AndFix不需要重启app即可实现bug修复,AndFix是“Android hot-fix”的缩写。
AndFix实现步骤:
1.通过注解的生成补丁包(.apatch)
2.通过获取.apatch中的补丁类,然后通过注解方式获取需要打补丁的方法。
3.补丁中的方法替换bug中的方法。
补丁包暂且不考虑,现在实现2、3步骤
获取补丁包中要替换的方法
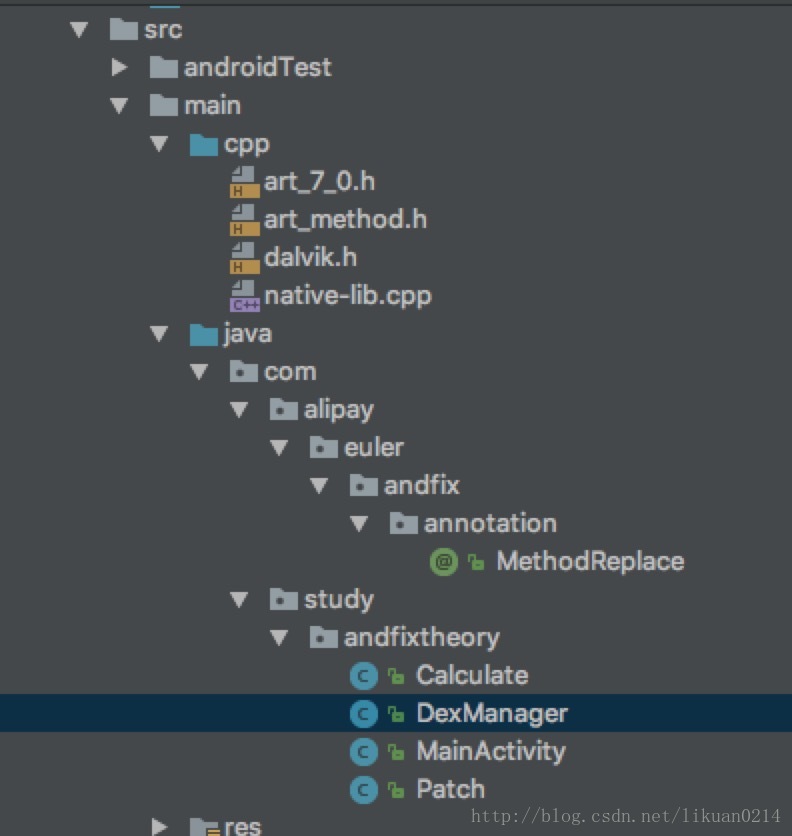
新建项目,项目最终结构如下:
注解方法MethdoReplace
package com.alipay.euler.andfix.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MethodReplace {
String clazz();
String method();
}
DexManager
package com.study.andfixtheory;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.Log;
import com.alipay.euler.andfix.annotation.MethodReplace;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import dalvik.system.DexFile;
/**
* Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
*/
public class DexManager {
private static volatile DexManager instance;
private Context context;
public static DexManager getInstance(){
if(instance == null){
synchronized (DexManager.class){
if(instance == null){
instance = new DexManager();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
private DexManager(){}
public void setContext(Context context){
this.context = context;
}
private static final String TAG = "DexManager";
public void loadFile(File file){
try{
//加载补丁中的dex文件到缓存目录
//public static DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName, int flags)
DexFile dexFile = DexFile.loadDex(file.getAbsolutePath(),
new File(context.getCacheDir(), "opt").getAbsolutePath(),
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
//遍历补丁中的类名
Enumeration<String> entry = dexFile.entries();
while (entry.hasMoreElements()){
//得到类名
String className = entry.nextElement();
//通过类名得到类的class
Class clazz = dexFile.loadClass(className, context.getClassLoader());
Log.i(TAG, "loadFile: className:" + className + " clazz:" + clazz);
if(clazz != null){
//修复
fixClass(clazz);
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void fixClass(Class rightClass) {
//得到补丁中的方法
Method[] methods = rightClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取补丁中的注解方法
MethodReplace replace = method.getAnnotation(MethodReplace.class);
if(replace == null)continue;
//得到bug的类名和方法名
String wrongClazzName=replace.clazz();
String wrongMethodName = replace.method();
try{
//通过类名,获取bug的类
Class wrongClazz = Class.forName(wrongClazzName);
//获取wrongMethod
Method wrongMethod = wrongClazz.getDeclaredMethod(wrongMethodName, method.getParameterTypes());
//新旧方法替换
//android 18以下是dalvik虚拟机 18以上是art虚拟机,需要区分处理
if(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= 18){
Log.i(TAG, "<= 18 fixClass: wrongMethod:" + wrongMethod + " rightMethod:" + method);
replaceDalvik(Build.VERSION.SDK_INT, wrongMethod, method);
}else {
Log.i(TAG, "> 18 fixClass: " + wrongMethod + " " + method);
replaceArt(Build.VERSION.PREVIEW_SDK_INT, wrongMethod, method);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private native void replaceDalvik(int sdk, Method wrongMethod, Method rightMethod);
private native void replaceArt(int sdk, Method wrongMethod, Method rightMethod);
}
Patch.java(为了获取方法的size)
package com.study.andfixtheory;
/**
* Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
*/
public class Patch {
final public static void f1(){};
final public static void f2(){};
}Calculate bug方法
package com.study.andfixtheory;
/**
* Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
*/
public class Calculate {
public int calculate(){
int i = 0;
int j = 10;
return j/i;
}
}MainActivity
package com.study.andfixtheory;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.File;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
private TextView tv;
private Button bt_cal;
private Button bt_fix;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
DexManager.getInstance().setContext(this);
