终于建了一个自己个人小站:https://huangtianyu.gitee.io,以后优先更新小站博客,欢迎进站,O(∩_∩)O~~
先上测试代码:
MyView.java
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.util.AttributeSet;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class MyView extends TextView {
- public MyView(Context context) {
- super(context);
- }
- public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(context, attrs);
- Log.e(”test”,“view constructor”);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
- super.onAttachedToWindow();
- Log.e(”test”, “onAttachedToWindow”);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
- super.onDetachedFromWindow();
- Log.e(”test”, “onDetachedFromWindow”);
- }
- }
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MyView extends TextView {
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
Log.e("test","view constructor");
}
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
Log.e("test", "onAttachedToWindow");
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
Log.e("test", "onDetachedFromWindow");
}
}
MainActivity.java
- import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- Log.e(”test”, “before setContextView”);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- Log.e(”test”, “after setContextView”);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onResume() {
- super.onResume();
- Log.e(”test”, “onResume”);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDestroy() {
- super.onDestroy();
- Log.e(”test”, “onDestroy”);
- }
- }
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.e("test", "before setContextView");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.e("test", "after setContextView");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.e("test", "onResume");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.e("test", "onDestroy");
}
}
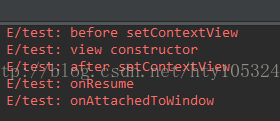
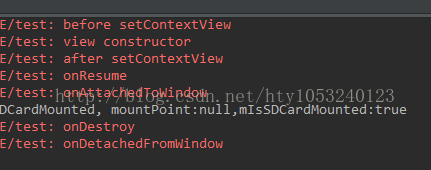
点击返回键退出后,输出的Log如下:
根据Log的onAttachedToWindow和onDetachedFromWindow的输出情况一目了然。
下面通过源码分析下,他两的调用时机到底在哪。
首先看下onAttachedToWindow的调用时机,在Android源码中onResume调用前会先调用了ActivityThread中的handleResumeActivity,下面是相应的代码:
ActivityThread.java
- final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
- boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
- // If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
- // we are back active so skip it.
- unscheduleGcIdler();
- mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
- // TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration
- ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide);
- if (r != null) {
- final Activity a = r.activity;
- if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
- TAG, ”Resume ” + r + “ started activity: ” +
- a.mStartedActivity + ”, hideForNow: ” + r.hideForNow
- + ”, finished: ” + a.mFinished);
- final int forwardBit = isForward ?
- WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
- // If the window hasn’t yet been added to the window manager,
- // and this guy didn’t finish itself or start another activity,
- // then go ahead and add the window.
- boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
- if (!willBeVisible) {
- try {
- willBeVisible = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().willActivityBeVisible(
- a.getActivityToken());
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- }
- if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
- r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
- View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
- decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
- ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
- WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
- a.mDecor = decor;
- l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
- l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
- if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
- a.mWindowAdded = true;
- wm.addView(decor, l);//这里调用了ViewManager中的addView方法。
- }
- // If the window has already been added, but during resume
- // we started another activity, then don’t yet make the
- // window visible.
- } else if (!willBeVisible) {
- if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
- TAG, ”Launch ” + r + “ mStartedActivity set”);
- r.hideForNow = true;
- }
- // Get rid of anything left hanging around.
- cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
- // The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not
- // simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity.
- if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible
- && r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
- if (r.newConfig != null) {
- r.tmpConfig.setTo(r.newConfig);
- if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
- r.tmpConfig.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
- }
- if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, “Resuming activity ”
- + r.activityInfo.name + ” with newConfig ” + r.tmpConfig);
- performConfigurationChanged(r.activity, r.tmpConfig);
- freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(r.activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(r.tmpConfig));
- r.newConfig = null;
- }
- if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, “Resuming ” + r + “ with isForward=”
- + isForward);
- WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
- if ((l.softInputMode
- & WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION)
- != forwardBit) {
- l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode
- & (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION))
- | forwardBit;
- if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
- ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
- View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
- wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l);
- }
- }
- r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true;
- mNumVisibleActivities++;
- if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
- r.activity.makeVisible();
- }
- }
- ….
- }
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
// TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration
ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide);
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " +
a.mStartedActivity + ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow
+ ", finished: " + a.mFinished);
final int forwardBit = isForward ?
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
// If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager,
// and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity,
// then go ahead and add the window.
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().willActivityBeVisible(
a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);//这里调用了ViewManager中的addView方法。
}
// If the window has already been added, but during resume
// we started another activity, then don't yet make the
// window visible.
} else if (!willBeVisible) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Launch " + r + " mStartedActivity set");
r.hideForNow = true;
}
// Get rid of anything left hanging around.
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
// The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not
// simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity.
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible
&& r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
if (r.newConfig != null) {
r.tmpConfig.setTo(r.newConfig);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
r.tmpConfig.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with newConfig " + r.tmpConfig);
performConfigurationChanged(r.activity, r.tmpConfig);
freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(r.activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(r.tmpConfig));
r.newConfig = null;
}
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming " + r + " with isForward="
+ isForward);
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION)
!= forwardBit) {
l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode
& (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION))
| forwardBit;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l);
}
}
r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true;
mNumVisibleActivities++;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
....
