 代理(使用 CGLIB)
------------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition 实例化:
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) {
setBeanClass(beanClass);
this.metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true);
}------------------------- 第 3 层 --------------------------
StandardAnnotationMetadata 实例化:初始化 字段信息;
public StandardAnnotationMetadata(Class<?> introspectedClass, boolean nestedAnnotationsAsMap) {
super(introspectedClass);
this.annotations = introspectedClass.getAnnotations();//获得类上的注解
this.nestedAnnotationsAsMap = nestedAnnotationsAsMap;
}------------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver . resolveScopeMetadata 方法
public ScopeMetadata resolveScopeMetadata(BeanDefinition definition) {
ScopeMetadata metadata = new ScopeMetadata();
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotatedBeanDefinition annDef = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) definition;
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(
annDef.getMetadata(), this.scopeAnnotationType);
if (attributes != null) {
metadata.setScopeName(attributes.getString("value"));
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");
if (proxyMode == null || proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
proxyMode = this.defaultProxyMode;
}
metadata.setScopedProxyMode(proxyMode);
}
}
return metadata;
}------------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
AnnotationBeanNameGenerator . generateBeanName 方法:返回 contextConfigLocation 配置的 bean 的 名称
public String generateBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
String beanName = determineBeanNameFromAnnotation((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) definition);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
// Explicit bean name found.
return beanName;
}
}
// Fallback: generate a unique default bean name.
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition, registry);
}
protected String determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedDef) {
AnnotationMetadata amd = annotatedDef.getMetadata();
Set<String> types = amd.getAnnotationTypes();
String beanName = null;
for (String type : types) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(amd, type);
if (isStereotypeWithNameValue(type, amd.getMetaAnnotationTypes(type), attributes)) {
Object value = attributes.get("value");
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = (String) value;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(strVal)) {
if (beanName != null && !strVal.equals(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stereotype annotations suggest inconsistent " +
"component names: '" + beanName + "' versus '" + strVal + "'");
}
beanName = strVal;
}
}
}
}
return beanName;
}
protected String buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition);
}
protected String buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition definition) {
String shortClassName = ClassUtils.getShortName(definition.getBeanClassName());
return Introspector.decapitalize(shortClassName);
}------------------------- 第3层 --------------------------
StandardAnnotationMetadata . getAnnotationTypes 方法:遍历 annotations 字段,获取所有的注解名字的 set 集合;
public Set<String> getAnnotationTypes() {
Set<String> types = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
for (Annotation ann : this.annotations) {
types.add(ann.annotationType().getName());
}
return types;
}AnnotationConfigUtils . applyScopedProxyMode 方法:
static BeanDefinitionHolder applyScopedProxyMode(
ScopeMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionHolder definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = metadata.getScopedProxyMode();
if (scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.NO)) {// 不使用代理
return definition;
}
boolean proxyTargetClass = scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
return ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(definition, registry, proxyTargetClass);// 使用代理
}------------------------- 第 3 层 --------------------------
若使用代理, ScopedProxyCreater . createScopeProxy :
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) {
return ScopedProxyUtils.createScopedProxy(definitionHolder, registry, proxyTargetClass);
}ScopeProxyUtils . createScopedProxy:
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(BeanDefinitionHolder definition,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) {
String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();
BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName);
// Create a scoped proxy definition for the original bean name,
// "hiding" the target bean in an internal target definition.
RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);
proxyDefinition.setDecoratedDefinition(new BeanDefinitionHolder(targetDefinition, targetBeanName));
proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(targetDefinition);
proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource());
proxyDefinition.setRole(targetDefinition.getRole());
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName);
if (proxyTargetClass) {
targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// ScopedProxyFactoryBean's "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don't need to set it explicitly here.
}
else {
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Copy autowire settings from original bean definition.
proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate());
proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary());
if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition);
}
// The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy.
targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false);
targetDefinition.setPrimary(false);
// Register the target bean as separate bean in the factory.
registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);
// Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition
// (potentially an inner bean).
