一、背景
BEV方案中,将图像视角转换到BEV视角的方法对模型性能影响较大,FastBEV的速度较快,但投影效果上限不高,LSS投影上限较高,但速度较慢 (耗时相对较高)。是否有折中的方案,在耗时增加相对较少的情况下,提升模型的上限(中高算力平台下,提升模型能力)?
二、视角转换关键算子-----gridsample
这是pytorch官网对gridsample算子使用方法说明,其支持4-D(FastBEV/IMP)和5-D(LSS)采样,将图像特征提取到对应的BEV特征中,完成相机视角转换:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.grid_sample.html

5-D gridsample相比4-D gridsample耗时剧增,假如在某智驾芯片上,4-D gridsample耗时是2ms,相同条件下5-D gridsample的耗时可能是200ms(具体耗时受特征图通道数影响),这种耗时急剧上升的方案,很难在智驾中落地应用。
三、LSS投影优化
1.先来对比4-D gridsample和5-D gridsample的输入输出关系:
4-D gridsample
input: (N, C, H_in, W_in);
bev_grid: (N, H_out, W_out, 2), 这里的2表示bev_grid坐标通过相机内外参投影到图像上的坐标(x,y);
output: (N, C, H_out, W_out)
5-D gridsample
input: (N, C, H_in, W_in);
LSS官方代码构建深度特征的方法:https://github.com/nv-tlabs/lift-splat-shoot/blob/master/src/models.py
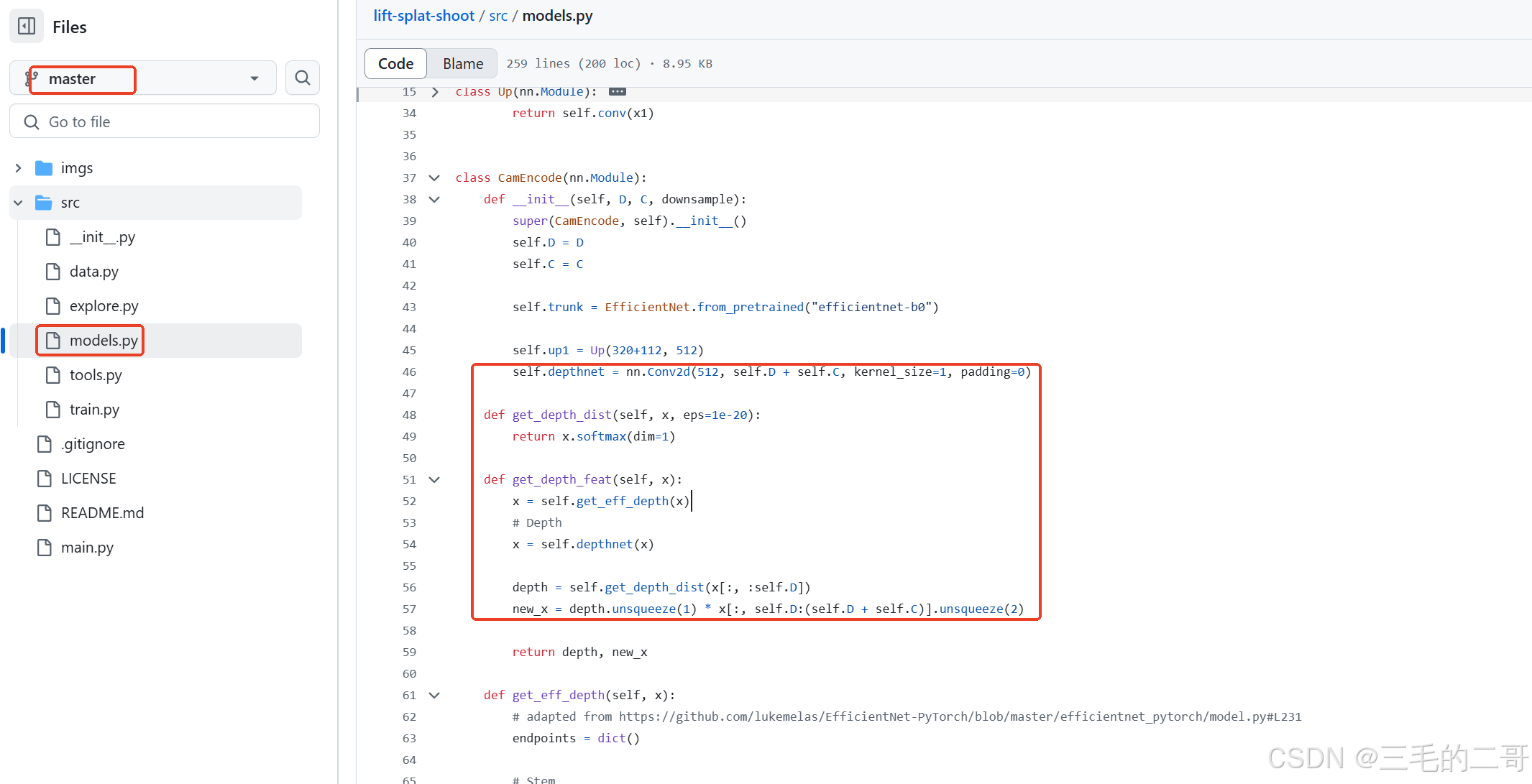
通过1x1卷积将C通道的输入特征变为C+D通道(这里的D表示深度估计的通道数),并对深度特征中的D通道特征进行softmax处理input_i:(N, D, H_in, W_in),按照dim=1堆叠起来得到input_i_1:(N, 1,D, H_in, W_in),然后将原始的(N, C, H_in, W_in)特征按照dim=2堆叠起来得到input_i_2:(N, C, 1,H_in, W_in),最后将input_i_1*input_i_2深度输入input_2:(N, C, D, H_in, W_in);
bev_grid: (N, Z_out, H_out, W_out, 3), 这里的3表示bev_grid坐标通过相机内外参投影到图像上的坐标(x,y,d), d为深度估计;
output: (N, C, Z_out, H_out, W_out);
由于获取深度信息需要用到5-D gridsample,想要降低耗时,考虑减少特征图通道对耗时的影响,即做5-D gridsample时,将通道C设为1;
2.具体方法-----拆解5-D gridsample
在得到深度输入input_2前,先对input_i_1和input_i_2进行gridsample,再将gridsample后的结果相乘得最终的投影结果。具体方法为:将5-D gridsample拆解为一个4-D gridsample和一个单通道(C=1)的5-D gridsample,4-D gridsample负责提取多通道特征信息,单通道5-D gridsample负责提取深度特征信息,最后将两个特征信息相乘,得到多通道下的深度信息,等效变换过程如下:
step1:
4-D gridsample
input: (N, C, H_in, W_in);
bev_grid: (N, Z_out, H_out, W_out, 2), 这里的2表示bev_grid坐标通过相机内外参投影到图像上的坐标(x,y);
for循环提取每个Z_out下的bev_grid_i: (N, Z_out, H_out, W_out, 2),通过4-D gridsample分别得到输出特征图output_i: (N, C, H_out, W_out),按照dim=2堆叠起来,得到最终的BEV特征图output_1(没有深度概率信息):
output_1: (N, C, Z_out, H_out, W_out)
step2:
单通道5-D gridsample
input: (N, C, H_in, W_in);
input经过softmax处理后的特征图input_2: (N, D, H_in, W_in),这里的D表示深度估计的通道数;将input_2在dim=1上扩展一个维度,得到input_3:(N, 1, D, H_in, W_in)
bev_grid: (N, Z_out, H_out, W_out, 3), 这里的3表示bev_grid坐标通过相机内外参投影到图像上的坐标(x,y,d), d为深度估计;
output_2: (N, 1, Z_out, H_out, W_out);
step3:
将output_1和output_2相乘得到有深度概率信息的BEV特征图
output = outptu_1 * output_2 = (N, C, Z_out, H_out, W_out) * (N, 1, Z_out, H_out, W_out) = (N, C, Z_out, H_out, W_out)
四、部分代码
1.IPM的BEV网格坐标索引
class UpdateIndicesIPM:
def __init__(self, height, range, voxel_size, feature_size, downsample):
self.height = height
self.range = range
self.voxel_size = voxel_size
self.feature_size = feature_size
self.ds_matrix = np.eye(4)
self.ds_matrix[:2] /= downsample
def __call__(self, data):
num = len(data["cam2egoes"])
ego2feats = torch.zeros((num, 4, 4), dtype=torch.float32)
for i in range(num):
ego2cam = np.linalg.inv(data["cam2egoes"][i])
tmp = np.eye(4)
tmp[:3, :3] = data["cam_intrinsics"][i]
