2024-01
1. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6 输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9-10^9 <= target <= 10^9- 只会存在一个有效答案
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
map<int, int> map;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i]; // 差值
if (map.find(complement) != map.end()) {
result.push_back(map[complement]);
result.push_back(i);
return result;
}
map[nums[i]] = i;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int target;
int temp;
while(cin>>temp){
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin>>target;
vector<int> result = twoSum(nums, target);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
2. 两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:

输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* curr = dummy;
int carry = 0; // 进位
while(l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL) {
int x = (l1 != NULL) ? l1->val : 0;
int y = (l2 != NULL) ? l2->val : 0;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
curr->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr->next;
if(l1 != NULL) l1 = l1->next;
if(l2 != NULL) l2 = l2->next;
}
// 增添1位
if(carry > 0) {
curr->next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
Solution solution;
ListNode* list1 = createList();
ListNode* list2 = createList();
ListNode* result = solution.addTwoNumbers(list1, list2);
printList(result);
return 0;
}3. 无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = "bbbbb" 输出: 1 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = "pwwkew" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",所以其长度为 3。请注意,你的答案必须是子串的长度,"pwke"是一个子序列,不是子串。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 10^4s由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
// 使用滑动窗口来找出最长的不含重复字符的子串
int n = s.length();
int res = 0; // 记录最长子串的长度
vector<int> index(128, -1); // 记录每个字符在字符串s中最近出现的位置
for(int i = 0, j = 0; j < n; j++) {
i = max(i, index[s[j]] + 1); // 当遇到重复的字符时,将左边界i移动到该重复字符的下一个位置,确保窗口内没有重复字符
res = max(res, j - i + 1); // 每次更新窗口长度并与res比较,取较大者
index[s[j]] = j; // 更新字符在index数组中的位置为当前位置
}
return res;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
string s;
cin >> s;
cout << solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s);
return 0;
}4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
给定两个大小分别为 m 和 n 的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和 nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的 中位数 。
算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(log (m+n)) 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2] 输出:2.00000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4] 输出:2.50000 解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5 ^
提示:
nums1.length == mnums2.length == n0 <= m <= 10000 <= n <= 10001 <= m + n <= 2000-10^6 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^6
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int> curr;
int m = nums1.size();
int n = nums2.size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
curr.push_back(nums1[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
curr.push_back(nums2[i]);
}
sort(curr.begin(), curr.end());
if((m + n) % 2 == 0) {
return (curr[(m + n) / 2] + curr[(m + n) / 2 - 1] ) / 2.0;
} else {
return curr[(m + n) / 2];
}
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
vector<int> nums1, nums2;
int tmp;