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases());
}----------------------
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils . registerBeanDefinition 方法:
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
//该方法上面已经解析,维护 beanFactory 的 beanDefinitionMap,beanDefinitionNames 等字段
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}综上,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader . register 方法主要 向 beanFactory 的 beanDefinitionMap 中注册相关的 类;
------------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner . scan 方法:
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
综上, loadBeanDefinitions 方法 主要是 加载一些bean 定义,基于注解的相关 bean 定义,需要扫描的 bean 定义,web.xml 中配置的 bean 的定义
------------------------------------ loadBeanDefinitions end-----------------------------------------------------
综上,obtainFreshBeanFactory 方法 主要是 生成一个新的 beanFactory 并 进行相关参数的初步配置;
3.3.3 prepareBeanFactory()
此时的 beanFactory 对象 ,在初始化时 配置 了 部分的 ignoredDependencyInterfaces 和 部分的 beanDefinitionMap 属性;这里配置 bean 工厂 的 标准上下文特性,例如 上下文的 类加载器 和 后处理器(post-processors)
AbstractApplicationContext . prepareBeanFactory 方法:
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
//设置 bean 工厂的 beanClassLoader 属性
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
//使用 上下文 回调配置 bean 工厂
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
这里 和 之前的 配置 ignoredDependencyInterfaces 和 配置 post-processor 的代码 很类似;
相关类介绍:
StandardBeanExpressionResolver :BeanExpressionResolver 的标准实现类,功能是 使用 Spring 的 expression 模块 解析 Spring 的 EL 表达式;
ResourceEditorRegistrar:PropertyEditorRegistrar 接口的实现类,使用 资源 编辑器 填充 一个 用来创建 bean 的 PropertyEditorRegistry;
beanFactory 的 beanPostProcessors 属性值 :
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:BeanPostProcessor 的实现类 ,用于 将 ApplicationContext 对象 传递给 实现了 EnviromenAware 接口,EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口,ResourceLoaderAware 接口,ApplicationEventPublisherAware 接口,MessageSourceAware 接口 或者 ApplicationContextAware 接口 的 类 ;
BeanPostProcessor: 工厂的 钩子 ,允许 新的bean 实例 的 自定义修改,例如 检查标记接口 或者 使用 代理包装 他们;ApplicationContext 可以 在 他们 的 bean 定义时 自动检测到 BeanPostProcessor bean 并且 在 bean 创建之后 应用于 任意 的 bean. 普通 的 bean 工厂 允许 基于 编程式的 注册 post-processors,并 应用与 所有通过 该 工厂 创建的 bean;通常,像 post-processor 通过 标记接口 填充 beans 这类业务 应该 实现 postProcessorBeforeInitialization 方法,而 通过 代理 包装 beans 正常 应该 实现 postProcessorAfterInitialization 方法; ;两个抽象方法
// 在 bean 初始化 之前 回调该 函数
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
// 将 BeanPosterProcessor 应用到 新的 bean 实例,在 任意 bean 的初始化之后 回调
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;ApplicationListenerDetector:BeanPostProcessor 的 子类 ,用于 检测 实现了 ApplicationListener 接口 的 bean;
LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor:BeanPostProcessor 的实现类 , 使用 LoadTimeWeaver 构造的类,该类也实现了 LoadTimeWeaver 接口;ApplicationContext 会使用内置 的 BeanFactory 自动注册该类,即上面的代码;
beanFactory 的 ignoredDependencyInterfaces 属性值 :
Aware : 标记 接口,表示 一个 bean 需要通过 回调形式 的 方法 被 Sping 容器中的 一个 特殊的 框架对象 通知;
EnvironmentAware:实现该 接口的类 希望得到正在运行中的 Environment 对象的 通知;即 可以实时获取 当前的 Environment 对象
EmbeddedValueResolverAware:内部定义的值的解决方案
ResourceLoaderAware:任何实现该接口的 对象 希望得到 实时的 ResourceLoader 对象的通知(通常是 ApplicationContext)
ApplicationEventPublisherAware:
MessageSourceAware:
ApplicationContextAware:
beanFactory 的 resolvableDependencies 属性值:
BeanFactory:访问 Spring bean 容器 的 根 接口
ResourceLoader: 加载 资源的策略接口(例如 类路径下 或者 文件系统下 资源),ApplicationContext 需要提供 这个功能,通过 继承 ResourcePatternResolver 得到支持
ResourcePatternResolver:子接口,与 父类不同的是 , ResourceLoader 只能解析一个 Resource ,而 ResourcePatternResolver 支持 资源文件的多匹配,即可返回 Resource 数组
ApplicationEventPublisher:封装了 事件发布功能 的 接口,主要是为 ApplicationContext 提供服务 ;
ApplicationContext:为 应用 提供 配置 的 中央接口 ,当 应用程序在运行时,该接口是只读的,但是可以重新加载,如果实现支持的话;
一个 ApplicationContext 提供了:
① 访问 应用程序组件 的 bean 工厂方法,继承自 ListableBeanFactory;
② 以常规的方法 提供 加载 文件资源的 能力,继承自 ResourceLoader 接口;
③ 发布 事件 给 已注册的 监听器 的 能力,继承自 ApplicaitonEventPublisher 接口;
④ 解析消息 ,支持国际化的能力 ,继承自 MessageSource 接口;
⑤ 从 父上下文的继承,定义在 后代 上下文中 将总是 有优先执行权
包括 标准的 BeanFactory 的 生命周期能力,ApplicationContext 的实现 会发现 并 调用 ApplicationContextAware bean 以及 ResourceLoaderAware bean,ApplicationEventPublisherAware bean, 和 MessageAware bean;
综上,prepareBeanFactory 方法 主要是 对 beanFactory 进行标准化的配置;
3.3.4 postProcessorBeanFactory()
beanFactory 经过上面 标准的初始化之后,在这里 可以 更改 应用上下文 的 内置 bean 工厂的配置,针对不同 的 ApplicationContext 实现类的配置修改;
AbstractApplicationContext . postProcessBeanFactory 方法:
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}这里是一个抽象方法,应该也是 模版方法设计模式的应用,这里调用的是 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext 类中的实现:
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}相关类 简单介绍:
ServletContextAwareProcessor :BeanPostProcessor 的实现类,使用 ServletConfig 或者 ServletContext 类构造的 类;
ServletContextAware : 实现该接口的类 希望 得到 ServletContext 的通知 ,即可以实时获取 ServletContext;
ServletConfigAware:实现该接口的类 希望 得到 ServletConfig的通知 ,即可以实时获取 ServletConfig;
WebApplicationContextUtils . registerWebApplicationScopes():注册 请求域,session 域,应用域 以及 bean 工厂注册 resolvableDependencies,即配置 beanFactory 的 LinkedHashMap 类型的 scopes 的属性值
WebApplicationContextUtils . registerWebApplicationScopes 方法:
public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ServletContext sc) {
/** 将 作用域的 name 和实例 保存在beanFactory 的 scopes 字段中 begin **/
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope());
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope(false));
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION, new SessionScope(true));
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
/** 将 作用域的 name 和实例 保存在beanFactory 的 scopes 字段中 end**/
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
}WebApplicationContextUtils . registerEnvironmentBeans 方法:
public static void registerEnvironmentBeans(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf, ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
// 注册 ServletContext singleton
if (servletContext != null && !bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME, servletContext);
}
// 注册 ServletConfig singleton
if (servletConfig != null && !bf.containsBean(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME)) {
bf.registerSingleton(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.SERVLET_CONFIG_BEAN_NAME, servletConfig);
}
// 注册 contextParameters 中配置的 singleton
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, String> parameterMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletContext.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletContext.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
if (servletConfig != null) {
