遗传算法的具体已在前面的文章进行阐述,在此补充一个例子进行说明。
求函数极大值
F(X) = X[1]^2 - X[1]*X[2] + X[3]
其中
0 <= X[1] <= 5
0 <= X[2] <= 5
-2 <= X[3] <= 2
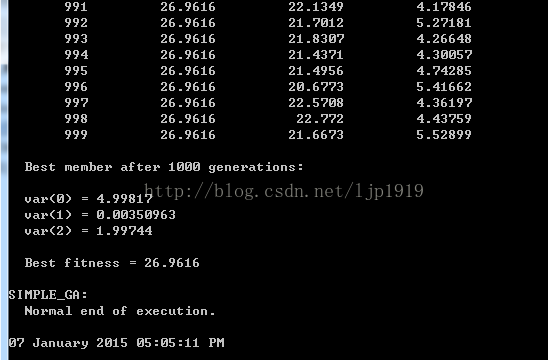
正解为[5,0,2]。
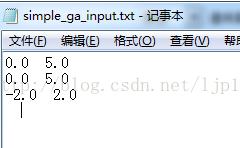
txt文本中的内容截图如下:
所表示的是各个变量的取值范围。第一列为所取的最小值,第二列为所取的最大值;每一行对应一个变量。
代码如下所示:
# include <cstdlib>
#include <stdio.h>
# include <iostream>
# include <iomanip>
# include <fstream>
# include <iomanip>
# include <math.h>
# include <ctime>
# include <cstring>
using namespace std;
// MAXGENS is the maximum number of generations.
// NVARS is the number of problem variables.
// PMUTATION is the probability of mutation.
// POPSIZE is the population size.
// PXOVER is the probability of crossover.
# define POPSIZE 50//种群内个体数量
# define MAXGENS 1000//最大的迭代次数
# define NVARS 3//变量个数,即用以表示基因型的bit数
# define PXOVER 0.8//交换率
# define PMUTATION 0.15//突变率
//
// Each GENOTYPE is a member of the population, with
// gene: a string of variables,
// fitness: the fitness
// upper: the variable upper bounds,
// lower: the variable lower bounds,
// rfitness: the relative fitness,
// cfitness: the cumulative fitness.
//
struct genotype
{
double gene[NVARS];
double fitness;
double upper[NVARS];
double lower[NVARS];
double rfitness;
double cfitness;
};
struct genotype population[POPSIZE+1];
struct genotype newpopulation[POPSIZE+1];
int main ( );
void crossover ( int &seed );//交叉操作。selects two parents for the single point crossover
void elitist ( );//stores the best member of the previous generation
void evaluate ( );//implements the user-defined valuation function
int i4_uniform_ab ( int a, int b, int &seed );//returns a scaled pseudorandom I4 between A and B
int Int_uniform_ab(int a, int b);//my own function to get a value between "a" and "b"
void initialize ( string filename, int &seed );//initializes the genes within the variables bounds
void keep_the_best ( );//keeps track of the best member of the population
void mutate ( int &seed );//performs a random uniform mutation
double r8_uniform_ab ( double a, double b, int &seed );//returns a scaled pseudorandom R8
double Dou_uniform_ab(double a, double b);//return a double value between "a" and "b"
void report ( int generation );//reports progress of the simulation
void selector ( int &seed );// is the selection function
double round(double number);//returns the integral value that is nearest to x, with halfway cases rounded away from zero
void timestamp ( );//prints the current YMDHMS date as a time stamp
void Xover ( int one, int two, int &seed );//performs crossover of the two selected parents
//****************************************************************************80
int main ( )
// Discussion:
//
// Each generation involves selecting the best
// members, performing crossover & mutation and then
// evaluating the resulting population, until the terminating
// condition is satisfied
//
// This is a simple genetic algorithm implementation where the
// evaluation function takes positive values only and the
// fitness of an individual is the same as the value of the
// objective function.
{
string filename = "simple_ga_input.txt";
int generation;
int i;
int seed;
timestamp ( );
cout << "\n";
cout << "SIMPLE_GA:\n";
cout << " C++ version\n";
cout << " A simple example of a genetic algorithm.\n";
if ( NVARS < 2 )
{
cout << "\n";
cout << " The crossover modification will not be available,\n";
cout << " since it requires 2 <= NVARS.\n";
}
seed = 123456789;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
initialize ( filename, seed );
evaluate ( );
keep_the_best ( );
for ( generation = 0; generation < MAXGENS; generation++ )
{
selector ( seed );
crossover ( seed );
mutate ( seed );
report ( generation );
evaluate ( );
elitist ( );
}
cout << "\n";
cout << " Best member after " << MAXGENS << " generations:\n";
cout << "\n";
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
cout << " var(" << i << ") = " << population[POPSIZE].gene[i] << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
cout << " Best fitness = " << population[POPSIZE].fitness << "\n";
//
// Terminate.