}- package android.view;
- /** Interface to let you add and remove child views to an Activity. To get an instance
- * of this class, call {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService(java.lang.String) Context.getSystemService()}.
- */
- public interface ViewManager
- {
- /**
- * Assign the passed LayoutParams to the passed View and add the view to the window.
- * <p>Throws {@link android.view.WindowManager.BadTokenException} for certain programming
- * errors, such as adding a second view to a window without removing the first view.
- * <p>Throws {@link android.view.WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException} if the window is on a
- * secondary {@link Display} and the specified display can’t be found
- * (see {@link android.app.Presentation}).
- * @param view The view to be added to this window.
- * @param params The LayoutParams to assign to view.
- */
- public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
- public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
- public void removeView(View view);
- }
package android.view;
/** Interface to let you add and remove child views to an Activity. To get an instance
* of this class, call {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService(java.lang.String) Context.getSystemService()}.
*/
public interface ViewManager
{
/**
* Assign the passed LayoutParams to the passed View and add the view to the window.
* <p>Throws {@link android.view.WindowManager.BadTokenException} for certain programming
* errors, such as adding a second view to a window without removing the first view.
* <p>Throws {@link android.view.WindowManager.InvalidDisplayException} if the window is on a
* secondary {@link Display} and the specified display can't be found
* (see {@link android.app.Presentation}).
* @param view The view to be added to this window.
* @param params The LayoutParams to assign to view.
*/
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public void removeView(View view);
}WindowManagerImpl.java
- /*
- * @see WindowManager
- * @see WindowManagerGlobal
- * @hide
- */
- ublic final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
- private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
- private final Display mDisplay;
- private final Window mParentWindow;
- private IBinder mDefaultToken;
- public WindowManagerImpl(Display display) {
- this(display, null);
- }
- private WindowManagerImpl(Display display, Window parentWindow) {
- mDisplay = display;
- mParentWindow = parentWindow;
- }
- public WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) {
- return new WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow);
- }
- public WindowManagerImpl createPresentationWindowManager(Display display) {
- return new WindowManagerImpl(display, mParentWindow);
- }
- /**
- * Sets the window token to assign when none is specified by the client or
- * available from the parent window.
- *
- * @param token The default token to assign.
- */
- public void setDefaultToken(IBinder token) {
- mDefaultToken = token;
- }
- @Override
- public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
- applyDefaultToken(params);
- mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
- }
- @Override
- public void updateViewLayout(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
- applyDefaultToken(params);
- mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params);
- }
- private void applyDefaultToken(@NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
- // Only use the default token if we don’t have a parent window.
- if (mDefaultToken != null && mParentWindow == null) {
- if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams”);
- }
- // Only use the default token if we don’t already have a token.
- final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
- if (wparams.token == null) {
- wparams.token = mDefaultToken;
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void removeView(View view) {
- mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
- }
- @Override
- public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
- mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
- }
- @Override
- public Display getDefaultDisplay() {
- return mDisplay;
- }
/*
* @see WindowManager
* @see WindowManagerGlobal
* @hide
*/
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
private final Display mDisplay;
private final Window mParentWindow;
private IBinder mDefaultToken;
public WindowManagerImpl(Display display) {
this(display, null);
}
private WindowManagerImpl(Display display, Window parentWindow) {
mDisplay = display;
mParentWindow = parentWindow;
}
public WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow);
}
public WindowManagerImpl createPresentationWindowManager(Display display) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(display, mParentWindow);
}
/**
* Sets the window token to assign when none is specified by the client or
* available from the parent window.
*
* @param token The default token to assign.
*/
public void setDefaultToken(IBinder token) {
mDefaultToken = token;
}
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
@Override
public void updateViewLayout(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params);
}
private void applyDefaultToken(@NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Only use the default token if we don't have a parent window.
if (mDefaultToken != null && mParentWindow == null) {
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
// Only use the default token if we don't already have a token.
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (wparams.token == null) {
wparams.token = mDefaultToken;
}
}
}
@Override
public void removeView(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
}
@Override
public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
}
@Override
public Display getDefaultDisplay() {
return mDisplay;
}
}
从中可以看到addView又调用了 WindowManagerGlobal.java类中的addView,下面看看WindowManagerGlobal.java类的源码:
WindowManagerGlobal.java
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,Display display, Window parentWindow) {if (view == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(“view must not be null”);}if (display == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(“display must not be null”);}if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams”);}final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;if (parentWindow != null) {parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);} else {// If there’s no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is// set from the application’s hardware acceleration setting.final Context context = view.getContext();if (context != null&& (context.getApplicationInfo().flags& ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;}}ViewRootImpl root;View panelParentView = null;synchronized (mLock) {// Start watching for system property changes.if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {synchronized (mLock) {for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; –i) {mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties();}}}};SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);}int index = findViewLocked(view, false);if (index >= 0) {if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {// Don’t wait for MSG_DIE to make it’s way through root’s queue.mRoots.get(index).doDie();} else {throw new IllegalStateException(“View ” + view+ ” has already been added to the window manager.”);}// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.}// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being// attached to for future reference.if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {final int count = mViews.size();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) {panelParentView = mViews.get(i);}}}root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);view.setLayoutParams(wparams);mViews.add(view);mRoots.add(root);mParams.add(wparams);}// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing thingstry {root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);//这里调用ViewRootImpl类中的setView方法,在该方法中触发了<span style=”color:rgb(101,123,131);font-family:Menlo, Monaco, Consolas, ‘Courier New’, monospace;line-height:20.4px;white-space:pre-wrap;background-color:rgb(246,246,246);”>ViewRootImpl.performTraversals()</span>} catch (RuntimeException e) {// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.synchronized (mLock) {final int index = findViewLocked(view, false);if (index >= 0) {removeViewLocked(index, true);}}throw e;}}
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (display == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
} else {
// If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is
// set from the application's hardware acceleration setting.
