1.bean的三种实例化方式
<1>默认构造
<bean id="" class=""></bean>
就是默认构造, 在容器构造对象时,使用的是默认构造函数,若是重写构造函数此方 法就会出错。
<2>静态工厂:常用语Spring整合其他的框架(工具)
静态工厂:是用于生产实例对象,该工厂 的所有方法是静态方法
<bean id="" class="工厂的全限定类名" factory-mothed="静态方法">
<!-- 静态工厂配置 -->
<!-- id容器中类的唯一表示 class是静态工厂类的全限定类名=包名+类名 factory-method是静态工厂中的静态方法-->
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.spring.Ioc_static_factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="createService"></bean>
静态工厂类:
package com.spring.Ioc_static_factory;
import studySpring.UserService;
import studySpring.UserServiceImp;
public class StaticFactory {
public static UserService createService() {
return new UserServiceImp();
}
}
测试类
@Test
public void testStaticFactory1() {
String xmlPath = " com/spring/Ioc_static_factory/ApplicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService u =(UserService)context.getBean("userServiceId");
u.addUSer();
}
<3>实例工厂:必须先有工厂的实例对象,再通过工厂对象的方法生产目标对象,注:实例工厂的所有方法都是非静态方法。
第一步:写出实例化工厂
package com.spring.Ioc_c_factory;
import studySpring.UserService;
import studySpring.UserServiceImp;
public class CommonFactory {
public UserService createService() {
return new UserServiceImp();
}
}
第二部:配置文件
<!-- 实例工厂配置
创建工厂对象
-->
<bean id="commonFactory" class="com.spring.Ioc_c_factory.CommonFactory" ></bean>
<!--获得userService factory-bean是实例工厂 factory-method是实例化对象的方法 -->
<bean id="userService" factory-bean="commonFactory" factory-method="createService"></bean>
第三步:测试
@Test
public void testStaticFactory1() {
String xmlPath = "com/spring/Ioc_c_factory/ApplicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService u =context.getBean("userService",UserService.class);
u.addUSer();
}
2.作用域:用以确定spring创建实例的个数
 <1>Singleton:单例, 不管调用几次getBean()方法,只会创建一个对象
<1>Singleton:单例, 不管调用几次getBean()方法,只会创建一个对象
<2>prototype:多例:每调用一次getBean()方法都会生成一个对象。
<3>配置信息:scope就是作用域
例:
<bean id="userService" class="com.spring.scope.UserServiceImp" scope="prototype"></bean>
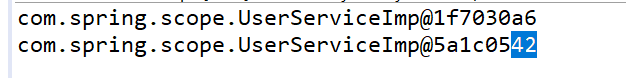
测试结果:
3.生命周期
<1>初始化和销毁:目标方法执行前后的初始化和销毁
目标类:目标类中要有目标方法还有Init-method和destory-method方法
public class UserServiceImp implements UserService {
public void addUSer() {
System.out.println("Ioc Add user");
}
//在创建创建实例的时候就调用
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("初始化放噶");
}
//在容器关闭的时候才调用
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
配置文件
init-method方法:用于初始化一些必要要的数据,例如:数据连接池
detory-metho方法:用于释放资源
<bean id="userService" class="com.spring.liveTime.UserServiceImp"
init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory"></bean>
```注:init-method方法:在目标方法执行之前就执行
destory-method方法:在spring的容器关闭之后才执行,而且作用域必须是singleton
<2>
<3>
<4>
<6>





















 354
354

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








