一、稀疏数组
概念:

简单例子:
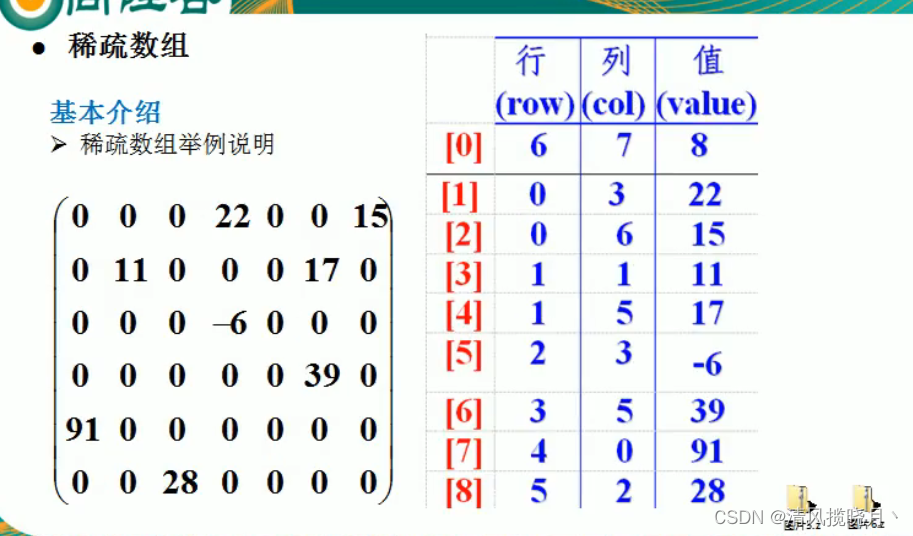
(1) 二维数组->稀疏数组 || 稀疏数组->二维数组

(2)存入文件
package 稀疏数组;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/1/1
*/
public class SparseArrayFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建一个原始数组11*11
//0表示没有棋子;1表示黑子;2表示蓝子
int chessArray1[][] = new int[11][11];
chessArray1[1][2] = 1;
chessArray1[2][3] = 2;
System.out.println("原始的二维数组:");
for (int[] row : chessArray1) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
//二维数组->稀疏数组
//1.遍历二维数组,获取非0数据个数
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chessArray1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chessArray1.length; j++) {
if (chessArray1[i][j] != 0) {
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("sum =" + sum);
//2.创建对应的稀疏数组
int sparseArray[][] = new int[sum + 1][3];
//给稀疏数组赋值
sparseArray[0][0] = chessArray1.length;
sparseArray[0][1] = chessArray1[0].length;
sparseArray[0][2] = sum;
//遍历二维数组,将非0数据存放到稀疏数组
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chessArray1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chessArray1.length; j++) {
if (chessArray1[i][j] != 0) {
count++;
sparseArray[count][0] = i;
sparseArray[count][1] = j;
sparseArray[count][2] = chessArray1[i][j];
}
}
}
//保存稀疏数组
File file = new File("D:\\桌面\\数据结构\\DataStructure\\File\\Map.data");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");
//输出稀疏数组的形式
System.out.println();
System.out.println("稀疏数组的形式为:");
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArray.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t\n",sparseArray[i][0],sparseArray[i][1],sparseArray[i][2]);
if (i == sparseArray.length-1) {
outputStreamWriter.append(sparseArray[i][0]+","+sparseArray[i][1]+","+sparseArray[i][2]);
}else {
outputStreamWriter.append(sparseArray[i][0]+","+sparseArray[i][1]+","+sparseArray[i][2]+",");
}
}
System.out.println("-----------写入文件中");
outputStreamWriter.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("-----------打开文件中");
Desktop.getDesktop().open(file);
System.out.println("-----------读取Map.data");
//创建FileReader对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//读取
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, "UTF-8");
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while (inputStreamReader.ready()){
sb.append((char)inputStreamReader.read());// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
inputStreamReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close();
System.out.println("-------------------------------恢复稀疏数组SparseArrayFile");
//创建对应的稀疏数组
String[] str = sb.toString().split(",");
int[][] SparseArrayFile = new int[str.length/3][3];
//给稀疏数组赋值
int i = 0;
for (String s : str) {
SparseArrayFile[(i - i % 3) / 3][i % 3]= Integer.parseInt(s);
i++;
}
System.out.println("----------------恢复成二维数组chessArray2");
//恢复
int[][] chessArray2 = new int[SparseArrayFile[0][1]][SparseArrayFile[0][1]];
for (int j = 1; j < SparseArrayFile.length; j++) {
chessArray2[SparseArrayFile[j][0]][SparseArrayFile[j][1]]=SparseArrayFile[j][2];
}
//输出恢复后的二维数组
System.out.println();
for (int[] ints : chessArray2) {
for (int data : ints) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------恢复完成");
}
}
二、队列

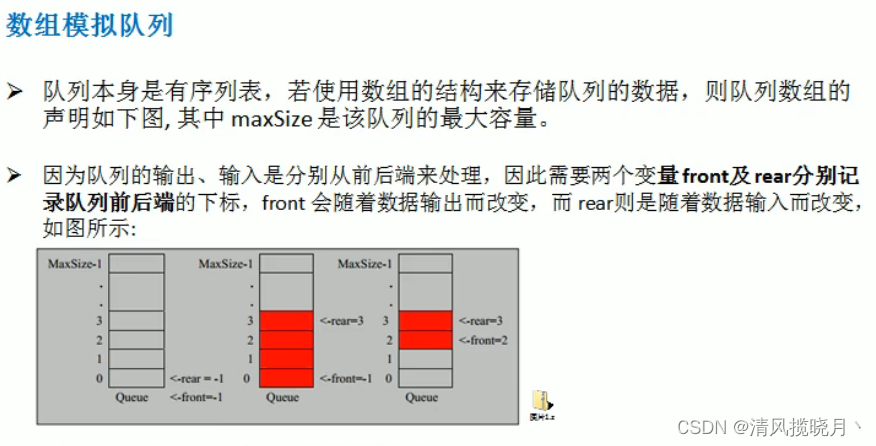
(1)数组模拟队列
package 队列;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/1/3
*/
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key =' ';//接受输入数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean flag = true;
while (flag){
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列中取出数据");
System.out.println("h(show):查看队列的头数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0); //接收一个字符
switch (key){
case 's':
arrayQueue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输入一个数据:");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
arrayQueue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.getHeadQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n",res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
flag = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
class ArrayQueue{
private int maxSize; //表示数组的最大容量
private int front;//队列头,front指向队列头的前一个位置
private int rear;//队列尾,指向队列尾的数据
private int[] arr;//模拟队列,存放数据
//创建队列的构造器
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxsize) {
maxSize=arrMaxsize;
arr=new int[maxSize];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
//判断队列是否为满
public boolean isFull(){
return rear == maxSize-1;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
//添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列满了,不能加入");
return;
}
rear++;
arr[rear]=n;
}
//获取队列的数据,出队列
public int getQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,获取不到数据");
}
front++;
return arr[front];
}
//获取队列的所有数据
public void showQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,获取不到数据");
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length ;i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
}
//显示队列头数据
public int getHeadQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,获取不到数据");
}
return arr[front+1];
}
}
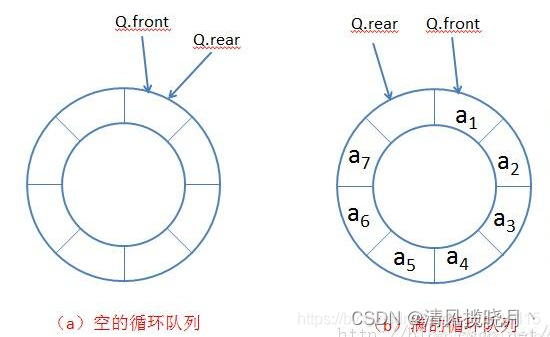
(2)环形队列
第一种方式数组不能复用,复用需要取模 %
改进思路:

其中判断队列满的思想的话,可以看下图,因为是环形的,起初front=rear=0,每当添加元素时,将rear++,但是其实预留了一个长度没有用,比如定义的队列数组长度为5时,但是实际上可以使用的地址就是0,1,2,3,此时rear=4, 4这个空间用来判断队满的条件(rear+1)%maxSize==front
package 队列;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/1/5
*
* rear指向了最后一个元素的后一个位置,
* 对应的头也从前一个位置改成了第一个元素,
* 如果不加1,取模就相当于再循环一次,就相当于队尾等于队列头,重合了一个位置
*/
public class ArrayQueueCircle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个环形队列,maxSize设置说明,4,其队列的有效数据最大为3
CircleQueue circleQueue = new CircleQueue(4);
// 接收用户输入
char key = ' ';
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
// 输出一个菜单
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show),显示队列数据");
System.out.println("e(exit),退出队列");
System.out.println("a(add),添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get),获取队列数据");
System.out.println("h(head),获取队列头数据");
// 接收输入的字符
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
circleQueue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输入一个数:");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
circleQueue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = circleQueue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res = circleQueue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
loop = false;
scanner.close();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("-----程序退出-----");
}
}
/**
* 环形队列类
* 构造器
* 判断是否已满、判断是否空、查看队列数据、显示队列的有效数据个数、入队列、出队列
*/
class CircleQueue {
// 数组的最大容量
private final int maxSize;
// front指向队列的第一个元素,初始值为0
private int front;
// rear指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置,空出一个空间作为约定,初始值为0
private int rear;
// 存放数据,模拟队列
private final int[] arr;
// 创建队列构造器
public CircleQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
// 判断队列是否已满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
// 查看队列数据,显示队列所有数据
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,没有数据!");
return;
}
// 从front开始遍历,注意遍历的元素个数,遍历有效数据个数
// front = 4 , rear = 3 , maxSize= 5
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// 求出当前队列有效数据的个数
// rear = 1
// front = 0
// maxSize =3
public int size() {
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
// 显示队列的头数据,注意不是取出数据
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列是空的,没有数据!");
}
return arr[front];
}
// 添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
System.out.println(n + "成功添加到队列");
// 将rear后移,这里必须考虑取模
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
// 从队列取出数据,,出队列
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无法取出数据");
}
// 这里需要分析出front是指向队列的第一个元素
// 1. 先把front对应的值保留到一个临时变量
// 2. 将front后移,考虑取模
// 3. 将临时保存的变量取回
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
}
三、链表
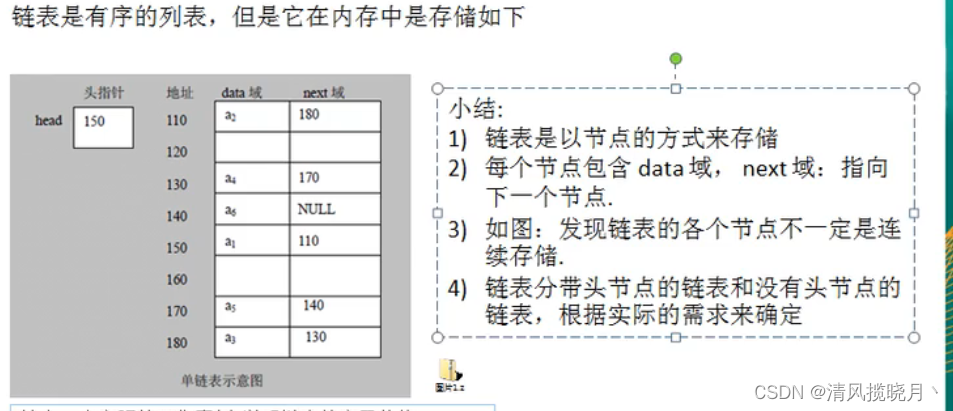
(1)单链表
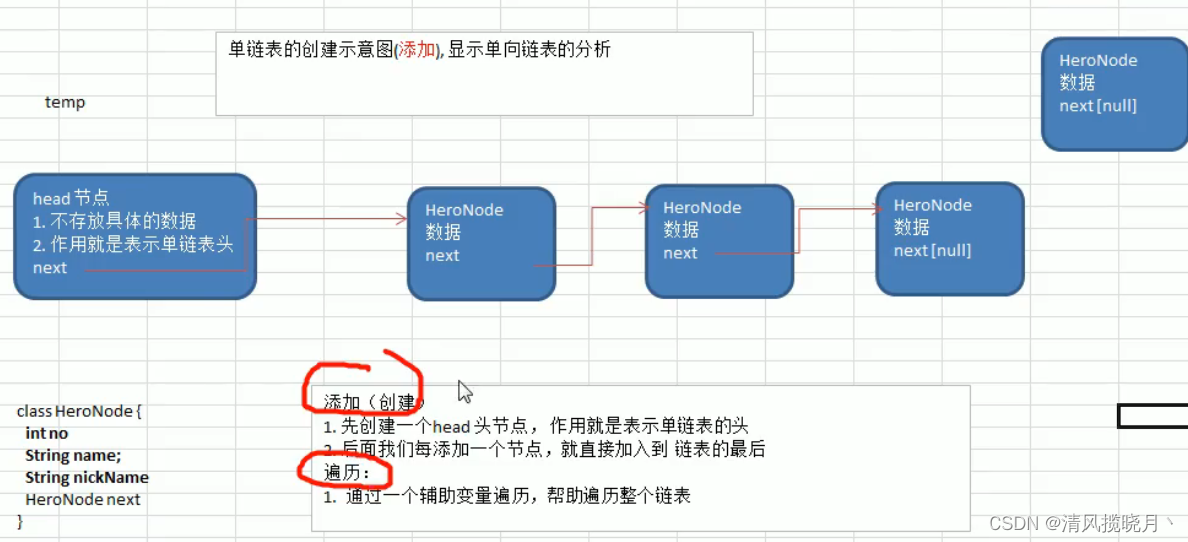
第一种添加方式:
//添加
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true){
if(temp.next==null) {
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
temp.next=heroNode;
}
//遍历
public void list(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//因为头节点不能动,所以定义一个变量
HeroNode temp = head.next;
//遍历
while (true){
//判断节点是否在最后
if (temp==null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(temp);
//节点后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
第二种添加方式:
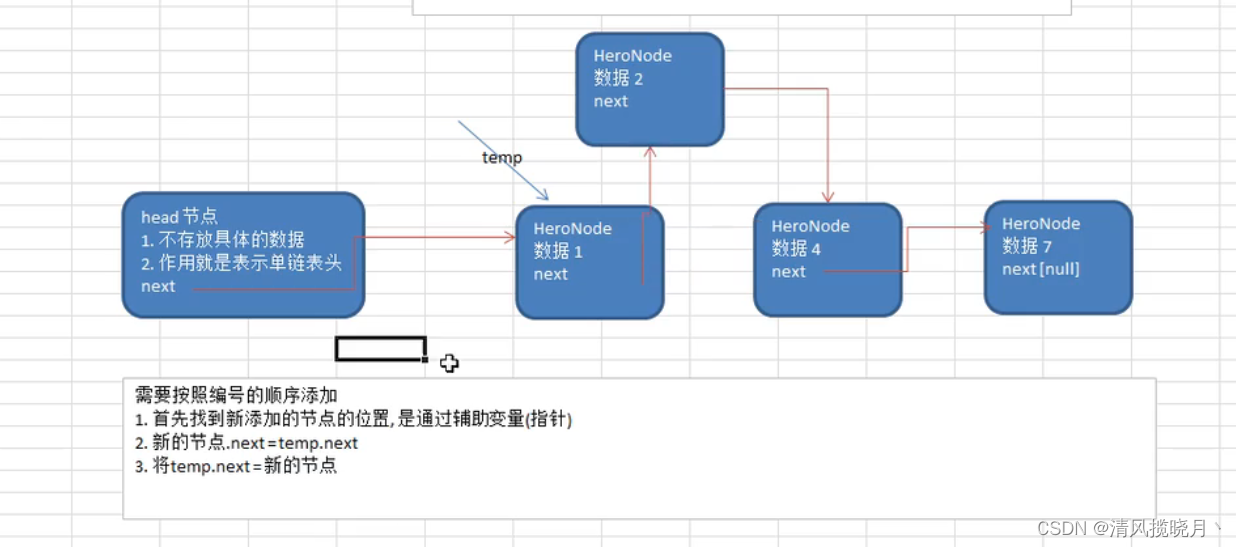
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;// 编号是否存在,默认为false
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if(temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
//位置找到,插入到temp后面
break;
}else if(temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
//说明编号存在
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//遍历链表
}
//判断flag的值
if(flag){
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号%d已经存在,不能加入\n",heroNode.no);
}else {
//插入到链表中,temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
单链表的修改

根据编号来找
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode){
//判断是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//找到需要修改的节点的编号no
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false; //表示是否找到该节点
while (true){
if(temp == null){
break;//遍历完链表
}
if(temp.no==newHeroNode.no){
//找到该节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
//根据flag判断是否找到节点
if(flag){
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
}else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号%d的节点\n",newHeroNode.no);
}
}
单链表的删除
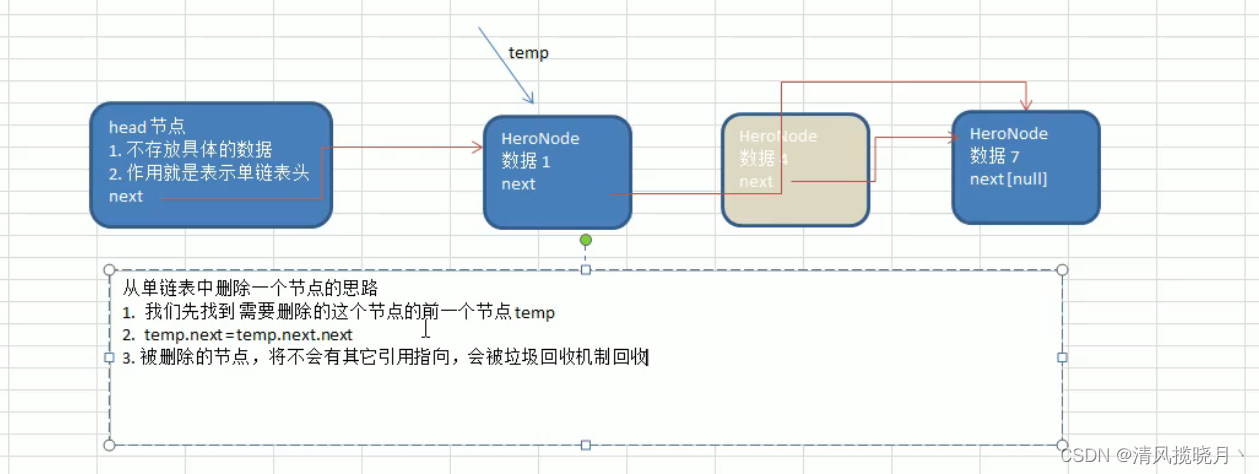
public void delete(int no){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if (temp.next.no==no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(flag){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点没找到\n",no);
}
}
单链表有效节点个数
/**
* @param head 链表的头节点
* @return 有效节点的个数
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode cur = head;
while (cur.next!=null){
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}
查找链表倒数第k个节点
//思路
//1.编写getHead方法获取head节点
//2.index 表示倒数第index个节点
//3.先把链表遍历,得到链表总长度length
//4.得到size后,我们从链表的第一个开始遍历(size-index)个节点,就可以得到
//5.如果找到了返回该节点,没找到返回null
public static HeroNode getNode(HeroNode head,int index){
if(head.next==null){
return null;
}
int size = getLength(head);
if(index <= 0 || index > size){
return null;
}
//定义辅助变量
HeroNode cur = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
单链表的反转

public static void reverseList(HeroNode head){
//当前链表为空或者只有一个节点,无需反转
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return ;
}
//定义一个辅助变量,帮助遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur = head.next;
HeroNode next = null; //当前节点[cur]的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0,"","");
//遍历原来的链表,每次遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表中
while (cur != null){
next = cur.next;//保存当前节点的下一个节点
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next ;//cur后移
}
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}
从尾打印单链表