final Context context = view.getContext();
if (context != null
&& (context.getApplicationInfo().flags
& ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {
wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
}
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system property changes.
if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {
mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties();
}
}
}
};
SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);
}
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {
// Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue.
mRoots.get(index).doDie();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
}
// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being
// attached to for future reference.
if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&
wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {
final int count = mViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) {
panelParentView = mViews.get(i);
}
}
}
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);//这里调用ViewRootImpl类中的setView方法,在该方法中触发了ViewRootImpl.performTraversals()
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
synchronized (mLock) {
final int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
}
throw e;
}
}
在该方法中的root.setView(view,wparams,panelParentView)方法,调用的是ViewRootImpl类中的setView方法,正是该setView方法触发了ViewRootImpl.performTraversals()方法,也就是View绘制的起点,之后会进行measure,layout,draw三个步骤从而完成一个View的显示工作。
ViewRootImpl.java
- /**
- * We have one child
- */
- public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
- synchronized (this) {
- if (mView == null) {
- mView = view;
- mAttachInfo.mDisplayState = mDisplay.getState();
- mDisplayManager.registerDisplayListener(mDisplayListener, mHandler);
- …
- mSoftInputMode = attrs.softInputMode;
- mWindowAttributesChanged = true;
- mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = WindowManager.LayoutParams.EVERYTHING_CHANGED;
- mAttachInfo.mRootView = view;
- mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired = mTranslator != null;
- mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale =
- mTranslator == null ? 1.0f : mTranslator.applicationScale;
- if (panelParentView != null) {
- mAttachInfo.mPanelParentWindowToken
- = panelParentView.getApplicationWindowToken();
- }
- mAdded = true;
- int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
- // Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
- // manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
- // any other events from the system.
- requestLayout();//这里开始请求view的绘制
- if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
- & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
- mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
- }
- try {
- mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
- mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
- collectViewAttributes();
- res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
- getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
- mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
- mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- mAdded = false;
- mView = null;
- mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
- mInputChannel = null;
- mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
- unscheduleTraversals();
- setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
- throw new RuntimeException(“Adding window failed”, e);
- } finally {
- if (restore) {
- attrs.restore();
- }
- }
- ….
- }
- }
- }
/**
* We have one child
*/
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
mAttachInfo.mDisplayState = mDisplay.getState();
mDisplayManager.registerDisplayListener(mDisplayListener, mHandler);
...
mSoftInputMode = attrs.softInputMode;
mWindowAttributesChanged = true;
mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = WindowManager.LayoutParams.EVERYTHING_CHANGED;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = view;
mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired = mTranslator != null;
mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale =
mTranslator == null ? 1.0f : mTranslator.applicationScale;
if (panelParentView != null) {
mAttachInfo.mPanelParentWindowToken
= panelParentView.getApplicationWindowToken();
}
mAdded = true;
int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();//这里开始请求view的绘制
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
....
}
}
}
ViewRootImpl.java
- void scheduleTraversals() {
- if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
- mTraversalScheduled = true;
- mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
- mChoreographer.postCallback(
- Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
- if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
- scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
- }
- notifyRendererOfFramePending();
- pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
- }
- }
- void scheduleTraversals() {
- if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
- mTraversalScheduled = true;
- mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
- mChoreographer.postCallback(
- Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
- if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
- scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
- }
- notifyRendererOfFramePending();
- pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
- }
- }
- final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- doTraversal();
- }
- }
- final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
- void doTraversal() {
- if (mTraversalScheduled) {
- mTraversalScheduled = false;
- mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
- if (mProfile) {
- Debug.startMethodTracing(”ViewAncestor”);
- }
- performTraversals();
- if (mProfile) {
- Debug.stopMethodTracing();
- mProfile = false;
- }
- }
- }
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
if (mProfile) {
Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor");
}
performTraversals();
if (mProfile) {
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
mProfile = false;
}
}
}查看ViewRootImpl.java中的performTraversals()的源码如下:
ViewRootImpl.java中的performTraversals()方法
- private void performTraversals() {
- // cache mView since it is used so much below…
- final View host = mView;
- …
- if (host == null || !mAdded)
- return;
- mIsInTraversal = true;
- mWillDrawSoon = true;
- boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
- boolean newSurface = false;
- boolean surfaceChanged = false;
- WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
- int desiredWindowWidth;
- int desiredWindowHeight;
- final int viewVisibility = getHostVisibility();
- boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
- || mNewSurfaceNeeded;
- WindowManager.LayoutParams params = null;
- if (mWindowAttributesChanged) {
- mWindowAttributesChanged = false;
- surfaceChanged = true;
- params = lp;
- }
- CompatibilityInfo compatibilityInfo = mDisplayAdjustments.getCompatibilityInfo();
- if (compatibilityInfo.supportsScreen() == mLastInCompatMode) {
- params = lp;
- mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
- mLayoutRequested = true;
- if (mLastInCompatMode) {
- params.privateFlags &= ~WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
- mLastInCompatMode = false;
- } else {
- params.privateFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
- mLastInCompatMode = true;
- }
- }
- mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = 0;
- Rect frame = mWinFrame;
- if (mFirst) {
- mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
- mLayoutRequested = true;
- if (lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR_PANEL
- || lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
- // NOTE – system code, won’t try to do compat mode.