ego2feats[i] = torch.tensor(self.ds_matrix @ tmp @ ego2cam)
grid = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([
torch.arange(self.range[0], self.range[3], self.voxel_size[0]),
torch.arange(self.range[1], self.range[4], self.voxel_size[1]),
torch.tensor(self.height), torch.tensor(1.0)
], indexing="ij")) # [4, 188, 64, 4, 1]
grid_h, grid_w = grid.shape[1:3]
grid = grid.view(1, 4, -1).expand(num, 4, -1) # [7, 4, 192512]
points_2d = torch.bmm(ego2feats[:, :3, :], grid)
x = (points_2d[:, 0] / points_2d[:, 2]).round().long()
y = (points_2d[:, 1] / points_2d[:, 2]).round().long()
z = points_2d[:, 2]
valid = ~((x >= 0) & (y >= 0) & (x < self.feature_size[1]) &
(y < self.feature_size[0]) & (z > 0))
x[valid] = 0
y[valid] = 0
x = (x.float() / self.feature_size[1] * 2.) - 1.0
y = (y.float() / self.feature_size[0] * 2.) - 1.0
indices = torch.cat([x.unsqueeze(2), y.unsqueeze(2)], dim=2)
indices = indices.reshape(-1, grid_h, grid_w, len(self.height), 2) # batch, num_img, bev_w, bev_h, num_height, 2
data["indices"] = indices
return data
2.FastBEV
class FastBevTransform(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feats_channels, num_height):
super().__init__()
self._num_height = num_height
self._conv = nn.Conv2d(feats_channels * num_height, feats_channels, kernel_size=1)
self._grid_sample = GridSample(mode="nearest",
padding_mode="zeros",
align_corners=True)
self._cat = Concat(dim=1)
def forward(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (7B, C, H, W), indices: (7B, Hg, Wg, Z, 2)
bev_feats = []
for i in range(self._num_height):
output = self._grid_sample(feats, indices[:,:,:,i])
bev_feats.append(output)
bev_feats = self._cat(bev_feats) # (7B, Z*C, Hg, Wg)
bev_feats = self._conv(bev_feats) # (7B, C, Hg, Wg)
return bev_feats
3.LSS的BEV网格坐标索引
class UpdateIndicesLSS:
def __init__(self, height, range, voxel_size, feature_size,
resolution, max_num_depth, downsample):
self.height = height
self.range = range
self.voxel_size = voxel_size
self.feature_size = feature_size
self.resolution = resolution
self.max_num_depth = max_num_depth
self.ds = np.eye(3)
self.ds[:2] /= downsample
def __call__(self, data):
num = len(data["cam2egoes"])
ego2cams = torch.zeros((num, 4, 4), dtype=torch.float32)
cam2feats = torch.zeros((num, 3, 3), dtype=torch.float32)
for i in range(num):
ego2cams[i] = torch.tensor(np.linalg.inv(data["cam2egoes"][i]))
cam2feats[i] = torch.tensor(self.ds @ data["cam_intrinsics"][i])
grid = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([
torch.arange(self.range[0], self.range[3], self.voxel_size[0]),
torch.arange(self.range[1], self.range[4], self.voxel_size[1]),
torch.tensor(self.height), torch.tensor(1.0)
], indexing="ij")) # [4, 188, 64, 4, 1]
grid_h, grid_w = grid.shape[1:3]
grid4 = grid.view(1, 4, -1).expand(num, 4, -1) # [7, 4, 192512]
points_2d = torch.bmm(ego2cams[:, :3, :], grid4)
