单链表详解
1. 引言
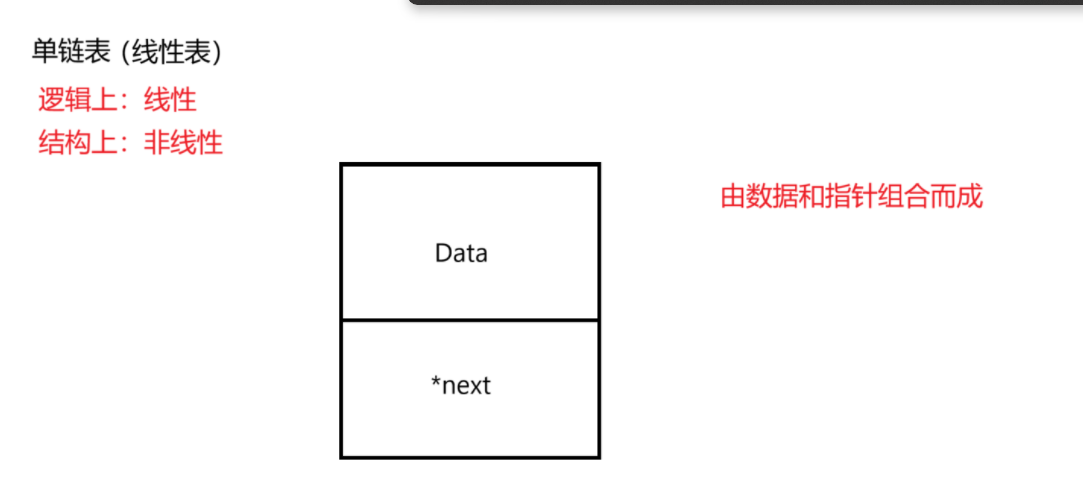
- 单链表的定义:作为一种线性数据结构,由节点组成,每个节点包含数据域(data)和指向下一个节点的指针(*next)。
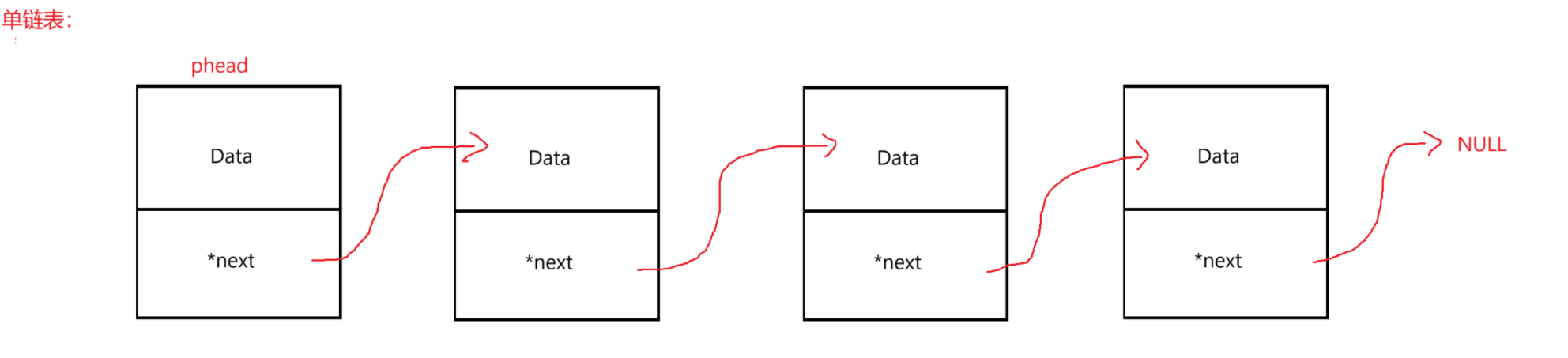
- 单链表:单向无头不循环链表
- 为什么使用单链表:如动态内存分配、高效插入删除操作(时间复杂度O(1))
2. 单链表的基本概念
- 节点结构:包括数据域(data)和指针域(*next)。
- 例如:节点定义包含
int data和struct Node* next。
- 例如:节点定义包含
- 链表结构:
3. C语言实现单链表
- 定义节点结构体:使用C语言结构体定义节点。
typedef int SListDatatype; typedef struct SListcode { SListDatatype data; struct SListcode* next; }SList; - 创建链表:展示如何初始化一个空链表,并动态分配内存。
//创建链表 SList* phead = NULL; // 初始化为空链表 - 内存管理基础:
malloc和free函数
4. 常见操作详解(附代码示例)
- 插入操作:
创建节点:
//创建一个节点 SList* SList_Buycode(SListDatatype x) { SList* newnode; newnode = (SList*)malloc(sizeof(SList)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("create newnode fail!"); exit(1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; return newnode; }- 头插法:在链表头部插入新节点,时间复杂度O(1)
//头插 void SList_PushFront(SList** pphead, SListDatatype x) { assert(pphead); SList* newnode = SList_Buycode(x); newnode->next = *pphead; *pphead = newnode; } - 尾插法:在链表尾部插入新节点,时间复杂度O(n)(需遍历找到尾部节点)
//查找 SList* SList_Find(SList* phead, SListDatatype x) { assert(phead); SList* pcur = phead; while (pcur ) { if (pcur->data == x) { return pcur; } pcur = pcur->next; } return -1; } //尾插 void SList_PushBack(SList** pphead, SListDatatype x) { assert(pphead); SList* newnode = SList_Buycode(x); if (*pphead == NULL) { *pphead = newnode; } else { SList* ptail = *pphead; while (ptail->next) { ptail = ptail->next; } ptail->next = newnode; } }- 指定位置插入:在中间节点前/后插入,讨论边界条件(如空链表或无效位置)。
- 头插法:在链表头部插入新节点,时间复杂度O(1)
//查找
SList* SList_Find(SList* phead, SListDatatype x)
{
assert(phead);
SList* pcur = phead;
while (pcur )
{
if (pcur->data == x)
{
return pcur;
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
return -1;
}
//指定位置前插入
void SList_InsertFront(SList** pphead, SListDatatype x, SListDatatype posx)
{
assert(pphead);
SList* pre = *pphead;
SList* newnode = SList_Buycode(x);
SList* pos = SList_Find(*pphead, posx);//有边界检查
if (pos != -1)
{
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SList_PushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