- Point size = new Point();
- mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
- desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
- desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
- } else {
- DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
- mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
- desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
- desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
- }
- // We used to use the following condition to choose 32 bits drawing caches:
- // PixelFormat.hasAlpha(lp.format) || lp.format == PixelFormat.RGBX_8888
- // However, windows are now always 32 bits by default, so choose 32 bits
- mAttachInfo.mUse32BitDrawingCache = true;
- mAttachInfo.mHasWindowFocus = false;
- mAttachInfo.mWindowVisibility = viewVisibility;
- mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
- viewVisibilityChanged = false;
- mLastConfiguration.setTo(host.getResources().getConfiguration());
- mLastSystemUiVisibility = mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility;
- // Set the layout direction if it has not been set before (inherit is the default)
- if (mViewLayoutDirectionInitial == View.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_INHERIT) {
- host.setLayoutDirection(mLastConfiguration.getLayoutDirection());
- }
- host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(mAttachInfo, 0);//这里调用了View的dispatchAttachedToWindow,也就是这里回调了onAttachedToWindow方法。
- mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnWindowAttachedChange(true);
- dispatchApplyInsets(host);
- //Log.i(TAG, “Screen on initialized: ” + attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn);
- } else {
- desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
- desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
- if (desiredWindowWidth != mWidth || desiredWindowHeight != mHeight) {
- if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(TAG,
- ”View ” + host + “ resized to: ” + frame);
- mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
- mLayoutRequested = true;
- windowSizeMayChange = true;
- }
- }
- …
- }
private void performTraversals() {
// cache mView since it is used so much below...
final View host = mView;
...
if (host == null || !mAdded)
return;
mIsInTraversal = true;
mWillDrawSoon = true;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
boolean newSurface = false;
boolean surfaceChanged = false;
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
int desiredWindowWidth;
int desiredWindowHeight;
final int viewVisibility = getHostVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
|| mNewSurfaceNeeded;
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = null;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged) {
mWindowAttributesChanged = false;
surfaceChanged = true;
params = lp;
}
CompatibilityInfo compatibilityInfo = mDisplayAdjustments.getCompatibilityInfo();
if (compatibilityInfo.supportsScreen() == mLastInCompatMode) {
params = lp;
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
if (mLastInCompatMode) {
params.privateFlags &= ~WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
mLastInCompatMode = false;
} else {
params.privateFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW;
mLastInCompatMode = true;
}
}
mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = 0;
Rect frame = mWinFrame;
if (mFirst) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
if (lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR_PANEL
|| lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
// NOTE -- system code, won't try to do compat mode.
Point size = new Point();
mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
} else {
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
}
// We used to use the following condition to choose 32 bits drawing caches:
// PixelFormat.hasAlpha(lp.format) || lp.format == PixelFormat.RGBX_8888
// However, windows are now always 32 bits by default, so choose 32 bits
mAttachInfo.mUse32BitDrawingCache = true;
mAttachInfo.mHasWindowFocus = false;
mAttachInfo.mWindowVisibility = viewVisibility;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
viewVisibilityChanged = false;
mLastConfiguration.setTo(host.getResources().getConfiguration());
mLastSystemUiVisibility = mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility;
// Set the layout direction if it has not been set before (inherit is the default)
if (mViewLayoutDirectionInitial == View.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_INHERIT) {
host.setLayoutDirection(mLastConfiguration.getLayoutDirection());
}
host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(mAttachInfo, 0);//这里调用了View的dispatchAttachedToWindow,也就是这里回调了onAttachedToWindow方法。
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnWindowAttachedChange(true);
dispatchApplyInsets(host);
//Log.i(TAG, "Screen on initialized: " + attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn);
} else {
desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
if (desiredWindowWidth != mWidth || desiredWindowHeight != mHeight) {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(TAG,
"View " + host + " resized to: " + frame);
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
...