x = (points_2d[:, 0] / points_2d[:, 2]) # [7, 48128]
y = (points_2d[:, 1] / points_2d[:, 2]) # [7, 48128]
z = points_2d[:, 2] # [7, 48128]
r = points_2d.norm(dim=1) # [B*N, Hg*Wg]
d = torch.floor(r / self.resolution)
distortions = torch.tensor(np.array(data["cam_distortions"]).T)
k1,k2,k3,p1,p2,k4,k5,k6 = distortions[:,:,None]
fovs = torch.tensor(data['crop_fovs']).unsqueeze(-1) / 2.0
in_fov = np.abs(np.arctan2(points_2d[:, 0], z)) < fovs
r2 = x**2 + y**2
ratio = (1 + k1 * r2 + k2 * r2**2 + k3 * r2**3) / (1 + k4 * r2 + k5 * r2**2 + k6 * r2**3)
x_undist = x * ratio + 2 * p1 * x * y + p2 * (r2 + 2 * x**2)
y_undist = y * ratio + p1 * (r2 + 2 * y**2) + 2 * p2 * x * y
x = cam2feats[:, 0, [0]] * x_undist + cam2feats[:, 0, [2]]
y = cam2feats[:, 1, [1]] * y_undist + cam2feats[:, 1, [2]]
valid = ~((x >= 0) & (y >= 0) & (x < self.feature_size[1]) & \
(y < self.feature_size[0]) & (z > 0) & in_fov & \
(d >= 0) & (d < self.max_num_depth)) # [7, 48128]
x[valid], y[valid], d[valid] = -1, -1, -1
x = (x.float() / self.feature_size[1] * 2.) - 1.0
y = (y.float() / self.feature_size[0] * 2.) - 1.0
d = (d.float() / self.max_num_depth * 2.) - 1.0
indices = torch.cat([x[:,:,None], y[:,:,None], d[:,:,None]], dim=2) # [7, 48128, 3]
indices = indices.reshape(-1, grid_h, grid_w, len(self.height), 3) # batch*num_img, bev_w, bev_h, num_height, 3(x, y, d)
data["indices"] = indices.permute(0, 3, 1, 2, 4) # batch*num_img, num_height, bev_w, bev_h, 3(x, y, d)
return data
4.LSS的BEV投影
class LssBevTransform(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, num_zs, max_num_depth):
super().__init__()
self._num_zs = num_zs
self._max_num_depth = max_num_depth
self._conv = nn.Conv2d(num_channels * num_zs, num_channels, kernel_size=1) # TODO:可以增加几层conv
self._depth_proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_channels, max_num_depth, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.Softmax(dim=1)
)
self._grid_sampler = opm.GridSample(mode="nearest",
padding_mode="zeros",
align_corners=True)
def forward(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 3) where 3 dims represent (w, h, d).
bev_feats = self._sample_bev_feats(feats, indices[..., :2]) # (B*N, C, Z, X, Y)
depth_feats = self._sample_depth_feats(feats, indices) # (B*N, 1, Z, X, Y)
final_feats = bev_feats * depth_feats # (B*N, C, Z, Y, X)
N, C, Z, Y, X = final_feats.shape
final_feats = final_feats.view(N, C * Z, Y, X) # (B*N, Z*C, Hg, Wg)
final_feats = self._conv(final_feats) # (B*N, C, Hg, Wg)
return final_feats
def _sample_bev_feats(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 2) where 2 dims represent (w, h)
bev_feats = [self._grid_sampler(feats, indices[:, i]) for i in range(self._num_zs)]
return torch.stack(bev_feats, dim=2) # (B*N, C, Z, X, Y)
def _sample_depth_feats(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 3) where 3 dims represent (w, h, d).