方式二
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head.next == null){
return;
}
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur = head.next;
//所有节点压入栈
while (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
//打印
while (stack.size() > 0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
合并两个有序单链表
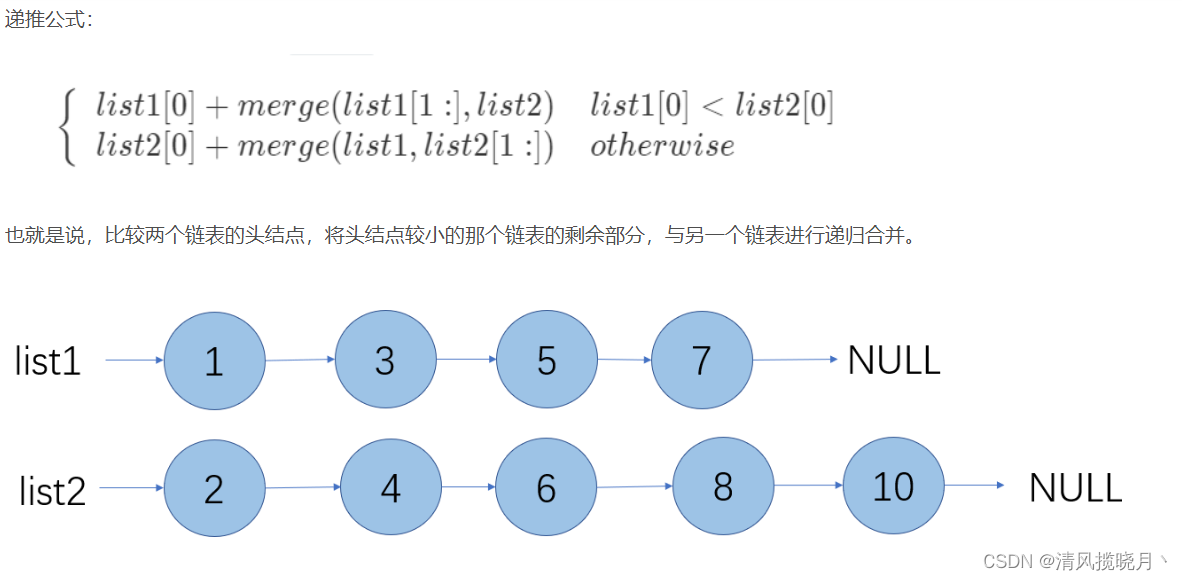
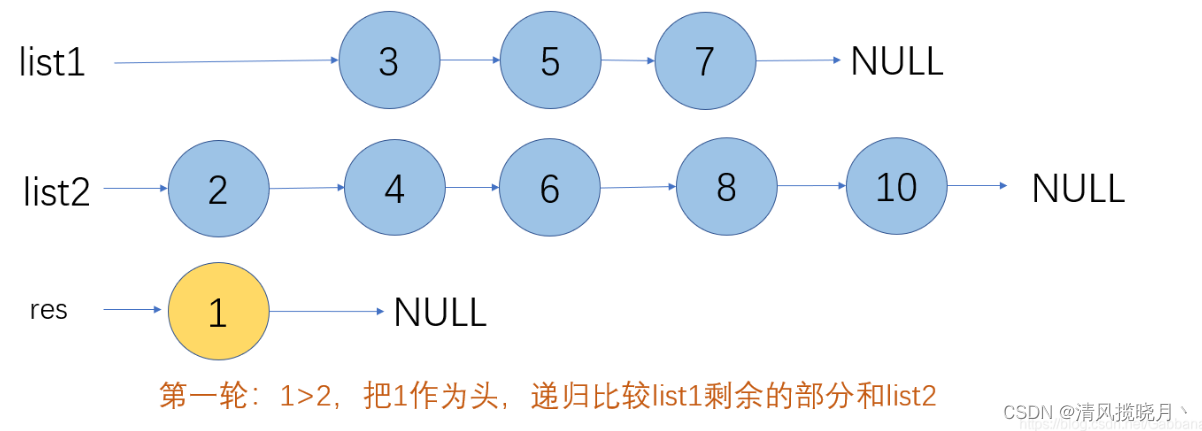
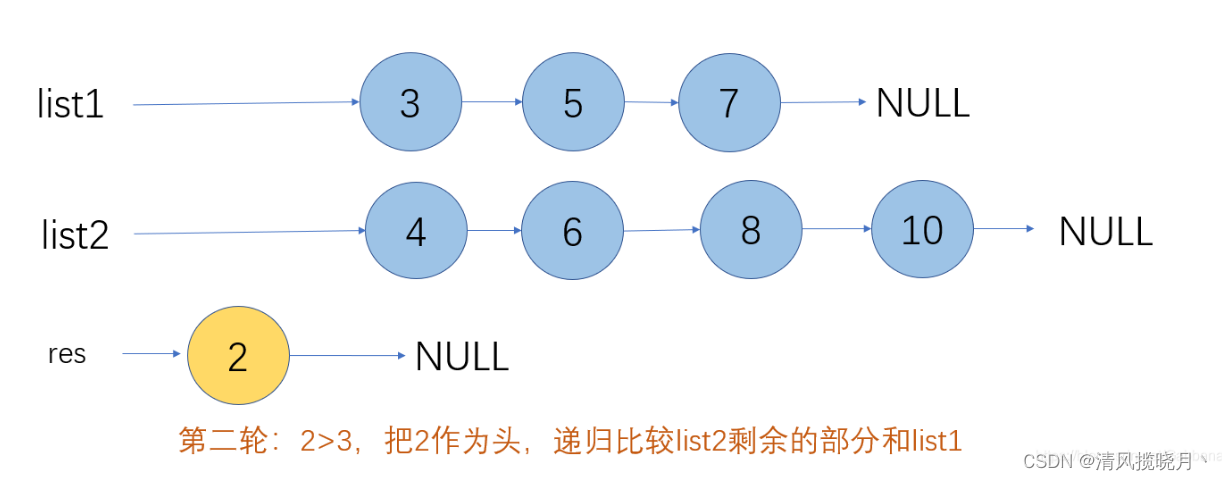
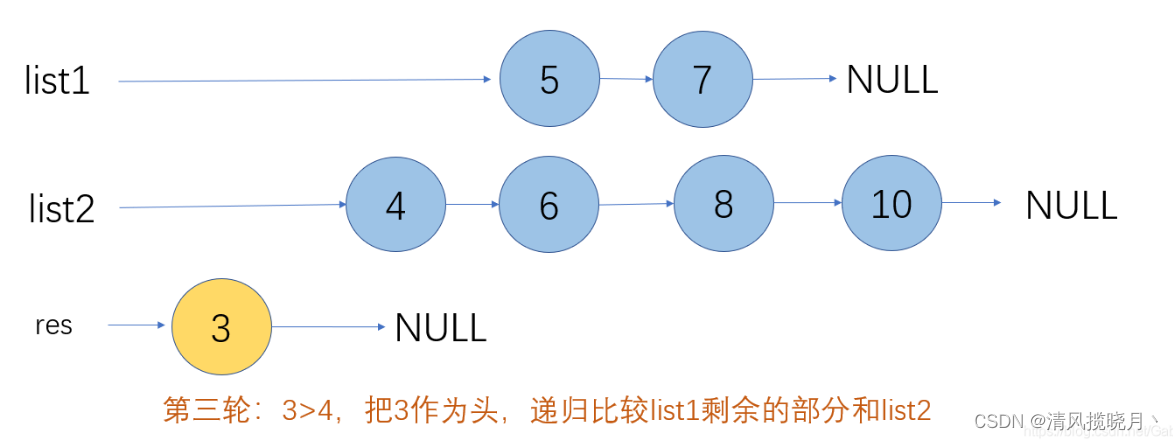
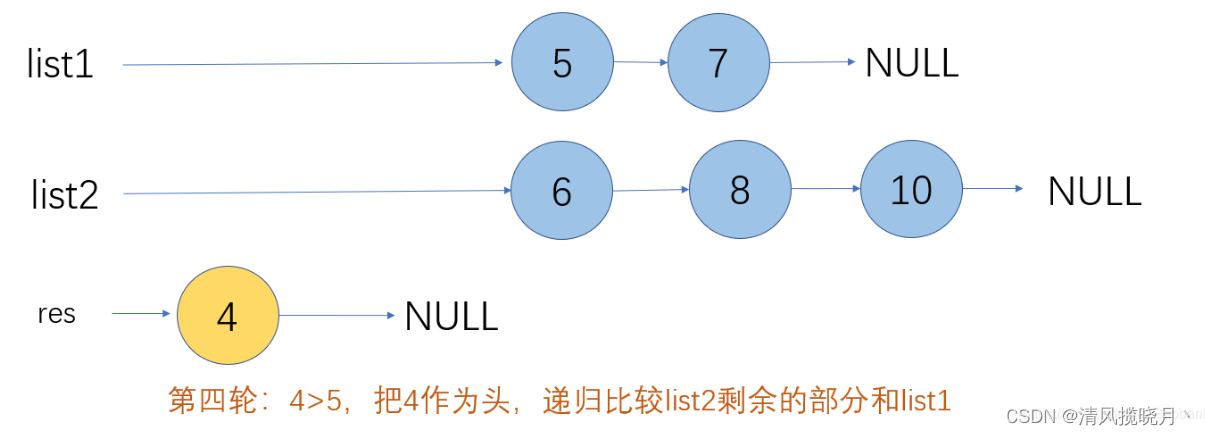
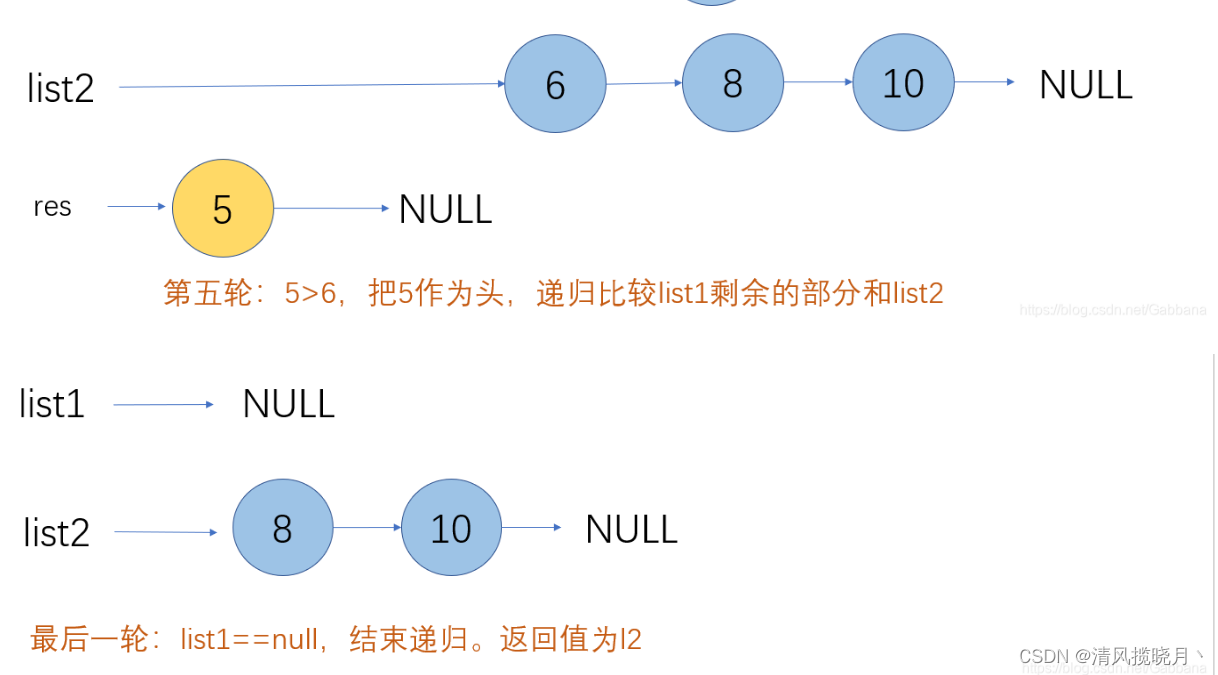
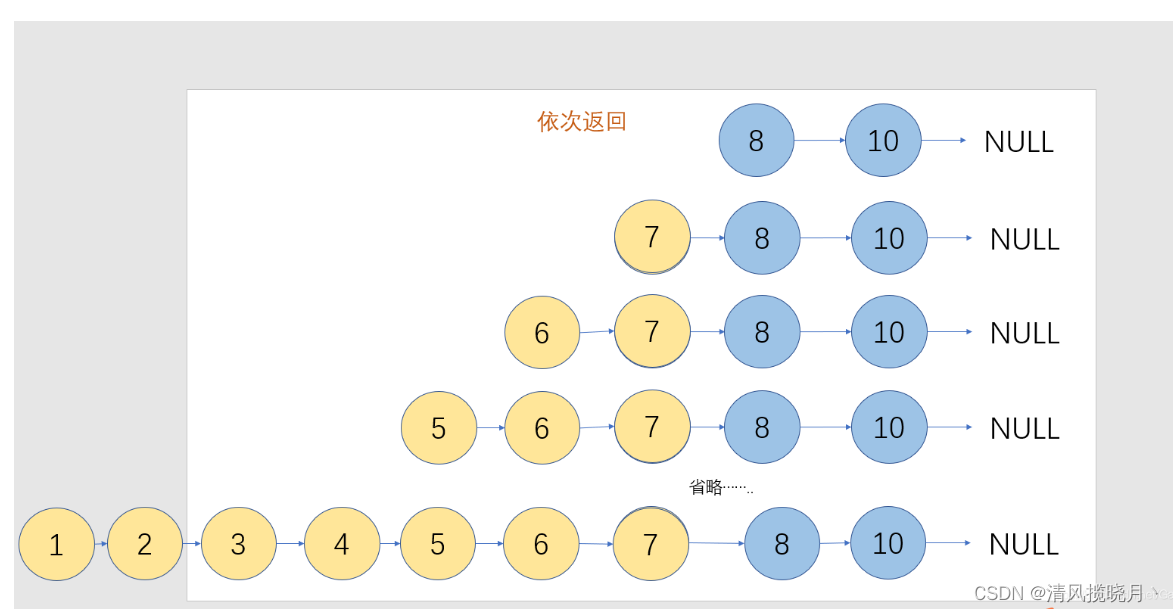
public ListNode method2(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
//如果某一个链表为空,返回另一个不为空的链表
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
if(l1.val<=l2.val){
//如果list1的头结点小于list的头结点,递归 合并list1剩余的部分和list2
l1.next = method2(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else {
l2.next = method2(l2.next, l1);
return l2;
}
}
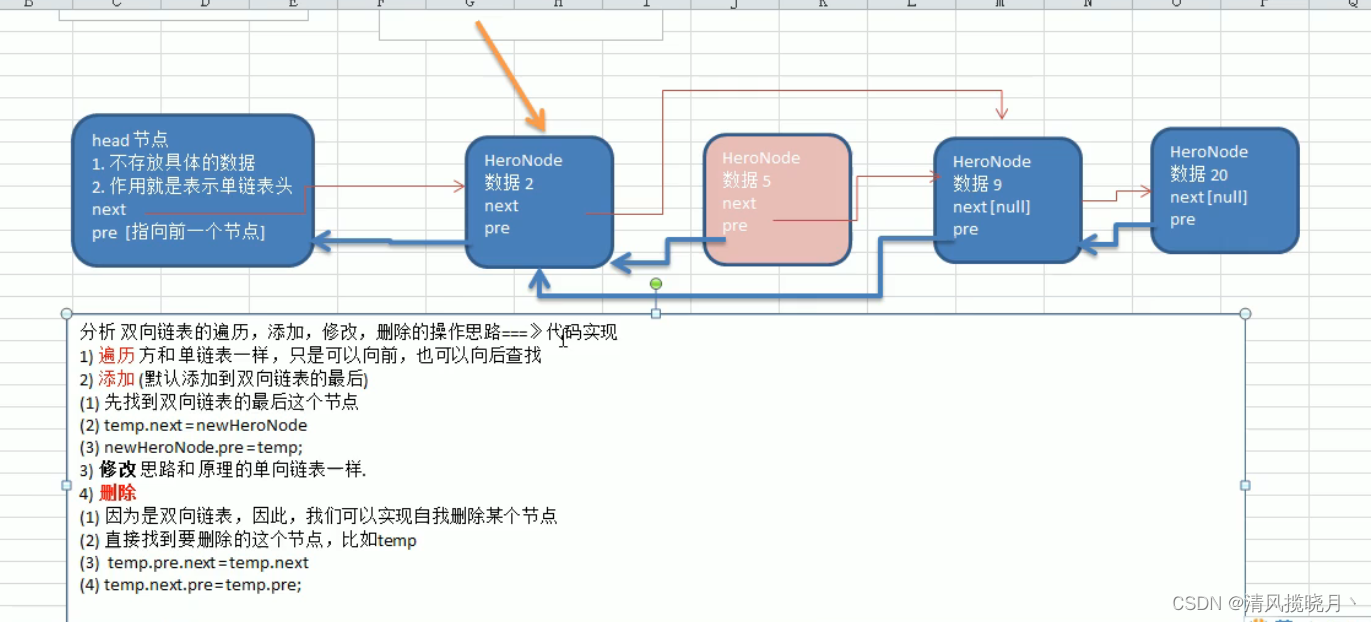
(2)双向链表