}
在该方法中调用了host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(mAttachInfo, 0);方法。host是上面传下来的DecodView,该类继承与FrameLayout类,也就是ViewGroup的子类,所以先调用的是ViewGroup中的dispatchAttachedToWindow,其代码如下:
ViewGroup.java
- @Override
- void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
- mGroupFlags |= FLAG_PREVENT_DISPATCH_ATTACHED_TO_WINDOW;
- super.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info, visibility);//这里先调用父类,也就是View的dispathcAttachedToWindow。
- mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_PREVENT_DISPATCH_ATTACHED_TO_WINDOW;
- final int count = mChildrenCount;
- final View[] children = mChildren;
- for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
- final View child = children[i];
- child.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info,
- combineVisibility(visibility, child.getVisibility()));//这里调用子View的<span style=”font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;”>dispatchAttachedToWindow</span>
- }
- final int transientCount = mTransientIndices == null ? 0 : mTransientIndices.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < transientCount; ++i) {
- View view = mTransientViews.get(i);
- view.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info,
- combineVisibility(visibility, view.getVisibility()));
- }
- }
@Override
void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_PREVENT_DISPATCH_ATTACHED_TO_WINDOW;
super.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info, visibility);//这里先调用父类,也就是View的dispathcAttachedToWindow。
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_PREVENT_DISPATCH_ATTACHED_TO_WINDOW;
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
child.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info,
combineVisibility(visibility, child.getVisibility()));//这里调用子View的dispatchAttachedToWindow
}
final int transientCount = mTransientIndices == null ? 0 : mTransientIndices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < transientCount; ++i) {
View view = mTransientViews.get(i);
view.dispatchAttachedToWindow(info,
combineVisibility(visibility, view.getVisibility()));
}
}下面查看对应的View类中的dispatchAttacToWindow。代码如下:
View.java
- void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
- //System.out.println(“Attached! ” + this);
- mAttachInfo = info;
- if (mOverlay != null) {
- mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchAttachedToWindow(info, visibility);
- }
- mWindowAttachCount++;
- // We will need to evaluate the drawable state at least once.
- mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY;
- if (mFloatingTreeObserver != null) {
- info.mTreeObserver.merge(mFloatingTreeObserver);
- mFloatingTreeObserver = null;
- }
- if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER) != 0) {
- mAttachInfo.mScrollContainers.add(this);
- mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED;
- }
- performCollectViewAttributes(mAttachInfo, visibility);
- onAttachedToWindow();//快看,快看,在这里!终于找到这个方法调用的位置了
- ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
- final CopyOnWriteArrayList<OnAttachStateChangeListener> listeners =
- li != null ? li.mOnAttachStateChangeListeners : null;
- if (listeners != null && listeners.size() > 0) {
- // NOTE: because of the use of CopyOnWriteArrayList, we *must* use an iterator to
- // perform the dispatching. The iterator is a safe guard against listeners that
- // could mutate the list by calling the various add/remove methods. This prevents
- // the array from being modified while we iterate it.
- for (OnAttachStateChangeListener listener : listeners) {
- listener.onViewAttachedToWindow(this);//
- }
- }
- int vis = info.mWindowVisibility;
- if (vis != GONE) {
- onWindowVisibilityChanged(vis);
- }
- // Send onVisibilityChanged directly instead of dispatchVisibilityChanged.
- // As all views in the subtree will already receive dispatchAttachedToWindow
- // traversing the subtree again here is not desired.
- onVisibilityChanged(this, visibility);
- if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY) != 0) {
- // If nobody has evaluated the drawable state yet, then do it now.
- refreshDrawableState();
- }
- needGlobalAttributesUpdate(false);
- }
void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
//System.out.println("Attached! " + this);
mAttachInfo = info;
if (mOverlay != null) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchAttachedToWindow(info, visibility);
}
mWindowAttachCount++;
// We will need to evaluate the drawable state at least once.
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY;
if (mFloatingTreeObserver != null) {
info.mTreeObserver.merge(mFloatingTreeObserver);
mFloatingTreeObserver = null;
}
if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER) != 0) {
mAttachInfo.mScrollContainers.add(this);
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED;
}
performCollectViewAttributes(mAttachInfo, visibility);
onAttachedToWindow();//快看,快看,在这里!终于找到这个方法调用的位置了
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
final CopyOnWriteArrayList<OnAttachStateChangeListener> listeners =
li != null ? li.mOnAttachStateChangeListeners : null;
if (listeners != null && listeners.size() > 0) {
// NOTE: because of the use of CopyOnWriteArrayList, we *must* use an iterator to
// perform the dispatching. The iterator is a safe guard against listeners that
// could mutate the list by calling the various add/remove methods. This prevents
// the array from being modified while we iterate it.
for (OnAttachStateChangeListener listener : listeners) {
listener.onViewAttachedToWindow(this);//
}
}
int vis = info.mWindowVisibility;
if (vis != GONE) {
onWindowVisibilityChanged(vis);
}
// Send onVisibilityChanged directly instead of dispatchVisibilityChanged.
// As all views in the subtree will already receive dispatchAttachedToWindow
// traversing the subtree again here is not desired.
onVisibilityChanged(this, visibility);
if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY) != 0) {
// If nobody has evaluated the drawable state yet, then do it now.
refreshDrawableState();
}
needGlobalAttributesUpdate(false);
}好,下面来分析下onDetachedFromWindow方法的调用时机。在onDestory调用前会调用ActivityThread.java中的handleDestroyActivity方法,贴出代码:
ActivityThread.java
- private void handleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing,
- int configChanges, boolean getNonConfigInstance) {
- ActivityClientRecord r = performDestroyActivity(token, finishing,
- configChanges, getNonConfigInstance);
- if (r != null) {
- cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
- WindowManager wm = r.activity.getWindowManager();
- View v = r.activity.mDecor;
- if (v != null) {
- if (r.activity.mVisibleFromServer) {
- mNumVisibleActivities–;
- }
- IBinder wtoken = v.getWindowToken();
- if (r.activity.mWindowAdded) {
- if (r.onlyLocalRequest) {
- // Hold off on removing this until the new activity’s
- // window is being added.