//
cout << "\n";
cout << "SIMPLE_GA:\n";
cout << " Normal end of execution.\n";
cout << "\n";
timestamp ( );
return 0;
}
//****************************************************************************80
void crossover ( int &seed )
// CROSSOVER selects two parents for the single point crossover.
// Local parameters:
//
// Local, int FIRST, is a count of the number of members chosen.
//
// Parameters:
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, a seed for the random number generator.
//
{
const double a = 0.0;
const double b = 1.0;
int mem;
int one;
int first = 0;
double x;
for ( mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; ++mem )
{
//x = r8_uniform_ab ( a, b, seed );
x = Dou_uniform_ab( a, b);
if ( x < PXOVER )
{
++first;
if ( first % 2 == 0 )
{
Xover ( one, mem, seed );
}
else
{
one = mem;
}
}
}
return;
}
void elitist ( )
// ELITIST stores the best member of the previous generation.
//
// Discussion:
//
// The best member of the previous generation is stored as
// the last in the array. If the best member of the current
// generation is worse then the best member of the previous
// generation, the latter one would replace the worst member
// of the current population.
// Local parameters:
//
// Local, double BEST, the best fitness value.
//
// Local, double WORST, the worst fitness value.
//
{
int i;
double best;
int best_mem;
double worst;
int worst_mem;
best = population[0].fitness;
worst = population[0].fitness;
for ( i = 0; i < POPSIZE - 1; ++i )
{
if ( population[i+1].fitness < population[i].fitness )
{
if ( best <= population[i].fitness )
{
best = population[i].fitness;
best_mem = i;
}
if ( population[i+1].fitness <= worst )
{
worst = population[i+1].fitness;
worst_mem = i + 1;
}
}
else
{
if ( population[i].fitness <= worst )
{
worst = population[i].fitness;
worst_mem = i;
}
if ( best <= population[i+1].fitness )
{
best = population[i+1].fitness;
best_mem = i + 1;
}
}
}
//
// If the best individual from the new population is better than
// the best individual from the previous population, then
// copy the best from the new population; else replace the
// worst individual from the current population with the
// best one from the previous generation
//
if ( population[POPSIZE].fitness <= best )
{
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
population[POPSIZE].gene[i] = population[best_mem].gene[i];
}
population[POPSIZE].fitness = population[best_mem].fitness;
}
else
{
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
population[worst_mem].gene[i] = population[POPSIZE].gene[i];
}
population[worst_mem].fitness = population[POPSIZE].fitness;
}
return;
}
void evaluate ( )
// EVALUATE implements the user-defined valuation function
// Discussion:
//
// Each time this is changed, the code has to be recompiled.
// The current function is: x[1]^2-x[1]*x[2]+x[3]
{
int member;
int i;
double x[NVARS+1];
for ( member = 0; member < POPSIZE; member++ )
{
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
x[i+1] = population[member].gene[i];
}
population[member].fitness = ( x[1] * x[1] ) - ( x[1] * x[2] ) + x[3];
}
return;
}
int i4_uniform_ab ( int a, int b, int &seed )
// I4_UNIFORM_AB returns a scaled pseudorandom I4 between A and B.
//
// Discussion:
//
// The pseudorandom number should be uniformly distributed
// between A and B.
// Parameters:
//
// Input, int A, B, the limits of the interval.
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, the "seed" value, which should NOT be 0.
// On output, SEED has been updated.
//
// Output, int I4_UNIFORM, a number between A and B.
//
{
int c;
const int i4_huge = 2147483647;
int k;
float r;
int value;
if ( seed == 0 )
{
cerr << "\n";
cerr << "I4_UNIFORM_AB - Fatal error!\n";
cerr << " Input value of SEED = 0.\n";
exit ( 1 );
}
//
// Guarantee A <= B.
//
if ( b < a )
{
c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
k = seed / 127773;
seed = 16807 * ( seed - k * 127773 ) - k * 2836;
if ( seed < 0 )
{
seed = seed + i4_huge;
}
r = ( float ) ( seed ) * 4.656612875E-10;
//
// Scale R to lie between A-0.5 and B+0.5.
//
r = ( 1.0 - r ) * ( ( float ) a - 0.5 )
+ r * ( ( float ) b + 0.5 );
//
// Use rounding to convert R to an integer between A and B.
