4 图中的路径
4.1 距离
两顶点距离 指两者间最短路径的长度
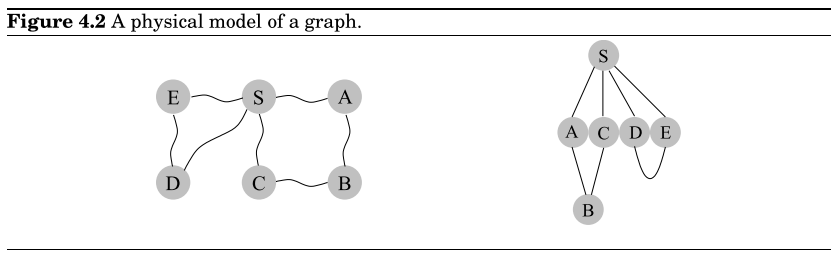
将边 看作绳子,把源点提起,即可得到源点到各点的最短距离
4.2 广度优先搜索
procedure BFS(G,s)
Input: Graph G = (V,E),directed or undirected;vertex s ∈ V
Output: For all vertices u reachable from s,dist(u) is set
to the distance from s to u.
for all u ∈ V:
dist(u)= ∞
dist(s)=0
Q=[s] //queue containing just s
while Q is not empty:
u=eject(Q)
for all edges (u,v) ∈ E
if dist(v)= ∞
inject(Q,v)
dist(v)=dist(u)+14.3 边的长度
Annotate every edge e∈E with a length le . If e=(u,v) , we will sometimes also write l(u,v) or luv .
4.4 Dijkstra算法
4.4.1 广度优先搜索的一个改进
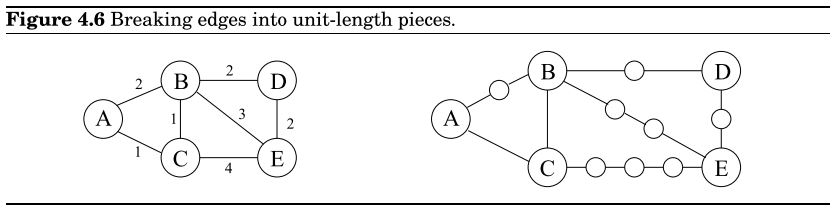
当 边长e=(u,v) 为整数时,在u和v之间增加 le−1 个顶点,再运行BFS即可计算G中的距离。
闹钟算法
在时刻0为顶点s设定一个闹钟
重复以下直到没有闹钟为止:
假定针对顶点u的下一个闹钟闹铃的时刻为T,则:
- 从s到u的距离是T。
- 对于G中u的每个邻居v:
- 如果还未给v设定闹钟,则为其设定闹钟时刻 T+l(u,v)
- 如果v的闹钟时刻设定的比 T+l(u,v) 要晚,则将它设定为 T+l(u,v)
Dijkstra算法
procedure dijkstra(G,l,s)
Input: Graph G=(V,E), directed or undirected;
positive edge lengths {le:e ∈ E};
vertex s ∈ V
Output: For all vertices u reachable from s,dist(u) is set
to the distance from s to u.
for all u ∈ V
dist(u) = ∞
prev(u) = nil
dist(s)=0
H=makequeue(V) //using dist-valus as keys
while H is not empty:
u=deletemin(H)
for all edges (u,v) ∈ E:
if dist(v) > dist(u)+l(u,v):
dist(v)=dist(u)+l(u,v)
prev(v)=u
decreasekey(H,v)4.4.2 另一种解释
procedure dijkstra(G,l,s)
Input: Graph G=(V,E), directed or undirected;
positive edge lengths {le:e ∈ E};
vertex s ∈ V
Output: For all vertices u reachable from s,dist(u) is set
to the distance from s to u.