- r.mPendingRemoveWindow = v;
- r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = wm;
- } else {
- wm.removeViewImmediate(v);//看这里,看这里
- }
- }
- if (wtoken != null && r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
- WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().closeAll(wtoken,
- r.activity.getClass().getName(), ”Activity”);
- }
- r.activity.mDecor = null;
- }
- if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
- // If we are delaying the removal of the activity window, then
- // we can’t clean up all windows here. Note that we can’t do
- // so later either, which means any windows that aren’t closed
- // by the app will leak. Well we try to warning them a lot
- // about leaking windows, because that is a bug, so if they are
- // using this recreate facility then they get to live with leaks.
- WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().closeAll(token,
- r.activity.getClass().getName(), ”Activity”);
- }
- // Mocked out contexts won’t be participating in the normal
- // process lifecycle, but if we’re running with a proper
- // ApplicationContext we need to have it tear down things
- // cleanly.
- Context c = r.activity.getBaseContext();
- if (c instanceof ContextImpl) {
- ((ContextImpl) c).scheduleFinalCleanup(
- r.activity.getClass().getName(), ”Activity”);
- }
- }
- if (finishing) {
- try {
- ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityDestroyed(token);
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
- // If the system process has died, it’s game over for everyone.
- }
- }
- mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
- }
private void handleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing,
int configChanges, boolean getNonConfigInstance) {
ActivityClientRecord r = performDestroyActivity(token, finishing,
configChanges, getNonConfigInstance);
if (r != null) {
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
WindowManager wm = r.activity.getWindowManager();
View v = r.activity.mDecor;
if (v != null) {
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromServer) {
mNumVisibleActivities--;
}
IBinder wtoken = v.getWindowToken();
if (r.activity.mWindowAdded) {
if (r.onlyLocalRequest) {
// Hold off on removing this until the new activity's
// window is being added.
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = v;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = wm;
} else {
wm.removeViewImmediate(v);//看这里,看这里
}
}
if (wtoken != null && r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().closeAll(wtoken,
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
r.activity.mDecor = null;
}
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
// If we are delaying the removal of the activity window, then
// we can't clean up all windows here. Note that we can't do
// so later either, which means any windows that aren't closed
// by the app will leak. Well we try to warning them a lot
// about leaking windows, because that is a bug, so if they are
// using this recreate facility then they get to live with leaks.
WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().closeAll(token,
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
// Mocked out contexts won't be participating in the normal
// process lifecycle, but if we're running with a proper
// ApplicationContext we need to have it tear down things
// cleanly.
Context c = r.activity.getBaseContext();
if (c instanceof ContextImpl) {
((ContextImpl) c).scheduleFinalCleanup(
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
}
if (finishing) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityDestroyed(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// If the system process has died, it's game over for everyone.
}
}
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
}
WindowManagerImpl.java
- @Override
- public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
- mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
- }
@Override
public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
}
WindowManagerGlobal.java
- public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) {
- if (view == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(“view must not be null”);
- }
- synchronized (mLock) {
- int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
- View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView();
- removeViewLocked(index, immediate);
- if (curView == view) {
- return;
- }
- throw new IllegalStateException(“Calling with view ” + view
- + ” but the ViewAncestor is attached to ” + curView);
- }
- }
- private void removeViewLocked(int index, boolean immediate) {
- ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
- View view = root.getView();
- if (view != null) {
- InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
- if (imm != null) {
- imm.windowDismissed(mViews.get(index).getWindowToken());
- }
- }
- boolean deferred = root.die(immediate);
- if (view != null) {
- view.assignParent(null);
- if (deferred) {
- mDyingViews.add(view);
- }
- }
- }
public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView();
removeViewLocked(index, immediate);
if (curView == view) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Calling with view " + view
+ " but the ViewAncestor is attached to " + curView);
}
}
private void removeViewLocked(int index, boolean immediate) {
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
View view = root.getView();
if (view != null) {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
if (imm != null) {
imm.windowDismissed(mViews.get(index).getWindowToken());
}
}
boolean deferred = root.die(immediate);
if (view != null) {
view.assignParent(null);
if (deferred) {
mDyingViews.add(view);
}
}
}
ViewRootImpl.java
- /**
- * @param immediate True, do now if not in traversal. False, put on queue and do later.
- * @return True, request has been queued. False, request has been completed.
- */
- boolean die(boolean immediate) {
- // Make sure we do execute immediately if we are in the middle of a traversal or the damage
- // done by dispatchDetachedFromWindow will cause havoc on return.