cout << "请输入nums1数组的元素:" << endl;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums1.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cout << "请输入nums2数组的元素:" << endl;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums2.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cout << solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2);
return 0;
}解法二:
class Solution {
public:
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int> curr;
int m = nums1.size();
int n = nums2.size();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while(i < m && j < n) {
if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
curr.push_back(nums1[i]);
i++;
}
else {
curr.push_back(nums2[j]);
j++;
}
}
while(i < m) {
curr.push_back(nums1[i]);
i++;
}
while(j < n) {
curr.push_back(nums2[j]);
j++;
}
if((m + n) % 2 == 0) {
return (curr[(m + n) / 2] + curr[(m + n) / 2 - 1] ) / 2.0;
} else {
return curr[(m + n) / 2];
}
}
};5. 最长回文子串
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
如果字符串的反序与原始字符串相同,则该字符串称为回文字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "babad" 输出:"bab" 解释:"aba" 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2:
输入:s = "cbbd" 输出:"bb"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s仅由数字和英文字母组成
// C++
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int n = s.size();
if(n < 2) {
return s;
}
int maxLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
//dp[i][j]表示s[i··j]是否为回文串
vector<vector <int> > dp(n,vector<int>(n, true));
//递归开始
//先枚举子串长度
for(int L = 2; L <= n; L++) {
//枚举左边界,左边界的上限设置可以宽松一些
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j = L + i - 1;
//如果右边界越界,就可以退出当前循环
if(j >= n) {
break;
}
if(s[i] != s[j]) {
dp[i][j] = false;
} else {
if(j-i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
// 只要dp[i][j] == true成立,就表示子串s[i···L]是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置。
if(dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
return s.substr(begin,maxLen);
}
};
int main() {
string s = "";
cin>>s;
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.longestPalindrome(s)<<endl;
return 0;
}解法二:
// C++
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
if(s.empty()) {
return "";
}
int start = 0, end = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int len = max(len1, len2);
if(len > end - start) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substr(start, end - start + 1);
}
int expandAroundCenter(string s, int left, int right) {
while(left >= 0 && right < s.size() && s[left] == s[right]) {
left--;
right++;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
};
int main() {
string s = "";
cin>>s;
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.longestPalindrome(s)<<endl;
return 0;
}6. Z字型变换
将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。
比如输入字符串为 "PAYPALISHIRING" 行数为 3 时,排列如下:
P A H N A P L S I I G Y I R
之后,你的输出需要从左往右逐行读取,产生出一个新的字符串,比如:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"。
请你实现这个将字符串进行指定行数变换的函数:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
示例 1:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3 输出:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
示例 2:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4 输出:"PINALSIGYAHRPI" 解释: P I N A L S I G Y A H R P I
示例 3:
输入:s = "A", numRows = 1 输出:"A"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s由英文字母(小写和大写)、','和'.'组成1 <= numRows <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string covert(string s, int numRows) {
if(numRows == 1) return s;
int n = s.size();
