A.c 和B.c两个c文件中使用了两个相同名字的static变量,编译的时候会不会有问题?
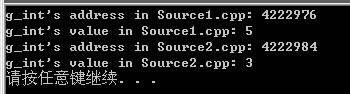
在头文件中定义static,然后这个头文件被不同的文件引用。我们知道,static的作用域是定义它的源文件中,这样的方式,会在每个引用它的文件中都生成一个本地的static 变量。static 变量是静态变量,和全局变量一样,都存放在静态存储区,但是,值得注意的是,编译器在编译的时候,对他们的命名是不同的。因此,存放的位置也不同,这时,在头文件中定义的static变量,在不同的文件中引用,就是不同的静态变量。例子如下图。
在vs2010中,无法include .h文件,很奇怪,没有解决。可以引用.c,所以,例子中引用.c。
test.c中只是定义了变量g_int,充当.h文件。
static int g_int = 3;
test1.cpp中引用test.c文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "test.c"
void TestSource1()
{
g_int= 5;
printf("g_int's address in Source1.cpp: %d\n", &g_int);
printf("g_int's value in Source1.cpp: %d\n", g_int);
}
test2.cpp中引用test.c文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "test.c"
void TestSource2()
{
printf("g_int's address in Source2.cpp: %d\n", &g_int);
printf("g_int's value in Source2.cpp: %d\n", g_int);
}
func.c文件声明了函数。
void TestSource1();
void TestSource2();
main函数执行测试
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "func.c"
void main()
{
TestSource();
TestSource2();
system("pause");
}
从该博客中学习,http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4a3946360100yagx.html,讲述很到位。







 本文探讨了在C语言中,当两个不同源文件中使用相同名称的static变量时,是否会产生编译问题。通过实际代码示例说明了static变量在各源文件中的独立性及其存储特性。
本文探讨了在C语言中,当两个不同源文件中使用相同名称的static变量时,是否会产生编译问题。通过实际代码示例说明了static变量在各源文件中的独立性及其存储特性。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