// Example of a call to a native method
tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_result);
bt_cal = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_cal);
bt_fix = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_fix);
bt_cal.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int result = new Calculate().calculate();
tv.setText("结果:" + result);
}
});
bt_fix.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), "out.apatch");
DexManager.getInstance().loadFile(file);
}
});
}
}补丁方法替换bug方法
由于android 4.3以下是dalvik虚拟机,andorid4.4是dalvik + art虚拟机,android 5.0以上是art虚拟机。
所以需要对dalvik和art进行区分处理。
dalvik.h
//
// Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
//
#ifndef ANDFIXTHEORY_DALVIK_H
#define ANDFIXTHEORY_DALVIK_H
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
* Copyright (c) 2015, alipay.com
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
/*
* dalvik.h
*
*
* @author : sanping.li@alipay.com
*
*/
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdint.h> /* C99 */
typedef uint8_t u1;
typedef uint16_t u2;
typedef uint32_t u4;
typedef uint64_t u8;
typedef int8_t s1;
typedef int16_t s2;
typedef int32_t s4;
typedef int64_t s8;
/*
* access flags and masks; the "standard" ones are all <= 0x4000
*
* Note: There are related declarations in vm/oo/Object.h in the ClassFlags
* enum.
*/
enum {
ACC_PUBLIC = 0x00000001, // class, field, method, ic
ACC_PRIVATE = 0x00000002, // field, method, ic
ACC_PROTECTED = 0x00000004, // field, method, ic
ACC_STATIC = 0x00000008, // field, method, ic
ACC_FINAL = 0x00000010, // class, field, method, ic
ACC_SYNCHRONIZED = 0x00000020, // method (only allowed on natives)
ACC_SUPER = 0x00000020, // class (not used in Dalvik)
ACC_VOLATILE = 0x00000040, // field
ACC_BRIDGE = 0x00000040, // method (1.5)
ACC_TRANSIENT = 0x00000080, // field
ACC_VARARGS = 0x00000080, // method (1.5)
ACC_NATIVE = 0x00000100, // method
ACC_INTERFACE = 0x00000200, // class, ic
ACC_ABSTRACT = 0x00000400, // class, method, ic
ACC_STRICT = 0x00000800, // method
ACC_SYNTHETIC = 0x00001000, // field, method, ic
ACC_ANNOTATION = 0x00002000, // class, ic (1.5)
ACC_ENUM = 0x00004000, // class, field, ic (1.5)
ACC_CONSTRUCTOR = 0x00010000, // method (Dalvik only)
ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED = 0x00020000, // method (Dalvik only)
ACC_CLASS_MASK = (ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_FINAL | ACC_INTERFACE | ACC_ABSTRACT
| ACC_SYNTHETIC | ACC_ANNOTATION | ACC_ENUM),
ACC_INNER_CLASS_MASK = (ACC_CLASS_MASK | ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_PROTECTED
| ACC_STATIC),
ACC_FIELD_MASK = (ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_PROTECTED | ACC_STATIC
| ACC_FINAL | ACC_VOLATILE | ACC_TRANSIENT | ACC_SYNTHETIC
| ACC_ENUM),
ACC_METHOD_MASK = (ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_PROTECTED | ACC_STATIC
| ACC_FINAL | ACC_SYNCHRONIZED | ACC_BRIDGE | ACC_VARARGS
| ACC_NATIVE | ACC_ABSTRACT | ACC_STRICT | ACC_SYNTHETIC
| ACC_CONSTRUCTOR | ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED),
};
typedef struct DexProto {
u4* dexFile; /* file the idx refers to */
u4 protoIdx; /* index into proto_ids table of dexFile */
} DexProto;
typedef void (*DalvikBridgeFunc)(const u4* args, void* pResult,
const void* method, void* self);
struct Field {
void* clazz; /* class in which the field is declared */
const char* name;
const char* signature; /* e.g. "I", "[C", "Landroid/os/Debug;" */
u4 accessFlags;
};
struct Method;
struct ClassObject;
typedef struct Object {
/* ptr to class object */
struct ClassObject* clazz;
/*
* 类的加载过程
* A word containing either a "thin" lock or a "fat" monitor. See
* the comments in Sync.c for a description of its layout.