class DoubleLinkedList{
//初始化头节点
private HeroNode2 head = new HeroNode2(0,"","");
//返回头节点
public HeroNode2 getHead() {
return head;
}
//显示链表[遍历]
public void list(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//因为头节点不能动,所以定义一个变量
HeroNode2 temp = head.next;
//遍历
while (true){
//判断节点是否在最后
if (temp==null){
break;
}
//输出信息
System.out.println(temp);
//节点后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//添加一个双向链表到最后
public void add(HeroNode2 heroNode){
HeroNode2 temp = head;
while (true){
if(temp.next==null) {
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
temp.next = heroNode;
heroNode.pre = temp;
}
public void update(HeroNode2 newHeroNode){
//判断是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//找到需要修改的节点的编号no
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode2 temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false; //表示是否找到该节点
while (true){
if(temp == null){
break;//遍历完链表
}
if(temp.no==newHeroNode.no){
//找到该节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
//根据flag判断是否找到节点
if(flag){
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
}else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号%d的节点\n",newHeroNode.no);
}
}
public void delete(int no){
if(head.next ==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,无法删除");
return;
}
HeroNode2 temp = head.next;//单链表删除需要遍历到删除节点的前一个,双向链表需要遍历到当前节点
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if(temp==null){
break;
}
if (temp.no==no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(flag){
// temp.next = temp.next.next;//【单向链表】
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
if(temp.next != null) {
temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
}
}else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点没找到\n",no);
}
}
}
双向链表按照序号顺序添加
public void addByOrder(HeroNode2 heroNode){
HeroNode2 temp = head;
boolean flag = false;// 编号是否存在,默认为false
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if(temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
//位置找到,插入到temp后面
break;
}else if(temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
//说明编号存在
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//遍历链表
}
//判断flag的值
if(flag){
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号%d已经存在,不能加入\n",heroNode.no);
}else {
//插入到链表中,temp的后面[单向链表]
// heroNode.next = temp.next;
// temp.next = heroNode;
//双向链表1.heroNode指向temp节点的下一个节点
heroNode.next = temp.next;
if (temp.next != null){
temp.next.pre = heroNode;
}
//2.temp节点指向heroNode
temp.next = heroNode;
heroNode.pre = temp;
}
}
单向环形链表(约瑟夫问题)
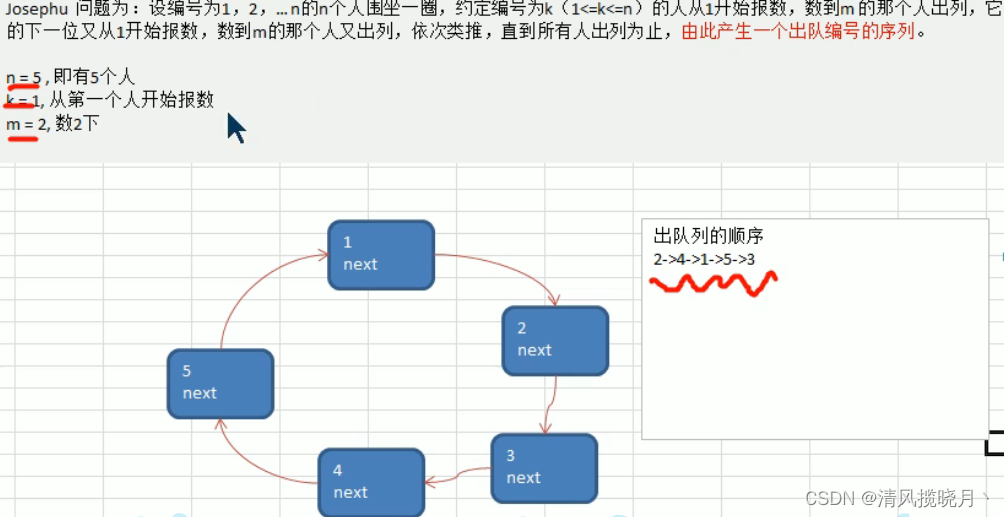
环形链表:
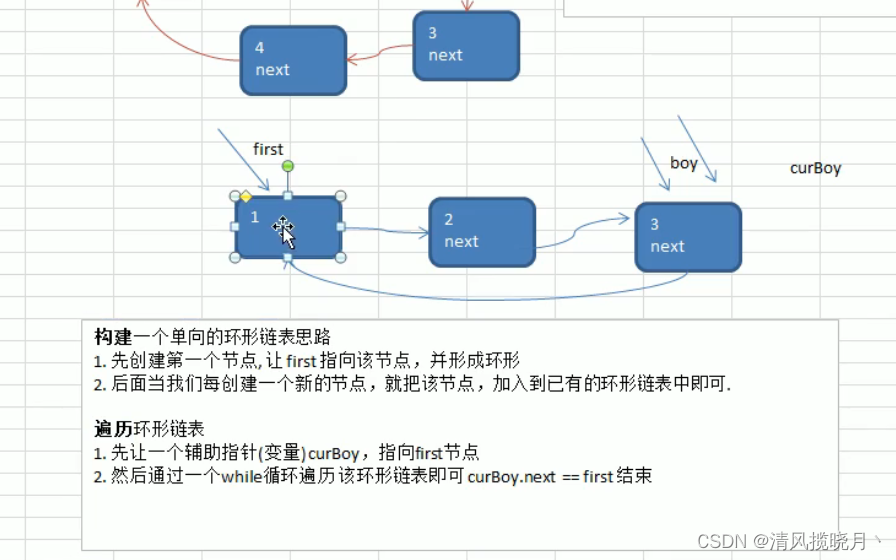
//环形单向链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList{
//创建一个first节点
private Boy first = new Boy(-1);
//添加一个小孩节点,构建环形链表
public void addBaby(int nums){
if(nums < 1){
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null; //帮助指针,创建环形链表
//使用for循环创建环形链表
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++) {
//根据编号创建小孩节点
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
//如果是第一个小孩
if(i == 1){
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);//构成环
curBoy = first; //让帮助指针指向第一个小孩
}else {
curBoy.setNext(boy); //最后一个节点指向新节点
boy.setNext(first); //新节点连接首节点
curBoy = boy; //帮助指针回到最后节点【新节点】
}
}
}
//遍历当前环形链表
public void showBoy(){
//判断链表是否为空
if (first == null){
System.out.println("没有任何小孩");
return;
}
//因为first指针不能动,所以需要辅助指针
Boy curBoy = first;
while (true){
System.out.printf("小孩的编号 %d \n",curBoy.getNo());
if (curBoy.getNext() == first){
break;
}
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();
}
}
}
class Boy{
private int no;
private Boy next;
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
问题思路:
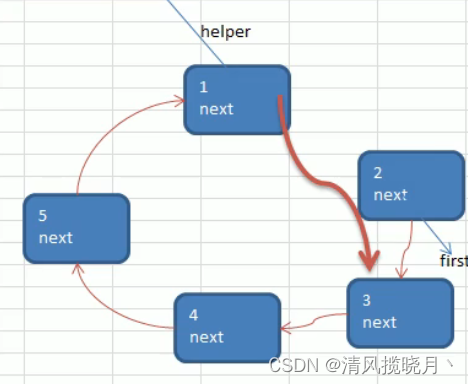

/**
* @param startNo 表示从第几个小孩开始数数
* @param countNum 表示数几下
* @param nums 表示最初有多少小孩在圈中
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums){
//对数据进行检验
if(first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums){
System.out.println("输入参数不合法");
return;
}
//创建辅助指针,帮小孩出圈
Boy helper = first;
//将辅助指针指向链表最后节点
while (true){
if (helper.getNext() == first){
break;
}
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//开始数数前,first和helper需要移动 startNo-1 次
for (int i = 0; i < startNo - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//开始数数时,first和helper需要同时移动 countNum-1 次
while (true){
if (helper == first){ //说明圈中只剩下一个节点
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < countNum - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
//此时的first节点指向的是出圈节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n",first.getNo());
//将first指向的节点出圈
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的节点%d\n",helper.getNo());
}
四丶栈
介绍:
 应用场景:
应用场景:

代码实现:
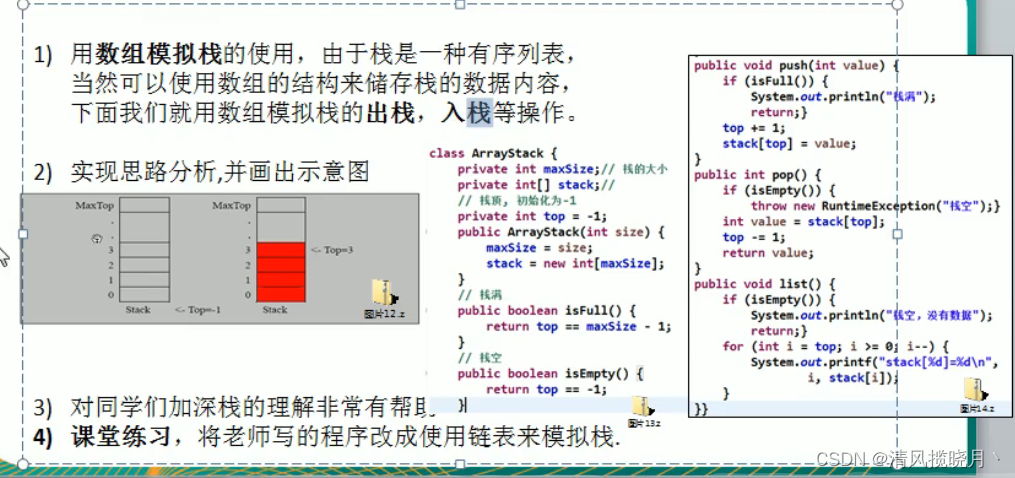
数组模拟思路
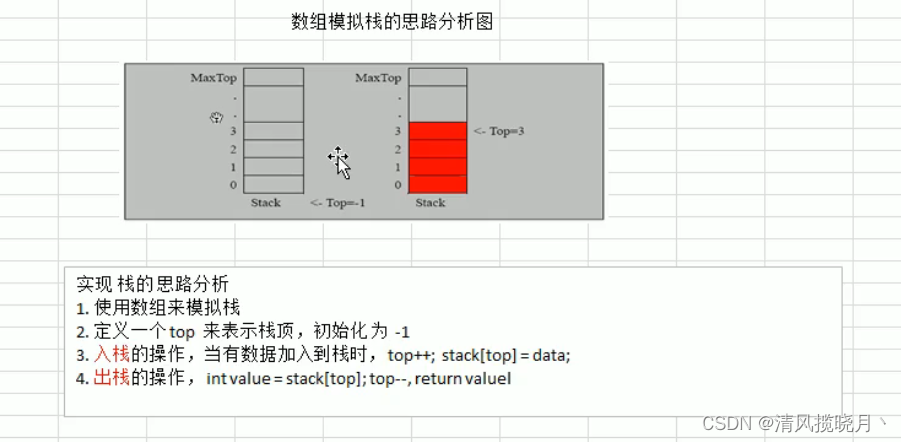
class ArrayStack{
private int maxSize; //栈的大小
private int[] stack; //数组模拟栈
private int top = -1; //栈顶
//构造器
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull(){
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
//入栈
public void push(int value){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
//出栈
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
//遍历栈
public void list(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据");
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]);
}
}
}
使用栈完成算术运算符的表达
思路:

解决处理多位数问题
package D栈;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "70+2*6-2";
//创建两个栈
ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
int index = 0;//用于扫描表达式
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' ';
String keepNum = "";//用于拼接多位数
while (true) {
ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (operStack.isOper(ch)) {//扫描到是符号
if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
//如果当前遍历到的符号优先级小于或等于符号栈中符号的优先级,
//则从数栈中pop出两个数,从符号栈中pop出一个符号,进行运算,
// 然后将运算结果入数栈,将当前遍历到的符号入符号栈;
if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
operStack.push(ch);
} else {
//如果**当前遍历到的符号优先级大于符号栈中符号优先级**,则将该符号直接入符号栈
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {
//若符号栈为空则入符号栈;
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {//扫描到是数字
//numStack.push(ch-48);
//处理多位数:
// 当index扫描到数字后 再往后扫描一位 若后一位是符号则将该数字入数栈 否则继续扫描
// 需要定义一个变量字符串用于拼接数字
//如果ch已经是expression的最后一位则直接入栈
keepNum += ch;
if (index == expression.length() - 1) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
} else {
if (operStack.isOper(expression.substring(index + 1, index + 2).charAt(0))) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
//注意要将keepNum清空
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
index++;
if (index >= expression.length()) {
break;
}
}
//表达式遍历完毕后,则按顺序从数栈和符号栈中pop出值进行运算
while (true) {
if (operStack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
}
System.out.printf("表达式%s的结果为:%d", expression, numStack.pop());
}
}
class ArrayStack2 {
private int maxSize;//栈的最大容量
private int[] stack;//定义一个数组 栈的数据存在数组中
private int top = -1;//指向栈顶
public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[maxSize];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//显示当前栈顶元素
public int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
//入栈
public void push(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.printf("栈满,无法入栈");
return;
} else {
top++;
stack[top] = data;
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空");
} else {
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
}
//显示栈
public void show() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空");
} else {
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
//返回运算符的优先级 规定数字越大优先级越高
public int priority(int oper) {
if (oper == '*' || oper == '/') return 1;
else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') return 0;
else return -1;//假设当前只有+ - * /四种符号
}
//判断是否是符号
public boolean isOper(int oper) {
return oper == '+' || oper == '-' || oper == '*' || oper == '/';
}
//定义运算规则
public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
}
前,中,后缀表达式
(1)前缀表达式
(2)中缀表达式

(3)后缀表达式
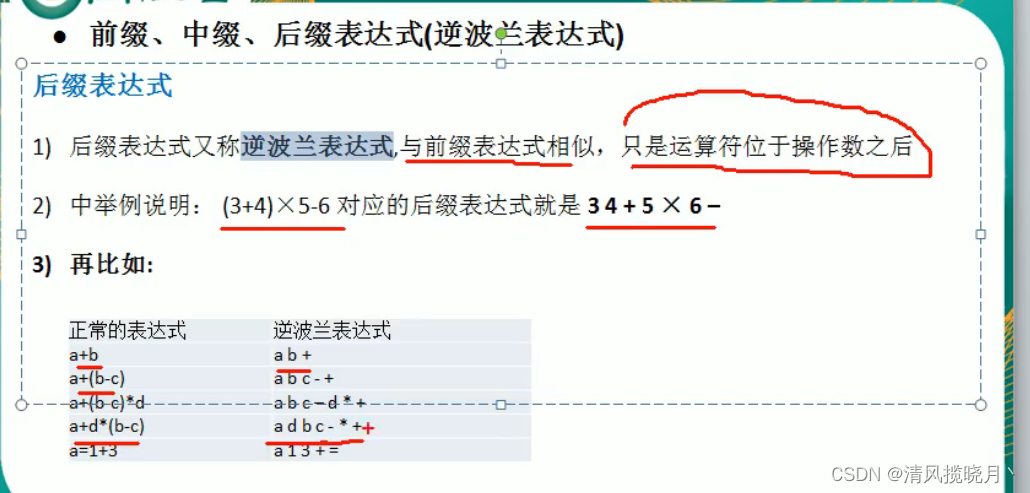

(4)逆波兰表达式运算器

public class PoLandLocation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先定义逆波兰表达式
//(3+4)*5-6 -> 3 4 + 5 * 6 -
//4*5-8+60+8/2 -> 4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +
//说明为了方便,逆波兰表达式 的数字和符号使用空格隔开
String suffixExpression2 = "3 4 + 5 * 6 -";
String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +";
//思路
//1.先将逆波兰表达式放入ArrayList中
//2.将ArrayList传递给一个方法,配合栈完成计算
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
strings = getListString(suffixExpression);
System.out.println(strings);
System.out.println("结果为:"+calculate(strings));
}
//方法存入表达式
public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression){
//将表达式分割
String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ele: split) {
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
//方法运算
public static int calculate(List<String> ls){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String ele: ls) {
//使用正则表达式取出数
if(ele.matches("\\d+")){
//匹配数字入栈
stack.push(ele);
}else {
//否则pop两个数计算结果入栈
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if(ele.equals("+")){
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (ele.equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
}else if (ele.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
}else if (ele.equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("包含错误运算符");
}
stack.push(""+res);
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
(5)中缀转后缀表达式
思路:


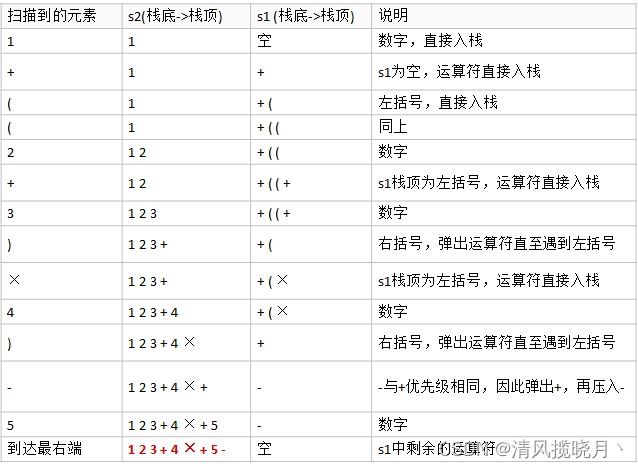
package D栈;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
// 逆波兰表达式完整版(可以匹配小数点)
public class PolandNotationFullVersion {
//完成将一个中缀表达式转成后缀表达式的功能
//说明
//1. 1+((2+3)×4)-5 => 转成 1 2 3 + 4 × + 5 –
//2. 因为直接对str 进行操作,不方便,因此 先将 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" =》 中缀的表达式对应的List
// 即 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" => ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5]
//3. 将得到的中缀表达式对应的List => 后缀表达式对应的List
// 即 ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5+10/61";
List<String> expressionList = expressionSplit(expression);
List<String> postfixExpression = postfixExpressionChange(expressionList);
System.out.println("中缀转后缀表达式:"+postfixExpression);
double ans = calculate(postfixExpression);
System.out.println(expression + "=" + ans);
}
/*
1.将字符串的表达式拆分开来,保存到List中,目的是为了方便后续的计算。
*/
public static List<String> expressionSplit(String str) {
List<String> expressionList = new ArrayList<String>();
String temp = "";
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++) {
char item = str.charAt(i);
if(!numberJudge(item)) {
expressionList.add(String.valueOf(item));
}else if( item>= 48 && item<= 57 || item == 46) {
temp+= item;
if(i+1==str.length() || !numberJudge(str.charAt(i+1))) {
expressionList.add(String.valueOf(temp));
temp = "";
}
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("表达式格式不正确");
}
}
return expressionList;
}
/*
2. 根据规则,将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式。一个stack,一个List存储结果
*/
public static List<String> postfixExpressionChange(List<String> expressionSplited){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); //存储符号
List<String> postfixExpression = new ArrayList<String>(); //存储后缀表达式
for(String item : expressionSplited) {
if(numberJudge(item.toCharArray()[0])) {
postfixExpression.add(item);
}else {
// 初始状态,符号栈里面什么都没有
if(stack.size()==0) {
stack.push(item);
} else {
Operation2 oprCls = new Operation2();
String lastOpr = stack.peek();
if(item.equals("(") || oprCls.oprPriority(item) > oprCls.oprPriority(lastOpr)) {
stack.push(item);
}else if(item.equals(")")) {
while(stack.size()>0 && !stack.peek().equals("(")) {
postfixExpression.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.pop();
}else {
postfixExpression.add(stack.pop());
stack.push(item);
}
lastOpr = "";
}
}
}
while(stack.size()!=0) {
postfixExpression.add(stack.pop());
}
return postfixExpression;
}
/*
3.根据逆波兰表达式直接给计算器进行相应的计算
*/
public static Double calculate(List<String> list) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
for(String item : list) {
if(item.matches("((\\d+)(\\.\\d+)?)")) {
stack.push(item);
}else {
String num2Str = stack.pop();
String num1Str = stack.pop();
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(num2Str),
num1 = Double.parseDouble(num1Str),
ans = 0;
if(item.equals("+")) {
ans = num1 + num2;
}else if(item.equals("-")) {
ans = num1 - num2;
}else if(item.equals("*")) {
ans = num1 * num2;
}else if(item.equals("/")) {
ans = num1 / num2;
}
stack.push("" + ans);
}
}
return Double.parseDouble(stack.pop());
}
/*
* 4.定义一个方法,判断该字符是数字还是符号
*/
public static Boolean numberJudge(char ch) {
String oprRegEx = "[\\+\\-\\*\\/()]";
if(Pattern.matches(oprRegEx,String.valueOf(ch))) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
class Operation2 {
private int BRACKET = 0;
private int ADD = 1;
private int DELETE = 1;
private int MULTIPLY = 2;
private int DIVIDE = 2;
public Integer oprPriority(String opr) {
int result = 0;
switch(opr) {
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = DELETE;
break;
case "*":
result = MULTIPLY;
break;
case "/":
result = DIVIDE;
break;
default:
result = BRACKET;
break;
}
return result;
}
}
五、递归
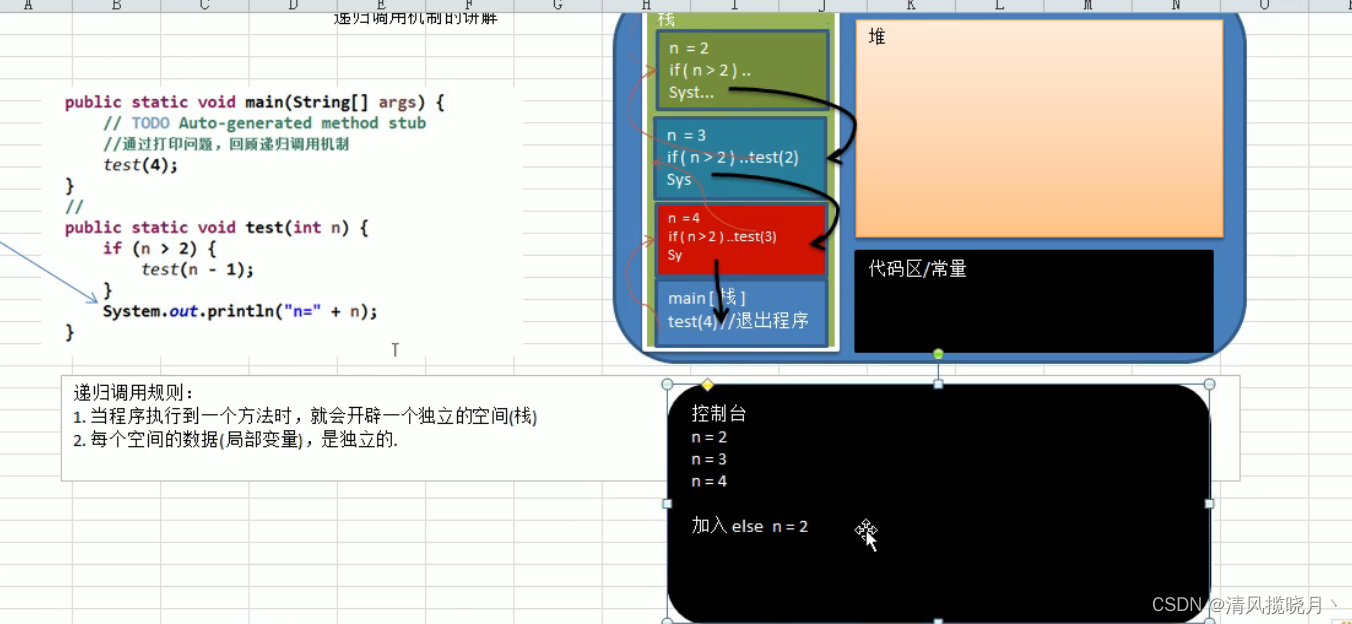
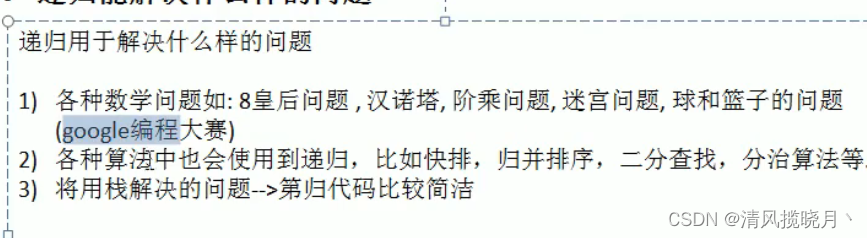

