第三章 数据结构
3.1 线性表
3.1.6 栈
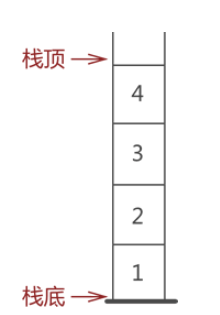
栈也是线性表数据结构的一种 : 栈是一种只能从表的一端存取数据且遵循 "先进后出" 原则的线性存储结构。

栈对于数据存和取有特殊要求 :
- 栈只能从表的一端存取数据,另一端是封闭的
- 在栈中,无论是存数据还是取数据,都必须遵循"先进后出"的原则,即最先进栈的元素最后出栈。
栈的开口端被称为栈顶;相应地,封口端被称为栈底。
LIFO : Last In First Out 后进先出
FILO : First In Last Out 先进后出
进栈和出栈
基于栈结构的特点,在实际应用中,通常只会对栈执行以下两种操作:
- 向栈中添加元素,此过程被称为"进栈"(入栈或压栈);
- 从栈中提取出指定元素,此过程被称为"出栈"(或弹栈);
进栈的具体实现
- 顺序栈:采用顺序存储结构可以模拟栈存储数据的特点,从而实现栈存储结构,数组实现.
- 链栈:采用链式存储结构实现栈结构,链表实现.
栈的API设计
链表实现栈的设计 :
| 类名 | LinkStack<T> |
| 构造方法 | LinkStack() : 创建栈对象对象 |
| 成员方法 |
|
| 成员变量 |
|
| 成员内部类 | private class Node<T> |
链表实现 :
public class LinkStack<T> implements Iterable<T> {
private int N;
private Node head = null;
public LinkStack() {
this.N = 0;
head = new Node(null,null);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0 ;
}
public int length() {
return N;
}
public void push(T t) {
Node newNode = new Node(t, head.next);
head.next = newNode;
N++;
}
public T pop() {
if (head.next == null) return null;
T t = head.next.item;
head.next = head.next.next;
N--;
return t;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new StackIterator();
}
public class StackIterator implements Iterator{
private Node current;
public StackIterator() {
this.current = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return current.next != null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
current = current.next;
return current.item;
}
}
public class Node {
public T item;
public Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
}测试代码
public class TestLinkStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkStack<String> linkStack = new LinkStack<String>();
linkStack.push("11");
linkStack.push("12");
linkStack.push("13");
//遍历测试
for (String s : linkStack) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println(linkStack.isEmpty());
System.out.println(linkStack.length());
//弹栈
System.out.println(linkStack.pop());
System.out.println(linkStack.length());
System.out.println(linkStack.pop());
System.out.println(linkStack.pop());
System.out.println(linkStack.pop());
linkStack.push("14");
System.out.println(linkStack.pop());
}
}
数组实现:
public class ArrayStack<T> implements Iterable<T> {
private int init = 5;
private int N;
private T[] stack;
public ArrayStack() {
N = 0;
stack = (T[]) new Object[init];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0 ;
}
public int length() {
return N;
}
public void push(T t) {
//判断是否要增加数组
if (N == init ) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[2 * init];
init = 2*init;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
newArray[i]=stack[i];
}
stack = (T[]) newArray;
}
stack[N++] = t;
System.out.println("push:" + t + ",长度" + stack.length);
}
public T pop() {
if (N == 0) return null;
//判断是否要减少数组
if (init > 5 && N == init/4 ) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[init/2];
init = init/2;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
newArray[i]=stack[i];
}
stack = (T[]) newArray;
}
System.out.println("pop: 长度" + stack.length);