int k = 2 * numRows - 2; // 计算 Z 字形的周期长度,即每个完整的 Z 字形有多少个字符
vector<string> a(numRows);
// 创建一个长度为 numRows 的字符串数组 a,用于存储 Z 字形排列后的每一行字符串
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[min(k - i % k, i % k)] += s[i];
// k - i % k 和 i % k 分别表示当前字符在 Z 字形周期中的上半部分和下半部分的位置
}
return accumulate(a.begin(), a.end(), string("")); // 拼接
}
};
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
int numRows;
cin >> numRows;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.covert(s, numRows);
return 0;
}
7. 整数反转
给你一个 32 位的有符号整数 x ,返回将 x 中的数字部分反转后的结果。
如果反转后整数超过 32 位的有符号整数的范围 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1] ,就返回 0。
假设环境不允许存储 64 位整数(有符号或无符号)。
示例 1:
输入:x = 123 输出:321
示例 2:
输入:x = -123 输出:-321
示例 3:
输入:x = 120 输出:21
示例 4:
输入:x = 0 输出:0
提示:
-2^31 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int reverse(int x) {
// if(x == 0) return 0;
int res = 0;
while(x != 0) {
if(res < INT_MIN / 10 || res > INT_MAX / 10) {
return 0;
}
res = res * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return res;
}
};
int main() {
int x;
cin >> x;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.reverse(x) << endl;
return 0;
}8. 字符串转换正数(atoi)
请你来实现一个 myAtoi(string s) 函数,使其能将字符串转换成一个 32 位有符号整数(类似 C/C++ 中的 atoi 函数)。
函数 myAtoi(string s) 的算法如下:
- 读入字符串并丢弃无用的前导空格
- 检查下一个字符(假设还未到字符末尾)为正还是负号,读取该字符(如果有)。 确定最终结果是负数还是正数。 如果两者都不存在,则假定结果为正。
- 读入下一个字符,直到到达下一个非数字字符或到达输入的结尾。字符串的其余部分将被忽略。
- 将前面步骤读入的这些数字转换为整数(即,"123" -> 123, "0032" -> 32)。如果没有读入数字,则整数为
0。必要时更改符号(从步骤 2 开始)。 - 如果整数数超过 32 位有符号整数范围
[−231, 231 − 1],需要截断这个整数,使其保持在这个范围内。具体来说,小于−231的整数应该被固定为−231,大于231 − 1的整数应该被固定为231 − 1。 - 返回整数作为最终结果。
注意:
- 本题中的空白字符只包括空格字符
' '。 - 除前导空格或数字后的其余字符串外,请勿忽略 任何其他字符。
示例 1:
输入:s = "42"
输出:42
解释:加粗的字符串为已经读入的字符,插入符号是当前读取的字符。
第 1 步:"42"(当前没有读入字符,因为没有前导空格)
^
第 2 步:"42"(当前没有读入字符,因为这里不存在 '-' 或者 '+')
^
第 3 步:"42"(读入 "42")
^
解析得到整数 42 。
由于 "42" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 42 。
示例 2:
输入:s = " -42"
输出:-42
解释:
第 1 步:" -42"(读入前导空格,但忽视掉)
^
第 2 步:" -42"(读入 '-' 字符,所以结果应该是负数)
^
第 3 步:" -42"(读入 "42")
^
解析得到整数 -42 。
由于 "-42" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 -42 。
示例 3:
输入:s = "4193 with words"
输出:4193
解释:
第 1 步:"4193 with words"(当前没有读入字符,因为没有前导空格)
^
第 2 步:"4193 with words"(当前没有读入字符,因为这里不存在 '-' 或者 '+')
^
第 3 步:"4193 with words"(读入 "4193";由于下一个字符不是一个数字,所以读入停止)
^
解析得到整数 4193 。
由于 "4193" 在范围 [-231, 231 - 1] 内,最终结果为 4193 。
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 200s由英文字母(大写和小写)、数字(0-9)、' '、'+'、'-'和'.'组成
#include<iostream>
#include<ctype.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
int i = 0; // 索引
int sign = 1; // 符号位
long long result = 0;
// 跳过前面的空格字符
while(i < s.size() && s[i] == ' ') {
i++;
}
// 检查最终结果为正数还是负数
if(i < s.size() && (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')) {
sign = (s[i++] == '-' ? -1 : 1);
}
// 把字符串转换成数字
while(i < s.size() && isdigit(s[i])) {
result = result * 10 + (s[i++] - '0');
if(result * sign > INT_MAX) {
return INT_MAX;
}
if(result * sign < INT_MIN) {
return INT_MIN;
}
}
return result * sign;
}
};
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.myAtoi(s);
return 0;
}
9. 回文数
给你一个整数 x ,如果 x 是一个回文整数,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
- 例如,
121是回文,而123不是。
示例 1:
输入:x = 121 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:x = -121 输出:false 解释:从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不是一个回文数。
示例 3:
输入:x = 10 输出:false 解释:从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
提示:
-2^31 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool isPalindrome(int num){
if(num < 0){
return false;
}
int original = num;
long long reversed = 0;
while(num > 0) {
reversed = reversed * 10 + num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return original == reversed;
}
int main()
{
int num;
cin>>num;
cout<<boolalpha<<isPalindrome(num)<<endl;
return 0;
}10. 正则表达式匹配
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符规律 p,请你来实现一个支持 '.' 和 '*' 的正则表达式匹配。
'.'匹配任意单个字符'*'匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素
所谓匹配,是要涵盖 整个 字符串 s的,而不是部分字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aa", p = "a" 输出:false 解释:"a" 无法匹配 "aa" 整个字符串。
示例 2:
输入:s = "aa", p = "a*" 输出:true 解释:因为 '*' 代表可以匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素, 在这里前面的元素就是 'a'。因此,字符串 "aa" 可被视为 'a' 重复了一次。
示例 3:
输入:s = "ab", p = ".*" 输出:true 解释:".*" 表示可匹配零个或多个('*')任意字符('.')。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 201 <= p.length <= 20s只包含从a-z的小写字母。p只包含从a-z的小写字母,以及字符.和*。- 保证每次出现字符
*时,前面都匹配到有效的字符
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int m = s.size();
int n = p.size();
vector<vector<bool>> dp(m + 1, vector<bool>(n + 1, false));
dp[0][0] = true;
/*
使用两层循环遍历dp数组,其中i表示s的长度,j表示p的长度。
在内层循环中,分情况讨论:
如果p[j-1]为'',则dp[i][j]为dp[i][j-2](''匹配0次)或者(s的第i个字符和p的第j-1个字符匹配,
并且dp[i-1][j]为true)。
如果p[j-1]不为'*',则dp[i][j]为dp[i-1][j-1](s的第i个字符和p的第j个字符匹配)。
*/
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[j - 1] == '*') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] || (i > 0 && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 2] || p[j - 2] == '.') && dp[i - 1][j]);
} else {
dp[i][j] = i > 0 && dp[i - 1][j - 1] && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == '.');
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
int main() {
string s, p;
cin >> s >> p;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isMatch(s, p);
return 0;
}11. 盛最多的水
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
示例 1:
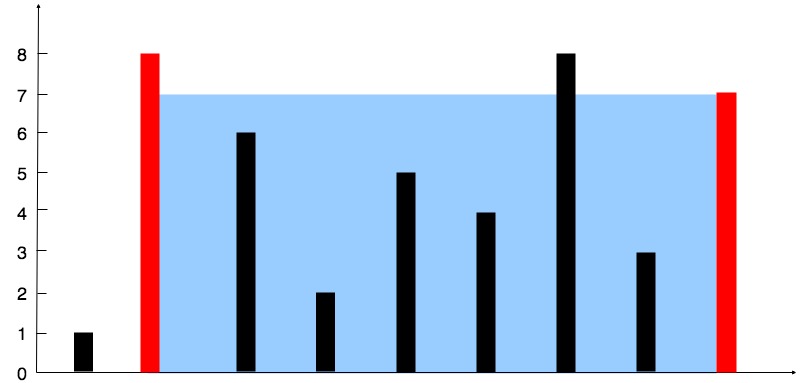
输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] 输出:49 解释:图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1] 输出:1
提示:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 10^50 <= height[i] <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int n = height.size();
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
int result = 0;
while(left < right) {
result = max(result, (right - left) * min(height[left], height[right]));
if(height[left] > height[right]) {
--right;
} else {
++left;
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
vector<int> height;
int tmp;
while(cin >> tmp) {
height.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cout << solution.maxArea(height);
return 0;
}12. 整数转罗马数字
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值 I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000
例如, 罗马数字 2 写做 II ,即为两个并列的 1。12 写做 XII ,即为 X + II 。 27 写做 XXVII, 即为 XX + V + II 。
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
I可以放在V(5) 和X(10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。X可以放在L(50) 和C(100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。C可以放在D(500) 和M(1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给你一个整数,将其转为罗马数字。
示例 1:
输入: num = 3 输出: "III"
示例 2:
输入: num = 4 输出: "IV"
示例 3:
输入: num = 9 输出: "IX"
示例 4:
输入: num = 58 输出: "LVIII" 解释: L = 50, V = 5, III = 3.
示例 5:
输入: num = 1994 输出: "MCMXCIV" 解释: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90, IV = 4.