//Returns the integral value that is nearest to x
value = round ( r );//Vs2008中并没有此函数,需要自己实现。是最近取整
//
// Guarantee A <= VALUE <= B.
//
if ( value < a )
{
value = a;
}
if ( b < value )
{
value = b;
}
return value;
}
//my new design function of the distribution
int Int_uniform_ab(int a, int b)
{ int tmp;
tmp = (rand() % (b-a+1))+ a;
return tmp;
}
//****************************************************************************80
void initialize ( string filename, int &seed )
// INITIALIZE initializes the genes within the variables bounds.
//
// Discussion:
//
// It also initializes (to zero) all fitness values for each
// member of the population. It reads upper and lower bounds
// of each variable from the input file `gadata.txt'. It
// randomly generates values between these bounds for each
// gene of each genotype in the population. The format of
// the input file `gadata.txt' is
// var1_lower_bound var1_upper bound
// var2_lower_bound var2_upper bound ...
// Parameters:
// Input, string FILENAME, the name of the input file.
// Input/output, int &SEED, a seed for the random number generator.
{
int i;
ifstream input;
int j;
double lbound;
double ubound;
input.open ( filename.c_str ( ) );
if ( !input )
{
cerr << "\n";
cerr << "INITIALIZE - Fatal error!\n";
cerr << " Cannot open the input file!\n";
exit ( 1 );
}
//
// Initialize variables within the bounds
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
input >> lbound >> ubound;
for ( j = 0; j < POPSIZE; j++ )
{
population[j].fitness = 0;
population[j].rfitness = 0;
population[j].cfitness = 0;
population[j].lower[i] = lbound;
population[j].upper[i]= ubound;
//population[j].gene[i] = r8_uniform_ab ( lbound, ubound, seed );
population[j].gene[i] = Dou_uniform_ab( lbound, ubound );
}
}
input.close ( );
return;
}
//****************************************************************************80
void keep_the_best ( )
// KEEP_THE_BEST keeps track of the best member of the population.
//
// Discussion:
//
// Note that the last entry in the array Population holds a
// copy of the best individual.
//
// Local parameters:
//
// Local, int CUR_BEST, the index of the best individual.
//
{
int cur_best;
int mem;
int i;
cur_best = 0;
for ( mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++ )
{
if ( population[POPSIZE].fitness < population[mem].fitness )
{
cur_best = mem;
population[POPSIZE].fitness = population[mem].fitness;
}
}
//
// Once the best member in the population is found, copy the genes.
//
for ( i = 0; i < NVARS; i++ )
{
population[POPSIZE].gene[i] = population[cur_best].gene[i];
}
return;
}
//****************************************************************************80
void mutate ( int &seed )
//
// MUTATE performs a random uniform mutation.
//
// Discussion:
//
// A variable selected for mutation is replaced by a random value
// between the lower and upper bounds of this variable.
// Parameters:
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, a seed for the random number generator.
//
{
const double a = 0.0;
const double b = 1.0;
int i;
int j;
double lbound;
double ubound;
double x;
for ( i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++ )
{
for ( j = 0; j < NVARS; j++ )
{
//x = r8_uniform_ab ( a, b, seed );
x = Dou_uniform_ab( a, b);
if ( x < PMUTATION )
{
lbound = population[i].lower[j];
ubound = population[i].upper[j];
//population[i].gene[j] = r8_uniform_ab ( lbound, ubound, seed );
population[i].gene[j] = Dou_uniform_ab( lbound, ubound );
}
}
}
return;
}
//****************************************************************************80
double r8_uniform_ab ( double a, double b, int &seed )
// R8_UNIFORM_AB returns a scaled pseudorandom R8.
//
// Discussion:
//
// The pseudorandom number should be uniformly distributed
// between A and B.
//
// Parameters:
//
// Input, double A, B, the limits of the interval.
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, the "seed" value, which should NOT be 0.
// On output, SEED has been updated.
//
// Output, double R8_UNIFORM_AB, a number strictly between A and B.
//
{
int i4_huge = 2147483647;
int k;
double value;
if ( seed == 0 )
{
cerr << "\n";
cerr << "R8_UNIFORM_AB - Fatal error!\n";
cerr << " Input value of SEED = 0.\n";
exit ( 1 );
}
k = seed / 127773;
seed = 16807 * ( seed - k * 127773 ) - k * 2836;
if ( seed < 0 )
{
seed = seed + i4_huge;
}
value = ( double ) ( seed ) * 4.656612875E-10;
value = a + ( b - a ) * value;
return value;
}
// my new function of product a value between "a" and "b"
double Dou_uniform_ab(double a, double b)
{
double tmp;
//rand() / double(RAND_MAX)可以生成0~1之间的浮点数
tmp = a + static_cast<double>(rand())/RAND_MAX*(b-a);
return tmp;
}
void report ( int generation )
// REPORT reports progress of the simulation.
