1. Transaction Management (事物管理)
1.1 介绍
综合使用 Spring 框架 最大的原因应该是 集成 了对事物的支持 。
Spring 框架 为 事物 管理 提供了一致性的抽象 ,此做法有以下有点 :
★ 不同的事物接口拥有一致的编程模型 。如 Java Transaction API(JTA),JDBC,Hibernate,Java Persistence API(JPA),Java Data Objects(JDA)
★ 支持声明式的事物注解
★ 对于编程式的事务管理拥有简单的 API
★ 和 Spring 的 数据访问抽象很好的集成
1.2 理解 Spring 框架 的 事物抽象
关键 是 事物策略的概念。事物 策略和以下接口相关:
org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager方法如下 :
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}PlatformTransactionManager 的相关实现类 提供了正常 的环境需求 : JDBC 、JTA 、Hibernate .
JDBC 栗子 :
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean><bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>Hibernate 栗子:
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mappingResources">
<list>
<value>org/springframework/samples/petclinic/hibernate/petclinic.hbm.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<value>
hibernate.dialect=${hibernate.dialect}
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>
</bean>TransactionDefinition 接口定义了如下内容 : 这些 内容 和标准的 事物 概念等同
★ 隔离 (Isolation) : 定义隔离级别
四种隔离级别 (低→高): (案例帮助理解戳这里)
Read uncommitted : 脏读、不可重复读、幻读 都会发生
Read committed : 脏读被阻止,不可重复读、幻读会发生 (oracle 默认的隔离级别,大多数数据库)
Repeatable read : 脏读和不可重复读被阻止 , 幻读会发生 (mysql默认的隔离级别)
Serializable : 脏读、不可重复读、幻读 都被阻止
★ 传播(Propagation): 定义传播范围
七种传播特性
★ 超时(TimeOut)
★ 只读状态(Read-only status)
TransactionStatus :定义的状态 对于所有 事物 API 应该是通用的
public interface TransactionStatus extends SavepointManager, Flushable {
boolean isNewTransaction();
boolean hasSavepoint();
void setRollbackOnly();
boolean isRollbackOnly();
void flush();
boolean isCompleted();
}1.3 使用事物 同步资源
1.4 声明式事物管理
使用 Spring 的 AOP 实现声明式事物管理
1.4.1 理解
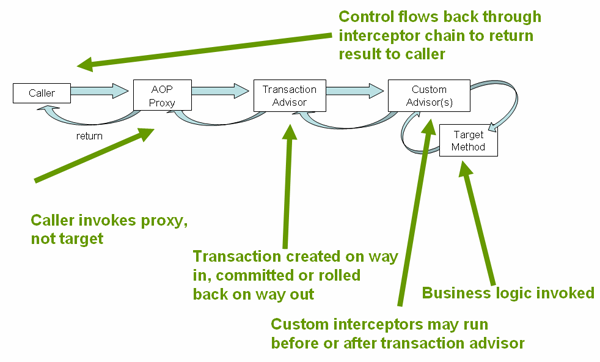
通过 AOP 代理实现 。大概的流程如下:
1.4.2 案例
service
// the service interface that we want to make transactional
package x.y.service;
public interface FooService {
Foo getFoo(String fooName);
Foo getFoo(String fooName, String barName);
void insertFoo(Foo foo);
void updateFoo(Foo foo);
}service 实现类
// an implementation of the above interface
package x.y.service;
public class DefaultFooService implements FooService {
public Foo getFoo(String fooName) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Foo getFoo(String fooName, String barName) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void insertFoo(Foo foo) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void updateFoo(Foo foo) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}Spring XML 配置 :
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional -->
<bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/>
<!-- the transactional advice (what 'happens'; see the <aop:advisor/> bean below) -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<!-- the transactional semantics... -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- all methods starting with 'get' are read-only -->
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<!-- other methods use the default transaction settings (see below) -->
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- ensure that the above transactional advice runs for any execution
of an operation defined by the FooService interface -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="fooServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.FooService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="fooServiceOperation"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- don't forget the DataSource -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@rj-t42:1521:elvis"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</bean>
<!-- similarly, don't forget the PlatformTransactionManager -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- other <bean/> definitions here -->
</beans>1.4.3 <tx:advise/> 配置
| Attribute | Required? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| Yes | Method name(s) with which the transaction attributes are to be associated. The wildcard (*) character can be used to associate the same transaction attribute settings with a number of methods; for example, | |
|
| No | REQUIRED | Transaction propagation behavior. |
|
| No | DEFAULT | Transaction isolation level. |
|
| No | -1 | Transaction timeout value (in seconds). |
|
| No | false | Is this transaction read-only? |
|
| No |
| |
|
| No |
|
默认值 : transaction 是可读可写 ,默认 任何的运行时异常都会 rollback ,任何可检测异常不会回滚 。
1.4.4 使用 @Transactional :
上面的栗子是基于 XML ,而此方法是基于注解。
栗子:
service 的实现类:
// the service class that we want to make transactional
@Transactional
public class DefaultFooService implements FooService {
Foo getFoo(String fooName);
Foo getFoo(String fooName, String barName);
void insertFoo(Foo foo);
void updateFoo(Foo foo);
}XML 少量配置:
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional -->
<bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/>