提示:
1 <= num <= 3999
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string intToRoman(int num) {
vector<int> values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};
vector<string> symbols = {"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"};
string result = "";
for(int i = 0; i < values.size(); i++) {
while(num >= values[i]) {
num -= values[i];
result += symbols[i];
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
int num;
cin >> num;
cout << solution.intToRoman(num);
return 0;
}解法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string intToRoman(int num) {
map<int, string> romanMap;
romanMap[1] = "I";
romanMap[4] = "IV";
romanMap[5] = "V";
romanMap[9] = "IX";
romanMap[10] = "X";
romanMap[40] = "XL";
romanMap[50] = "L";
romanMap[90] = "XC";
romanMap[100] = "C";
romanMap[400] = "CD";
romanMap[500] = "D";
romanMap[900] = "CM";
romanMap[1000] = "M";
string result = "";
for(auto it = romanMap.rbegin(); it != romanMap.rend(); ++it) {
while(num >= it->first) {
result += it->second;
num -= it->first;
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
int num;
cin >> num;
cout << solution.intToRoman(num);
return 0;
}13. 罗马数字转整数
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值 I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000
例如, 罗马数字 2 写做 II ,即为两个并列的 1 。12 写做 XII ,即为 X + II 。 27 写做 XXVII, 即为 XX + V + II 。
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。但也存在特例,例如 4 不写做 IIII,而是 IV。数字 1 在数字 5 的左边,所表示的数等于大数 5 减小数 1 得到的数值 4 。同样地,数字 9 表示为 IX。这个特殊的规则只适用于以下六种情况:
I可以放在V(5) 和X(10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。X可以放在L(50) 和C(100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。C可以放在D(500) 和M(1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
给定一个罗马数字,将其转换成整数。
示例 1:
输入: s = "III" 输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: s = "IV" 输出: 4
示例 3:
输入: s = "IX" 输出: 9
示例 4:
输入: s = "LVIII" 输出: 58 解释: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
示例 5:
输入: s = "MCMXCIV" 输出: 1994 解释: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90, IV = 4.
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 15s仅含字符('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M')- 题目数据保证
s是一个有效的罗马数字,且表示整数在范围[1, 3999]内 - 题目所给测试用例皆符合罗马数字书写规则,不会出现跨位等情况。
- IL 和 IM 这样的例子并不符合题目要求,49 应该写作 XLIX,999 应该写作 CMXCIX 。
- 关于罗马数字的详尽书写规则,可以参考 罗马数字 - Mathematics 。
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int romanToInt(string s){
map<char, int> romanMap;
romanMap['I'] = 1;
romanMap['V'] = 5;
romanMap['X'] = 10;
romanMap['L'] = 50;
romanMap['C'] = 100;
romanMap['D'] = 500;
romanMap['M'] = 1000;
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(i < s.length() - 1 && romanMap[s[i]] < romanMap[s[i + 1]]) {
result -= romanMap[s[i]];
} else {
result += romanMap[s[i]];
}
}
return result;
}
int main(){
string romanNum;
cin>>romanNum;
cout<<romanToInt(romanNum);
return 0;
} 14. 最长公共前缀
编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 ""。
示例 1:
输入:strs = ["flower","flow","flight"] 输出:"fl"
示例 2:
输入:strs = ["dog","racecar","car"] 输出:"" 解释:输入不存在公共前缀。
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 2000 <= strs[i].length <= 200strs[i]仅由小写英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if(strs.empty()) {
return "";
}
string ans = strs[0];
for(int i = 1; i < strs.size(); i++) {
int j = 0;
for(; j < ans.length() && j < strs[i].length(); j++) {
if(ans[j] != strs[i][j])
break;
}
ans = ans.substr(0, j);
if(ans == "")
return ans;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
vector<string> strs;
string tmp;
while(cin>>tmp) {
strs.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cout<<longestCommonPrefix(strs)<<endl;
return 0;
} 15. 三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,1] 输出:[] 解释:唯一可能的三元组和不为 0 。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0,0,0] 输出:[[0,0,0]] 解释:唯一可能的三元组和为 0 。
提示:
3 <= nums.length <= 3000-10^5 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int> > result;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue; // 重复
}
int target = -nums[i];
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum < target) { // 小于0
left++;
} else if(sum > target) { // 大于0
right--;
} else { // 等于0
result.push_back({nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 2]) {
left++;
}
while(left < right &&nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int tmp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int>> result = solution.threeSum(nums);