*/
u4 lock;
} Object;
struct InitiatingLoaderList {
/* a list of initiating loader Objects; grown and initialized on demand */
void** initiatingLoaders;
/* count of loaders in the above list */
int initiatingLoaderCount;
};
enum PrimitiveType {
PRIM_NOT = 0, /* value is a reference type, not a primitive type */
PRIM_VOID = 1,
PRIM_BOOLEAN = 2,
PRIM_BYTE = 3,
PRIM_SHORT = 4,
PRIM_CHAR = 5,
PRIM_INT = 6,
PRIM_LONG = 7,
PRIM_FLOAT = 8,
PRIM_DOUBLE = 9,
}typedef PrimitiveType;
enum ClassStatus {
CLASS_ERROR = -1,
CLASS_NOTREADY = 0, CLASS_IDX = 1, /* loaded, DEX idx in super or ifaces */
CLASS_LOADED = 2, /* DEX idx values resolved */
CLASS_RESOLVED = 3, /* part of linking */
CLASS_VERIFYING = 4, /* in the process of being verified */
CLASS_VERIFIED = 5, /* logically part of linking; done pre-init */
CLASS_INITIALIZING = 6, /* class init in progress */
CLASS_INITIALIZED = 7, /* ready to go */
}typedef ClassStatus;
typedef struct ClassObject {
struct Object o; // emulate C++ inheritance, Collin
/* leave space for instance data; we could access fields directly if we
freeze the definition of java/lang/Class */
u4 instanceData[4];
/* UTF-8 descriptor for the class; from constant pool, or on heap
if generated ("[C") */
const char* descriptor;
char* descriptorAlloc;
/* access flags; low 16 bits are defined by VM spec */
u4 accessFlags;
/* VM-unique class serial number, nonzero, set very early */
u4 serialNumber;
/* DexFile from which we came; needed to resolve constant pool entries */
/* (will be NULL for VM-generated, e.g. arrays and primitive classes) */
void* pDvmDex;
/* state of class initialization */
ClassStatus status;
/* if class verify fails, we must return same error on subsequent tries */
struct ClassObject* verifyErrorClass;
/* threadId, used to check for recursive <clinit> invocation */
u4 initThreadId;
/*
* Total object size; used when allocating storage on gc heap. (For
* interfaces and abstract classes this will be zero.)
*/
size_t objectSize;
/* arrays only: class object for base element, for instanceof/checkcast
(for String[][][], this will be String) */
struct ClassObject* elementClass;
/* arrays only: number of dimensions, e.g. int[][] is 2 */
int arrayDim;
PrimitiveType primitiveType;
/* superclass, or NULL if this is java.lang.Object */
struct ClassObject* super;
/* defining class loader, or NULL for the "bootstrap" system loader */
struct Object* classLoader;
struct InitiatingLoaderList initiatingLoaderList;
/* array of interfaces this class implements directly */
int interfaceCount;
struct ClassObject** interfaces;
/* static, private, and <init> methods */
int directMethodCount;
struct Method* directMethods;
/* virtual methods defined in this class; invoked through vtable */
int virtualMethodCount;
struct Method* virtualMethods;
/*
* Virtual method table (vtable), for use by "invoke-virtual". The
* vtable from the superclass is copied in, and virtual methods from
* our class either replace those from the super or are appended.
*/
int vtableCount;
struct Method** vtable;
} ClassObject;
typedef struct Method {
struct ClassObject *clazz;
u4 accessFlags;
//u2 methodIndex 方法表里面的索引
u2 methodIndex;
u2 registersSize; /* ins + locals */
u2 outsSize;
u2 insSize;
/* method name, e.g. "<init>" or "eatLunch" */
const char* name;
/*
* Method prototype descriptor string (return and argument types).
*
* TODO: This currently must specify the DexFile as well as the proto_ids
* index, because generated Proxy classes don't have a DexFile. We can
* remove the DexFile* and reduce the size of this struct if we generate
* a DEX for proxies.
*/
DexProto prototype;
/* short-form method descriptor string */
const char* shorty;
/*
* The remaining items are not used for abstract or native methods.
* (JNI is currently hijacking "insns" as a function pointer, set
* after the first call. For internal-native this stays null.)