<!-- enable the configuration of transactional behavior based on annotations -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/><!-- a PlatformTransactionManager is still required -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- (this dependency is defined somewhere else) -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- other <bean/> definitions here -->
</beans>如果使用 java配置元数据,可以直接使用注解而不需要再配置 XML
@EnableTransactionManagement@Transactional 可以 注解在 接口上 ,接口的方法上 ,类上 ,或者 类的 公共方法上 。(如果定义在了 protected 或者 private 方法上,不会报错,但也没有效果)
当然 Spring 推荐只 注解在 实体类上(或者实体类的方法上) ,当然接口上也可以注解,但是该处的 事物只有当 使用基于接口的代理时才有效(JDK 的动态代理即基于接口)
定义 @EnableTransactionManagement 和 <tx:annotaion-driven/> 仅仅是 为了 可以在代码中识别 @Transactional 的注解 ,不会识别其他的注解 。
当类上和方法中同时注解了 @Transactional ,则 Spring 遵从 最原始的位置具有优先权 ,如下 栗子:
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class DefaultFooService implements FooService {
public Foo getFoo(String fooName) {
// do something
}
// these settings have precedence for this method 优先权更高
@Transactional(readOnly = false, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateFoo(Foo foo) {
// do something
}
}@Transactional 的配置
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | Optional qualifier specifying the transaction manager to be used. | |
| enum: | Optional propagation setting. | |
|
| enum: | Optional isolation level. |
|
| boolean | Read/write vs. read-only transaction |
|
| int (in seconds granularity) | Transaction timeout. |
|
| Array of | Optional array of exception classes that must cause rollback. |
|
| Array of class names. Classes must be derived from | Optional array of names of exception classes that must cause rollback. |
|
| Array of | Optional array of exception classes that must not cause rollback. |
|
| Array of | Optional array of names of exception classes that must notcause rollback. |
默认值 :传播默认 Required ,transaction 默认可读可写 。
多个事物管理 :互相不干扰
public class TransactionalService {
@Transactional("order")
public void setSomething(String name) { ... }
@Transactional("account")
public void doSomething() { ... }
}<tx:annotation-driven/>
<bean id="transactionManager1" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
...
<qualifier value="order"/>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager2" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
...
<qualifier value="account"/>
</bean> 1.5 编程式的事物管理 (此方法和业务代码耦合高)
★ 使用 TransactionTemplate (推荐使用)
★ 使用 PlatformTransactionManager
<补充 :
现在的项目里使用的 框架是 Spring +Spring mvc + jdbi + Druid连接池 ,而且 Spring 和 Spring mvc 使用的是基于注解的配置方式,那么该如何完成事物管理呢?
两种选择 :
1. 使用 Jdbi 提供 的事物管理
Jdbi 处理事物要求 在同一个业务逻辑中的所有数据库操作都要使用同一个 handle 来处理 ,否则不能保证事物正常回滚 。这就给 事物的管理提供了难度 ,通常我们的事物管理都是在 Service 层 进行 ,而且牵扯到多个 不同的 Dao 处理数据也是经常的事 ,所以 不能简单的使用 @Transaction 注解 来进行事物管理 ,详细请参看 :How to use Transactions in JDBI
2. 使用 Spring 提供的事物管理 。
对于常规的 事物 管理 ,使用JDBC ,Hibernate , JTA ,Spring 都提供了相对应的 TransactionManager 实现类 ,所以配置起来很方便,网上也有很多的教程。但是对于 使用 Jdbi 处理数据,Jdbi 需要 将 普通的 DataSource 对象 注入到 IDBI 的实现类 DBI 中以便 获取 handle 处理 SQL 。
完成Spring 事物管理的步骤如下 :
★ 配置 DataSource (original ds)(普通的连接数据库的对象)
★ 将 original ds 注入到 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy (proxy ds) 实例中
★ 将 proxy ds 注入到 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager 实例中
★ 将 proxy ds 注入到 org.skife.jdbi.v2.DBI 的 实例中
Spring 的事物管理的主要代码配置如下 :
DataSource 连接数据库的配置 DevConfig.java
package com.peptalk.springconfig;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
@Configuration
@Profile("dev")
public class DevConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:oracle:thin:@hostname:orcl");
dataSource.setUsername("***");
dataSource.setPassword("****");
dataSource.setMaxActive(20);
dataSource.setMaxWait(2000);
dataSource.setFilters("stat,wall");
return dataSource;
}
}
ApplicationContext.xml 的基于注解的 java 配置
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ComponentScan(basePackages={ "com.peptalk.security", "com.peptalk.service"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
// original ds
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean
public BeanPostProcessor lifecycleBeanPostProcessor() {
return new LifecycleBeanPostProcessor();
}
// 用于上传的 解析器
@Bean
public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver() {
CommonsMultipartResolver commonsMultipartResolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver();
commonsMultipartResolver.setDefaultEncoding("utf-8");
commonsMultipartResolver.setMaxUploadSize(50000000);
return commonsMultipartResolver;
}
// Spring代理的 ds 对象
@Bean
public TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(){
TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = new TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy(dataSource);
return dataSourceProxy;
}
// Spring 的 事物管理对象
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSourceProxy());
return transactionManager;
}
// Spring 代理的 ds 对象注入到 DBI
@Bean
public IDBI database() {
IDBI dbi = new DBI(dataSourceProxy());
return dbi;
}
}






















 1633
1633

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