Enumeration<?> paramNameEnum = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNameEnum.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(paramName, servletConfig.getInitParameter(paramName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(parameterMap));
}
// 注册 contextAttributes 中 配置的 singleton
if (!bf.containsBean(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME)) {
Map<String, Object> attributeMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
if (servletContext != null) {
Enumeration<?> attrNameEnum = servletContext.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNameEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNameEnum.nextElement();
attributeMap.put(attrName, servletContext.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
bf.registerSingleton(WebApplicationContext.CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(attributeMap));
}
}3.3.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:
AbstractApplicationContext . invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors :调用 上下文中已 注册 为 bean 的 处理器(processor)
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}
// 实例化 并 调用 所有已注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}------------------- 第 1 层 --------------------------
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate . invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 方法 :首先分别过滤 beanFactory 类的 beanDefinitionMap 属性中的 实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口 和 Ordered 接口 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型的 bean 定义;根据过滤后的 postProcessor 注册相关的 bean定义,并且解析 Configuration 注解类;最后根据 postProcessor
使用 CGLIB 加强 Configruation 注解的类;
其次分别过滤 beanFactory 类的 beanDefinitionMap 属性中的 实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口 和 Ordered 接口 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 类型的 bean 定义;最后根据 postProcessor 使用CGLIB 加强Configruation 注解的类;
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
// 向上转型为 registry
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessors =
new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
// 注册 beanFactoryPostProcessors 属性中的 postProcessor(即注册 自定义的 beanFactoryPostProcessors,此处为 null)
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryPostProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryPostProcessors.add(registryPostProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// 这里先不初始化 FactoryBeans,需要分离出 未初始化的 常规 bean,让 bean 工厂的 post-processors 处理
// 根据类 的 Class 获取 bean 的名称,用于过滤 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的 bean 定义
String[] postProcessorNames = // 返回的是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// First, 调用 实现了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 处理器,这里 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 满足
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);// 排序
registryPostProcessors.addAll(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, registry);//注册处理器
// Next, 调用实现了 Ordered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
registryPostProcessors.addAll(orderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, registry);
// Finally, 调用所有其他的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 处理器.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class);
registryPostProcessors.add(pp);
processedBeans.add(ppName);
pp.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
reiterate = true;
}
}
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessors, beanFactory);//调用过滤后的 postProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
//这里和 上面处理的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 逻辑一样 ,这里处理的是 BeanFactroyPostProcessor 的子类
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 清除 merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}BeanFactoryPostProcessor:顶级接口,允许 应用上下文 的 bean definition 的 自定义修改,上下文内置 bean 工厂 的 bean 属性值的 改写;
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor: BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子接口,标准的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor SPI 的 扩展 ;
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor : BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 唯一实现类,用于引导 @Configuration 注解的 类的 处理,当使用了 <context:annotation-config> 或者 <context:component-scan> 配置时,被默认的注册,否则,可以与 其他的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 一起 手动声明;
------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
DefaultListableBeanFactory . getBeanNamesForType 方法:这里是 对 beanFactory 中 的 beanDefinitionNames 字段以及 manualSingletonNames 字段进行过滤,匹配对象为 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ,包括其子类;
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
if (!isConfigurationFrozen() || type == null || !allowEagerInit) {
return doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
}
Map<Class<?>, String[]> cache =
(includeNonSingletons ? this.allBeanNamesByType : this.singletonBeanNamesByType);
String[] resolvedBeanNames = cache.get(type);
if (resolvedBeanNames != null) {
return resolvedBeanNames;
}
resolvedBeanNames = doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType.forRawClass(type), includeNonSingletons, true);
if (ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(type, getBeanClassLoader())) {
cache.put(type, resolvedBeanNames);
}
return resolvedBeanNames;
}
private String[] doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
// 循环所有的 bean 定义
for (String beanName : this.beanDefinitionNames) {
// Only consider bean as eligible if the bean name
// is not defined as alias for some other bean.
if (!isAlias(beanName)) {
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);//与父类合并后的 definition
// Only check bean definition if it is complete.
if (!mbd.isAbstract() && (allowEagerInit ||
((mbd.hasBeanClass() || !mbd.isLazyInit() || isAllowEagerClassLoading())) &&
!requiresEagerInitForType(mbd.getFactoryBeanName()))) {
// In case of FactoryBean, match object created by FactoryBean.
boolean isFactoryBean = isFactoryBean(beanName, mbd);
boolean matchFound = (allowEagerInit || !isFactoryBean ||
(mbd.getDecoratedDefinition() != null && !mbd.isLazyInit()) ||
containsSingleton(beanName)) &&
(includeNonSingletons || isSingleton(beanName)) &&
isTypeMatch(beanName, type);
if (!matchFound && isFactoryBean) {
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean instance itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
matchFound = (includeNonSingletons || mbd.isSingleton()) && isTypeMatch(beanName, type);
}
if (matchFound) {
result.add(beanName);
}
}
}
catch (CannotLoadBeanClassException ex) {
if (allowEagerInit) {
throw ex;
}
// Probably contains a placeholder: let's ignore it for type matching purposes.