depths = self._depth_proj(feats)[:, None] # (B*N, 1, D, H, W)
return self._grid_sampler(depths, indices) # (B*N, 1, Z, X, Y)
五、展望
LSS投影时将input_3:(N, 1, D, H_in, W_in)中D和H_in进行reshape合并后得(N, 1, D*H_in, W_in),可以完全通过4-D gridsample提取特征,耗时进一步降低(注意合并维度不要写错了!!!),等效替代测试代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import unittest
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GridSampleTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_grid_sample_equivalence(self):
D, H, W = 100, 144, 256
Y, X = 64, 128
C = 32
# Generate random features.
feats_5d = torch.randn(1, C, D, H, W)
# Generate random indices.
d = torch.randint(high=D, size=(Y, X))
h = torch.randint(high=H, size=(Y, X))
w = torch.randint(high=W, size=(Y, X))
# Prepare grid for 5D grid_sample.
indices_5d = torch.stack([
2.0 * w / (W - 1) - 1.0,
2.0 * h / (H - 1) - 1.0,
2.0 * d / (D - 1) - 1.0
], dim=-1).view(1, 1, Y, X, 3)
bev_feats_5d = F.grid_sample(feats_5d, indices_5d, mode="nearest", align_corners=True).view(C, Y, X)
# Flatten D and H dimensions and prepare grid for 4D grid_sample.
dh = d * H + h
indices_4d = torch.stack([
2.0 * w / (W - 1) - 1.0,
2.0 * dh / (D * H - 1) - 1.0
], dim=-1).view(1, Y, X, 2)
feats_4d = feats_5d.view(1, C, D * H, W)
# 下方注释为错误写法:合并维度错误
# dw = d * W + w
# indices_4d = torch.stack([
# 2.0 * dw / (D * W - 1) - 1.0,
# 2.0 * h / (H - 1) - 1.0
# ], dim=-1).view(1, Y, X, 2)
# feats_4d = feats_5d.view(1, C, H, D * W)
bev_feats_4d = F.grid_sample(feats_4d, indices_4d, mode="nearest", align_corners=True).view(C, Y, X)
# Check if the results are close.
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(bev_feats_5d, bev_feats_4d, atol=1e-6))
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
涉及到两个维度合并后进行索引取特征,注意索引坐标要提前取整,否则部分浮点数据经过合并计算后再取整会有细小的差别,导致最终取到的特征有一定偏差。
代码更新:
1.LSS 4D gridsample的BEV网格坐标索引
def _get_lss_fixed_resolution_depth(self, r, resolution):
d = torch.floor(r / resolution)
return d
def get_fov(self, intrinsic, distortion):
# 假设camera_matrix和dist_coeffs是通过相机标定得到的
# camera_matrix = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
# [0, fy, cy],
# [0, 0, 1]])
# dist_coeffs = np.array([k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]) # 这里k1, k2, p1, p2, k3是相机畸变系数
# # 去畸变前的点(假设是一个二维点)
# src_point = np.array([[x, y]], dtype=np.float32) # x, y是去畸变前点的坐标
# # 去畸变后的点
# dst_point = cv2.undistortPoints(src_point, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, P=camera_matrix)
# dst_point = dst_point.astype(np.int) # 如果需要整数坐标
# 绘制去畸变后的点(如果需要)
# cv2.circle(img, tuple(dst_point[0][0]), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 注意:img是去畸变前的图像,如果需要对整个图像去畸变,需要遍历图像中的所有点
fx = intrinsic[0][0] #x方向(水平方向)焦距
cx = intrinsic[0][2]
fy = intrinsic[1][1] #y方向(垂直方向)焦距
cy = intrinsic[1][2]
point0 = np.array([cx, cy]) # 原始光轴中心点(图像中心点)
point1 = np.array([[0, cy]]) # 在图像平面上选择一个点 (此处选择图像的左边缘)
# 反投影点(去畸变点)
dst_point = cv2.undistortPoints(point1, intrinsic, distortion, P=intrinsic)
# 计算两个点之间的距离
dis = point0 - dst_point[0][0]
dis = math.sqrt(dis[0]*dis[0] + dis[1]*dis[1])
# 计算视场角 (FOV,水平方向)
tan = dis/fx
fov = 2 * math.atan(tan)
fov = fov * 180 / 3.14
return fov
def _preprocess_img_lss(self, data):
# data["imgs"] = data["imgs"].reshape(-1, 3, 576, 1024) # [8, 7, 3, 576, 1024] -> [56, 3, 576, 1024]
data["imgs"] = data["imgs"].reshape(-1, 3, self.camera_in_image_size[0], self.camera_in_image_size[1])
ego2cam = data["aug_ego2cam"].reshape(-1, 4, 4).float()
grid = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([
torch.arange(self.cam_range[0], self.cam_range[3], self.cam_voxel_size[0]),
torch.arange(self.cam_range[1], self.cam_range[4], self.cam_voxel_size[1]),
torch.tensor(self.cam_height),
], indexing="ij")).to(ego2cam.device) # torch.Size([3, 376, 128, 4]) #[3, 188, 64, 4]
channel, grid_size_x, grid_size_y, z = grid.shape
grid = grid.view(1, 3, -1).expand(data["imgs"].shape[0], 3, -1) # [7, 3, 192512] # [56, 3, 48128]
grid = torch.cat((grid, torch.ones_like(grid[:, :1])), dim=1) # [7, 4, 192512] 坐标齐次化 #[56, 4, 48128]
points_2d = torch.bmm(ego2cam[:, :3, :], grid)
