介绍
dijkstra算法也是解决单源最短路径问题的一种方法。它要求图中路径都是非负的。而且,它的效率要高于bellman算法。
实现
首先定义图的结点信息和边信息。
struct _Node;
typedef struct _Vertex
{
int distance;
int vertex;
struct _Node *parent;
}Vertex;
typedef struct _Node
{
Vertex *pVertex;
struct _Node *next;
}Node;
typedef struct Edge_
{
int x;
int y;
bool operator == (const struct Edge_& l)
{
return x == l.x && y == l.y;
}
}Edge;
bool operator < (const Edge& r, const Edge& l)
{
if (r.x == l.x)
{
return r.y < l.y;
}
return r.x < l.x;
}
map<Edge, int> g_edges;这是图中的基本信息定义,图的信息初始化如下:
Node* initNode(Node **graph, int vertex)
{
Node *p = new Node;
p->pVertex = graph[vertex - 1]->pVertex;
p->next = nullptr;
return p;
}
void InsertVertex(Node **graph, Node *node, int vertex, int weight)
{
Node *p = node;
while (nullptr != p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = initNode(graph, vertex);
Edge edge;
edge.x = node->pVertex->vertex;
edge.y = vertex;
g_edges.insert(std::pair<Edge, int>(edge, weight));
}
int getSentinel()
{
return numeric_limits<int>::max();
}
void initGraph(Node **list, int vertexCount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; ++ i)
{
list[i] = new Node;
list[i]->next = nullptr;
list[i]->pVertex = new Vertex;
list[i]->pVertex->parent = nullptr;
list[i]->pVertex->vertex = i + 1;
list[i]->pVertex->distance = 0;
}
}权重提取:
int w(int x, int y)
{
Edge edge;
edge.x = x;
edge.y = y;
return g_edges[edge];
}inline int parent(int node)
{
return node >> 1;
}
inline int left(int node)
{
return node << 1;
}
inline int right(int node)
{
return (node << 1) + 1;
}
void minHeapify(Node **t, int heapLength, int node)
{
/// 求出左子叶及右子叶
int l = left(node);
int r = right(node);
int smallest = node;
/// 然后把左子叶,右子叶与父节点比较,求出最小节点
if (l < heapLength && t[l]->pVertex->distance < t[smallest]->pVertex->distance)
{
smallest = l;
}
if (r < heapLength && t[r]->pVertex->distance < t[smallest]->pVertex->distance)
{
smallest = r;
}
/// 交换最小节点,继续求下一节点
if (node != smallest)
{
swap(t[node], t[smallest]);
minHeapify(t, heapLength, smallest);
}
}
void buildMinHeap(Node **t, int length)
{
int heapLength = length;
/// 从底向上把数组变成堆 从length/2开始,因为length/2+1到length是是叶子节点,不需要进行操作
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; -- i)
{
minHeapify(t, heapLength, i);
}
}
Node* heapExtractMin(Node **t, int heapLength)
{
if (heapLength < 1)
{
throw std::exception("heap underflow");
}
/// 把最小值和末尾值进行交换,并重新建立最小堆
Node *min= t[0];
swap(t[0], t[heapLength - 1]);
//t[0] = t[heapLength - 1];
-- heapLength;
minHeapify(t, heapLength, 0);
return min;
}
int search(Node **t, int length, Node *node)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++ i)
{
if (node->pVertex->vertex == t[i]->pVertex->vertex)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void heapDecreaseKey(Node **t, int node, int key)
{
if (key > t[node]->pVertex->distance)
{
throw std::exception("new key is bigger than current key");
}
t[node]->pVertex->distance = key;
/// 遍历父节点,直到遇到不小于父节点为止
while(node > 0 && t[parent(node)]->pVertex->distance > t[node]->pVertex->distance)
{
swap(t[node], t[parent(node)]);