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Ignoring bean class loading failure for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
if (allowEagerInit) {
throw ex;
}
// Probably contains a placeholder: let's ignore it for type matching purposes.
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Ignoring unresolvable metadata in bean definition '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
onSuppressedException(ex);
}
}
}
// 循环所有手动注册的单例
for (String beanName : this.manualSingletonNames) {
try {
// In case of FactoryBean, match object created by FactoryBean.
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
if ((includeNonSingletons || isSingleton(beanName)) && isTypeMatch(beanName, type)) {
result.add(beanName);
// Match found for this bean: do not match FactoryBean itself anymore.
continue;
}
// In case of FactoryBean, try to match FactoryBean itself next.
beanName = FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName;
}
// Match raw bean instance (might be raw FactoryBean).
if (isTypeMatch(beanName, type)) {
result.add(beanName);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Shouldn't happen - probably a result of circular reference resolution...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to check manually registered singleton with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws BeansException {
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
RootBeanDefinition mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
if (mbd != null) {
return mbd;
}
return getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName, getBeanDefinition(beanName));//从beanDefinitionMap中获取 beanDefinition
}
// 将 beanDefiniton 和 其 父类(如果有的话)进行合并,最后保存在 mergedBeanDefinitions 属性中
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition bd)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName, bd, null);
}
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(
String beanName, BeanDefinition bd, BeanDefinition containingBd)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
synchronized (this.mergedBeanDefinitions) {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = null;
// Check with full lock now in order to enforce the same merged instance.
if (containingBd == null) {
mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
}
if (mbd == null) {
if (bd.getParentName() == null) {
// Use copy of given root bean definition.
if (bd instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
mbd = ((RootBeanDefinition) bd).cloneBeanDefinition();
}
else {
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(bd);
}
}
else {
// Child bean definition: needs to be merged with parent.
BeanDefinition pbd;
try {
String parentBeanName = transformedBeanName(bd.getParentName());
if (!beanName.equals(parentBeanName)) {
pbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
BeanFactory parent = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
pbd = ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) parent).getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(parentBeanName,
"Parent name '" + parentBeanName + "' is equal to bean name '" + beanName +
"': cannot be resolved without an AbstractBeanFactory parent");
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve parent bean definition '" + bd.getParentName() + "'", ex);
}
// Deep copy with overridden values.
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(pbd);
mbd.overrideFrom(bd);
}
// Set default singleton scope, if not configured before.
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(mbd.getScope())) {
mbd.setScope(RootBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON);
}
// A bean contained in a non-singleton bean cannot be a singleton itself.
// Let's correct this on the fly here, since this might be the result of
// parent-child merging for the outer bean, in which case the original inner bean
// definition will not have inherited the merged outer bean's singleton status.
if (containingBd != null && !containingBd.isSingleton() && mbd.isSingleton()) {
mbd.setScope(containingBd.getScope());
}
// Only cache the merged bean definition if we're already about to create an
// instance of the bean, or at least have already created an instance before.
if (containingBd == null && isCacheBeanMetadata()) {
this.mergedBeanDefinitions.put(beanName, mbd);
}
}
return mbd;
}
}-------------------------------
PriorityOrdered:Ordered 接口的扩展,表示 优先级顺序;空接口
------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate . sortPostProcessors() 方法:将过滤的 post processor 按某种规则 排序
private static void sortPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<?> postProcessors) {
Comparator<Object> comparatorToUse = null;
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
comparatorToUse = ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).getDependencyComparator();
}
if (comparatorToUse == null) {
comparatorToUse = OrderComparator.INSTANCE;
}
Collections.sort(postProcessors, comparatorToUse);
}------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate . invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors()方法: 处理 bean 定义的记录器
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor . postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法为抽象方法;
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor . postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 为实现方法:再次给 bean 工厂 添加 bean 定义(维护 beanDefinitionMap,beanDefinitionNames,manualSingletonName 字段),这里添加的bean 定义为 :
ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的内部静态类,实现了 BeanPostProcessor,BeanFactoryAware,PriorityOrdered 接口;beanDefinitionMap 中对应的key 值为:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.importAwareProcessor
EnhancedConfigurationBeanPostProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的内部静态类,实现了 BeanFactoryAware,PriorityOrdered 接口,继承了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter 类;beanDefinitionMap 中对应的key 值为:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.enhancedConfigurationProcessor
,并解析 Configuration 注解的类;
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
RootBeanDefinition iabpp = new RootBeanDefinition(ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor.class);
iabpp.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(IMPORT_AWARE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, iabpp);
RootBeanDefinition ecbpp = new RootBeanDefinition(EnhancedConfigurationBeanPostProcessor.class);
ecbpp.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(ENHANCED_CONFIGURATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, ecbpp);