(1)迷宫问题

package E栈;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/2/25
*/
public class MIGONG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个二维数组模拟迷宫
int [][] map = new int [8][7];
//使用1表示墙,上下置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
//左右置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
//设置挡板 第四行二三列
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
//输出地图
System.out.println("地图的情况:");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//输出新地图
setWay(map,1,1);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("新地图的情况:");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//使用递归给小球找路
//1. map表示地图
//2. i,j表示从地图的哪个位置出发(1,1)
//3. 如果小球能到map[6][5]位置,则说明通路找到
//4. 约定:当map[i][j] 为0表示该点没有走过 当为 1 表示墙 ;2 表示通路可以走 ; 3 表示该路已经走过,但是走不通
//5. 走迷宫,需要定义一个策略(方法) 下->右->上->左 , 如果该点走不通,再回溯
/**
*
* @param map 表示地图
* @param i 从哪个位置开始
* @param j
* @return 找到通路返回true,返回false
*/
public static boolean setWay(int[][] map,int i,int j){
if(map[6][5] == 2){ //通路找到
return true;
}else {
if(map[i][j] == 0){ //当前点还未走过
//按照策略,下右上左
map[i][j] =2; //假设该点可以走通
if(setWay(map,i+1,j)){//向下走
return true;
} else if (setWay(map,i,j+1)) {//向右走
return true;
} else if (setWay(map,i,j-1)) {//向左走
return true;
} else if (setWay(map,i-1,j)) {//向下走
return true;
}else {
//说明该点走不通
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
(2)八皇后

具体的执行过程如下:
先将第一个皇后放在第一行第一列,然后将第二个皇后放在第二行第一列,判断该种摆法是否符合要求。很明显这样摆不行,有两个皇后会在同一列。再将第二个皇后放在第二行第二列,这样也不行,两个皇后会在一条斜线上。将第二个皇后放在第二行第三列,这样满足当前条件。
目前已经有两个皇后满足条件,接下来放第三个,还是从第三行第一列开始放置,不满足条件再放第二列,第三列…一直到第8个皇后也能放在一个不冲突的位置,此时找到一个符合要求的解。
然后我们开始回溯,将第一个皇后放在第一行第二列,后面的就继续按上面的方式循环,一直到回溯完毕,找出所有符合条件的解为止。
参考文献2有张图,比较详细的用图描述了上面的过程,贴出来大家参考。下面图描述的是4皇后的回溯过程,原理跟8皇后是一致的。

package E栈;
public class NQueueV2 {
public static int N = 8;
public static int[][] boards = new int[N][N];
public static int result = 0;
public static void putQueQue(int k) {
if (k == N) {
result++;
for(int row=0; row<N; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<N; col++) {
System.out.print(boards[row][col] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
} else {
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
if (check(k, i)) {
boards[k][i] = 1;
putQueQue(k+1);
boards[k][i] = 0;
}
}
}
}
public static boolean check(int row, int column) {
//判断同一列
for(int i=0; i<row; i++) {
if (boards[i][column] == 1) {
return false;
}
}
//左斜线
for(int m=row-1, n=column-1; m>=0 && n >= 0; m--, n--) {
if (boards[m][n] == 1) {
return false;
}
}
//右斜线
for(int m=row-1, n=column+1; m>=0 && n<N; m--, n++) {
if (boards[m][n] == 1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
putQueQue(0);
System.out.println("result is: " + result);
}
}
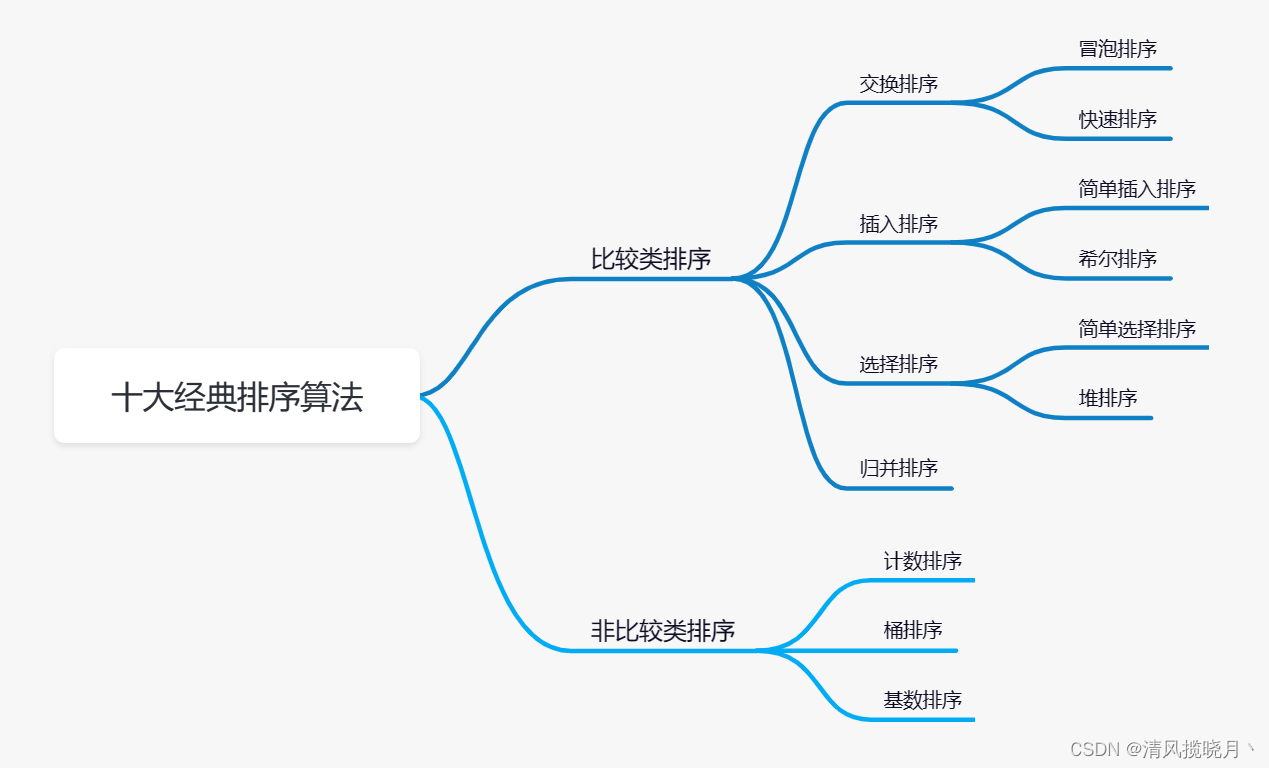
六、排序
大概:
(1)冒泡排序

一共需要排序 arr.length - 1 趟
第一趟排序4次
第二趟排序3次
第三趟排序2次
第四趟排序1次
第 i + 1 趟排序 arr.length - 1 - i 次
1、简易版本
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arr = new int[]{3,-1,4,-6,0};
int temp = 0; //临时变量
System.out.println("原数组:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//冒泡排序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"趟冒泡排序:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
2、优化
某趟排序可能没有发生过一次交换,可提前结束冒泡排序
public class BubbleSortN {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arr = new int[]{3,9,-1,10,20};
System.out.println("排序前:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
BubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void BubbleSort(int[] arr){
int temp = 0;
boolean flag = false;
//冒泡排序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
flag = true;
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
if(!flag){
break;
}else {
flag = false;
}
}
}
}
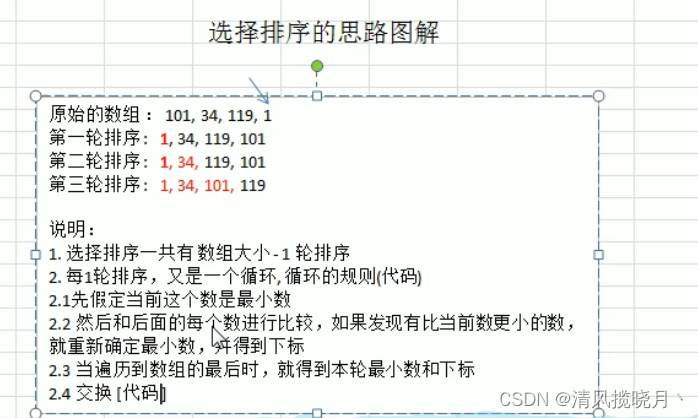
(2)选择排序
思路:
public class SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{104,34,119,1};
selectSort(arr);
}
public static void selectSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
int min = arr[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(min > arr[j]){ //重置最小值
min = arr[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
//最小值交换
if(minIndex != i) {
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = min;
}
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"轮:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
选择排序运行速度比冒泡排序快
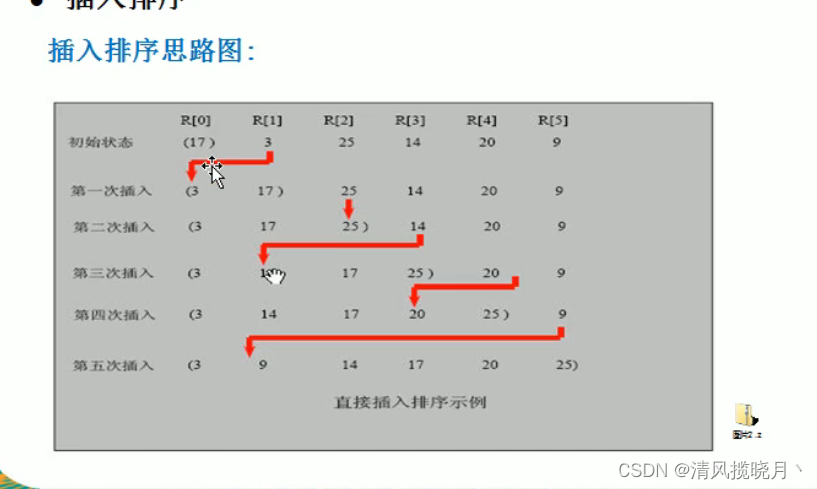
(3)插入排序
思路