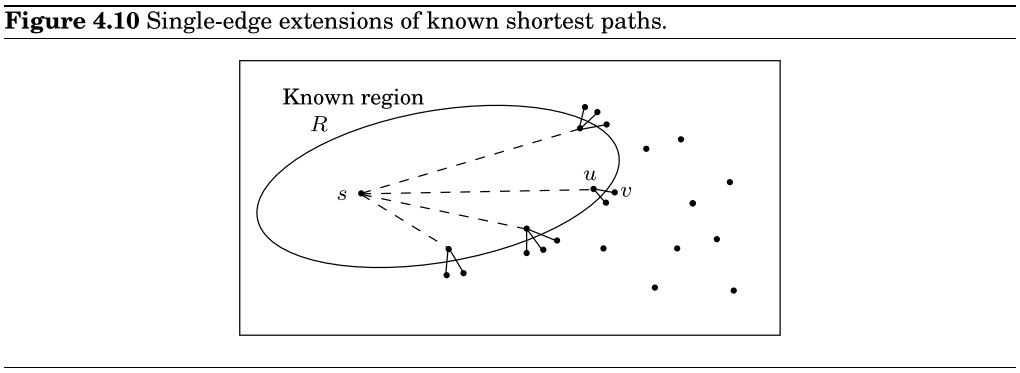
Initialize dist(s) to 0,other dist(·) to ∞
R={} //the "known regions"
while R ≠ V:
Pick the node v ∉ R with smallest dist(·)
Add v to R
for all edges (v,z) ∈ E:
if dist(z) > dist(v)+l(v,z)
dist(z)=dist(v)+l(v,z)4.4.3 运行时间
Dijkstra算法结构与BFS相同,一共需要 |V| 次deletemin(H),和 |V|+|E| 次decreasekey(H,v);如采用二分堆数据结构实现优先队列,则最优边复杂度为 O(log|V|) ;则算法复杂度为 O((|V|+|E|)log|V|) 。
4.5 优先队列的实现
| 实现方式 | deletemin(H) | decreasekey(H,v) | |V|*del+(|V|+|E|)*decrease |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数组 | O(∥V∥) | O(1) | O(∥V∥2) |
| 二分堆 | O(log∥V∥) | O(log∥V∥) | O((∥V∥+∥E∥)log∥V∥) |
| d堆 | O(d log∥V∥logd) | O(log∥V∥log d) | O((∥V∥ d+∥E∥)log∥V∥logd) |
| Fibonacci堆 | O(log∥V∥) | O(1) (平摊后) | O(∥V∥log∥V∥+∥E∥) |
4.6 含有负边的图的最短路径
4.6.1 负边
Bellman-Ford算法 :更新所有的边,每条边更新 |V|−1 次。复杂度 O(|V|∗|E|) 。
procedure shortest-paths(G,l,s)
Input: Graph G=(V,E), directed;
edge lengths {le:e ∈ E} with no negative cycles;
vertex s ∈ V
Output: For all vertices u reachable from s,dist(u) is set
to the distance from s to u.
for all u ∈ V
dist(u)= ∞
prev(u)= nil
dist(s)=0
repeat |V|-1 times:
for all e ∈ E:
update(e)4.6.2 负环
图中一旦出现负环,讨论最短路径没有意义。一旦检测到负环,就要适时地发出警告。
图中存在 负环,当且仅当第|V|次迭代中有某个dist的值被减小。
4.7 有向无环图的最短路径
不存在负环的图:
- 不含 负边 的图
- 不含 环 的图(dag)
procedure dag-shortest-paths(G,l,s)
Input: Graph G=(V,E), dag;
edge lengths {le:e ∈ E};
vertex s ∈ V
Output: For all vertices u reachable from s,dist(u) is set
to the distance from s to u.
for all u ∈ V
dist(u)= ∞
prev(u)= nil
dist(s)=0
Linearize G //通过深度优先搜索线性化(拓扑排序)
for each u ∈ V in Linearized order:
for all edges (u,v) ∈ E:
update(u,v)





















 1319
1319

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