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor . processConfigBeanDefintions()方法:创建和验证 基于 registry 的 configuration 模型;即解析 registry beanDefinitionMap 中 Configuration 注解的 类
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
Collections.sort(configCandidates, new Comparator<BeanDefinitionHolder>() {
@Override
public int compare(BeanDefinitionHolder bd1, BeanDefinitionHolder bd2) {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return (i1 < i2) ? -1 : (i1 > i2) ? 1 : 0;
}
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry singletonRegistry = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
singletonRegistry = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet && singletonRegistry.containsSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR)) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) singletonRegistry.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<ConfigurationClass>(configCandidates.size());
do {
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<ConfigurationClass>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<String>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(beanDef.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (singletonRegistry != null) {
if (!singletonRegistry.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
singletonRegistry.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}相关类介绍:
SingletonBeanRegistry:顶层接口,定义了一个用于 共享 bean 实例 的 registry,ConfigurableBeanFactory 接口 继承了该接口;
ConfigurationClassParser 类:用于解析 一个 Configuration 标注的 类 的 定义,得到的是一个 ConfiguraionClass 对象的集合(解析一个单独的 Configuration 类可以产生多个 ConfigurationClass 对象,因为一个 Configuration 类 可以使用 import 注解导入其他的 Configuration 类);
构造需要的类:MetadataReaderFactory:MetadataReader 实例的 工厂接口;用于获取 MetadataReader
ProblemReporter:在 beanDefinition 的 解析 过程中 允许工具 和 外部的 处理器(processor)处理 错误 和 警告 报告;
Environment:
ResourceLoader:
BeanNameGenerator:
BeanDefinitionRegistry:
ConfigurationClass:代表 用户使用 @Configuration 注解 定义 的 Cofiguration 类,包含了一组 bean 方法(@Bean 注解的方法)
------------------- 第 2 层 --------------------------
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate . invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法:调用给定的 BeanFactoryPostPrecessor bean,这里是调用过滤后的 postProcesser
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}------------------- 第 3 层 --------------------------
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor . postProcessBeanFactory():处理 Configuration 注解类的 postProcessor
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory);
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory);
}
this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId);
if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported...
// Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then.
processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
}
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
}------------------- 第 4 层 --------------------------
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor . enhenceConfigurationClasses() 方法:查找 Configuration 注解的类 的 beanDefinition,并通过 ConfigurationClassEnhancer类 加强
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<String, AbstractBeanDefinition>();
/** 查找 beanDefinitionNames 中的 configuration 注解类的 bean 定义 begin**/
for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" +
beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass");
}
else if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
logger.warn("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName +
"' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " +
"is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " +
"return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.");
}
configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef);
}
}
/** 查找 beanDefinitionNames 中的 configuration 注解类的 bean 定义 end**/
if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) {
// nothing to enhance -> return immediately
return;
}
// 增强 Configuration 注解的 类,这里的增强就是使用代理(CGLIB)
ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer();
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue();
// If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class
beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
// Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean class
Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader);//增强前的类
Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader);//增强后的类
if (configClass != enhancedClass) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " +
"enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));
}
beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
}
}相关类介绍:
ConfigurationClassEnhancer:通过生成一个 CGLIB 子类 来 增强 Configuration 注解的类;每个 Bean 注解的方法 将会在 生成的子类中被重写,如果 容器 请求了 新实例的构造函数,则委托给 Bean 注解方法的 真正的实现类,否则 ,对 bean 注解的方法的 调用 相当于对这个容器的引用,根据 名称 获得 相关 bean;
------------------- 第 5 层 --------------------------
ConfigurationClassEnhancer . enhence()方法:加载指定的 类,生成 CGLIB 子类
public Class<?> enhance(Class<?> configClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (EnhancedConfiguration.class.isAssignableFrom(configClass)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("Ignoring request to enhance %s as it has " +
"already been enhanced. This usually indicates that more than one " +
"ConfigurationClassPostProcessor has been registered (e.g. via " +
"<context:annotation-config>). This is harmless, but you may " +
"want check your configuration and remove one CCPP if possible",
configClass.getName()));
}
return configClass;
}
Class<?> enhancedClass = createClass(newEnhancer(configClass, classLoader));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("Successfully enhanced %s; enhanced class name is: %s",
configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));
}
return enhancedClass;
}
------------------- 第 6 层 --------------------------
newEnhancer:创建一个 新的 CGLIB Enhancer 实例;
private Enhancer newEnhancer(Class<?> superclass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(superclass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class});
enhancer.setUseFactory(false);
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER);
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes());
return enhancer;
}createClass() 方法:使用 enhancer 生成超类的子类,并为新 的子类 注册 回调函数;
private Class<?> createClass(Enhancer enhancer) {
Class<?> subclass = enhancer.createClass();
// Registering callbacks statically (as opposed to thread-local)
// is critical for usage in an OSGi environment (SPR-5932)...
