项目要求
实现Time类中的运算符重载。(关于时刻的加减乘除)
class CTime
{
private:
unsigned short int hour; // 时
unsigned short int minute; // 分
unsigned short int second; // 秒
public:
CTime(int h=0,int m=0,int s=0);
void setTime(int h,int m,int s);
void display();
//二目的比较运算符重载
bool operator > (CTime &t);
bool operator < (CTime &t);
bool operator >= (CTime &t);
bool operator <= (CTime &t);
bool operator == (CTime &t);
bool operator != (CTime &t);
//二目的加减运算符的重载
//返回t规定的时、分、秒后的时间
//例t1(8,20,25),t2(11,20,50),t1+t2为19:41:15
CTime operator+(CTime &t);
CTime operator-(CTime &t);//对照+理解
CTime operator+(int s);//返回s秒后的时间
CTime operator-(int s);//返回s秒前的时间
//二目赋值运算符的重载
CTime operator+=(CTime &c);
CTime operator-=(CTime &c);
CTime operator+=(int s);//返回s秒后的时间
CTime operator-=(int s);//返回s秒前的时间
};提示1:并不是所有比较运算重载函数都很复杂
//比较运算返回的是比较结果,是bool型的true或false
//可以直接使用已经重载了的运算实现新运算,例如果已经实现了 > ,则实现 <= 就可以很方便了……
bool CTime::operator <= (CTime &t) // 判断时间t1<=t2
{
if (*this > t) return false;
return true;
}
甚至可以如下面的代码般简练:
bool CTime::operator <= (CTime &t)
{
return !(*this > t)
}提示2:并不是所有复合赋值运算重载函数都需要很复杂
//可以直接使用已经重载了的加减运算实现
//这种赋值, 例如 t1+=20,直接改变当前对象的值,所以在运算完成后,将*this作为返回值
CTime CTime::operator+=(CTime &c)
{
*this=*this+c;
return *this;
}提示3:请自行编制用于测试的main()函数,有些结果不必依赖display()函数,提倡用单步执行查看结果
代码如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CTime
{
private:
unsigned short int hour; // 时
unsigned short int minute; // 分
unsigned short int second; // 秒
public:
CTime(int h=0,int m=0,int s=0);
void setTime(int h,int m,int s);
void display();
//二目的比较运算符重载
bool operator > (CTime &t);
bool operator < (CTime &t);
bool operator >= (CTime &t);
bool operator <= (CTime &t);
bool operator == (CTime &t);
bool operator != (CTime &t);
//二目的加减运算符的重载
//返回t规定的时、分、秒后的时间
//例t1(8,20,25),t2(11,20,50),t1+t2为19:41:15
CTime operator+(CTime &t);
CTime operator-(CTime &t);//对照+理解
CTime operator+(int s);//返回s秒后的时间
CTime operator-(int s);//返回s秒前的时间
//二目赋值运算符的重载
CTime operator+=(CTime &c);
CTime operator-=(CTime &c);
CTime operator+=(int s);//返回s秒后的时间
CTime operator-=(int s);//返回s秒前的时间
};
//
CTime::CTime(int h,int m,int s)
{
hour=h;
minute=m;
second=s;
return;
}
void CTime::setTime(int h,int m,int s)
{
hour=h;
minute=m;
second=s;
return;
}
void CTime::display()
{
cout<<hour<<": "<<minute<<": "<<second<<endl;
return;
}
//
bool CTime::operator > (CTime &t)
{
if (hour>t.hour)return true;
if (hour<t.hour)return false;
if (minute>t.minute)return true;
if (minute<t.minute)return false;
if (second>t.second)return true;
if (second<t.second)return false;
}
bool CTime::operator < (CTime &t)
{
if (hour<t.hour)return true;
if (hour>t.hour)return false;
if (minute<t.minute)return true;
if (minute>t.minute)return false;
if (second<t.second)return true;
if (second>t.second)return false;
}
bool CTime::operator >= (CTime &t)
