1、综述
set是C++STL中众多的Container(容器)之一,用于储存数据并且能从一个数据集合中取出数据,它的每个元素的值必须惟一。set内部通过自建红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树)实现,可以对数据自动排序。构造set集合主要目的是为了快速检索,不可直接去修改键值。
2、set的常见操作
首先,在使用map之前需包含头文件#include<set>,下面简要介绍map的常见操作,详细信息可参见http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/set/
(1)构造函数:
构造函数有多种实现形式,如下举例:
//四种构造函数形式举例
set<int> Myset1;
int Myint[] = {2,4,6,8,10};
set<int> Myset2(Myint,Myint+5);
set<int> Myset3(Myset2);
set<int> Myset4(Myset2.begin(),Myset2.end());(2)插入数据:
for (int i=1; i<=5; ++i) //插入1 2 3 4 5
Myset1.insert(i);
int Myint3[] = {3,6,9,12,15};
Myset3.insert(Myint3,Myint3+5);(3)查找元素:
利用find()方法,find()函数返回一个对应查找值迭代器,如果没找到就返回指向set尾部的迭代器。
set<int>::iterator itr;//迭代器
itr = Myset1.find(3);//查找3
if(itr!= Myset1.end())
cout<<"在Myset1找到元素3!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"在Myset1找不到元素3!"<<endl;(4)元素遍历:
利用迭代器实现,也可以进行逆向遍历。示例如下:
cout<<"\nMyset1中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset1.begin();itr!=Myset1.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<"\nMyset4中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
itr = Myset4.begin();
while(itr != Myset4.end())
cout<<*itr ++ << " ";
//逆向遍历Myset4
cout<<"\nMyset4逆向遍历结果如下:"<<endl;
set<int>::reverse_iterator itr2 = Myset4.rbegin();
while(itr2 != Myset4.rend())
cout<<*itr2++ << " ";
cout<<endl;(5)元素删除:
采用erase()方法实现:
for(int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
Myset3.erase(i*2);
//或者用itr删除,
itr = Myset4.begin();
itr ++;//此时itr指向第二个元素
Myset4.erase(itr);
//删除多个元素
itr = Myset4.find(6);
Myset4.erase(itr,Myset4.end());(6)swap()方法:
实现的是对两个set的整体交换。
Myset1.swap(Myset2);(7)size()方法:
返回set的大小,即元素的个数。
(8)empty()方法
判断map是否为空,若map为空,则返回true。
(9)begin()方法:
返回指向map头部的迭代器
(10)end()方法:
返回指向map尾部的迭代器
(11)clear()方法:
清除整个set的内容
3、常见操作程序示例
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
void test_set()
{
//四种构造函数形式举例
set<int> Myset1;
int Myint2[] = {2,4,6,8,10};
set<int> Myset2(Myint2,Myint2 + 5);
set<int> Myset3(Myset2);
set<int> Myset4(Myset2.begin(),Myset2.end());
//插入数据
for (int i=1; i<=5; ++i) //插入1 2 3 4 5
Myset1.insert(i);
int Myint3[] = {3,15,9,6,12};//尽管数组本身,但插入set之后是有序的,且注意对于重复元素(6)是不能重复插入的
Myset3.insert(Myint3,Myint3+5);
//查找操作
set<int>::iterator itr;//迭代器
itr = Myset1.find(3);//查找2
if(itr!= Myset1.end())
cout<<"在Myset1找到元素3!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"在Myset1找不到元素3!"<<endl;
//元素遍历,两种形式
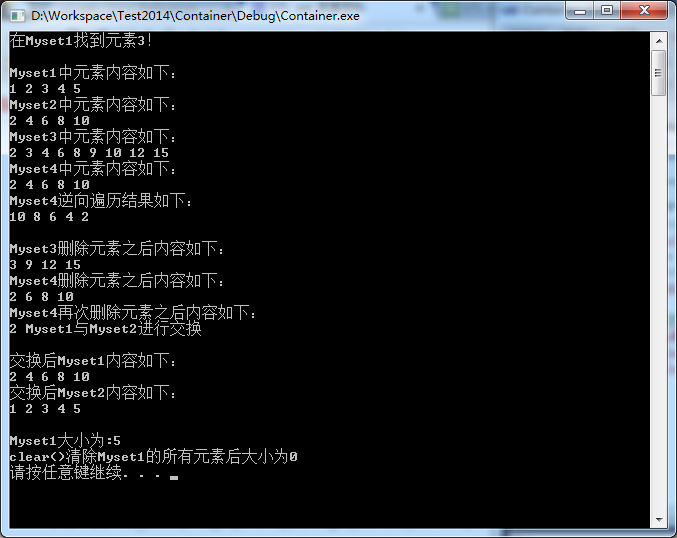
cout<<"\nMyset1中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset1.begin();itr!=Myset1.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<"\nMyset2中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset2.begin();itr!=Myset2.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<"\nMyset3中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset3.begin();itr!=Myset3.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<"\nMyset4中元素内容如下:"<<endl;
itr = Myset4.begin();
while(itr != Myset4.end())
cout<<*itr ++ << " ";
//逆向遍历Myset4
cout<<"\nMyset4逆向遍历结果如下:"<<endl;
set<int>::reverse_iterator itr2 = Myset4.rbegin();
while(itr2 != Myset4.rend())
cout<<*itr2++ << " ";
cout<<endl;
//删除操作
for(int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
Myset3.erase(i*2);
cout<<"\nMyset3删除元素之后内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset3.begin();itr!=Myset3.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
//或者用itr删除,
itr = Myset4.begin();
itr ++;//此时itr指向4
Myset4.erase(itr);
cout<<"\nMyset4删除元素之后内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset4.begin();itr!=Myset4.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
itr = Myset4.find(6);
Myset4.erase(itr,Myset4.end());
cout<<"\nMyset4再次删除元素之后内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset4.begin();itr!=Myset4.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
//交换
Myset1.swap(Myset2);
cout<<"Myset1与Myset2进行交换"<<endl;
cout<<"\n交换后Myset1内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset1.begin();itr!=Myset1.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<"\n交换后Myset2内容如下:"<<endl;
for(itr = Myset2.begin();itr!=Myset2.end();itr++)
cout<<*itr<<" ";
cout<<endl;
//清除与求大小
cout<<"\nMyset1大小为:"<<Myset1.size()<<endl;
Myset1.clear();
cout<<"clear()清除Myset1的所有元素后大小为"<<Myset1.size()<<endl;
}






















 5234
5234

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