newnode->next = pos;
while (pre->next != pos)
{
pre = pre->next;
}
pre->next = newnode;
}
}
else
{
printf("插入错误!\n");
}
}
//指定位置之后插入
void SList_InsertBack(SList** pphead, SListDatatype x, SListDatatype posx)
{
assert(pphead);
SList* pos = SList_Find(*pphead, posx);
SList* newnode = SList_Buycode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
SList_PushBack(pphead, x);
}
else
{
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
}
- 删除操作:
- 删除头节点:移除链表第一个节点。
//头删 void SList_PopFront(SList** pphead) { assert(pphead && &pphead); SList* pre = *pphead; *pphead = (*pphead)->next; free(pre); pre = NULL; }- 删除指定节点:基于值或位置删除,并处理内存释放。
//删除指定位置节点 void SList_Del(SList** pphead, SListDatatype posx) { assert(pphead && *pphead); SList* pos = SList_Find(*pphead, posx); SList* pre = *pphead; if (pos == *pphead) { free(pos); pos = NULL; *pphead = NULL; } else { while (pre->next != pos) { pre = pre->next; } pre->next = pos->next; free(pos); pos = NULL; } }
- 遍历与查找:
- 遍历链表:打印所有节点值,使用循环遍历。
//打印链表 void Slist_Print(SList* phead) { assert(phead); SList* pcur = phead; while (pcur) { printf("%d->", pcur->data); pcur = pcur->next; } printf("NULL\n"); }- 查找节点:基于值查找位置,返回指针或索引。
//查找 SList* SList_Find(SList* phead, SListDatatype x) { assert(phead); SList* pcur = phead; while (pcur ) { if (pcur->data == x) { return pcur; } pcur = pcur->next; } return -1; } - 其他操作:链表销毁
//链表销毁
void SList_Destroy(SList** pphead)
{
assert(pphead && *pphead);
SList* pcur = *pphead;
SList* pnext = *pphead;
while (pnext)
{
pcur = pnext;
pnext = pnext->next;
free(pcur);
}
*pphead = NULL;
pcur = NULL;
}
5. 单链表的优缺点分析
- 优点:
- 动态大小调整:无需预先分配固定内存
- 高效插入删除:在头部或已知位置操作时,时间复杂度低
- 内存利用率高:只分配所需空间
- 缺点:
- 随机访问慢:查找第k个节点需遍历,时间复杂度O(n)
- 额外指针开销:每个节点需存储指针,增加内存占用
- 不支持反向遍历:单链表只能单向访问
6. 常见问题与解决方案
- 内存泄漏:忘记释放节点内存,导致资源浪费
- 解决方案:遍历链表并调用
free,确保删除操作释放内存
- 解决方案:遍历链表并调用
- 空指针错误:操作空链表时未检查头指针
- 解决方案:添加条件判断,如assert(head)
- 循环链表检测:指针错误形成无限循环
- 解决方案:使用快慢指针算法
- 边界条件处理:如插入到空链表或删除最后一个节点。
8. 总结
- 核心回顾:强调单链表的核心概念、操作效率和C语言实现要点。
- 学习建议:推荐练习常见算法题(如反转链表、合并链表),并注意内存管理。
- 扩展阅读:提示后续学习双链表或循环链表。




















 1178
1178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








