1.小强再次受到打击
小强今天又折了!!被问到了一个场景题,感觉还是还是没答到面试官满意的程度!!! 越想越难受

事情是这样子的!!!!
面试官上来就摆了一个(停车场停车)场景题
假设每一个线程都代表一辆车,每次有一辆车停车,显示屏就会显示剩余车位减一,每次有一辆车出去,显示屏上就显示剩余车位加1,当显⽰屏上的剩余车位为0时,停车场⼊⼝的栏杆就不会再打开,车辆就⽆法进⼊停车场了,直到有⼀辆车从停车场出去为⽌,让写个方法去实现下。
此时小强很高兴,这不是昨晚准备过的么,太爽了~~上来一顿操作

2.代码疯狂输出
public class SemaphoreTest {
/**
* 实现一个同时只能存放5个汽车的车厂
*/
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5);
/**
* 定义一个线程池
*/
private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
/**
* 模拟执行方法
*/
private static AtomicInteger sortNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void exec() {
int i = sortNum.addAndGet(1);
try {
semaphore.acquire(1);
// 开始入车
System.out.println("入车" + i);
// 开始停车
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//准备出车
semaphore.release(1);
System.out.println("出车" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
{
for (; ; ) {
Thread.sleep(100);
// 模拟请求以10个/s的速度
executor.execute(() -> exec());
}
}
}
}
运行完之后,可以看到结果先是5个车进车场,到之后1号车出时,6号车才进。
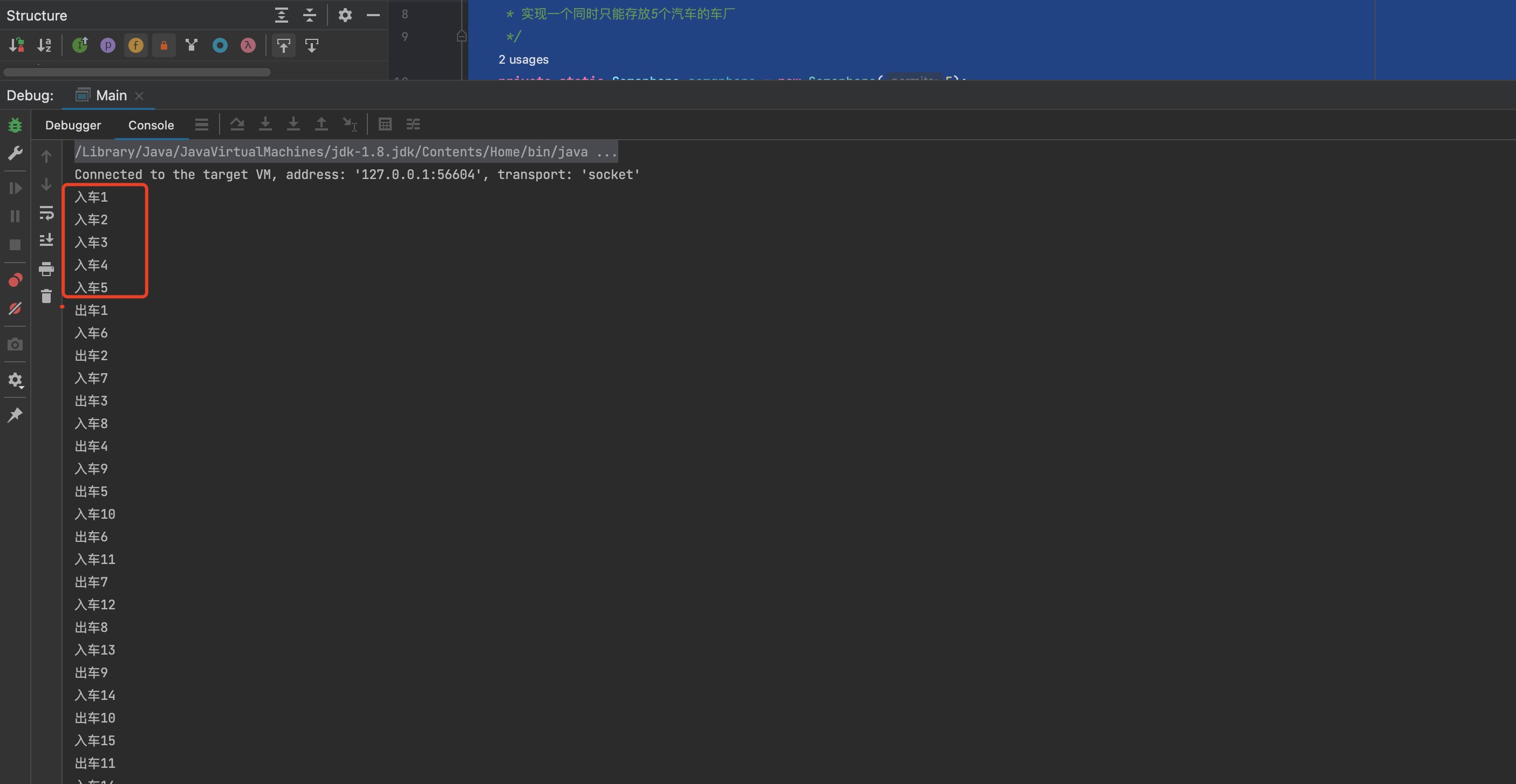
此时,小强很自信的看着面试官,面试官也笑了下,小伙子可以呀!!继续问到,那你知道他们在底层是如何实现的么,小强沉默了,他思考着之前有个夜晚,正准备要学习这个的时候,正好赶上朋友叫他五排!!
他不甘心,王者荣耀以后不玩了,开始搞起里面的关键方法:
3.源码底层开整
1.构造方法
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5);
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
//设置state的值
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
}
2.acquire()方法
public void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
//对state相减,减完之后如果小于0,则加入阻塞队列
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
下面这块最好先看下之前讲的AQS
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
//加入队列
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
//阻塞
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
其实总结下来就是先减去state,假如state<0时,才去加到任务等待队列中。
3.release方法
public void release(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.releaseShared(permits);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
//
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
//对state增加releases,成功,则返回空
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
这个方法会去唤醒所有的线程等待节点
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
//当没有线程入队时,则不进入判断
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
//是否需要唤醒后面的节点
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
总结:
每次解锁的时候都会增加state的个数,其实就是相当于空出车位的概念。
如果增加 state成功,则会去doReleaseShared去唤醒节点。此时会出现两种情况:
- 当执行semaphore.acquire方法的时候,state在减少之后如果大于等于0,则不会加入到等待队列中,此时在调用doReleaseShared()方法时,if (h != null && h != tail)不会满足,但是if (h == head) 满足,则会跳出循环,相当于什么都不做。
- 当执行semaphore.acquire()时,如果state在减少之后小于0,则会加入到等待队列中,此时在调用doReleaseShared()方法时,if (h != null && h != tail)条件会满足,会唤醒在等待队列中等待执行的全部线程。

在此刻,电话突然想起,电话的那一头传来一个声音: “赶紧上号,干啥呢?磨磨唧唧,今晚带你上大分”。。。。。























 153
153











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