// for(const auto& triplet : result) {
// cout << "[";
// for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// cout << triplet[i];
// if(i < 2) {
// cout << ", ";
// }
// }
// cout << "] ";
// }
cout << "[";
for(vector<vector<int> >::iterator it = result.begin(); it != result.end(); ++it) {
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
cout << (*it)[i];
if(i < 2) {
cout << ",";
}
}
if(it == result.end() - 1) {
cout << "]";
} else {
cout << "], ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
} 16. 最接近的三数之和
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums 和 一个目标值 target。请你从 nums 中选出三个整数,使它们的和与 target 最接近。
返回这三个数的和。
假定每组输入只存在恰好一个解。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1 输出:2 解释:与 target 最接近的和是 2 (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2) 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,0], target = 1 输出:0
提示:
3 <= nums.length <= 1000-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000-10^4 <= target <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int closestSum = INT_MAX;
int minDiff = INT_MAX;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++) {
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
int diff = abs(sum - target);
if(diff < minDiff) { // 更新最小差值
minDiff = diff;
closestSum = sum;
}
if(sum < target) {
++left; // 偏小
} else if(sum > target) {
--right; // 偏大
} else {
return sum; // 相等
}
}
}
return closestSum;
}
};
int main() {
int target;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> target) {
nums.push_back(target);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.threeSumClosest(nums, target);
return 0;
}17. 电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。

示例 1:
输入:digits = "23" 输出:["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
示例 2:
输入:digits = "" 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:digits = "2" 输出:["a","b","c"]
提示:
0 <= digits.length <= 4digits[i]是范围['2', '9']的一个数字。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
vector<string> result;
if (digits.empty()) {
return result;
}
unordered_map<char, string> digitToLetters = {
{'2', "abc"},
{'3', "def"},
{'4', "ghi"},
{'5', "jkl"},
{'6', "mno"},
{'7', "pqrs"},
{'8', "tuv"},
{'9', "wxyz"}
};
string current;
backtrack(digits, 0, current, result, digitToLetters);
return result;
}
void backtrack(string& digits, int index, string& current, vector<string>& result, unordered_map<char, string>& digitToLetters) {
if (index == digits.length()) {
result.push_back(current);
return;
}
char digit = digits[index];
string letters = digitToLetters[digit];
for (char letter : letters) {
current.push_back(letter);
backtrack(digits, index + 1, current, result, digitToLetters);
current.pop_back();
}
}
};
int main() {
string digits;
cin >> digits;
Solution solution;
vector<string> result = solution.letterCombinations(digits);
for (string& combination : result) {
cout << combination << " ";
}
return 0;
}
18. 四数之和
给你一个由 n 个整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标值 target 。请你找出并返回满足下述全部条件且不重复的四元组 [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]] (若两个四元组元素一一对应,则认为两个四元组重复):
0 <= a, b, c, d < na、b、c和d互不相同nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0 输出:[[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8 输出:[[2,2,2,2]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 200-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9-10^9 <= target <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int n = nums.size();
if(n < 4) {
return result;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < n - 3; i++) {
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
for(int j = i + 1; j < n - 2; j++) {
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = n - 1;
while(left < right) {
long sum = static_cast<long>(nums[i]) + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum < target) {
++left;
} else if(sum > target) {
--right;
} else {
result.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]});
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
++left;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
--right;
}
++left;
--right;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int target;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> target) {
nums.push_back(target);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int>> result = solution.fourSum(nums, target);
for(vector<int>& quadruplet : result) {