- if (immediate && !mIsInTraversal) {
- doDie();
- return false;
- }
- if (!mIsDrawing) {
- destroyHardwareRenderer();
- } else {
- Log.e(TAG, ”Attempting to destroy the window while drawing!\n” +
- ” window=” + this + “, title=” + mWindowAttributes.getTitle());
- }
- mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_DIE);
- return true;
- }
- void doDie() {
- checkThread();
- if (LOCAL_LOGV) Log.v(TAG, “DIE in ” + this + “ of ” + mSurface);
- synchronized (this) {
- if (mRemoved) {
- return;
- }
- mRemoved = true;
- if (mAdded) {
- dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//看这里,看这里
- }
- if (mAdded && !mFirst) {
- destroyHardwareRenderer();
- if (mView != null) {
- int viewVisibility = mView.getVisibility();
- boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility;
- if (mWindowAttributesChanged || viewVisibilityChanged) {
- // If layout params have been changed, first give them
- // to the window manager to make sure it has the correct
- // animation info.
- try {
- if ((relayoutWindow(mWindowAttributes, viewVisibility, false)
- & WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_FIRST_TIME) != 0) {
- mWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow);
- }
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- }
- mSurface.release();
- }
- }
- mAdded = false;
- }
- WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().doRemoveView(this);
- }
/**
* @param immediate True, do now if not in traversal. False, put on queue and do later.
* @return True, request has been queued. False, request has been completed.
*/
boolean die(boolean immediate) {
// Make sure we do execute immediately if we are in the middle of a traversal or the damage
// done by dispatchDetachedFromWindow will cause havoc on return.
if (immediate && !mIsInTraversal) {
doDie();
return false;
}
if (!mIsDrawing) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Attempting to destroy the window while drawing!\n" +
" window=" + this + ", title=" + mWindowAttributes.getTitle());
}
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_DIE);
return true;
}
void doDie() {
checkThread();
if (LOCAL_LOGV) Log.v(TAG, "DIE in " + this + " of " + mSurface);
synchronized (this) {
if (mRemoved) {
return;
}
mRemoved = true;
if (mAdded) {
dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//看这里,看这里
}
if (mAdded && !mFirst) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
if (mView != null) {
int viewVisibility = mView.getVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged || viewVisibilityChanged) {
// If layout params have been changed, first give them
// to the window manager to make sure it has the correct
// animation info.
try {
if ((relayoutWindow(mWindowAttributes, viewVisibility, false)
& WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_FIRST_TIME) != 0) {
mWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
mSurface.release();
}
}
mAdded = false;
}
WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().doRemoveView(this);
}ViewRootImpl.java
- void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
- if (mView != null && mView.mAttachInfo != null) {
- mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnWindowAttachedChange(false);
- mView.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//看这里,看这里
- }
- mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager.ensureNoConnection();
- mAccessibilityManager.removeAccessibilityStateChangeListener(
- mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager);
- mAccessibilityManager.removeHighTextContrastStateChangeListener(
- mHighContrastTextManager);
- removeSendWindowContentChangedCallback();
- destroyHardwareRenderer();
- setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
- mView.assignParent(null);
- mView = null;
- mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
- mSurface.release();
- if (mInputQueueCallback != null && mInputQueue != null) {
- mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueDestroyed(mInputQueue);
- mInputQueue.dispose();
- mInputQueueCallback = null;
- mInputQueue = null;
- }
- if (mInputEventReceiver != null) {
- mInputEventReceiver.dispose();
- mInputEventReceiver = null;
- }
- try {
- mWindowSession.remove(mWindow);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- // Dispose the input channel after removing the window so the Window Manager
- // doesn’t interpret the input channel being closed as an abnormal termination.
- if (mInputChannel != null) {
- mInputChannel.dispose();
- mInputChannel = null;
- }
- mDisplayManager.unregisterDisplayListener(mDisplayListener);
- unscheduleTraversals();
- }
void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
if (mView != null && mView.mAttachInfo != null) {
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnWindowAttachedChange(false);
mView.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//看这里,看这里
}
mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager.ensureNoConnection();
mAccessibilityManager.removeAccessibilityStateChangeListener(
mAccessibilityInteractionConnectionManager);
mAccessibilityManager.removeHighTextContrastStateChangeListener(
mHighContrastTextManager);
removeSendWindowContentChangedCallback();
destroyHardwareRenderer();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
mView.assignParent(null);
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mSurface.release();
if (mInputQueueCallback != null && mInputQueue != null) {
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueDestroyed(mInputQueue);
mInputQueue.dispose();
mInputQueueCallback = null;
mInputQueue = null;
}
if (mInputEventReceiver != null) {
mInputEventReceiver.dispose();
mInputEventReceiver = null;
}
try {
mWindowSession.remove(mWindow);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
// Dispose the input channel after removing the window so the Window Manager
// doesn't interpret the input channel being closed as an abnormal termination.
if (mInputChannel != null) {
mInputChannel.dispose();
mInputChannel = null;
}
mDisplayManager.unregisterDisplayListener(mDisplayListener);
unscheduleTraversals();
}ViewGroup.java
- @Override
- void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
- // If we still have a touch target, we are still in the process of
- // dispatching motion events to a child; we need to get rid of that
- // child to avoid dispatching events to it after the window is torn
- // down. To make sure we keep the child in a consistent state, we
- // first send it an ACTION_CANCEL motion event.
