一、添加依赖
首先,我们需要在项目的 pom.xml 文件中添加 MyBatis-Plus 和达梦数据库的依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加dm8 jdbc jar 包依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dm</groupId>
<artifactId>DmJdbcDriver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
二、配置数据源
在 Spring Boot 的配置文件 application.properties 或 application.yml 中配置达梦数据库的连接信息:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:dm://localhost:5236
username: 账号
password: 密码
driver-class-name: dm.jdbc.driver.DmDriver之后可以使用MyBatisX生成以下代码
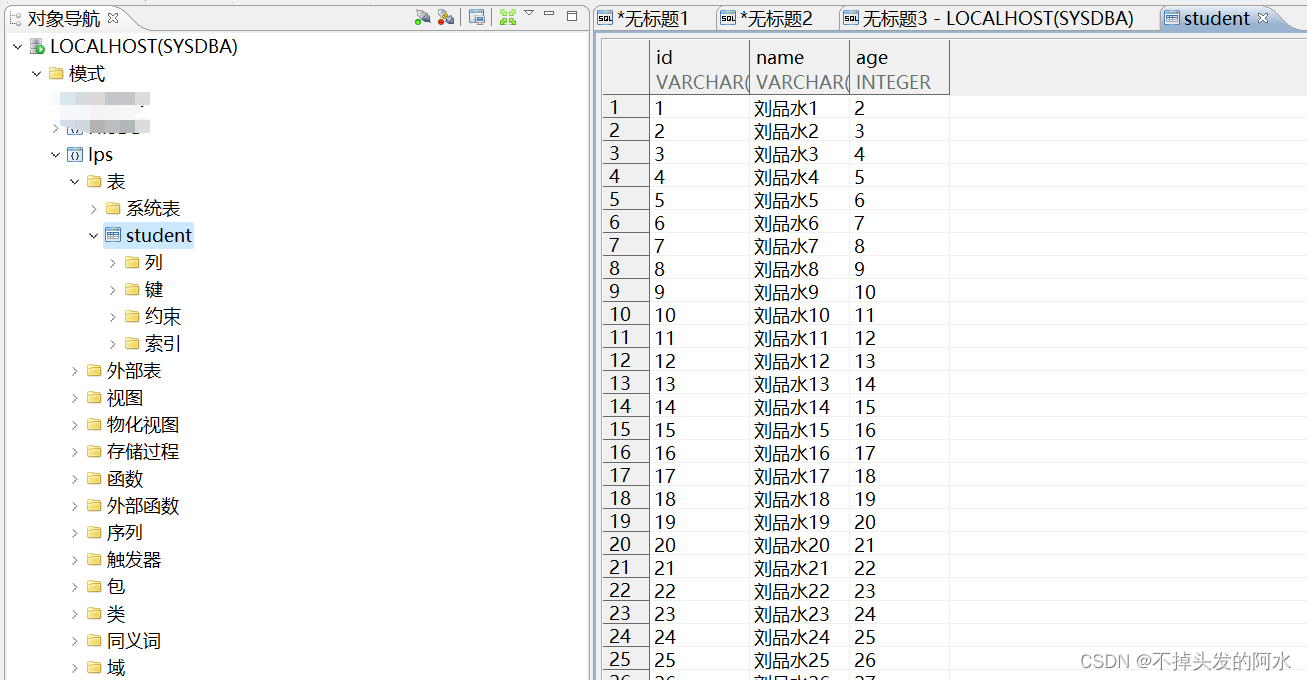
三、创建实体类和 Mapper 接口
创建与数据库表对应的实体类,并使用 MyBatis-Plus 注解标注主键和表名等信息:
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import java.io.Serializable;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* @TableName student
*/
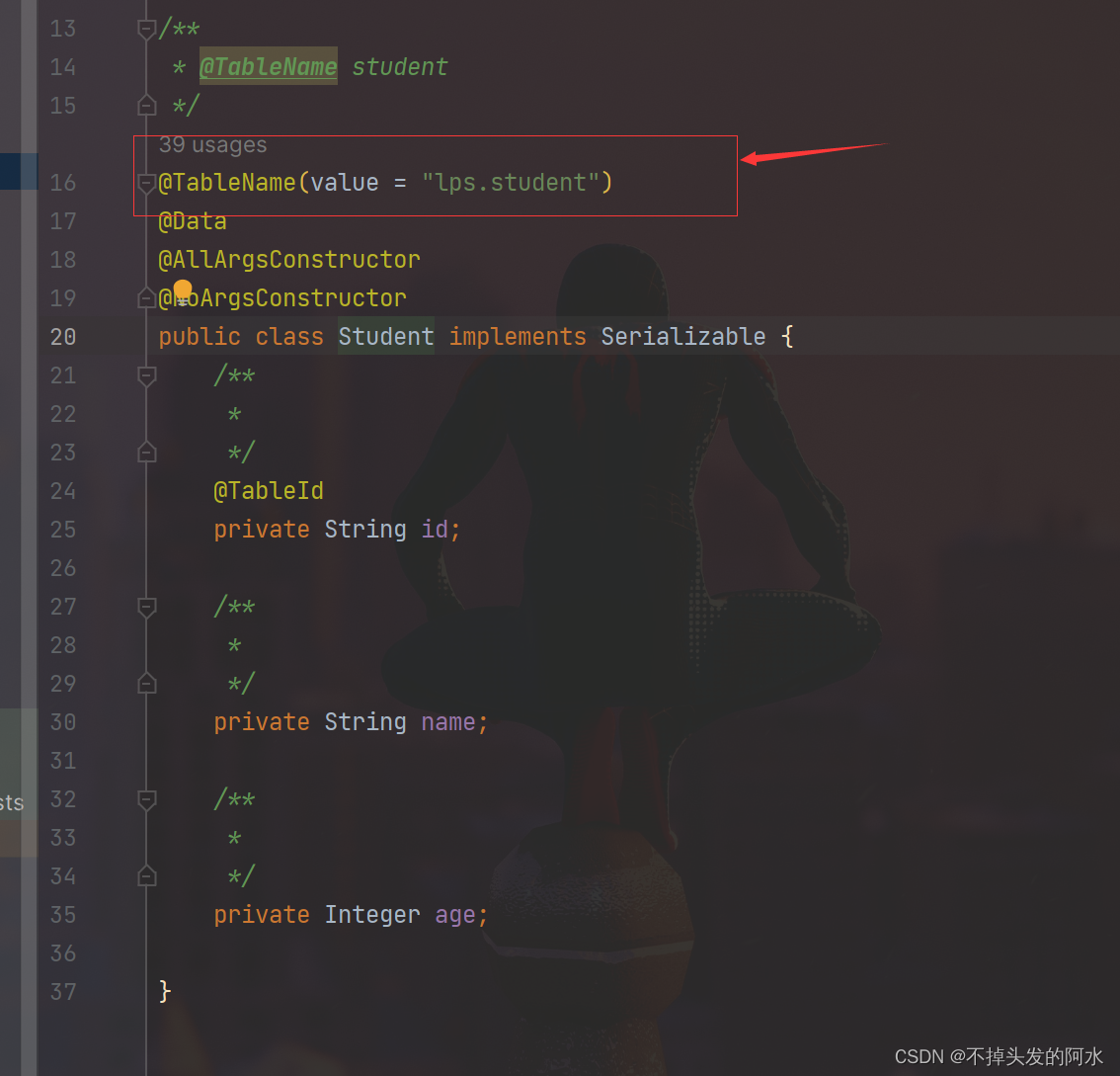
@TableName(value = "lps.student")
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
@TableId
private String id;
/**
*
*/
private String name;
/**
*
*/
private Integer age;
}接着,创建继承自 BaseMapper 的 Mapper 接口:
import com.lps.domain.Student;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @author 19449
* @description 针对表【student】的数据库操作Mapper
* @createDate 2023-08-01 16:10:31
* @Entity com.lps.domain.Student
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
完成mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lps.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.lps.domain.Student">
<id property="id" column="id" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="name" column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="age" column="age" jdbcType="OTHER"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id,name,age
</sql>
</mapper>
四、创建 Service 层
创建 Service 接口和实现类,继承自 IService 和 ServiceImpl:
import com.lps.domain.Student;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 19449
* @description 针对表【student】的数据库操作Service
