优先使用addListener(GenericFutureListener),而非await()或sysn()
优先使用addListener(GenericFutureListener),而非await()或sysn()
优先使用addListener(GenericFutureListener),而非await()或sysn()
重要的事说三遍。哈哈!!!!综述
ChannelFuture的作用是用来保存Channel异步操作的结果。
我们知道,在Netty中所有的I/O操作都是异步的。这意味着任何的I/O调用都将立即返回,而不保证这些被请求的I/O操作在调用结束的时候已经完成。取而代之地,你会得到一个返回的ChannelFuture实例,这个实例将给你一些关于I/O操作结果或者状态的信息。
对于一个ChannelFuture可能已经完成,也可能未完成。当一个I/O操作开始的时候,一个新的future对象就会被创建。在开始的时候,新的future是未完成的状态--它既非成功、失败,也非被取消,因为I/O操作还没有结束。如果I/O操作以成功、失败或者被取消中的任何一种状态结束了,那么这个future将会被标记为已完成,并包含更多详细的信息(例如:失败的原因)。请注意,即使是失败和被取消的状态,也是属于已完成的状态。
下面这张图来自于官方文档,用于说明各种状态的关系:
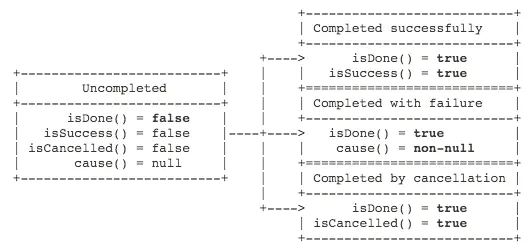
各种各样的方法被提供,用来检查I/O操作是否已完成、等待完成,并寻回I/O操作的结果。它同样允许你添加ChannelFutureListener,以便于在I/O操作完成的时候,你能够获得通知。
优先使用addListener(GenericFutureListener),而非await()
当做了一个I/O操作并有任何后续任务的时候,推荐优先使用addListener(GenericFutureListener)的方式来获得通知,而非await()。
addListener(GenericFutureListener)是非阻塞的。它会把特定的ChannelFutureListener添加到ChannelFuture中,然后I/O线程会在I/O操作相关的future完成的时候通知监听器。ChannelFutureListener会利于最佳的性能和资源的利用,因为它一点阻塞都没有。然而,如果你不使用基于事件驱动的编程方式,去实现一个后续式的逻辑会变得诡异和难于理解。
对比来看,await()是一个阻塞的操作。一旦被调用,调用者线程会阻塞,直到操作完成。使用await()来实现一个后续式的逻辑会更容易,但是调用者线程会非常没必要的阻塞直到I/O操作完成,并且内部的线程通知是相对来说代价昂贵的。更有甚者,在一些特定的情况下会产生死锁,下面是对这种情况的描述:
// BAD - NEVER DO THIS
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GoodByeMessage msg) {
ChannelFuture future = ctx.channel().close();
future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// Perform post-closure operation
// ...
}
// GOOD
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, GoodByeMessage msg) {
ChannelFuture future = ctx.channel().close();
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
// Perform post-closure operation
// ...
}
});
}撇开上面提到的缺点不谈,确实还是有一些情况在调用await()的时候会更方便的。在这种情况下,请确保你不是在一个I/O线程中调用的await()。否则,为了避免死锁的情况,BlockingOperationException将被提出。
不要混淆I/O timeout和await timeout
你在使用Future.await(long), Future.await(long, TimeUnit),Future.awaitUninterruptibly(long),或者Future.awaitUninterruptibly(long, TimeUnit)的时候,指定的timeout的值和I/O timeout一点关系都没有。如果一个操作超时了,future将会被标记为已完成-失败,就像上面的图中描述的那样。例如,连接超时应当通过一个传输特定的选项来配置:
// BAD - NEVER DO THIS
Bootstrap b = ...;
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(...);
f.awaitUninterruptibly(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (f.isCancelled()) {
// Connection attempt cancelled by user
} else if (!f.isSuccess()) {
// You might get a NullPointerException here because the future
// might not be completed yet.
f.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
// Connection established successfully
}
// GOOD
Bootstrap b = ...;
// Configure the connect timeout option.
b.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 10000);
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(...);
f.awaitUninterruptibly();
// Now we are sure the future is completed.
assert f.isDone();
if (f.isCancelled()) {
// Connection attempt cancelled by user
} else if (!f.isSuccess()) {
f.cause().printStackTrace();
} else {
// Connection established successfully
}























 327
327

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