// Local parameters:
//
// Local, double avg, the average population fitness.
//
// Local, best_val, the best population fitness.
//
// Local, double square_sum, square of sum for std calc.
//
// Local, double stddev, standard deviation of population fitness.
//
// Local, double sum, the total population fitness.
//
// Local, double sum_square, sum of squares for std calc.
//
{
double avg;
double best_val;
int i;
double square_sum;
double stddev;
double sum;
double sum_square;
if ( generation == 0 )
{
cout << "\n";
cout << " Generation Best Average Standard \n";
cout << " number value fitness deviation \n";
cout << "\n";
}
sum = 0.0;
sum_square = 0.0;
for ( i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++ )
{
sum = sum + population[i].fitness;
sum_square = sum_square + population[i].fitness * population[i].fitness;
}
avg = sum / ( double ) POPSIZE;
square_sum = avg * avg * POPSIZE;
stddev = sqrt ( ( sum_square - square_sum ) / ( POPSIZE - 1 ) );
best_val = population[POPSIZE].fitness;
cout << " " << setw(8) << generation
<< " " << setw(14) << best_val
<< " " << setw(14) << avg
<< " " << setw(14) << stddev << "\n";
return;
}
void selector ( int &seed )
// SELECTOR is the selection function.
//
// Discussion:
//
// Standard proportional selection for maximization problems incorporating
// the elitist model. This makes sure that the best member always survives.
// Parameters:
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, a seed for the random number generator.
//
{
const double a = 0.0;
const double b = 1.0;
int i;
int j;
int mem;
double p;
double sum;
//
// Find the total fitness of the population.
//
sum = 0.0;
for ( mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++ )
{
sum = sum + population[mem].fitness;
}
//
// Calculate the relative fitness of each member.
//
for ( mem = 0; mem < POPSIZE; mem++ )
{
population[mem].rfitness = population[mem].fitness / sum;
}
//
// Calculate the cumulative fitness.
//
population[0].cfitness = population[0].rfitness;
for ( mem = 1; mem < POPSIZE; mem++ )
{
population[mem].cfitness = population[mem-1].cfitness +
population[mem].rfitness;
}
//
// Select survivors using cumulative fitness.
//
for ( i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++ )
{
//p = r8_uniform_ab ( a, b, seed );
p = Dou_uniform_ab(a,b);
if ( p < population[0].cfitness )
{
newpopulation[i] = population[0];
}
else
{
for ( j = 0; j < POPSIZE; j++ )
{
if ( population[j].cfitness <= p && p < population[j+1].cfitness )
{
newpopulation[i] = population[j+1];
}
}
}
}
//
// Overwrite the old population with the new one.
//
for ( i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++ )
{
population[i] = newpopulation[i];
}
return;
}
//****************************************************************************80
double round(double number)
{
return number < 0.0 ? ceil(number - 0.5) : floor(number + 0.5);
}
void timestamp ( )
// TIMESTAMP prints the current YMDHMS date as a time stamp.
{
# define TIME_SIZE 40
static char time_buffer[TIME_SIZE];
const struct tm *tm;
size_t len;
time_t now;
now = time ( NULL );
tm = localtime ( &now );
//将时间格式化
len = strftime ( time_buffer, TIME_SIZE, "%d %B %Y %I:%M:%S %p", tm );
cout << time_buffer << "\n";
return;
# undef TIME_SIZE
}
//****************************************************************************80
void Xover ( int one, int two, int &seed )
// XOVER performs crossover of the two selected parents.
// Local parameters:
//
// Local, int point, the crossover point.
//
// Parameters:
//
// Input, int ONE, TWO, the indices of the two parents.
//
// Input/output, int &SEED, a seed for the random number generator.
//
{
int i;
int point;
double t;
// Select the crossover point.
//point = i4_uniform_ab ( 0, NVARS - 1, seed );
point = Int_uniform_ab(0, NVARS-1);
//
// Swap genes in positions 0 through POINT-1.
//
for ( i = 0; i < point; i++ )
{
t = population[one].gene[i];
population[one].gene[i] = population[two].gene[i];
population[two].gene[i] = t;
}
return;
}
运行结果截图:
所参考的文档:
http://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/cpp_src/simple_ga/simple_ga.html
























 643
643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