* @createDate 2023-08-01 16:10:31
*/
public interface StudentService extends IService<Student> {
List<Student> selectAll();
void insert(Student student);
void deleteBatch(List<Student> studentList);
void deleteAll();
}service实现类
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.lps.domain.Student;
import com.lps.service.StudentService;
import com.lps.mapper.StudentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author 19449
* @description 针对表【student】的数据库操作Service实现
* @createDate 2023-08-01 16:10:31
*/
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper, Student>
implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public List<Student> selectAll() {
return studentMapper.selectList(null);
}
@Override
public void insert(Student student) {
studentMapper.insert(student);
}
@Override
public void deleteBatch(List<Student> studentList) {
studentMapper.deleteBatchIds(studentList.stream().map(students -> students.getId()).collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Override
public void deleteAll() {
studentMapper.delete(null);
}
}
五、进行 CRUD 操作
现在就可以在业务逻辑中使用 YourService 进行增删改查操作了:
package com.lps;
import com.lps.domain.Student;
import com.lps.service.StudentService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootDm7ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@Test
void contextLoadSelectAll() {
List<Student> students = studentService.selectAll();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
/**
* 单条插入
*/
@Test
void contextLoadsInsert() {
Student student = new Student("666","刘品水",18);
studentService.insert(student);
}
/**
* 循环里做插入 主打就是挨训
*/
@Test
void contextLoadsInsert2() {
//还有优化空间 下篇博客见
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) {
Student student1 = new Student(i+"","刘品水"+i,1+i);
studentList.add(student1);
}
System.out.println(studentList.size());
