前提:已经在linux中安装好MuJS,MuJS安装比较简单,参考安装包中的readme文件
本章介绍的环境:vm+centos6.5 32bit
官网示例链接:http://dev.mujs.com/docs/examples.html
示例1
A stand-alone interpreter
interpreter.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mujs.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char line[256];
int ret;
//js_State *J = js_newstate(NULL, NULL, 0);
js_State *J = js_newstate(NULL, NULL, JS_STRICT);
//printf("JS_STRICT:%d\n", JS_STRICT);
while(fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin))
{
ret=js_dostring(J, line);
//printf("dostring ret:%d\n", ret);
}
js_freestate(J);
return 0;
}
标题:一个独立的解释器
功能:借助mujs的库用C实现的一个javascript脚本解释器;编译和运行由标准输入得到的js脚本命令,如果脚本有错误,则返回错误信息。
下面是编译操作,我这里加上了g选项用于gdb调试
执行结果如下
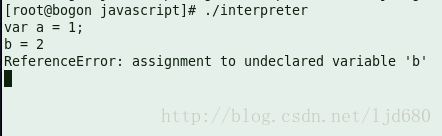
输入var a = 1; 回车系统执行成功,未报异常;输入b=2则返回异常,提示b变量未定义。在一般的javascript模式下定义变量不带var是可以的,但在strict严格模式下不带var是不允许的。
在mujs.h中找到JS_STRICT的宏定义,flag标记只有一个值
/* State constructor flags */
enum {
JS_STRICT = 1,
};下面做个尝试,将flag设置为0 ,即执行代码
js_State *J = js_newstate(NULL, NULL, 0);编译后,我们可以看到在终端中输入b=0时就没有上报异常了。
我们结合前一篇参考手册中js_dostring函数的说明来看
函数原型
int js_dostring(js_State *J, const char *source);
// J为js_State指针,与c进行交互的关键集合,需要先进行创建,
// source为javascript脚本,字符串格式。
// 如果发生错误,调用report上报异常,并返回1; 返回0表示成功。所以放开interpreter.c中的注释,可以看到执行成功时ret的值为0,失败时为1。
下面我们重点看看js_State结构体,这个太重要了,javascript和c的互相作用就靠它了,在文件jsi.h中可以找到定义。
/* State struct */
struct js_State
{
void *actx;
void *uctx;
js_Alloc alloc;
js_Report report;
js_Panic panic;
js_StringNode *strings;
int default_strict;
int strict;
......
......
int nextref; /* for js_ref use */
js_Object *R; /* registry of hidden values */
js_Object *G; /* the global object */
js_Environment *E; /* current environment scope */
js_Environment *GE; /* global environment scope (at the root) */
/* execution stack */
int top, bot;
js_Value *stack;
/* garbage collector list */
int gcmark;
int gccounter;
js_Environment *gcenv;
js_Function *gcfun;
js_Object *gcobj;
js_String *gcstr;
/* environments on the call stack but currently not in scope */
int envtop;
js_Environment *envstack[JS_ENVLIMIT];
/* debug info stack trace */
int tracetop;
js_StackTrace trace[JS_ENVLIMIT];
/* exception stack */
int trytop;
js_Jumpbuf trybuf[JS_TRYLIMIT]; //异常跟踪 jump_buf类型,被setjmp调用。
};
结构体中的注释已经很清楚了,里面stack有:
1.execution stack
2.environments on the call stack but currently not in scope
3.debug info stack trace
4.exception stack
示例2
Hello, world!
hello.c
//Hello, world!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mujs.h>
static void hello(js_State *J)
{
const char *name = js_tostring(J, 1);
printf("Hello, %s!\n", name);
js_pushundefined(J);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
js_State *J = js_newstate(NULL, NULL, JS_STRICT);
js_newcfunction(J, hello, "hello", 1);
js_setglobal(J, "hello"); //设置为全局变量
js_dostring(J, "hello('world');"); // 调用javascript
js_freestate(J); // 释放J
}执行结果为:
Hello world!
基本的逻辑如下图,hello函数是自定义的函数,用c语言实现,并封装为“js_CFunction”类型。javascript脚本通过js_newcfunction创建(注册)hello函数。然后c主程序调用js_dostring函数加载js脚本,在脚本中hello(‘world)’就是完成对hello函数的调用,带入的’world’为传入参数。
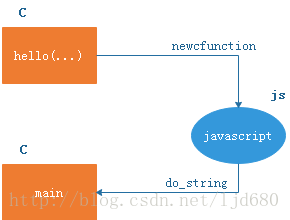
我们逐行代码解读,在进入到函数内部是,点到为止,不再深入。
首先看看hello函数
// 函数定义遵循js_CFunction的函数指针定义
// 在mujs中js_CFunction的定义为
// typedef void (*js_CFunction)(js_State *J);
static void hello(js_State *J)
{
// 从J->stack的1位置获取参数1,本例只有1个参数,且参数类型为
// string,所以调用js_tostring(J, 1)
const char *name = js_tostring(J, 1);
printf("Hello, %s!\n", name);
js_pushundefined(J); // 无返回值,压入undefined补全
}typedef 







 本文详细解析了MuJS官网的多个示例,包括如何使用MuJS库构建JavaScript解释器,理解JS_State结构体的重要性,以及C到JS回调函数的工作原理。通过示例代码和执行结果,阐述了变量定义、对象操作、配置文件读取和回调函数的实现细节。
本文详细解析了MuJS官网的多个示例,包括如何使用MuJS库构建JavaScript解释器,理解JS_State结构体的重要性,以及C到JS回调函数的工作原理。通过示例代码和执行结果,阐述了变量定义、对象操作、配置文件读取和回调函数的实现细节。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