Enhancer.registerStaticCallbacks(subclass, CALLBACKS);
return subclass;
}3.3.6 registerBeanPostProcessors():注册用于拦截 bean 定义的 bean 处理器,会添加到 beanFactory 的 alreadyCreated 属性中;
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}委托给 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 处理,还记得上面的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法同样是委托给该类处理;处理原理也很类似;
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate . registerBeanPostProcessors()方法:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 根据 类型 匹配 bean 定义
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
//注册 BeanPostProcessorChecker,在 BeanPostProcessor 实例化过程中
//当 一个 bean 被创建时用于打日志信息
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// 将实现 PriorityOrdered 和 Ordered 的BeanPostProcessor 分离
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}相关类:
BeanPostProcessorChecker:PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 的内部类,用于 在 BeanPostProcessor 实例化过程中,当 bean 被创建时用于打 日志信息;
-------------------------------------------------------------大分割线--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.3.7 initMessageSource()方法:为 应用上下文初始化 信息资源;即初始化 MessageSource ;
protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 判断此时的 bean 工厂是否已经初始化了 MessageSource
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}相关类:
DelegatingMessageSource 类:内含 空的 MessageSource,委托给 父类的 MessageSource 处理所有的调用,如果没有父 MessageSource,将不会处理 信息;
MessageSource 接口:解决 消息的 策略接口,支持 参数化 和 国际化 消息;
Spring 提供了两个 开箱即用的实现类 :
ResourceBundleMessageSource: 基于 ResourceBundle 的 最高标准创建;
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource:能够在 不重启 VM 的条件下 重新加载 消息定义;
-------------------------------------------------------------大分割线--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.3.8 initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法:为 应用上下文 初始化 事件的多路广播,即 初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaster,注册在 bean 工厂的 registeredSingletons 属性中
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +
APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}
相关类介绍:
ApplicationEventMulticaster 接口:实现该接口的对象可以管理多个 ApplicationListener 对象,并发布事件给 他们;一个 ApplicationEventPublisher,通常是 一个 Spring 的 ApplicationContext,可以使用 ApplicationEventMuticaster 作为 委托实际处发布事件;
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 类:ApplicationEventMulticaster 简单的实现类;多路广播 所有的事件 给 所有已注册的 监听器(listener);
3.3.9 onRefresh()方法:初始化在 具体的 上下文 的子类 中 指定的其他的 bean;
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}这里使用的是 模版方法设计模式,由不同的实现类去重写该方法,这里的相关子类是 AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext ,其重写方法如下:
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}UiApplicationContextUtils: UI 上下文应用的功能类,对 名称为 themeSource 的 特殊的 bean 提供支持;
initThemeSource()方法:
public static ThemeSource initThemeSource(ApplicationContext context) {
//判断是否已经初始化
if (context.containsLocalBean(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
ThemeSource themeSource = context.getBean(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, ThemeSource.class);
// Make ThemeSource aware of parent ThemeSource.
if (context.getParent() instanceof ThemeSource && themeSource instanceof HierarchicalThemeSource) {
HierarchicalThemeSource hts = (HierarchicalThemeSource) themeSource;
if (hts.getParentThemeSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent ThemeSource if no parent ThemeSource