x = (points_2d[:, 0] / points_2d[:, 2]) # [56, 48128]
y = (points_2d[:, 1] / points_2d[:, 2]) # [56, 48128]
z = points_2d[:, 2] # [56, 48128]
r = points_2d.norm(dim=1) # [B*N, Hg*Wg]
resolution = self.lss_grid_indices_parameter["fixed_depth_resolution"]["resolution"]
max_num_depth = self.lss_grid_indices_parameter["fixed_depth_resolution"]["max_num_depth"]
d = self._get_lss_fixed_resolution_depth(r, resolution)
temp_distortion = data["cam_distortions"]
distortion = []
for j in range(temp_distortion[0].shape[0]):
for i in range(len(temp_distortion)):
distortion.append(list(temp_distortion[i][j][0]))
distortion = torch.tensor(distortion)
k1 = distortion[:, 0].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
k2 = distortion[:, 1].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
k3 = distortion[:, 2].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
p1 = distortion[:, 3].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
p2 = distortion[:, 4].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
k4 = distortion[:, 5].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
k5 = distortion[:, 6].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
k6 = distortion[:, 7].unsqueeze(-1).to(x.device)
intrinsic = data["fov_cam_intrinsics"]
intrinsic = intrinsic.reshape(-1, 4, 4)
fov = []
fov_valid = []
img_num = len(data["imgs"])
for i in range(img_num):
current_intrinsic = np.array(intrinsic[i][:3,:3].to('cpu'))
current_fov = self.get_fov(current_intrinsic, \
np.array([np.array(k1[i].to('cpu')), np.array(k2[i].to('cpu')), np.array(p1[i].to('cpu')), np.array(p2[i].to('cpu')), np.array(k3[i].to('cpu')), np.array(k4[i].to('cpu')), np.array(k5[i].to('cpu')), np.array(k6[i].to('cpu'))]))
fov.append(current_fov)
fov_valid = (np.abs(np.arctan2(points_2d[:, 0].to('cpu'), z.to('cpu'))) / np.pi * 180 < torch.tensor([m / 2 for m in fov]).unsqueeze(-1)) & (z.to('cpu') > 0)
r2 = x**2 + y**2
x_temp = x * (1 + k1 * r2 + k2 * r2**2 + k3 * r2**3) / (1 + k4 * r2 + k5 * r2**2 + k6 * r2**3) + 2 * p1 * x * y + p2 * (r2 + 2 * x**2)
y_temp = y * (1 + k1 * r2 + k2 * r2**2 + k3 * r2**3) / (1 + k4 * r2 + k5 * r2**2 + k6 * r2**3) + p1 * (r2 + 2 * y**2) + 2 * p2 * x * y
intrinsic = data["aug_cam_intrinsics"]
intrinsic = intrinsic.reshape(-1, 4, 4)
x = intrinsic[:, 0, 0].unsqueeze(-1) * x_temp + intrinsic[:, 0, 1].unsqueeze(-1) * y_temp + intrinsic[:, 0, 2].unsqueeze(-1)
y = intrinsic[:, 1, 0].unsqueeze(-1) * x_temp + intrinsic[:, 1, 1].unsqueeze(-1) * y_temp + intrinsic[:, 1, 2].unsqueeze(-1)
x = torch.round(x) #取整,防止后续计算四舍五入出现异常值
y = torch.round(y)
d = torch.round(d)
valid = ~((x >= 0) & (y >= 0) & (x < self.cam_feature_size[1]) & (y < self.cam_feature_size[0]) & (z > 0) & fov_valid.to(x.device) \
& (d >= 0) & (d < max_num_depth)) # [56, 48128]
####################
x[valid] = 0 # (BN, ZXY)
y[valid] = 0 # (BN, ZXY)
d[valid] = 0 # (BN, ZXY)
yd = d.float() * self.cam_feature_size[0] + y #(BN, ZXY)
x = (x.float() / (self.cam_feature_size[1] - 1)) * 2.0 - 1.0
y = (y.float() / (self.cam_feature_size[0] - 1)) * 2.0 - 1.0
yd = (yd.float() / (self.cam_feature_size[0] * max_num_depth - 1)) * 2.0 - 1.0
indices = torch.stack([x, y, x, yd], dim=-1) # (BN, ZXY, 4)
indices = indices.view(-1, len(self.cam_height), grid_size_x, grid_size_y, 4)
self.batch_size = indices.shape[0] // self.num_cam
return indices
2.LSS 4D gridsample的BEV投影
class LssBevTransform(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, num_zs, max_num_depth):
super().__init__()
self._num_zs = num_zs
self._max_num_depth = max_num_depth
self._conv = nn.Conv2d(num_channels * num_zs, num_channels, kernel_size=1) # TODO:可以增加几层conv
self._depth_proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_channels, max_num_depth, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.Softmax(dim=1)
)
self._grid_sampler = opm.GridSample(mode="nearest",
padding_mode="zeros",
align_corners=True)
self._cat = opm.Concat(dim=1)
def forward(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 3) where 3 dims represent (w, h, d).
