在java io中包含流的操作主要有两种 字节流和字符流,两类都有输入输出操作。。字节流输出主要是OutputStream,输入InputStream,在字符流中输出主要是:Writer,输入主要是:Reader
![]()
![]()

java io 操作也有步骤,以文件为例
(1)使用File类来打开一个文件
(2)通过字节流或字符流的子类指定输出的位置
(3)进行读写操作
(4)关闭输入输出
1.字节流
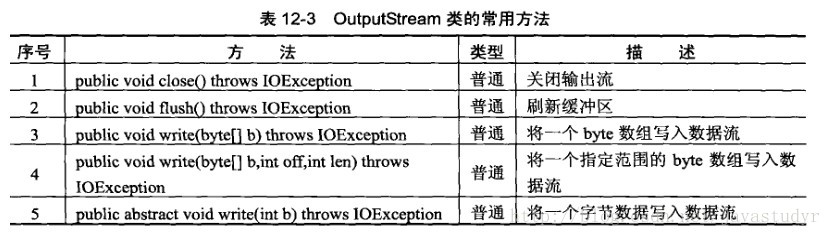
字节流只要是以操作byte数据,以byte数组为主,组要操作类是OutputStream,InputStream
2.字节输出流
看下源码:
public
abstract
class
OutputStream
implements
Closeable, Flushable {
public
abstract
void
write(
int
b)
throws
IOException;
public
void
write(
byte
b[])
throws
IOException {
write(b, 0, b.
length
);
}
public
void
write(
byte
b[],
int
off,
int
len)
throws
IOException {
if (b == null ) {throw new NullPointerException();} else if ((off < 0) || (off > b. length ) || (len < 0) ||((off + len) > b. length ) || ((off + len) < 0)) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();} else if (len == 0) {return ;}for ( int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {write(b[off + i]);}}
public
void
flush()
throws
IOException {
}
public
void
close()
throws
IOException {
}
}
关于它的实现,它实现了一个Closeable(关闭)和flushable(刷新)
它一共就这么多方法

3.一般字节输出流的文件操作用FileOutputStream
public
class
OutputStreamDemo {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception{
//第一步,找到一个文件:
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
//第二步,通过字节流的子类来实例化
OutputStream out=
null
;
out=
new
FileOutputStream(f);
//第三步,进行读写操作
String str=
"hello world"
;
byte
b[]=str.getBytes();
out.write(b);
//第四步,关闭流
out.close();
}
}
补充:如果上面文件不存在,会自动创建
4.你反复的执行上面的程序,你会发现每一运行都会覆盖原来的内容,现在我想在后面继续写,那就要用它的另外的构造方法
public
class
OutputStreamDemo1 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception{
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
OutputStream out=
new
FileOutputStream(f,
true
);
String str=
"hello like"
;
byte
b[]=str.getBytes();
for
(
int
i=0;i<b.
length
;i++){
out.write(b[i]);
//这里用一个一个的写入,和上面的效果一样,看自己喜欢那个就用那个
}
out.close();
}
}
补充:如果需要换行:String str="\r\n hello like";
5.字节输入流
看源码:
public
abstract
class
InputStream
implements
Closeable {
由于方法比较多,就不全部列举了,自己可以去看下

6.字节出入流文件操作
public
class
InputStreamDemo {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
InputStream in=
new
FileInputStream(f);
byte
b[]=
new
byte
[1024];
in.read(b);
in.close();
System.
out
.println(
new
String(b));
}
}
结果:
hello worldhello
从结果中发现后面还有很多空格,这是因为,我们的byte[]数组大小1024,所以我们要做处理
public
class
InputStreamDemo1 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception{
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
FileInputStream in=
new
FileInputStream(f);
byte
b[]=
new
byte
[1024];
int
len=in.read(b);
in.close();
System.
out
.println(
"读入数据的长度:"
+len);
System.
out
.println(
"内容为"
+
new
String(b,0,len));
}
}
结果:
读入数据的长度:21
内容为hello worldhello like
以上虽然解决了,但是治标不治本,它还是开辟那么的空间,我们要做到需要好多就开辟好多
public
class
InputStreamDemo2 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception{
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
InputStream in=
new
FileInputStream(f);
byte
b[]=
new
byte
[(
int
)f.length()];
in.read(b);
in.close();
System.
out
.println(
new
String(b));
}
}
结果:
hello worldhello like
还可以用另外一种读取方法:
public
class
InputStreamDemo3 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
File f=
new
File(
"f:"
+File.
separator
+
"a.txt"
);
InputStream in=
new
FileInputStream(f);
byte
b[]=
new
byte
[1024];
int
temp=0;
int
len=0;
while
((temp=in.read())!=-1){//读到文件最后才会出现-1
b[len]=(
byte
)temp;
len++;
}
in.close();
System.
out
.println(
new
String(b, 0,len));
}
}
结果:
hello worldhello like





















 407
407











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