package F排序;
import D栈.ArrayStackDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/2/28
*/
public class InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{104,34,119,1};
System.out.println("排序前:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
insertSort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void insertSort(int[]arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
//定义待插入数
int val = arr[i];
int j = i;
// 1.代插入数如果 val < val前面的数,需要进行交换
// 2.将索引后移继续对比,若还是小于前面的数,继续循环,不小于则符合条件arr[j] = val 将数插入到正确位置
// 3. j = 0 则说明待插入数已经是与比较部分的最小数了,直接arr[j] = val
while (j > 0 && val < arr[j - 1]){
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = val;
}
}
}
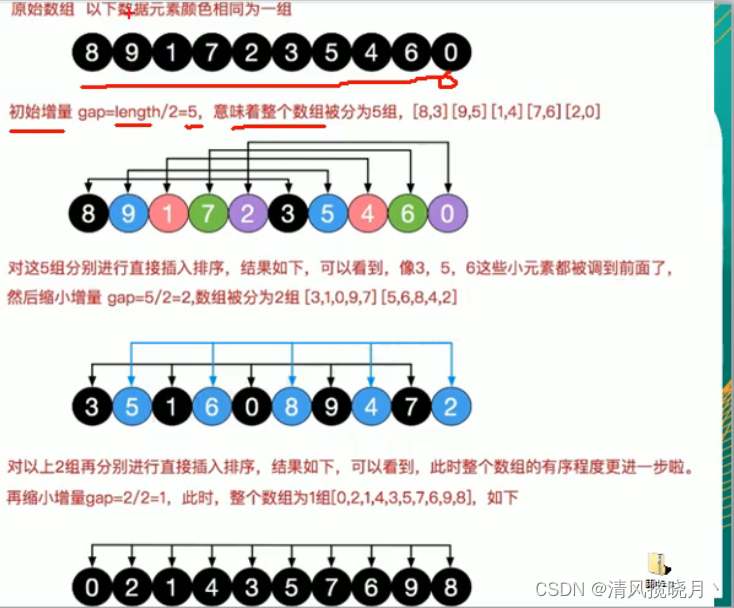
(4)希尔排序
思路

package F排序;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/3/1
*/
public class ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int []arr = new int[]{8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0};
// shellSort(arr);
int[] arr = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*8000000);
}
System.out.println("排序前:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println("排序前时间:"+format);
shellSort1(arr);
Date date2 = new Date();
String format2 = simpleDateFormat.format(date2);
System.out.println("排序后时间:"+format2);
}
//1.交换
public static void shellSort2(int []arr){
//根据前面逐步分析
int temp;
int count = 0;
for (int gap = arr.length / 2; gap > 0 ; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) {
//遍历各组所有元素,共有gap组,步长gap
for (int j = i - gap; j >= 0 ; j -= gap) {
//如果当前元素 > 加上步长的元素,则就进行交换
if(arr[j] > arr[j + gap]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + gap];
arr[j + gap] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("第"+(++count)+"轮"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
// int temp = 0;
// //第一轮 10/2
// for (int i = 5; i < arr.length; i++) {
// for (int j = i - 5; j >= 0 ; j -= 5) {
// if(arr[j] > arr[j + 5]){
// temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 5];
// arr[j + 5] = temp;
// }
// }
// System.out.println("第"+(i-4)+"轮:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
// }
//
// //第二轮 5/2
// for (int i = 2; i < arr.length; i++) {
// for (int j = i - 2; j >= 0 ; j -= 2) {
// if(arr[j] > arr[j + 2]){
// temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 2];
// arr[j + 2] = temp;
// }
// }
// System.out.println("第"+(i-1)+"轮:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
// }
//
// //第三轮 2/2
// for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0 ; j -= 1) {
// if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){
// temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
// arr[j + 1] = temp;
// }
// }
// System.out.println("第"+(i)+"轮:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
// }
}
//2.移位
public static void shellSort1(int []arr){
int count = 0;
int temp = 0;
int j =0;
for (int gap = arr.length / 2 ; gap > 0 ; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
j = i - gap;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp){
arr[j + gap] = arr[j];
j -= gap;
}
arr[j + gap] = temp;
System.out.println("第"+(++count)+"轮"+Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
}
}
在比较这两个希尔排序算法的性能时,我们可以看到一些明显的区别:
交换次数不同:在 shellSort1 中,内层循环是通过移动元素而非交换元素来实现的,而 shellSort2 中使用了交换操作。交换操作相对于移动操作来说,通常需要更多的时间开销。因此,shellSort1 的效率可能会比 shellSort2 更高。
增量序列选择:两种算法中的增量序列选择方式稍有不同。shellSort1 每次将增量 gap 减半,而 shellSort2 则是直接除以 2。在实际应用中,增量序列的选择会影响算法的性能,不同的增量序列可能导致不同的排序效率。
输出调试信息:shellSort2 在每一轮排序后都会输出当前数组状态,而 shellSort1 则是在整个排序结束后输出最终结果。输出操作会增加额外的IO开销,影响排序的性能。
综合上述几点,可以解释为什么 shellSort1 可能会比 shellSort2 快。主要原因在于 shellSort1 中避免了不必要的交换操作,并且输出调试信息的时机更为合适。另外,增量序列的选择也可能对排序性能产生影响。
(5)快速排序
思路:



package F排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/3/3
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arr = new int[]{-9,78,0,23,-567,70};
quickSort(arr,0,arr.length - 1);
System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void quickSort(int[]arr,int left,int right){
int l = left; //左下标
int r = right; //右下标
int temp = 0;
int pivot = arr[(right+left)/2]; //中轴值
while (l < r){
//从中轴值左边找 > pivot的
while (arr[l] < pivot){
l += 1;
}
//从中轴值右边找 < pivot的
while (arr[r] > pivot){
r -= 1;
}
//如果 l >= r 说明排序完成
if(l >= r){
break;
}
//从上面两个while循环找到相应值后,进行交换
temp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[l] == pivot 需要r--前移
if(arr[l] == pivot){
r -= 1;
}
//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[r] == pivot 需要l++后移
if(arr[r] == pivot){
l += 1;
}
}
//如果l == r,必须l++,r--,否则出现栈溢出
if(l == r){
l += 1;
r -= 1;
}
//向左递归
if(left < r){
quickSort(arr,left,r);
}
//向右递归
if (right > l){
quickSort(arr,l,right);
}
}
}
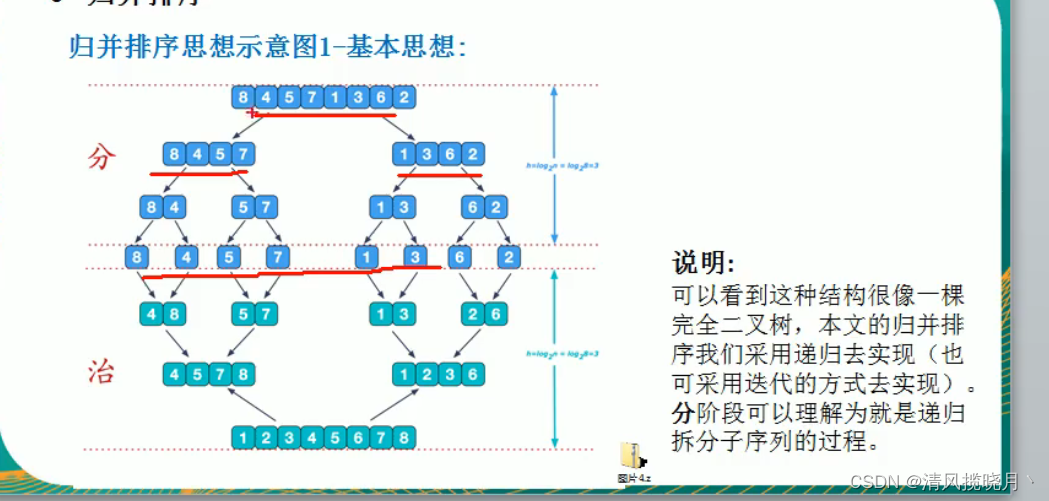
(6)归并排序
思路:

package F排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author: LBC
* @Date: 2024/3/4
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arr = {8 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 1 , 3 , 6 , 2};
int []temp = new int[arr.length];
mergeSort(arr,0, arr.length - 1,temp);
System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
//分+合的方法
public static void mergeSort(int[]arr,int left,int right,int[]temp){
if(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2; //中间索引
//左递归进行分解
mergeSort(arr,left,mid,temp);
//右递归进行分解
mergeSort(arr,mid + 1,right,temp);
//合并
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);
}
}
//合并的方法
/**
*
* @param arr 排序原始数组
* @param left 左边有序序列的初始索引
* @param mid 中间索引
* @param right 右边索引
* @param temp 做中转的数组
*/
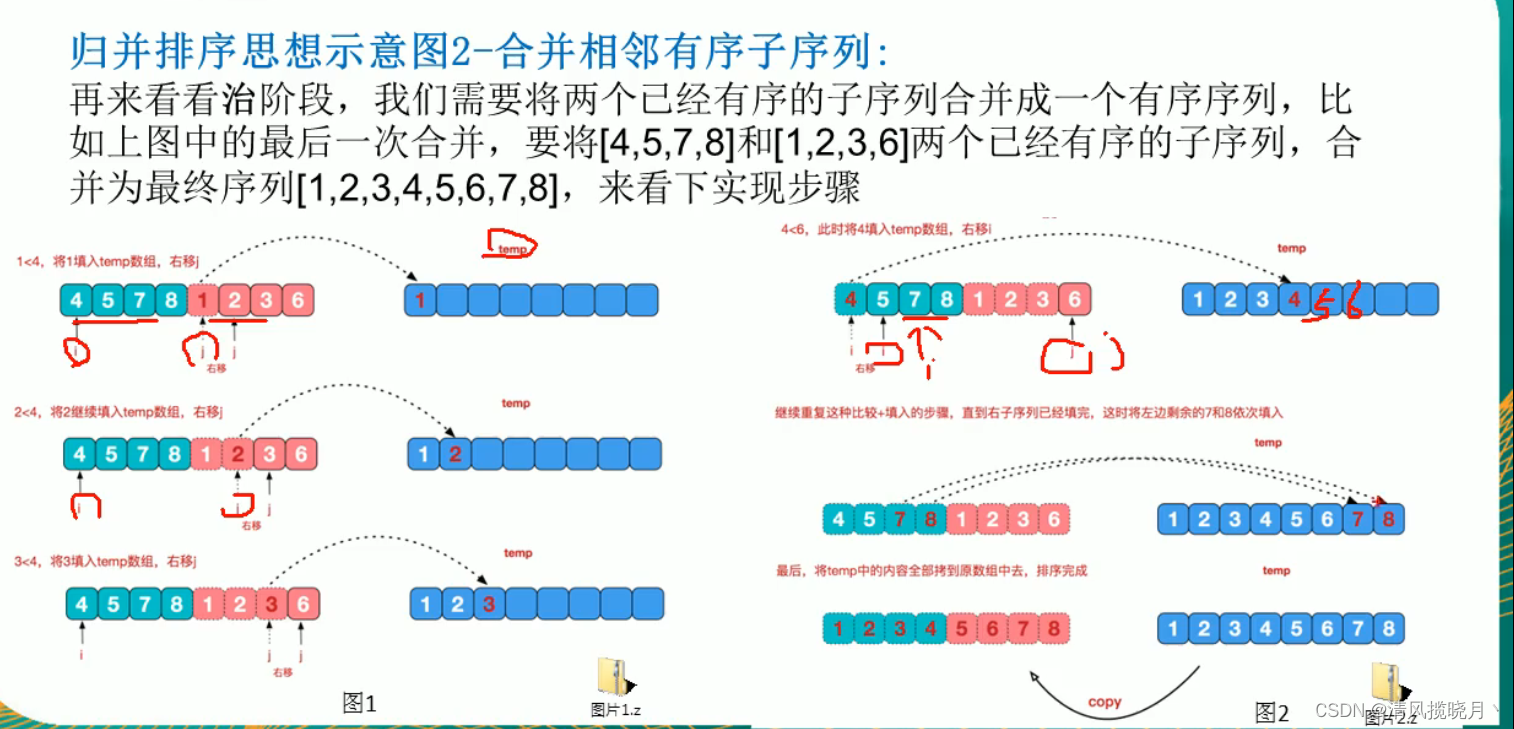
public static void merge(int[]arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[]temp){
int i = left; // 初始化i,左边有序序列的初始索引
int j = mid + 1; //初始化j,右边有序序列的初始索引
int t = 0; // 指向temp数组的当前索引
//(1)
//先把左右两边(有序)的数据按照规则填充到temp数组
//直到左右两边的有序序列,有一边处理完毕为止
while (i <= mid && j<= right){ //继续
//左边的有序序列的当前元素 <= 右边有序序列的当前元素
//将左边的当前元素拷贝到temp数组,然后i,t后移
if(arr[i] <= arr[j]){
temp[t] = arr[i];
t += 1;
i += 1;
}else {
//右边的有序序列的当前元素 <= 左边有序序列的当前元素
//将右边的当前元素拷贝到temp数组,然后j,t后移
temp[t] = arr[j];
t += 1;
j += 1;
}
}
//(2)
//把有剩余数据的一边数据依次全部填充到temp,可能左边剩,也可能右边剩
while (i <= mid){ //左边剩余,全部填充到temp
temp[t] = arr[i];
i += 1;
t += 1;
}
while (j <= right){//右边剩余
temp[t] = arr[j];
j += 1;
t += 1;
}
//(3)
//将temp数组的元素拷贝到arr
//并不是每次拷贝所有数据
t = 0;
int tempLeft = left;
System.out.println("tL:"+tempLeft+","+"r:"+right);
while (tempLeft <= right){
//例子int arr[] = {8,4,5,7,1,3,6,2}
//第一次合并 tempLeft = 0,right = 1
//第二次 tempLeft = 2,right = 3
//第三次 tempLeft = 0,right = 3
//最后一次 tL = 0,right = 7
arr[tempLeft] = temp[t];
tempLeft += 1;
t += 1;
}
}
}
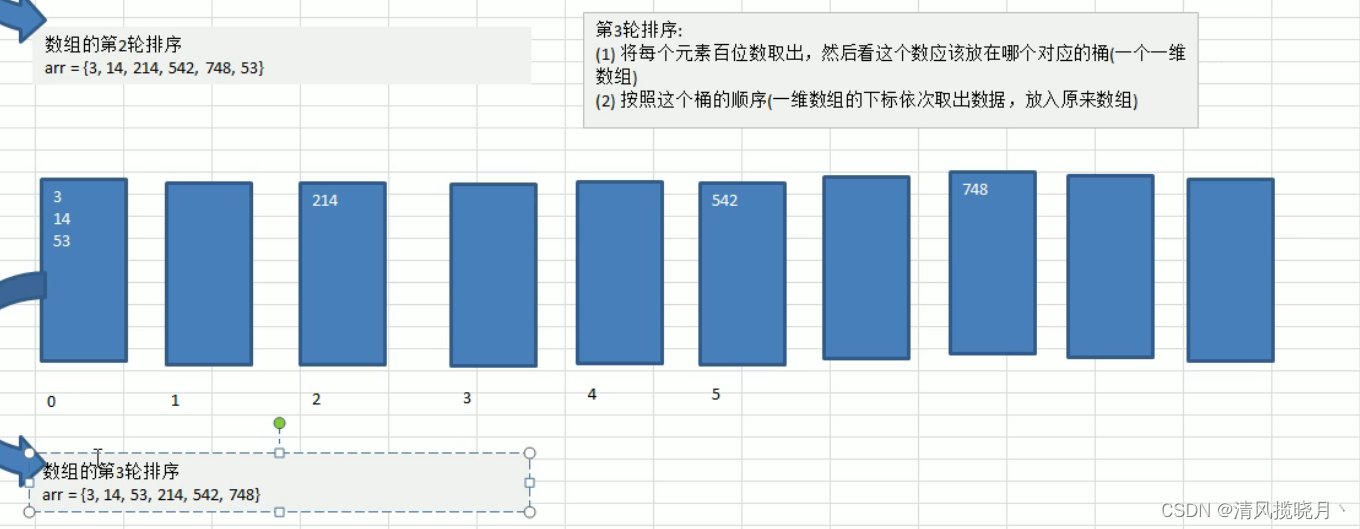
(7) 基数排序
思路:

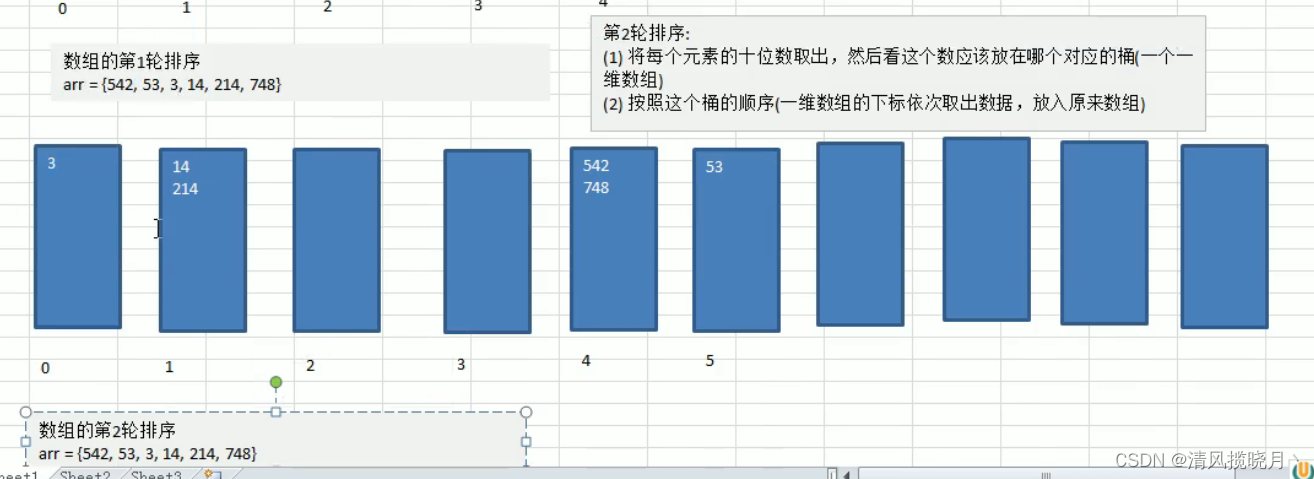
例子:

public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]arr = { 53, 3 , 542 , 748 , 14 , 214};
radixSort(arr);
}
public static void radixSort(int[]arr){
//最终版本
//1. 得到数组中最大的数的位数
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length ; i++) {
if(arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
}
}
//将int 转换为 char
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
//二维数组来表示10个桶,每个桶就是一个一维数组
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
//定义一个一维数组,来记录各个桶每次放入的数据个数
//例如:bucketElementCount[0]记录 bucket[0] 桶放入的个数
//bucketElementCount[1]记录 bucket[1] 桶放入的个数
int[] bucketElementCount = new int[10];
for (int i = 0,n = 1; i < maxLength; i++,n *= 10) {
//第一次是个位,第二次十位,第三次百位
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
//取出每个元素的个数
int digitOfElement = arr[j] / n % 10;
//放入到对应的桶中
bucket[digitOfElement][bucketElementCount[digitOfElement]] = arr[j];
bucketElementCount[digitOfElement]++;
}
//按照这个桶的顺序(一维数组的下标依次取出数据,放入原来数组)
int index = 0;
//遍历每一桶,并将桶中是数据,放入到原数组
for (int k = 0; k < bucketElementCount.length; k++) {
//如果桶中有数据我们才放入到原数组
if(bucketElementCount[k] != 0){
//循环该桶即第k个桶(即第k个一维数组),放入
for (int j = 0; j < bucketElementCount[k]; j++) {
//取出元素放入到arr中
arr[index++] = bucket[k][j];
//第一轮处理后,需要将每个bucketElementCount[k] = 0
}
// 重置所有桶的计数为0
bucketElementCount[k] = 0;
}
}
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"轮的排序处理 arr =" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
(8)排序总结
0、排序算法说明
0.1 排序的定义
对一序列对象根据某个关键字进行排序。
0.2 术语说明
稳定:如果a原本在b前面,而a=b,排序之后a仍然在b的前面;
不稳定:如果a原本在b的前面,而a=b,排序之后a可能会出现在b的后面;
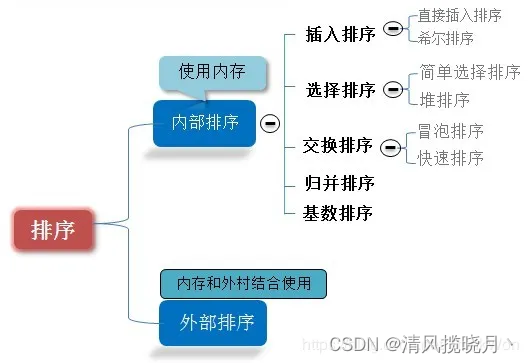
内排序:所有排序操作都在内存中完成;
外排序:由于数据太大,因此把数据放在磁盘中,而排序通过磁盘和内存的数据传输才能进行;
时间复杂度: 一个算法执行所耗费的时间。
空间复杂度:运行完一个程序所需内存的大小。
0.3 算法总结
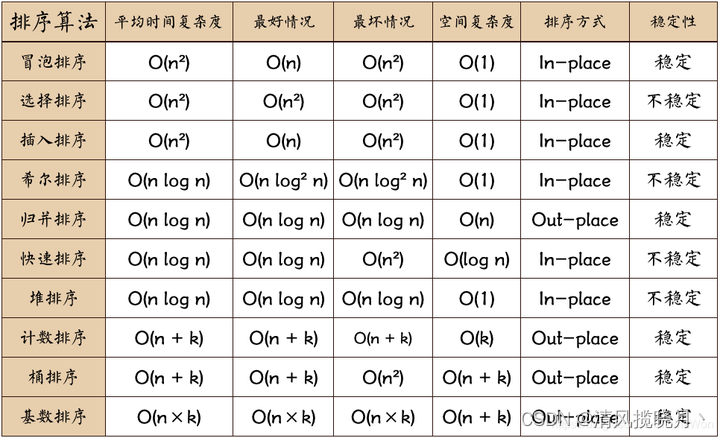
n: 数据规模
k: “桶”的个数
In-place: 占用常数内存,不占用额外内存
Out-place: 占用额外内存





















 33万+
33万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