*/
/* the actual code */
u2* insns;
/* cached JNI argument and return-type hints */
int jniArgInfo;
/*
* Native method ptr; could be actual function or a JNI bridge. We
* don't currently discriminate between DalvikBridgeFunc and
* DalvikNativeFunc; the former takes an argument superset (i.e. two
* extra args) which will be ignored. If necessary we can use
* insns==NULL to detect JNI bridge vs. internal native.
*/
DalvikBridgeFunc nativeFunc;
#ifdef WITH_PROFILER
bool inProfile;
#endif
#ifdef WITH_DEBUGGER
short debugBreakpointCount;
#endif
bool fastJni;
/*
* JNI: true if this method has no reference arguments. This lets the JNI
* bridge avoid scanning the shorty for direct pointers that need to be
* converted to local references.
*
* TODO: replace this with a list of indexes of the reference arguments.
*/
bool noRef;
} Method;
#endif //ANDFIXTHEORY_DALVIK_H
art_method.h
//
// Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
//
#ifndef ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_METHOD_H
#define ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_METHOD_H
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
* Copyright (c) 2015, alipay.com
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
/**
* art_5_1.h
*
* @author : sanping.li@alipay.com
*
*/
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdint.h> /* C99 */
typedef unsigned char u1;
typedef unsigned short u2;
typedef unsigned int u4;
typedef signed char s1;
typedef signed short s2;
typedef signed int s4;
namespace art {
namespace mirror {
class Object {
public:
// The number of vtable entries in java.lang.Object.
uint32_t klass_;
uint32_t monitor_;
};
class Class: public Object {
public:
// Interface method table size. Increasing this value reduces the chance of two interface methods
// colliding in the interface method table but increases the size of classes that implement
// (non-marker) interfaces.
// defining class loader, or NULL for the "bootstrap" system loader
uint32_t class_loader_;
// For array classes, the component class object for instanceof/checkcast
// (for String[][][], this will be String[][]). NULL for non-array classes.
uint32_t component_type_;
// DexCache of resolved constant pool entries (will be NULL for classes generated by the
// runtime such as arrays and primitive classes).
uint32_t dex_cache_;
// Short cuts to dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
uint32_t dex_cache_strings_;
// static, private, and <init> methods
uint32_t direct_methods_;
// instance fields
//
// These describe the layout of the contents of an Object.
// Note that only the fields directly declared by this class are
// listed in ifields; fields declared by a superclass are listed in
// the superclass's Class.ifields.
//
// All instance fields that refer to objects are guaranteed to be at
// the beginning of the field list. num_reference_instance_fields_
// specifies the number of reference fields.
uint32_t ifields_;
// The interface table (iftable_) contains pairs of a interface class and an array of the
// interface methods. There is one pair per interface supported by this class. That means one
// pair for each interface we support directly, indirectly via superclass, or indirectly via a
// superinterface. This will be null if neither we nor our superclass implement any interfaces.
//
// Why we need this: given "class Foo implements Face", declare "Face faceObj = new Foo()".
// Invoke faceObj.blah(), where "blah" is part of the Face interface. We can't easily use a
// single vtable.
//
// For every interface a concrete class implements, we create an array of the concrete vtable_
// methods for the methods in the interface.
uint32_t iftable_;
// Descriptor for the class such as "java.lang.Class" or "[C". Lazily initialized by ComputeName
uint32_t name_;
// Static fields
uint32_t sfields_;
// The superclass, or NULL if this is java.lang.Object, an interface or primitive type.
uint32_t super_class_;
// If class verify fails, we must return same error on subsequent tries.
uint32_t verify_error_class_;
// Virtual methods defined in this class; invoked through vtable.
uint32_t virtual_methods_;
// Virtual method table (vtable), for use by "invoke-virtual". The vtable from the superclass is
// copied in, and virtual methods from our class either replace those from the super or are
// appended. For abstract classes, methods may be created in the vtable that aren't in
// virtual_ methods_ for miranda methods.
uint32_t vtable_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by VM spec.
uint32_t access_flags_;
// Total size of the Class instance; used when allocating storage on gc heap.
// See also object_size_.
uint32_t class_size_;
// Tid used to check for recursive <clinit> invocation.
pid_t clinit_thread_id_;
// ClassDef index in dex file, -1 if no class definition such as an array.
// TODO: really 16bits
int32_t dex_class_def_idx_;
// Type index in dex file.
// TODO: really 16bits
int32_t dex_type_idx_;
// Number of instance fields that are object refs.
uint32_t num_reference_instance_fields_;
// Number of static fields that are object refs,
uint32_t num_reference_static_fields_;
// Total object size; used when allocating storage on gc heap.
// (For interfaces and abstract classes this will be zero.)