cout << "[";
for(int num : quadruplet) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << "] ";
}
return 0;
}19. 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
解题思路:要删除链表的倒数第n个结点,可以使用双指针技巧。首先定义两个指针,分别为快指针和慢指针,初始时均指向头节点。然后让快指针先向后移动n + 1步,这样快指针和慢指针之间就会相隔n个节点。接着同时移动快指针和慢指针,直到快指针指向链表末尾。此时慢指针指向的节点就是要删除的节点的前一个结点。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for single-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummy;
ListNode* slow = dummy;
// 向后移动n + 1步
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// 删除结点
ListNode * q = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
delete q;
return dummy->next;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = createList();
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
ListNode* result = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n);
printList(result);
return 0;
}20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = "(]" 输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> stk;
map<char, char> brackets;
brackets.insert(make_pair(')', '('));
brackets.insert(make_pair('}', '{'));
brackets.insert(make_pair(']', '['));
for(string::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {
char c = *it;
// 如果是右括号
if(brackets.find(c) != brackets.end()) {
// 栈为空或者栈顶元素与当前右括号不匹配,返回false
if(stk.empty() || stk.top() != brackets[c]) {
return false;
}
stk.pop();
} else {
stk.push(c); // 左括号
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
int main() {
string s;
cin>>s;
cout<<boolalpha<<isValid(s)<<endl;
return 0;
}2024-02
21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { // 递归
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
if(list1->val < list2->val) {
list1->next = mergeTwoLists(list1->next, list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2->next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2->next);
return list2;
}
}
};
int main() {
ListNode* list1 = NULL;
ListNode* list2 = NULL;
cout << "Enter elements for list1 (enter -1 to stop): ";
int val;
while (cin >> val && val != -1) {
ListNode* node = new ListNode(val);
if (list1 == NULL) {
list1 = node;
} else {
ListNode* temp = list1;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = node;
}
}
cout << "Enter elements for list2 (enter -1 to stop): ";
while (cin >> val && val != -1) {
ListNode* node = new ListNode(val);
if (list2 == NULL) {
list2 = node;
} else {
ListNode* temp = list2;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = node;
}
}
Solution solution;
ListNode* mergedList = solution.mergeTwoLists(list1, list2);
// Print the merged list
ListNode* temp = mergedList;
cout << "Merged list: ";
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->val << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
22. 括号生成
数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
输入:n = 3 输出:["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:["()"]
提示:
1 <= n <= 8
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void helper(vector<string>& result, string current, int open, int close, int n) {
if(current.size() == 2 * n) {
result.push_back(current);
return; // 递归结束
}
if(open < n) {
helper(result, current + "(", open + 1, close, n);
}
if(close < open) {
helper(result, current + ")", open, close + 1, n);
}
}
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
vector<string> result;
helper(result, "", 0, 0, n);
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
vector<string> result = solution.generateParenthesis(n);
cout << "[";
for(auto it = result.begin(); it != result.end(); ++it) {
if(it == result.end() - 1) {
cout << *it;
} else {
cout << *it <<", ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}23. 合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
解题思路:要合并K个升序链表,可以使用优先队列(最小堆)来实现。首先将每个链表的头节点加入到优先队列中,然后不断从优先队列中取出最小的节点,将其加入到结果链表中,并将该节点的下一个节点加入到优先队列中。重复这个过程直到优先队列为空。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
struct compare {
bool operator()(ListNode* a, ListNode* b) {
return a->val > b->val;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, compare> pq;
for(ListNode* list : lists) { // 添加各个链表的头节点
if(list) {
pq.push(list);
}
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = dummy;
while(!pq.empty()) {
ListNode* node = pq.top(); // 获取堆顶元素
pq.pop();
tail->next = node;
tail = tail->next;
if(node->next) {
// 把堆顶元素所在链表的下一个节点入队
pq.push(node->next);
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
vector<ListNode*> lists;
int flag = 0;