- cancelAndClearTouchTargets(null);
- // Similarly, set ACTION_EXIT to all hover targets and clear them.
- exitHoverTargets();
- // In case view is detached while transition is running
- mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = false;
- // Tear down our drag tracking
- mDragNotifiedChildren = null;
- if (mCurrentDrag != null) {
- mCurrentDrag.recycle();
- mCurrentDrag = null;
- }
- final int count = mChildrenCount;
- final View[] children = mChildren;
- for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
- children[i].dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//这里会先调子类的dispatchDetachedFromWindow
- }
- clearDisappearingChildren();
- final int transientCount = mTransientViews == null ? 0 : mTransientIndices.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < transientCount; ++i) {
- View view = mTransientViews.get(i);
- view.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
- }
- super.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//然后这里才调用自己的。
- }
@Override
void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
// If we still have a touch target, we are still in the process of
// dispatching motion events to a child; we need to get rid of that
// child to avoid dispatching events to it after the window is torn
// down. To make sure we keep the child in a consistent state, we
// first send it an ACTION_CANCEL motion event.
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(null);
// Similarly, set ACTION_EXIT to all hover targets and clear them.
exitHoverTargets();
// In case view is detached while transition is running
mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = false;
// Tear down our drag tracking
mDragNotifiedChildren = null;
if (mCurrentDrag != null) {
mCurrentDrag.recycle();
mCurrentDrag = null;
}
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
children[i].dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//这里会先调子类的dispatchDetachedFromWindow
}
clearDisappearingChildren();
final int transientCount = mTransientViews == null ? 0 : mTransientIndices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < transientCount; ++i) {
View view = mTransientViews.get(i);
view.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
}
super.dispatchDetachedFromWindow();//然后这里才调用自己的。
}View.java
- void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
- AttachInfo info = mAttachInfo;
- if (info != null) {
- int vis = info.mWindowVisibility;
- if (vis != GONE) {
- onWindowVisibilityChanged(GONE);
- }
- }
- onDetachedFromWindow();//绕了一大圈,还是找到你了。快看快看,揪出来了。
- onDetachedFromWindowInternal();
- InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
- if (imm != null) {
- imm.onViewDetachedFromWindow(this);
- }
- ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
- final CopyOnWriteArrayList<OnAttachStateChangeListener> listeners =
- li != null ? li.mOnAttachStateChangeListeners : null;
- if (listeners != null && listeners.size() > 0) {
- // NOTE: because of the use of CopyOnWriteArrayList, we *must* use an iterator to
- // perform the dispatching. The iterator is a safe guard against listeners that
- // could mutate the list by calling the various add/remove methods. This prevents
- // the array from being modified while we iterate it.
- for (OnAttachStateChangeListener listener : listeners) {
- listener.onViewDetachedFromWindow(this);
- }
- }
- if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED) != 0) {
- mAttachInfo.mScrollContainers.remove(this);
- mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED;
- }
- mAttachInfo = null;
- if (mOverlay != null) {
- mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
- }
- }
void dispatchDetachedFromWindow() {
AttachInfo info = mAttachInfo;
if (info != null) {
int vis = info.mWindowVisibility;
if (vis != GONE) {
onWindowVisibilityChanged(GONE);
}
}
onDetachedFromWindow();//绕了一大圈,还是找到你了。快看快看,揪出来了。
onDetachedFromWindowInternal();
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (imm != null) {
imm.onViewDetachedFromWindow(this);
}
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
final CopyOnWriteArrayList<OnAttachStateChangeListener> listeners =
li != null ? li.mOnAttachStateChangeListeners : null;
if (listeners != null && listeners.size() > 0) {
// NOTE: because of the use of CopyOnWriteArrayList, we *must* use an iterator to
// perform the dispatching. The iterator is a safe guard against listeners that
// could mutate the list by calling the various add/remove methods. This prevents
// the array from being modified while we iterate it.
for (OnAttachStateChangeListener listener : listeners) {
listener.onViewDetachedFromWindow(this);
}
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED) != 0) {
mAttachInfo.mScrollContainers.remove(this);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED;
}
mAttachInfo = null;
if (mOverlay != null) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
}
}这里总结下:
1.onAttachedToWindow调用顺序:ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity->WindowManagerImpl.addView->WindowManagerGlobal.addView->ViewRootImpl.performTraversals->ViewGroup.dispatchAttachedToWindow->View.dispatchAttachedToWindow->onAttachedToWindow
2.onDetachedFromWindow调用顺序:ActivityThread.handleDestroyActivity->WindowManagerImpl.removeViewImmediate->WindowManagerGlobal.removeView->ViewRootImpl.die->ViewRootImpl.doDie->ViewRootImpl.dispatchDetachedFromWindow->ViewGroup.dispatchDetachedFromWindow->View.dispatchDetachedFromWindow->onDetachedToWindow
3.onAttachedToWindow和onDetachedFromWindow的调用与visibility无关。
4.onAttachedToWindow是先调用自己,然后调用儿子View的。onDetachedFromWindow是先调用儿子View的,然后再调用自己的。
























 502
502











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