// See also class_size_.
uint32_t object_size_;
// Primitive type value, or Primitive::kPrimNot (0); set for generated primitive classes.
uint32_t primitive_type_;
// Bitmap of offsets of ifields.
uint32_t reference_instance_offsets_;
// Bitmap of offsets of sfields.
uint32_t reference_static_offsets_;
// State of class initialization.
int32_t status_;
// TODO: ?
// initiating class loader list
// NOTE: for classes with low serialNumber, these are unused, and the
// values are kept in a table in gDvm.
// InitiatingLoaderList initiating_loader_list_;
// The following data exist in real class objects.
// Embedded Imtable, for class object that's not an interface, fixed size.
// ImTableEntry embedded_imtable_[0];
// Embedded Vtable, for class object that's not an interface, variable size.
// VTableEntry embedded_vtable_[0];
// Static fields, variable size.
// uint32_t fields_[0];
// java.lang.Class
static void* java_lang_Class_;
};
class ArtField : public Object{
public:
uint32_t declaring_class_;
int32_t access_flags_;
int32_t field_dex_idx_;
int32_t offset_;
};
class ArtMethod: public Object {
public:
// Field order required by test "ValidateFieldOrderOfJavaCppUnionClasses".
// The class we are a part of. 适配andfix 不能做到这一改
uint32_t declaring_class_;
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access. dex
uint32_t dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
uint32_t dex_cache_resolved_types_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec.
uint32_t access_flags_;
/* Dex file fields. The defining dex file is available via declaring_class_->dex_cache_ */
// Offset to the CodeItem.
uint32_t dex_code_item_offset_;
// Index into method_ids of the dex file associated with this method.
uint32_t dex_method_index_;
/* End of dex file fields. */
// Entry within a dispatch table for this method. For static/direct methods the index is into
// the declaringClass.directMethods, for virtual methods the vtable and for interface methods the
// ifTable.
uint32_t method_index_;
// Fake padding field gets inserted here.
// Must be the last fields in the method.
struct PtrSizedFields {
// Method dispatch from the interpreter invokes this pointer which may cause a bridge into
// compiled code.java方法 ----》 虚拟机 ----》方法的入口 entry_point_from_interpreter_
//art 解释模式 机器码
void* entry_point_from_interpreter_;
// Pointer to JNI function registered to this method, or a function to resolve the JNI function.
void* entry_point_from_jni_;
// Method dispatch from quick compiled code invokes this pointer which may cause bridging into
// portable compiled code or the interpreter.
// 机器码模式
void* entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
} ptr_sized_fields_;
static void* java_lang_reflect_ArtMethod_;
};
}
}
#endif //ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_METHOD_H
art_7_0.h
//
// Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
//
#ifndef ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_7_0_H
#define ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_7_0_H
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
* Copyright (c) 2016, alipay.com
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
/**
* art_7_0.h
*
* @author : sanping.li@alipay.com
*
*/
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdint.h> /* C99 */
typedef unsigned char u1;
typedef unsigned short u2;
typedef unsigned int u4;
typedef signed char s1;
typedef signed short s2;
typedef signed int s4;
namespace art1 {
namespace mirror {
class Object {
public:
static uint32_t hash_code_seed;
uint32_t klass_;
uint32_t monitor_;
};
class Class: public Object {
public:
enum Status {
kStatusRetired = -2, // Retired, should not be used. Use the newly cloned one instead.
kStatusError = -1,
kStatusNotReady = 0,
kStatusIdx = 1, // Loaded, DEX idx in super_class_type_idx_ and interfaces_type_idx_.
kStatusLoaded = 2, // DEX idx values resolved.
kStatusResolving = 3, // Just cloned from temporary class object.
kStatusResolved = 4, // Part of linking.
kStatusVerifying = 5, // In the process of being verified.
kStatusRetryVerificationAtRuntime = 6, // Compile time verification failed, retry at runtime.
kStatusVerifyingAtRuntime = 7, // Retrying verification at runtime.
kStatusVerified = 8, // Logically part of linking; done pre-init.
kStatusInitializing = 9, // Class init in progress.
kStatusInitialized = 10, // Ready to go.
kStatusMax = 11,
};
// A magic value for reference_instance_offsets_. Ignore the bits and walk the super chain when
// this is the value.
// [This is an unlikely "natural" value, since it would be 30 non-ref instance fields followed by
// 2 ref instance fields.]
// Interface method table size. Increasing this value reduces the chance of two interface methods
// colliding in the interface method table but increases the size of classes that implement
// (non-marker) interfaces.
