import java.util.*;
/*
Set:无序,不可以重复元素。
|--HashSet:数据结构是哈希表。线程是非同步的。
保证元素唯一性的原理:判断元素的hashCode值是否相同。
如果相同,还会继续判断元素的equals方法,是否为true。
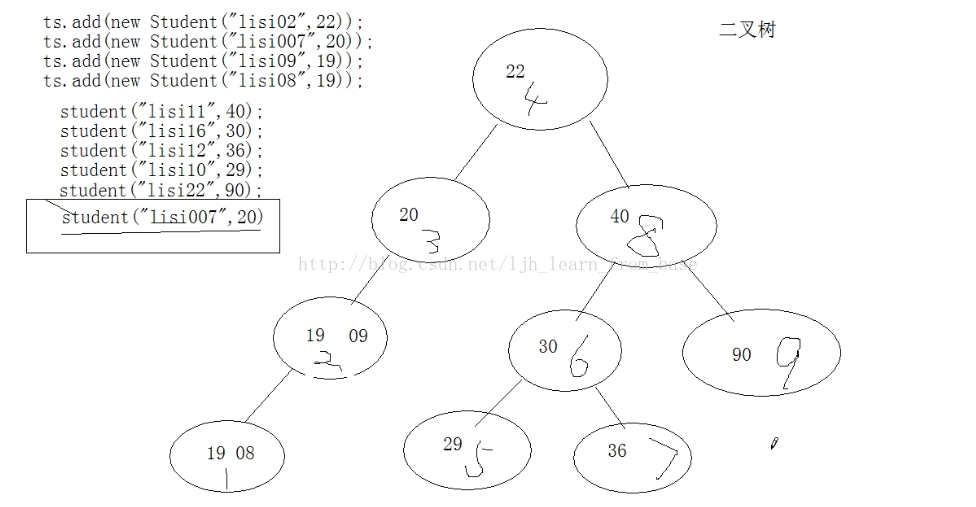
|--TreeSet:可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序。
底层数据结构是二叉树。
TreeSet排序时只看compareTo方法或者compare方法
保证元素唯一性的依据:
compareTo方法return 0.
TreeSet排序的第一种方式:让元素自身具备比较性。
元素需要实现Comparable接口,覆盖compareTo方法。
也种方式也成为元素的自然顺序,或者叫做默认顺序。
TreeSet的第二种排序方式。
当元素自身不具备比较性时,或者具备的比较性不是所需要的。
这时就需要让集合自身具备比较性。
在集合初始化时,就有了比较方式。TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator)
需求:
往TreeSet集合中存储自定义对象学生。
想按照学生的年龄进行排序。
记住,排序时,当主要条件相同时,一定判断一下次要条件。
*/
/*
当元素自身不具备比较性,或者具备的比较性不是所需要的。
这时需要让容器自身具备比较性。
定义了比较器,将比较器对象作为参数传递给TreeSet集合的构造函数。
当两种排序都存在时,以比较器为主。
定义一个类,实现Comparator接口,覆盖compare方法。
*/
class Student implements Comparable<Student>// 该接口强制让学生具备比较性。
{
private String name;
private int age;
Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int compareTo(Student obj) {
// return 0;
if (!(obj instanceof Student))
throw new RuntimeException("不是学生对象");
Student s = (Student) obj;
// System.out.println(this.name+"....compareto....."+s.name);
if (this.age > s.age)
return 1;
if (this.age == s.age) {
return this.name.compareTo(s.name);
}
return -1;
/**/
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
class TreeSetDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<>();
ts.add(new Student("lisi02", 22));
ts.add(new Student("lisi02", 21));
ts.add(new Student("lisi007", 20));
ts.add(new Student("lisi09", 19));
ts.add(new Student("lisi06", 18));
ts.add(new Student("lisi06", 18));
ts.add(new Student("lisi007", 29));
// ts.add(new Student("lisi007",20));
// ts.add(new Student("lisi01",40));
//jdk1.8新语法
ts.forEach((stu) -> {
System.out.println(stu.getName() + "..." + stu.getAge());
});
}
}
class MyCompare implements Comparator<Student> {
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num = s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
if (num == 0) {
//将基本数据类型封装成其包装类,基本数据类型和其包装类紧密相关
return new Integer(s1.getAge()).compareTo(new Integer(s2.getAge()));
/*
* if(s1.getAge()>s2.getAge())
* return 1;
* if(s1.getAge()==s2.getAge())
* return 0;
* return -1;
*/
}
return num;
}
}
























 558
558

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