// registered already.
hts.setParentThemeSource((ThemeSource) context.getParent());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ThemeSource [" + themeSource + "]");
}
return themeSource;
}
else {
// Use default ThemeSource to be able to accept getTheme calls, either
// delegating to parent context's default or to local ResourceBundleThemeSource.
//使用默认的 ThemeSource,委托给 父 上下文的 默认的 ThemeSource 处理 或者 本地的
// ResourceBundleThemeSource 处理
HierarchicalThemeSource themeSource = null;
if (context.getParent() instanceof ThemeSource) {
themeSource = new DelegatingThemeSource();
themeSource.setParentThemeSource((ThemeSource) context.getParent());
}
else {
themeSource = new ResourceBundleThemeSource();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ThemeSource with name '" + THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + themeSource + "]");
}
return themeSource;
}
}
ThemeSource 接口:实现类 可以 解决 Theme;可以为 指定的 theme 提供 消息的参数化 和 国际化 ;
HierarchicalThemeSource 接口:子接口,实现类可以 解决 消息 的 继承关系;
-------------------------------------------------------------大分割线--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.3.10 registerListeners()方法:检查 listener bean 并注册
protected void registerListeners() {
// 首先注册静态指定的 监听器,这里未指定
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
3.3.11 finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法:实例化所有剩余的 (非懒加载)单例
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 如果包含的话为上下文初始化 转换服务
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// 如果之前没有 post-processor (比如 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean)注册的话
// 注册一个默认的内置的 值解析器,主要用于注解的属性值的解析
// 保存到 bean 工厂的 embeddedValueResolvers 属性中
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() {
@Override
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal);
}
});
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
//停止使用临时的 ClassLoader 进行 类型匹配
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// 缓存所有的 bean 定义元数据,即缓存保存在 bean工厂的 beanDefinitionNames中的数据
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 实例化所有剩余的 单例
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}preInstantiateSingletons()方法:调用的是 DefaultListableBeanFactory 实现类 中的 方法:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 所有非懒加载的 单例 bean 进行初始化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
/** 将所有的 bean 定义初始化后,保存在 bean 工厂的 alreadyCreated 属性中 end**/
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
3.3.12 finishRefresh()方法: 发布相关事件
protected void finishRefresh() {
// 为应用上下文 初始化 LifecycleProcessor
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
initLifecycleProcessor():初始化 LifecycleProcessor;如果没有定义的话使用 DefaultLifecycleProcessor;
protected void initLifecycleProcessor() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.lifecycleProcessor =
beanFactory.getBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, LifecycleProcessor.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using LifecycleProcessor [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
else {
DefaultLifecycleProcessor defaultProcessor = new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();
defaultProcessor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.lifecycleProcessor = defaultProcessor;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, this.lifecycleProcessor);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate LifecycleProcessor with name '" +
LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
}相关类介绍:
LifecycleProcessor:处理 ApplicationContext 内的 bean 的生命周期 的 策略接口;
DefaultLifecycleProcessor:LifecycleProcessor 的默认 实现类,同时实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口;
------------------------------------
onRefresh()方法:调用的是 DefaultLifecycleProcessor 类中的实现方法;
public void onRefresh() {
startBeans(true);
this.running = true;
}startBeans()方法:会获取 bean 工厂中 的 bean 定义
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
//获取 bean 工厂中的 Lifecycle 类型的类
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<Integer, LifecycleGroup>();
for (Map.Entry<String, ? extends Lifecycle> entry : lifecycleBeans.entrySet()) {
Lifecycle bean = entry.getValue();
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle && ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
int phase = getPhase(bean);
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(phase);
if (group == null) {
group = new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly);
phases.put(phase, group);
}
group.add(entry.getKey(), bean);
}
}
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<Integer>(phases.keySet());
Collections.sort(keys);
for (Integer key : keys) {
phases.get(key).start();
}
}
}相关类介绍:
Lifecycle 接口:定义了 开启/停止 的生命周期控制 方法 的 通用接口,典型的使用场景是 控制 异步处理;包含了 start()、stop()、isRunning() 三个抽象方法;该接口 仅仅支持 顶层 的 单例 bean;
LifecycleGroup : DefaultLifecycleProcessor 的 内部 帮助类,用于 保存 一组 Lifecycle bean 对象,这些 bean 对象 应该是 同时 开启 和关闭的;
------------------------------------
publishEvent()方法:发布最终的事件;
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent(event, null);
}相关类介绍:
ApplicationEvent:继承了 jdk EventObject 类的抽象类;所有的应用事件 都应该继承该 抽象类;
ContextRefreshedEvent:ApplicationEvent 的实现类,当 ApplicationContext 初始化 或者 刷新 时,触发事件
PayloadApplicationEvent:主要内部使用;
publishEvent(event,null)方法:
protected void publishEvent(Object event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<Object>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent)applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
------------------------------------
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationConext()方法:加入
static void registerApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String mbeanDomain = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty(MBEAN_DOMAIN_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (mbeanDomain != null) {
synchronized (applicationContexts) {
if (applicationContexts.isEmpty()) {
try {
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
applicationName = applicationContext.getApplicationName();
server.registerMBean(new LiveBeansView(),
new ObjectName(mbeanDomain, MBEAN_APPLICATION_KEY, applicationName));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to register LiveBeansView MBean", ex);
}
}
applicationContexts.add(applicationContext);
}
}
}
这样就完成了 WebApplicationContext 的 初始化。
1.3 WebApplicationContext 的销毁
当关闭应用服务器时,触发 ContextLoaderListener 的 contextDestroyed 方法 ,该方法主要是关闭 WebApplicationContext,移除当前上下文应用 ,并且释放资源。
<到此 ContextLoaderListener 解析完毕,欢迎补充指正。~>








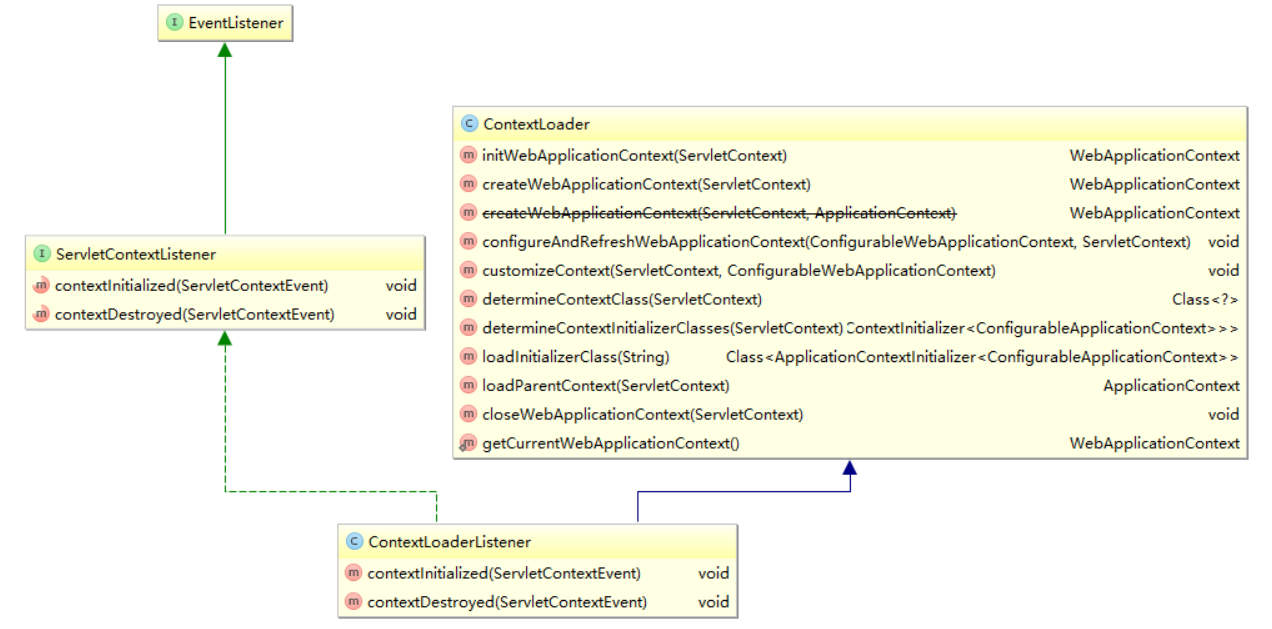
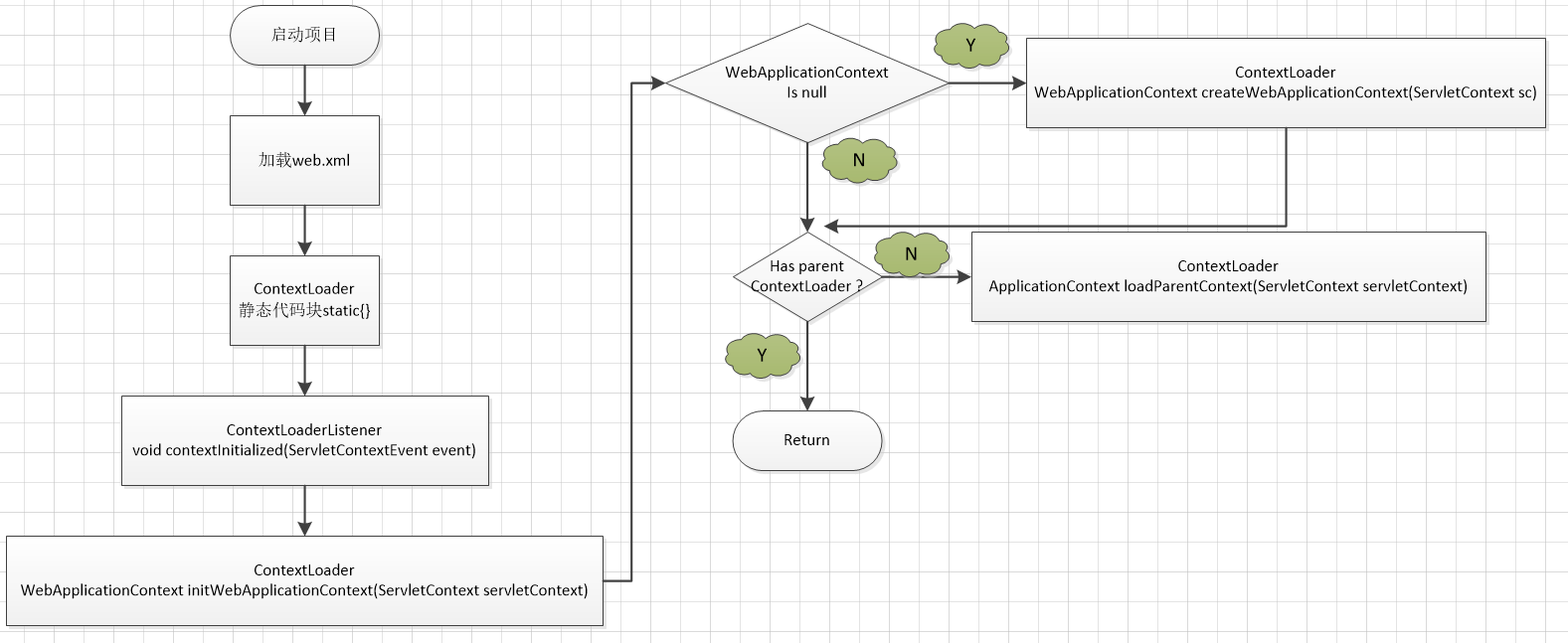

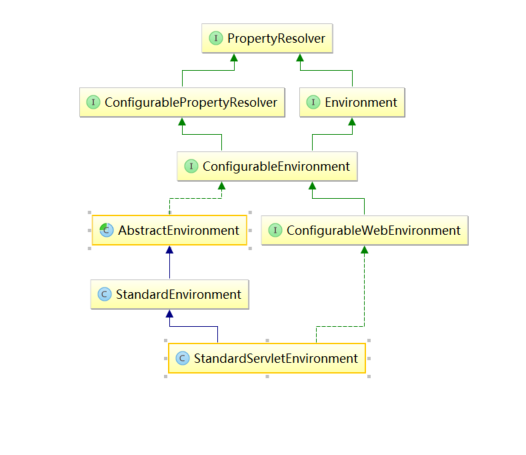
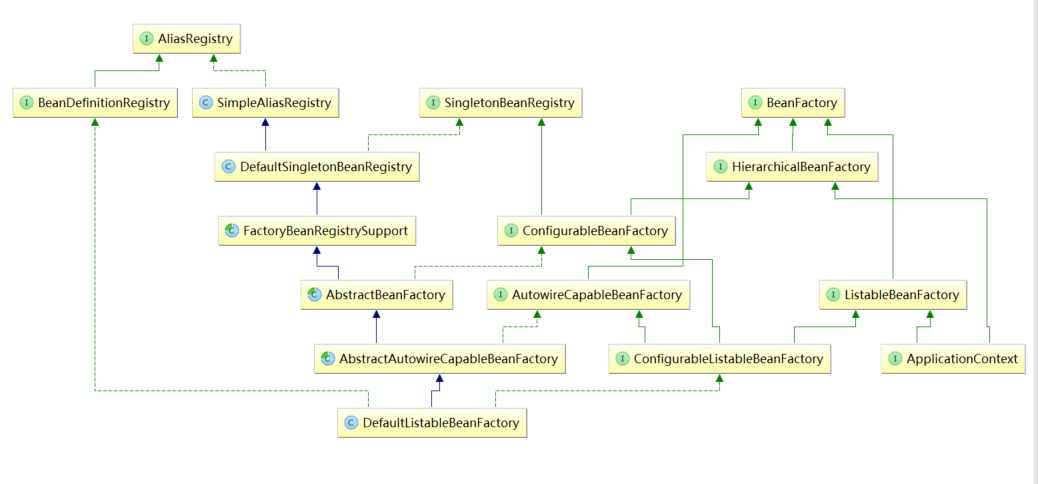














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