// 'Class' Object Fields
// Order governed by java field ordering. See art::ClassLinker::LinkFields.
uint32_t annotation_type_;
// Defining class loader, or null for the "bootstrap" system loader.
uint32_t class_loader_1;
// For array classes, the component class object for instanceof/checkcast
// (for String[][][], this will be String[][]). null for non-array classes.
uint32_t component_type_;
// DexCache of resolved constant pool entries (will be null for classes generated by the
// runtime such as arrays and primitive classes).
uint32_t dex_cache_;
// The interface table (iftable_) contains pairs of a interface class and an array of the
// interface methods. There is one pair per interface supported by this class. That means one
// pair for each interface we support directly, indirectly via superclass, or indirectly via a
// superinterface. This will be null if neither we nor our superclass implement any interfaces.
//
// Why we need this: given "class Foo implements Face", declare "Face faceObj = new Foo()".
// Invoke faceObj.blah(), where "blah" is part of the Face interface. We can't easily use a
// single vtable.
//
// For every interface a concrete class implements, we create an array of the concrete vtable_
// methods for the methods in the interface.
uint32_t iftable_;
// Descriptor for the class such as "java.lang.Class" or "[C". Lazily initialized by ComputeName
uint32_t name_;
// The superclass, or null if this is java.lang.Object or a primitive type.
//
// Note that interfaces have java.lang.Object as their
// superclass. This doesn't match the expectations in JNI
// GetSuperClass or java.lang.Class.getSuperClass() which need to
// check for interfaces and return null.
uint32_t super_class_;
// If class verify fails, we must return same error on subsequent tries. We may store either
// the class of the error, or an actual instance of Throwable here.
uint32_t verify_error_;
// Virtual method table (vtable), for use by "invoke-virtual". The vtable from the superclass is
// copied in, and virtual methods from our class either replace those from the super or are
// appended. For abstract classes, methods may be created in the vtable that aren't in
// virtual_ methods_ for miranda methods.
uint32_t vtable_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by VM spec.
// Note: Shuffled back.
uint32_t access_flags_;
// Short cuts to dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
uint64_t dex_cache_strings_;
// instance fields
//
// These describe the layout of the contents of an Object.
// Note that only the fields directly declared by this class are
// listed in ifields; fields declared by a superclass are listed in
// the superclass's Class.ifields.
//
// ArtFields are allocated as a length prefixed ArtField array, and not an array of pointers to
// ArtFields.
uint64_t ifields_;
// Pointer to an ArtMethod length-prefixed array. All the methods where this class is the place
// where they are logically defined. This includes all private, static, final and virtual methods
// as well as inherited default methods and miranda methods.
//
// The slice methods_ [0, virtual_methods_offset_) are the direct (static, private, init) methods
// declared by this class.
//
// The slice methods_ [virtual_methods_offset_, copied_methods_offset_) are the virtual methods
// declared by this class.
//
// The slice methods_ [copied_methods_offset_, |methods_|) are the methods that are copied from
// interfaces such as miranda or default methods. These are copied for resolution purposes as this
// class is where they are (logically) declared as far as the virtual dispatch is concerned.
//
// Note that this field is used by the native debugger as the unique identifier for the type.
uint64_t methods_;
// Static fields length-prefixed array.
uint64_t sfields_;
// Class flags to help speed up visiting object references.
uint32_t class_flags_;
// Total size of the Class instance; used when allocating storage on gc heap.
// See also object_size_.
uint32_t class_size_;
// Tid used to check for recursive <clinit> invocation.
pid_t clinit_thread_id_;
// ClassDef index in dex file, -1 if no class definition such as an array.
// TODO: really 16bits
int32_t dex_class_def_idx_;
// Type index in dex file.
// TODO: really 16bits
int32_t dex_type_idx_;
// Number of instance fields that are object refs.
uint32_t num_reference_instance_fields_;
// Number of static fields that are object refs,
uint32_t num_reference_static_fields_;
// Total object size; used when allocating storage on gc heap.
// (For interfaces and abstract classes this will be zero.)
// See also class_size_.
uint32_t object_size_;
// The lower 16 bits contains a Primitive::Type value. The upper 16
// bits contains the size shift of the primitive type.
uint32_t primitive_type_;
// Bitmap of offsets of ifields.
uint32_t reference_instance_offsets_;
// State of class initialization.
Status status_;
// The offset of the first virtual method that is copied from an interface. This includes miranda,
// default, and default-conflict methods. Having a hard limit of ((2 << 16) - 1) for methods
// defined on a single class is well established in Java so we will use only uint16_t's here.
uint16_t copied_methods_offset_;
// The offset of the first declared virtual methods in the methods_ array.
uint16_t virtual_methods_offset_;
// TODO: ?
// initiating class loader list
// NOTE: for classes with low serialNumber, these are unused, and the
// values are kept in a table in gDvm.
// InitiatingLoaderList initiating_loader_list_;
// The following data exist in real class objects.
// Embedded Imtable, for class object that's not an interface, fixed size.
// ImTableEntry embedded_imtable_[0];
// Embedded Vtable, for class object that's not an interface, variable size.