bev_feats = self._sample_bev_feats(feats, indices[..., :2]) # (B*N, C, Z, X, Y)
# depth_feats = self._sample_depth_feats(feats, indices) # (B*N, 1, Z, X, Y)
depth_feats = self._sample_depth_feats(feats, indices[..., 2:4]) # (B*N, 1, Z, X, Y)
final_feats = bev_feats * depth_feats # (B*N, C, Z, Y, X)
N, C, Z, Y, X = final_feats.shape
final_feats = final_feats.view(N, C * Z, Y, X) # (B*N, Z*C, Hg, Wg)
final_feats = self._conv(final_feats) # (B*N, C, Hg, Wg)
return final_feats
def _sample_bev_feats(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 2) where 3 dims represent (w, h)
bev_feats = [self._grid_sampler(feats, indices[:, i]) for i in range(self._num_zs)]
return torch.stack(bev_feats, dim=2) # (B*N, C, Z, Y, X)
def _sample_depth_feats(self, feats, indices):
# feats: (B*N, C, H, W)
# indices: (B*N, Z, X, Y, 3) where 3 dims represent (w, h, d).
# depths = self._depth_proj(feats)[:, None] # (B*N, 1, D, H, W)
# return self._grid_sampler(depths, indices) # (B*N, 1, Z, X, Y)
depths = self._depth_proj(feats)[:, None]
N, C, D, H, W = depths.shape
depths_new = depths.view(N, C, D * H, W)
bev_feats = [self._grid_sampler(depths_new, indices[:, i]) for i in range(self._num_zs)]
return torch.stack(bev_feats, dim=2)
相机内外参处理:
class ImageCropResizeAug3D:
"""Do crop, resize, FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT and rotate For multi channel images.
Args:
input_image_info: For load multi channel images, first do crop, then do resize,
for example, one of the params format like this:
- 'CAM_FRONT_SHORT': this is one of the camera_types, you can define in get_data_info, here is a map key;
- x_min, y_min:start of the crop coordinate, x_min is the width-axis direction, y_min is the height-axis direction;
- width, height: the image size of after crop;
- new_width, new_height: the image size of after resize;
input_image_info:
'CAM_FRONT_SHORT':
crop_params:
x_min_scale: 4
y_min_scale: 3
width_scale: 2
height_scale: 2
resize_params:
new_width: 1024
new_height: 576
rot_lim (list): range of image rotate
rand_flip (bool): Whether to FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT the img.
"""
def __init__(
self, input_image_info, rot_lim, rand_flip, is_train, crop_noise
):
self.input_image_info = input_image_info
self.rand_flip = rand_flip
self.rot_lim = rot_lim
self.is_train = is_train
self.crop_noise = crop_noise
print("start ImageCropResizeAug3D")
def get_fov(self, intrinsic, distortion):
# 假设camera_matrix和dist_coeffs是通过相机标定得到的
# camera_matrix = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
# [0, fy, cy],
# [0, 0, 1]])
# dist_coeffs = np.array([k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]) # 这里k1, k2, p1, p2, k3是相机畸变系数
# # 去畸变前的点(假设是一个二维点)
# src_point = np.array([[x, y]], dtype=np.float32) # x, y是去畸变前点的坐标
# # 去畸变后的点
# dst_point = cv2.undistortPoints(src_point, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, P=camera_matrix)
# dst_point = dst_point.astype(np.int) # 如果需要整数坐标
# 绘制去畸变后的点(如果需要)
# cv2.circle(img, tuple(dst_point[0][0]), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 注意:img是去畸变前的图像,如果需要对整个图像去畸变,需要遍历图像中的所有点
fx = intrinsic[0][0] #x方向(水平方向)焦距
cx = intrinsic[0][2]
fy = intrinsic[1][1] #y方向(垂直方向)焦距
cy = intrinsic[1][2]
point0 = np.array([cx, cy]) # 原始光轴中心点(图像中心点)
point1 = np.array([[0, cy]]) # 在图像平面上选择一个点 (此处选择图像的左边缘)
# 反投影点(去畸变点)
dst_point = cv2.undistortPoints(point1, intrinsic, distortion, P=intrinsic)
# 计算两个点之间的距离
dis = point0 - dst_point[0][0]
dis = math.sqrt(dis[0]*dis[0] + dis[1]*dis[1])
# 计算视场角 (FOV,水平方向)
tan = dis/fx
fov = 2 * math.atan(tan)
fov = fov * 180 / 3.14
return fov
def sample_augmentation(self, results, index):
# print("start ImageCropResizeAug3D sample_augmentation")
image_type = results["image_types"]
# print("start get image_type")
image_crop_resize_params = copy.deepcopy(self.input_image_info[image_type[index]])
crop_params = image_crop_resize_params["crop_params"]
#判断图像fov是否符合设计要求
current_file_path = results['path']
intrinsic = results['cam_intrinsics'][index][:3, :3]
distortion = results['cam_distortions'][index][0]
camera_matrix = np.array(intrinsic)
if len(distortion) == 5:
results['cam_distortions'][index] = np.array([np.array([distortion[0],distortion[1],distortion[2],distortion[3],distortion[4], 0, 0, 0])])
distortion = results['cam_distortions'][index][0]
elif len(distortion) == 4:
results['cam_distortions'][index] = np.array([np.array([distortion[0],distortion[1],distortion[2],distortion[3], 0, 0, 0, 0])])
distortion = results['cam_distortions'][index][0]
if len(distortion) == 8:
distortion = np.array([distortion[0],distortion[1],distortion[3],distortion[4],distortion[2],distortion[5],distortion[6],distortion[7]])
else:
print(f"!!!error:{current_file_path} lenth of distortion is {len(distortion)} not 8 or 5")
# exit()
# 判断每帧数据的fov是否在误差范围内
current_caluate_cam_fov = self.get_fov(camera_matrix, distortion)