return stack[--N];
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new StackIterator();
}
public class StackIterator implements Iterator {
private int length;
private T[] iter;
public StackIterator() {
this.length = N;
this.iter = stack;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return length != 0;
}
@Override
public T next() {
return iter[--length];
}
}
}
测试代码 :
public class TestArrayStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack<>();
arrayStack.push(100);
arrayStack.push(101);
arrayStack.push(102);
arrayStack.push(103);
arrayStack.push(104);
arrayStack.push(105);
arrayStack.push(106);
arrayStack.push(107);
arrayStack.push(108);
arrayStack.push(109);
arrayStack.push(110);
arrayStack.push(111);
arrayStack.push(112);
arrayStack.push(113);
//迭代
for (Integer integer : arrayStack) {
System.out.println("迭代 : "+integer);
}
System.out.println(arrayStack.isEmpty());
System.out.println(arrayStack.length());
//弹栈
System.out.println("------弹栈-------");
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.length());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
arrayStack.push(103);
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
System.out.println(arrayStack.pop());
}
}
括号匹配问题
例如 :
(上海)(北京) 匹配正确
上海((北京)) 匹配正确
上海(北京(深圳)(广州)) 匹配正确
(上海北京(深圳)(广州)) 匹配正确
代码实现 :
public class BracketMatchProblem {
private static String left = "(";
private static String right = ")";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "上海(北京(深圳)(广州))";
Boolean match = isMatch(str);
System.out.println(match);
}
private static Boolean isMatch(String str) {
//1.创建栈
LinkStack<String> strStack = new LinkStack<>();
//2.遍历字符串
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
String x = str.charAt(i)+"";
//2.1 是left存入栈
if (x.equals(left)) {
strStack.push(x);
}
//2.2 是right弹栈
if (x.equals(right)) {
String pop = strStack.pop();
//弹出的结果如果是null,说明无左括弧, 返回false
if (pop == null) {
return false;
}
}
}
//循环结束,判断栈是否有左括号
if (strStack.length() != 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
逆波兰表达式问题
前缀表达式 : 波兰式 : 前缀表达式的运算符位于操作数之前 - × + 3 4 5 6 ; 实际含义就是 3-4×5+6
中缀表达式 : 最常见的运算表达式 : 如(3+4)×5-6 , 最直观的表达式, 人最容易识别,但是计算机处理中缀表达式却不是方便
后缀表达式:逆波兰表达式, 是运算符位于操作数之后 比如 : 3 4 + 5 × 6 - , 实际含义3+4x5-6
| 中缀表达式 | 后缀表达式 |
| a+b | ab+ |
| a+(b-c) | abc-+ |
| a+(b-c)*d | abc-d*+ |
| a*(b-c)+d | abc-*d+ |
逆波兰表达式的计算 : 使用栈计算
**
* 逆波兰问题
* <p>
* 遍历数组,
* 如果是操作数就存入栈,
* 如果是操作符,就弹栈两次,弹出来操作两个操作数和运算符做运算,运算结束后,再入栈,
*/
public class ReversePolishNotation {
//中 表达式 3*(17-15)+18/6
//逆波兰表达式 3 17 15 - * 18 6 / +
private static String calculating_signs = "+-*/";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] notation = {"3", "17", "15", "-", "*", "18", "6", "/", "+"};
int result = calculate(notation);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int calculate(String[] notation) {
//创建栈
LinkStack<Integer> linkStack = new LinkStack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < notation.length; i++) {
if (calculating_signs.contains(notation[i])) {
String sign = notation[i];