// VTableEntry embedded_vtable_[0];
// Static fields, variable size.
// uint32_t fields_[0];
// java.lang.Class
static uint32_t java_lang_Class_;
};
class ArtField {
public:
uint32_t declaring_class_;
uint32_t access_flags_;
uint32_t field_dex_idx_;
uint32_t offset_;
};
class ArtMethod {
public:
// Field order required by test "ValidateFieldOrderOfJavaCppUnionClasses".
// The class we are a part of.
uint32_t declaring_class_;
// Access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec.
uint32_t access_flags_;
/* Dex file fields. The defining dex file is available via declaring_class_->dex_cache_ */
// Offset to the CodeItem.
uint32_t dex_code_item_offset_;
// Index into method_ids of the dex file associated with this method.
uint32_t dex_method_index_;
/* End of dex file fields. */
// Entry within a dispatch table for this method. For static/direct methods the index is into
// the declaringClass.directMethods, for virtual methods the vtable and for interface methods the
// ifTable.
uint16_t method_index_;
// The hotness we measure for this method. Incremented by the interpreter. Not atomic, as we allow
// missing increments: if the method is hot, we will see it eventually.
uint16_t hotness_count_;
// Fake padding field gets inserted here.
// Must be the last fields in the method.
// PACKED(4) is necessary for the correctness of
// RoundUp(OFFSETOF_MEMBER(ArtMethod, ptr_sized_fields_), pointer_size).
struct PtrSizedFields {
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
ArtMethod** dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
// Short cuts to declaring_class_->dex_cache_ member for fast compiled code access.
void* dex_cache_resolved_types_;
// Pointer to JNI function registered to this method, or a function to resolve the JNI function,
// or the profiling data for non-native methods, or an ImtConflictTable.
void* entry_point_from_jni_;
// Method dispatch from quick compiled code invokes this pointer which may cause bridging into
// the interpreter.
void* entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
} ptr_sized_fields_;
};
}
}
#endif //ANDFIXTHEORY_ART_7_0_H
native-lib.cpp
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
#include "dalvik.h"
#include "art_method.h"
#include "art_7_0.h"
typedef Object *(*FindObject)(void *thread, jobject jobject1);
typedef void* (*FindThread)();
FindObject findObject;
FindThread findThread;
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_study_andfixtheory_DexManager_replaceDalvik(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jint sdk, jobject wrongMethod, jobject rightMethod) {
//找到虚拟机对应的method结构体
Method *wrong = (Method*)env->FromReflectedMethod(wrongMethod);
Method *right = (Method*)env->FromReflectedMethod(rightMethod);
void *dvm_hand = dlopen("libdvm.so", RTLD_NOW);
findObject = (FindObject) dlsym(dvm_hand, sdk > 10 ? "_Z20dvmDecodeIndirectRefP6ThreadP8_jobject" : "dvmDecodeIndirectRef");
findThread = (FindThread) dlsym(dvm_hand, sdk > 10 ? "_Z13dvmThreadSelfv" : "dvmThreadSelf");
//Method.getDeclaringClass();
jclass methodClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/reflect/Method");
jmethodID methodId = env->GetMethodID(methodClass, "getDeclaringClass", "()Ljava/lang/Class");
jobject ndkObject = env->CallObjectMethod(rightMethod, methodId);
ClassObject *firstField = (ClassObject *)findObject(findThread(), ndkObject);
firstField->status = CLASS_INITIALIZED;
wrong->accessFlags |= ACC_PUBLIC;
wrong->methodIndex = right->methodIndex;
wrong->jniArgInfo = right->jniArgInfo;
wrong->registersSize = right->registersSize;
wrong->outsSize = right->outsSize;
wrong->prototype = right->prototype;
wrong->insns = right->insns;
wrong->nativeFunc = right->nativeFunc;
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_study_andfixtheory_DexManager_replaceArt(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jint sdk, jobject wrongMethod, jobject rightMethod) {
if(sdk < 24){
art::mirror::ArtMethod *wrong = (art::mirror::ArtMethod *) env->FromReflectedMethod(wrongMethod);
art::mirror::ArtMethod *right = (art::mirror::ArtMethod *) env->FromReflectedMethod(rightMethod);
jclass jcls = env->FindClass("com/study/andfixtheory/Patch");
size_t firMid = (size_t)env->GetStaticMethodID(jcls, "f1", "()V");
size_t secMid = (size_t)env->GetStaticMethodID(jcls, "f2", "()V");
int size = secMid - firMid;
memcpy(wrong, right, size);
} else{
//andorid 7.0适配
art1::mirror::ArtMethod *wrong = (art1::mirror::ArtMethod *) env->FromReflectedMethod(wrongMethod);
art1::mirror::ArtMethod *right = (art1::mirror::ArtMethod *) env->FromReflectedMethod(rightMethod);
jclass jcls = env->FindClass("com/study/andfixtheory/Patch");
size_t firMid = (size_t)env->GetStaticMethodID(jcls, "f1", "()V");
size_t secMid = (size_t)env->GetStaticMethodID(jcls, "f2", "()V");
int size = secMid - firMid;
memcpy(wrong, right, size);
}
// wrong->declaring_class_=right->declaring_class_;
//
// wrong->dex_code_item_offset_=right->dex_code_item_offset_;
// wrong->method_index_=right->method_index_;
// wrong->dex_method_index_=right->dex_method_index_;
//
//
入口
// wrong->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_=right->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_;
// // 机器码模式
// wrong->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_=right->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
//
不一样
// wrong->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_=right->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_;
// wrong->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_methods_=right->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
// wrong->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_types_=right->ptr_sized_fields_.dex_cache_resolved_types_;
// wrong->hotness_count_=right->hotness_count_;
}生成补丁包
1.在AndFix中下载apkpatch工具,解压
2.生成bug包old.apk和修复后的new.apk
修复后代码:
package com.study.andfixtheory;
/**
* Created by ygdx_lk on 17/12/1.