current_camera_design_fov = image_crop_resize_params["crop_params"]["design_fov"]
if image_type[index] == 'CAM_BACK_MIDDLE':
if abs(current_camera_design_fov - current_caluate_cam_fov) > 5:
if abs(60 - current_caluate_cam_fov) < 5: #历史数据中部分数据后视相机为60度
crop_params["x_min_scale"] = 18.00
crop_params["y_min_scale"] = 18.00
crop_params["width_scale"] = 1.125
crop_params["height_scale"] = 1.125
elif abs(120 - current_caluate_cam_fov) < 5: #历史数据中部分数据后视相机为120度
crop_params["x_min_scale"] = 3.60
crop_params["y_min_scale"] = 3.60
crop_params["width_scale"] = 2.25
crop_params["height_scale"] = 2.25
else:
print(f"!!!error:the {image_type[index]} fov of {current_file_path} is {current_caluate_cam_fov}, not match disign fov {current_camera_design_fov} or 60 or 120!!!")
# exit()
else:
# assert (abs(current_camera_design_fov - current_caluate_cam_fov) < 5), f"!!!error:the {image_type[index]} fov of {current_file_path} is {current_caluate_cam_fov}, not match disign fov {current_camera_design_fov} !!!"
if abs(current_camera_design_fov - current_caluate_cam_fov) >= 5:
print (f"!!!error:the {image_type[index]} fov of {current_file_path} is {current_caluate_cam_fov}, not match disign fov {current_camera_design_fov} !!!")
if self.crop_noise > 0:
crop_noise = random.randint(-self.crop_noise, self.crop_noise)
else:
crop_noise = 0
if (crop_params["x_min_scale"] - 1) < 1e-6:
x_min = 0
fov_x_min = x_min
else:
x_min = round(float(results["ori_shape"][index][0]) / float(crop_params["x_min_scale"]))
fov_x_min = x_min
x_min += crop_noise
if (crop_params["y_min_scale"] - 1) < 1e-6:
y_min = 0
fov_y_min = y_min
else:
y_min = round(float(results["ori_shape"][index][1]) / float(crop_params["y_min_scale"]))
fov_y_min = y_min
y_min += crop_noise
width = round(float(results["ori_shape"][index][0]) / float(crop_params["width_scale"]))
height = round(float(results["ori_shape"][index][1]) / float(crop_params["height_scale"]))
crop_area = (x_min, y_min, x_min + width, y_min + height)
fov_crop_area = (fov_x_min, fov_y_min, fov_x_min + width, fov_y_min + height)
resize_params = image_crop_resize_params["resize_params"]
resize = float(resize_params["new_width"])/float(width)
resize_dims = (resize_params["new_width"], resize_params["new_height"])
flip = self.rand_flip and np.random.choice([0, 1])
rotate = np.random.uniform(*self.rot_lim)
results["img_shape"].append(resize_dims)
return resize, resize_dims, crop_area, flip, rotate, fov_crop_area
def img_transform(
self, img, rotation, translation, resize, resize_dims, crop, flip, rotate
):
# 公式原理参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/608931944
# 这里改变了crop和resize的顺序,先crop后resize
# adjust image
img = img.crop(crop)
# resampling_method = {0:'Resampling.NEAREST',2:'Resampling.BILINEAR',3:'Resampling.HAMMING', 4:'Resampling.BICUBIC'}
img = img.resize(resize_dims,resample=random.choice([0,2,3]))
if flip:
img = img.transpose(method=Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
img = img.rotate(rotate)
# post-homography transformation
rotation *= resize
translation -= (resize*torch.Tensor(crop[:2]))
if flip:
A = torch.Tensor([[-1, 0], [0, 1]])
b = torch.Tensor([crop[2] - crop[0], 0])
rotation = A.matmul(rotation)
translation = A.matmul(translation) + resize*b
theta = rotate / 180 * np.pi
A = torch.Tensor(
[
[np.cos(theta), np.sin(theta)],
[-np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)],
]
)
b = resize*torch.Tensor([crop[2] - crop[0], crop[3] - crop[1]]) / 2
b = A.matmul(-b) + b
rotation = A.matmul(rotation)
translation = A.matmul(translation) + b
return img, rotation, translation
def __call__(self, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
imgs = data["imgs"]
new_imgs = []
transforms = []
fov_transforms = []
for index, img in enumerate(imgs):
resize, resize_dims, crop, flip, rotate, fov_crop_area = self.sample_augmentation(data, index)
post_rot = torch.eye(2)
post_tran = torch.zeros(2)
new_img, rotation, translation = self.img_transform(
img,
post_rot,
post_tran,
resize=resize,
resize_dims=resize_dims,
crop=crop,
flip=flip,
rotate=rotate,
)
transform = torch.eye(4)
transform[:2, :2] = rotation
transform[:2, 3] = translation
new_imgs.append(new_img)
transforms.append(transform.numpy())
fov_post_rot = torch.eye(2)
fov_post_tran = torch.zeros(2)
fov_rotation = fov_post_rot * resize
fov_translation = fov_post_tran - (resize*torch.Tensor(fov_crop_area[:2]))
fov_transform = torch.eye(4)
fov_transform[:2, :2] = fov_rotation
fov_transform[:2, 3] = fov_translation
fov_transforms.append(fov_transform.numpy())
data["imgs"] = new_imgs
# update the calibration matrices
data["img_aug_matrix"] = transforms
data["img_fov_aug_matrix"] = fov_transforms
return data
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class UpdateEgo2img:
"""update final ego2img matrix.