node = parent(node);
}
}
void heapDecreaseKey(Node **t, int length, Node *node)
{
int index = search(t, length, node);
if (-1 == index)
{
return;
}else
{
heapDecreaseKey(t, index, node->pVertex->distance);
}
}
void minHeapInsert(Node **t, int length, Node *node)
{
int heapLength = length;
++ heapLength;
t[heapLength - 1] = node;
int key = node->pVertex->distance;
/// 使用哨兵作为特殊值,任何值都比他大,然后调用增加某个值的函数
t[heapLength - 1]->pVertex->distance = numeric_limits<int>::max();
heapDecreaseKey(t, heapLength - 1, key);
}dijkstra算法主体:
void initializeSingleSource(Node **graph, Node *root)
{
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX_NUMBER; ++ i)
{
graph[i]->pVertex->distance = getSentinel();
graph[i]->pVertex->parent = nullptr;
}
root->pVertex->distance = 0;
}
void relax(Node *u, Node *v, int weight)
{
if (v->pVertex->distance > u->pVertex->distance + weight)
{
v->pVertex->distance = u->pVertex->distance + weight;
v->pVertex->parent = u;
}
}
void dijkstra()
{
Node *graph[VERTEX_NUMBER] = {0};
initGraph(graph, VERTEX_NUMBER);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[0], 2, 10);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[0], 4, 5);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[1], 3, 1);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[1], 4, 2);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[2], 5, 4);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[3], 2, 3);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[3], 3, 9);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[3], 5, 2);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[4], 1, 7);
InsertVertex(graph, graph[4], 3, 6);
initializeSingleSource(graph, graph[0]);
buildMinHeap(graph, VERTEX_NUMBER);
int queueLength = VERTEX_NUMBER;
while(0 != queueLength)
{
Node *node = heapExtractMin(graph, queueLength);
-- queueLength;
cout << node->pVertex->vertex << " ";
Node *p = node->next;
while(nullptr != p)
{
int weight = w(node->pVertex->vertex, p->pVertex->vertex);
if (p->pVertex->distance > node->pVertex->distance
&& p->pVertex->distance > node->pVertex->distance + weight)
{
p->pVertex->distance = node->pVertex->distance + weight;
p->pVertex->parent = node;
heapDecreaseKey(graph, queueLength, p);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX_NUMBER; ++ i)
{
if (nullptr != graph[i]->pVertex->parent)
{
cout << "edge:" << graph[i]->pVertex->parent->pVertex->vertex
<< "," << graph[i]->pVertex->vertex << endl;
}
}
}首先,初始化图各个结点的距离为无穷大以及父结点为空并选任意结点初始化距离为0,然后全部加入到最小优先级队列当中去。接着循环从最小优先级队列中提取出最小值,并计算它与它的邻接表结点的距离,如果它们之间的权重小于当前结点保存的距离值,则重置当前结点的distance值,并重置父结点。直到算法结束时,单源最短路径便生成了。
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
copyright();
cout << "dijkstra algorithm: " << endl;
dijkstra();
return 0;
}可以看下运算结果:
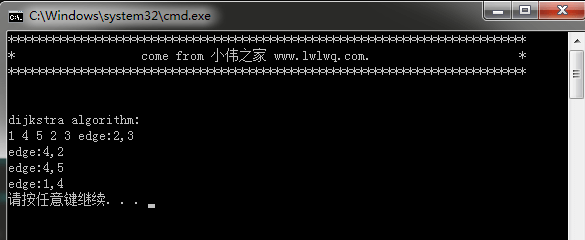
dijkstra算法代码运行结果
dijkstra算法图解过程如下:
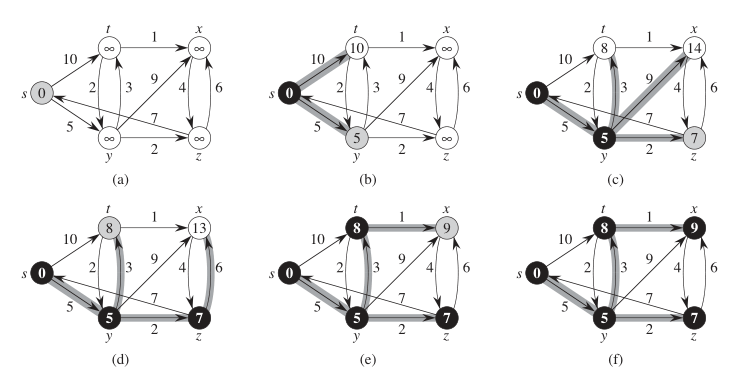
dijkstra算法过程图解
从上面可以看出,dijkstra算法和prim算法很相似。都是使用最小优先级队列来计算它们之间的最小权重。






















 447
447

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