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Student student : studentList) {
studentService.insert(student);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long spendTime = endTime - beginTime;
System.out.println("用时:"+spendTime+"毫秒");
}
/**
* 批量插入
*/
@Test
void contextLoadsSaveBatch() {
//还有优化空间 下篇博客见
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000000; i++) {
Student student1 = new Student(i+"","刘品水"+i,1+i);
studentList.add(student1);
}
System.out.println(studentList.size());
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
studentService.saveBatch(studentList,1000000);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long spendTime = endTime - beginTime;
System.out.println("用时:"+spendTime+"毫秒");
}
/**
* 批量保存或者批量更新
*/
@Test
void contextLoadSaveOrUpdateBatch() {
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<>();
Student student1 = new Student("668","吴彦祖",18);
Student student2 = new Student("669","彭于晏",18);
Student student3 = new Student("670","霍建华",18);
studentList.add(student1);
studentList.add(student2);
studentList.add(student3);
studentService.saveOrUpdateBatch(studentList);
}
/**
* 批量删除
*/
@Test
void contextLoadDeleteBatch() {
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<>();
Student student1 = new Student("123456","刘品水",18);
Student student2 = new Student("654321","刘品水",18);
Student student3 = new Student("77777","刘品水",18);
studentList.add(student1);
studentList.add(student2);
studentList.add(student3);
studentService.deleteBatch(studentList);
}
/**
* 删除所有
*/
@Test
void contextLoadDeleteBatchAll() {
studentService.deleteAll();
}
}
六、总结
本文介绍了如何结合 MyBatis-Plus 和达梦数据库来实现高效的数据持久化操作。通过配置数据源、创建实体类、Mapper 接口和 Service 层,我们可以轻松地完成增删改查等数据库操作。MyBatis-Plus 的强大功能和简便的操作方式,大大提高了开发效率,使得数据持久化变得更加轻松愉快。
最重要的就是实体类上要记得加上你的模式名
























 3481
3481











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