"""
def __init__(self, downsample):
self.downsample = downsample
print("start UpdateEgo2img")
def update_ego2img(self, cam_intrinsics, rot, tran, img_aug_matrix, img_fov_aug_matrix, lidar_aug_matrix, downsample):
lidar2img = np.zeros((len(rot), 3, 4), dtype=np.float32)
aug_cam_intrinsics = np.zeros((len(rot), 4, 4), dtype=np.float32)
fov_cam_intrinsics = np.zeros((len(rot), 4, 4), dtype=np.float32)
aug_lidar2cam = np.zeros((len(rot), 4, 4), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(len(rot)):
# 获取cam2ego的旋转平移变换矩阵
transform = np.zeros((4, 4), dtype=np.float32)
transform[:3, :3] = rot[i]
transform[:3, -1] = tran[i]
transform[-1, -1] = 1.0
# 计算lidar数据增强后cam2lidar的变换矩阵
new_transform = lidar_aug_matrix @ transform
rotation = new_transform[:3, :3]
translation = new_transform[:3, 3]
# 计算lidar2cam的旋转平移变换矩阵
lidar2cam_r = np.linalg.inv(rotation)
lidar2cam_t = translation @ lidar2cam_r.T
lidar2cam_rt = np.eye(4)
lidar2cam_rt[:3, :3] = lidar2cam_r.T
lidar2cam_rt[3, :3] = -lidar2cam_t
intrinsic = cam_intrinsics[i][:3, :3]
# 将图像增强矩阵应用于相机内参
viewpad = np.eye(4)
if img_aug_matrix is not None:
assert img_aug_matrix is not None, img_aug_matrix
post_rot = img_aug_matrix[i][:3, :3]
post_tran = img_aug_matrix[i][:3, 3]
viewpad[:3, :2] = post_rot @ intrinsic[:3, :2]
viewpad[:3, 2] = post_rot @ intrinsic[:3, 2]
viewpad[:3, 2] += post_tran
else:
viewpad[:intrinsic.shape[0], :intrinsic.shape[1]] = intrinsic
#fov 内外参变化
fov_viewpad = np.eye(4)
if img_fov_aug_matrix is not None:
assert img_fov_aug_matrix is not None, img_fov_aug_matrix
fov_post_rot = img_fov_aug_matrix[i][:3, :3]
fov_post_tran = img_fov_aug_matrix[i][:3, 3]
fov_viewpad[:3, :2] = fov_post_rot @ intrinsic[:3, :2]
fov_viewpad[:3, 2] = fov_post_rot @ intrinsic[:3, 2]
fov_viewpad[:3, 2] += fov_post_tran
else:
fov_viewpad[:intrinsic.shape[0], :intrinsic.shape[1]] = intrinsic
# 根据下采样因子更新相机内参矩阵
intrinsic=np.eye(4)
intrinsic[:2] /= downsample
viewpad = intrinsic @ viewpad
aug_cam_intrinsics[i] = copy.deepcopy(viewpad)
fov_viewpad = intrinsic @ fov_viewpad
fov_cam_intrinsics[i] = copy.deepcopy(fov_viewpad)
aug_lidar2cam[i] = copy.deepcopy(lidar2cam_rt.T)
# 计算激光雷达到图像坐标系的变换矩阵并存储
lidar2img[i] = (viewpad @ lidar2cam_rt.T)[:3]
return lidar2img, aug_cam_intrinsics, fov_cam_intrinsics, aug_lidar2cam
def __call__(self, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# 将模型代码中的bev特征点映射操作,与模型解耦,放在预处理的位置做,更新ego2img参数
ego2img, aug_cam_intrinsics, fov_cam_intrinsics, aug_lidar2cam = self.update_ego2img(
data["cam_intrinsics"], data["rot"], data["tran"],
data["img_aug_matrix"],
data["img_fov_aug_matrix"],
data["lidar_aug_matrix"],
self.downsample
)
data["ego2img"] = ego2img
data["aug_cam_intrinsics"] = np.array(aug_cam_intrinsics)
data["fov_cam_intrinsics"] = np.array(fov_cam_intrinsics)
data["aug_ego2cam"] = np.array(aug_lidar2cam)
# print("finished UpdateEgo2img")
return data
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








