工厂模式:
- 实现了创建者和调用者的分离,实例化对象,用工厂方法代替new操作。将选择实现类、创建对象统一管理和控制。从而将调用者跟我们的实现类解耦。
- 详细分类:
1、简单工厂模式
用来生产同一等级结构中的任意产品。(对于增加新的产品,需要修改已有的代码)
2、工厂方法模式
用来生产同一等级结构中的固定产品。(支持增加任意产品)
3、抽象工厂模式
用来生产不同产品族的全部产品。(对于增加新的产品,无能为力;支持增加产品族)
一、简单工厂模式的实现
要点:
1、简单工厂模式也叫静态工厂模式,就是工厂类一般是使用静态方法,通过接收的参数的不同来返回不同的对象实例。
2、对于增加新产品无能为力(必须需要工厂方法)!不修改代码的话,是无法扩展的。
public interface Car {
void run();
}
public class Audi implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("奥迪在跑!");
}
}
public class Benz implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("奔驰在跑!");
}
}
public class CarSimpleFactory {
public static Car createCar(String type) {
if("奥迪".equals(type)){
return new Audi();
}else if("奔驰".equals(type)){
return new Benz();
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* 简单工厂模式下,调用者只需跟工厂打交道生产对象,而不需要跟具体实现类打交道
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Client {//调用者
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c1 = CarSimpleFactory.createCar("奥迪");
Car c2 = CarSimpleFactory.createCar("奔驰");
c1.run();
c2.run();
}
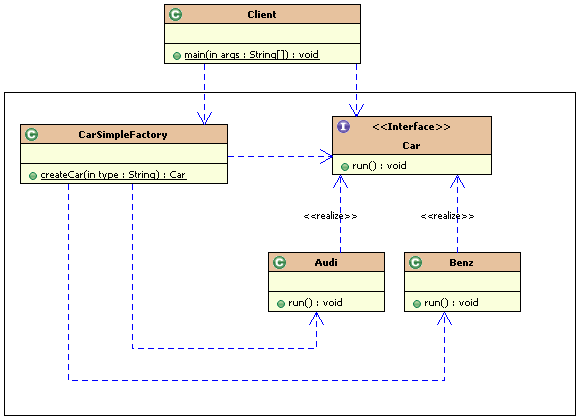
}简单工厂模式的类图如下:
二、工厂方法模式的实现
要点:
1、工厂方法模式和简单工厂模式的不同在于,简单工厂模式只有一个工厂类,而工厂方法模式有一组实现了相同接口的工厂类。
public interface Car {
void run();
}
public interface CarFactory {
Car createCar();
}
public class Audi implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("奥迪在跑!");
}
}
public class AudiFactory implements CarFactory{
public Car createCar() {
return new Audi();
}
}
public class Benz implements Car{
public void run() {
System.out.println("奔驰在跑!");
}
}
public class BenzFactory implements CarFactory{
public Car createCar() {
return new Benz();
}
}
/**
* 工厂方法模式测试
*/
public class Client {//调用者
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c1 = new AudiFactory().createCar();
Car c2 = new BenzFactory().createCar();
c1.run();
c2.run();
}
}
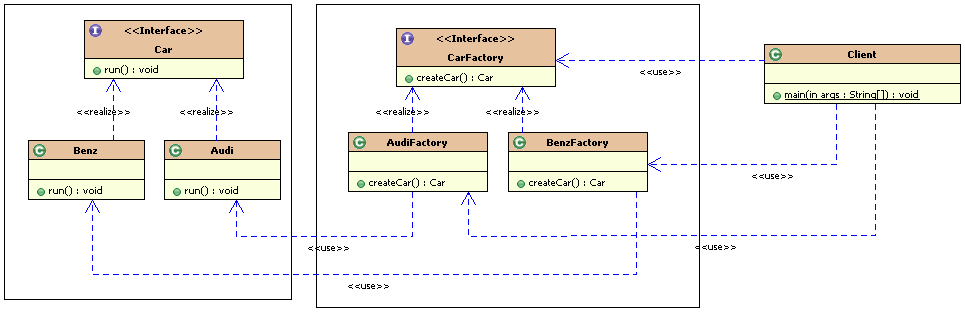
工厂方法模式的类图如下:
三、抽象工厂模式的实现
用来生产不同产品族的全部产品。
抽象工厂模式是工厂方法模式的升级版本,在有多个业务品种、业务分类时,通过抽象工厂模式生产需要的对象是一种非常好的解决方式。
/**
* 发动机
*/
public interface Engine {
void run();
void start();
}
/**
* 高端发动机
*/
class LuxuryEngine implements Engine{
public void run() {
System.out.println("转得快!");
}
public void start() {
System.out.println("启动快!");
}
}
/**
* 低端发动机
*/
class LowEngine implements Engine{
public void run() {
System.out.println("转得慢!");
}
public void start() {
System.out.println("启动慢!");
}
}
public interface Seat {
//材质
void material();
}
/**
* 高端座椅
*/
class LuxurySeat implements Seat{
public void material() {
System.out.println("真皮座椅!");
}
}
/**
* 低端座椅
*/
class LowSeat implements Seat{
public void material() {
System.out.println("绒布座椅!");
}
}
public interface Tyre {
//摩擦性能
void friction();
}
/**
* 高端轮胎
*/
class LuxuryTyre implements Tyre{
public void friction() {
System.out.println("耐摩损,耐热性能高,较好的缓冲!");
}
}
/**
* 低端轮胎
*/
class LowTyre implements Tyre{
public void friction() {
System.out.println("不耐摩,易爆胎!");
}
}
public interface CarFactory {
Engine createEngine();
Seat createSea();
Tyre createTyre();
}
/**
* 低端汽车
*/
public class LowCarFactory implements CarFactory{
public Engine createEngine() {
return new LowEngine();
}
public Seat createSea() {
return new LowSeat();
}
public Tyre createTyre() {
return new LowTyre();
}
}
/**
* 高端汽车
*/
public class LuxuryCarFactory implements CarFactory{
public Engine createEngine() {
return new LuxuryEngine();
}
public Seat createSea() {
return new LuxurySeat();
}
public Tyre createTyre() {
return new LuxuryTyre();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CarFactory factory = new LuxuryCarFactory();
factory.createEngine();
factory.createSea();
factory.createTyre();
}
}























 525
525

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