{
if (*this<t)return false;
else return true;
}
bool CTime::operator <= (CTime &t)
{
if (*this>t)return false;
else return true;
}
bool CTime::operator == (CTime &t)
{
if (*this<t||*this>t)return false;
else return true;
}
bool CTime::operator != (CTime &t)
{
if (*this==t)return false;
else return true;
}
//
CTime CTime::operator+(CTime &t)
{
int h,m,s;
h=hour+t.hour;
m=minute+t.minute;
s=second+t.second;
if (s>59)
{
m++;
s-=60;//(莫忘了这一步)
}
if (m>59)
{
h++;
m-=60;
}
if (h>23)
{
h-=24;
}
CTime t1(h,m,s);//注意不能写成 hour=h;minute=m;second=s; 应不改变原值
return t1;
}
CTime CTime::operator-(CTime &t)
{
int h,m,s;
h=hour-t.hour;
m=minute-t.minute;
s=second-t.second;
if (s<0)
{
m--;
s+=60;//莫忘了这一步
}
if (m<0)
{
h--;
m+=60;
}
if (h<0)
{
h+=24;
}
CTime t1(h,m,s);//注意不能写成 hour=h;minute=m;second=s; 应不改变原值
return t1;
}
CTime CTime::operator+(int s)
{
int ss=s%60, mm=(s/60)%60, hh=s/3600;
CTime t(hh,mm,ss);
return *this+t;
/*之前用的下面这段,有点复杂了,而且减法不好处理
int ss=second+s,mm=minute,hh=hour;
if (ss>59)
{
mm+=ss/60;
ss%=60;
}
if (mm>59)
{
hh+=mm/60;
mm%=60;
}
if (hh>23)
{
hh%=24;
}
CTime t1(hh,mm,ss);
return t1;
*/
}
CTime CTime::operator-(int s)
{
int ss=s%60, mm=(s/60)%60, hh=s/3600;
CTime t(hh,mm,ss);
return *this-t;
}
//
CTime CTime::operator+=(CTime &c)
{
*this=*this+c;
return *this;
}
CTime CTime::operator-=(CTime &c)
{
*this=*this-c;
return *this;
}
CTime CTime::operator+=(int s)
{
*this=*this+s;
return *this;
}
CTime CTime::operator-=(int s)
{
*this=*this-s;
return *this;
}
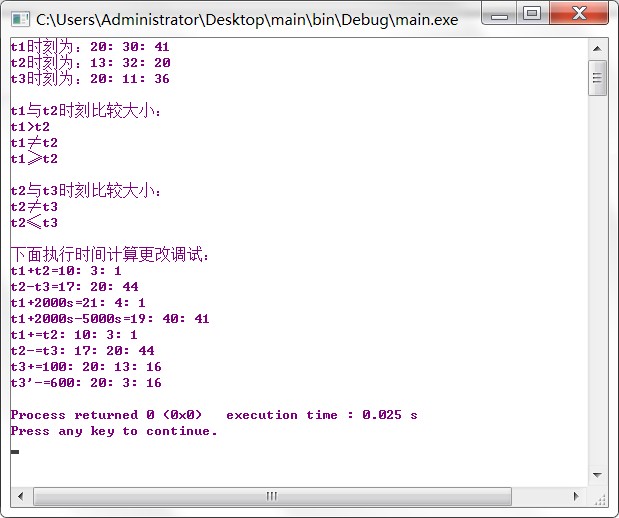
int main()
{
CTime t1(20,30,41),t2(13,32,20),t3(20,11,36),tt1,tt2,tt3;
cout<<"t1时刻为:";
t1.display();
cout<<"t2时刻为:";
t2.display();
cout<<"t3时刻为:";
t3.display();
cout<<endl;
//
cout<<"t1与t2时刻比较大小:"<<endl;
if (t1>t2)
cout<<"t1>t2"<<endl;
if (t1<t2)
cout<<"t1<t2"<<endl;
if (t1==t2)
cout<<"t1=t2"<<endl;
if (t1!=t2)
cout<<"t1≠t2"<<endl;
if (t1>=t2)
cout<<"t1≥t2"<<endl;
if (t1<=t2)
cout<<"t1≤t2"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
//
cout<<"t2与t3时刻比较大小:"<<endl;
if (t2>t3)
cout<<"t2>t3"<<endl;
if (t1<t3)
cout<<"t2<t3"<<endl;
if (t2==t3)
cout<<"t2=t3"<<endl;
if (t2!=t3)
cout<<"t2≠t3"<<endl;
if (t2>=t3)
cout<<"t2≥t3"<<endl;
if (t2<=t3)
cout<<"t2≤t3"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
//在测试下面的代码时,请采用单步执行的方法跟踪
cout<<"下面执行时间计算更改调试:"<<endl;
cout<<"t1+t2=";
tt1=t1+t2;
tt1.display();
cout<<"t2-t3=";
tt2=t2-t3;
tt2.display();
cout<<"t1+2000s=";
tt3=t1+2000;
tt3.display();
cout<<"t1+2000s-5000s=";
tt3=tt3-5000;
tt3.display();
cout<<"t1+=t2: ";
t1+=t2;
t1.display();
cout<<"t2-=t3: ";
t2-=t3;
t2.display();
cout<<"t3+=100: ";
t3+=100;
t3.display();
cout<<"t3'-=600: ";
t3-=600;
t3.display();
return 0;
}
运行结果
学习心得
贺老的提示很值得学习。






















 240
240

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