Integer next = linkStack.pop();
Integer prior = linkStack.pop();
if ("+".equals(sign)) {
linkStack.push(prior + next);
}
if ("-".equals(sign)) {
linkStack.push(prior - next);
}
if ("*".equals(sign)) {
linkStack.push(prior * next);
}
if ("/".equals(sign)) {
linkStack.push(prior / next);
}
} else {
linkStack.push(new Integer(notation[i]));
}
}
return linkStack.pop();
}
}
3.1.7 队列
队列和栈一样,也是一种对数据的"存"和"取"有严格要求的线性存储结构。
队列的两端都"开口",要求数据只能从一端进,从另一端出
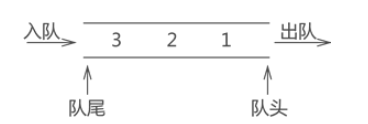
通常,称进数据的一端为 "队尾",出数据的一端为 "队头",数据元素进队列的过程称为 "入队",出队列的过程称为 "出队"。
队列中数据的进出要遵循 "先进先出" 的原则,即最先进队列的数据元素,同样要最先出队列。 FIFO : First In First Out
队列的实现
队列存储结构的实现有以下两种方式:
- 顺序队列:在顺序表的基础上实现的队列结构;
- 链队列:在链表的基础上实现的队列结构;
顺序队列 : 数组实现 (数组相对链表麻烦,也不是很难 ,以后有时间再写,)
链队列 : 链表实现 (这种方式比较方便)
| 类名 | LinkQueue<T> |
| 构造方法 | LinkQueue() : 创建队列 |
| 成员方法 |
|
| 成员变量 |
|
| 成员内部类 | private class Node<T> 结点类 |
插入元素
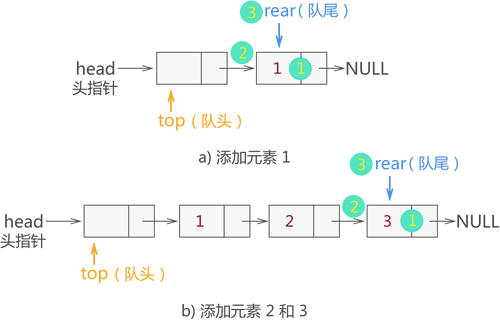
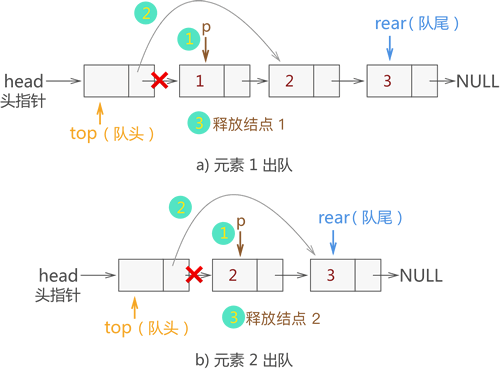
删除元素 :

public class LinkQueue<T> implements Iterable<T> {
private int N;
//head 指向队头
private Node head;
//head 指向队尾
private Node last;
public LinkQueue() {
this.N = 0;
head = new Node(null, null);
last = new Node(null, null);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.N > 0;
}
public int length() {
return this.N;
}
/**
* 添加一个元素
*
* @param t
*/
public void enqueue(T t) {
//创建尾结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
if (head.next == null) {
head.next = newNode;
}
if (last.next != null) {
//尾结点指向新的尾结点
last.next.next = newNode;
}
//尾结点的指针更新
last.next = newNode;
N++;
}
/**
* 弹出一个元素
*
* @return
*/
public T dequeue() {
if (head.next == null) return null;
T t = head.next.t;
head.next = head.next.next;
N--;
return t;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new QueueIterator();
}
/**
* 迭代实现
*/
public class QueueIterator implements Iterator {
private Node current;
public QueueIterator() {
this.current = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return current.next != null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
current = current.next;
return current.t;
}
}
private class Node {
public T t;
public Node next;
public Node(T t, Node next) {
this.t = t;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
测试代码 :
public class TestLinkQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkQueue<>();
queue.enqueue(100);
queue.enqueue(101);
queue.enqueue(102);
for (Integer integer : queue) {
System.out.println("queue:" + integer);
}
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println( "length :"+queue.length());
System.out.println("----dequeue---");
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println("length :"+queue.length());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
queue.enqueue(100);
queue.enqueue(200);
queue.enqueue(300);
for (Integer integer : queue) {
System.out.println("queue:" + integer);
}
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
}





















 867
867











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