*/
public class Calculate {
public int calculate(){
int i = 1;
int j = 10;
return j/i;
}
}
3.使用apkpatch工具生成补丁out.apatch
使用介绍:
usage: apkpatch -f <new> -t <old> -o <output> -k <keystore> -p <***> -a <alias> -e <***>
-a,--alias <alias> keystore entry alias.
-e,--epassword <***> keystore entry password.
-f,--from <loc> new Apk file path.
-k,--keystore <loc> keystore path.
-n,--name <name> patch name.
-o,--out <dir> output dir.
-p,--kpassword <***> keystore password.
-t,--to <loc> old Apk file path.将old.apk、new.apk和签名key,拷贝到apkpatch目录下,执行下面命令
./apkpatch.sh -f new.apk -t old.apk -o out -k key -p test123 -a test -e test123生成补丁包:
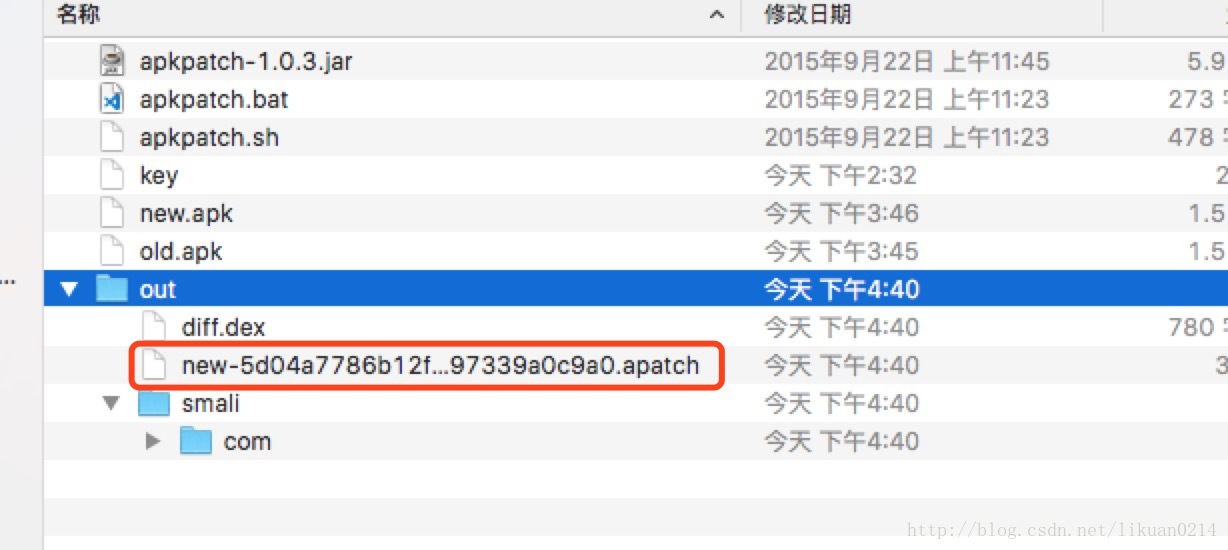
改名为:out.apatch,并移动到apkpatch目录下
4.安装old.apk到手机
adb install old.apk5.拷贝out.apatch到手机sd卡目录
adb push out.apatch /sdcard6.打开手机
不修复的情况下,点击运算(崩溃)
调用修复方法,点击运算,没有发生崩溃,说明bug已修复。






















 2919
2919

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