while(true) {
cout << "请输入链表元素:";
ListNode* head = createList();
lists.push_back(head);
cout << "是否需要继续创建链表数组:0(继续), 1(结束):";
cin >> flag;
if(flag == 1) { // flag = 1时,结束创建链表数组
break;
}
}
cout << "Merged List: ";
Solution solution;
ListNode* mergedList = solution.mergeKLists(lists);
printList(mergedList);
return 0;
}24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *prev = dummy;
while(prev->next && prev->next->next) {
ListNode *first = prev->next;
ListNode *second = prev->next->next;
prev->next = second;
first->next = second->next;
second->next = first;
prev = first;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode *head = NULL;
ListNode *current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n') {
break;
}
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
Solution solution;
ListNode *head = createList();
ListNode *result = solution.swapPairs(head);
printList(result);
return 0;
}25. K个一组翻转链表
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
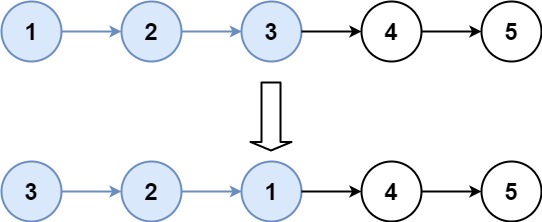
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
进阶:你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head || k == 1) {
return head;
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* pre = dummy;
int count = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur) {
count++;
ListNode* nextNode = cur->next;
if(count == k) {
pre = reverse(pre, nextNode); // 翻转
count = 0;
}
cur = nextNode;
}
return dummy->next;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* end) {
if(!pre || !pre->next || !pre->next->next) {
return pre->next;
}
ListNode* head = pre->next;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while(cur != end) {
head->next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre->next;
pre->next = cur;
cur = head->next;
}
return head;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode *head = NULL;
ListNode *current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n') {
break;
}
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
Solution solution;
ListNode *head = createList();
int k;
cin >> k;
ListNode *result = solution.reverseKGroup(head, k);
printList(result);
return 0;
}26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
给你一个 非严格递增排列 的数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。然后返回 nums 中唯一元素的个数。
考虑 nums 的唯一元素的数量为 k ,你需要做以下事情确保你的题解可以被通过:
- 更改数组
nums,使nums的前k个元素包含唯一元素,并按照它们最初在nums中出现的顺序排列。nums的其余元素与nums的大小不重要。 - 返回
k。
判题标准:
系统会用下面的代码来测试你的题解:
int[] nums = [...]; // 输入数组
int[] expectedNums = [...]; // 长度正确的期望答案
int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // 调用
assert k == expectedNums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
}
如果所有断言都通过,那么您的题解将被 通过。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出:2, nums = [1,2,_] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2,并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2 。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4] 输出:5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且原数组 nums 的前五个元素被修改为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4nums已按 非严格递增 排列
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int size = nums.size();
int left = 0, right = 1;
while(--size) {
if(nums[left] == nums[right]) {
right++;
} else {
nums[left + 1] = nums[right];
right++;
left++;
}
}
return left + 1;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);
return 0;
}解法2:使用STL中的unique函数进行优化。unique函数可以将重复的元素移动到数组的末尾,并返回指向不重复部分的尾后迭代器。我们可以利用这个特性来简化代码。只需要调用unique函数,并返回结果与数组起始位置之间的距离,即为不重复元素的个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
return distance(nums.begin(), unique(nums.begin(), nums.end()));
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);
return 0;
}解法3:在这个优化后的代码中,我们使用了两个指针left和right,其中left指针指向不重复部分的最后一个元素,right指针用于遍历数组。当遇到一个与left指针指向的元素不相同的元素时,将该元素移动到left指针的下一个位置,并将left指针后移一位。遍历完成后,left指针的位置加1即为不重复元素的个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n < 2) {
return n;
}
int left = 0;
for(int right = 1; right < n; right++) {
if(nums[left] != nums[right]) {
left++;
nums[left] = nums[right];
}
}
return left + 1;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.removeDuplicates(nums);
return 0;
}27. 移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参作任何拷贝
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中 该长度范围内 的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3 输出:2, nums = [2,2] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。例如,函数返回的新长度为 2 ,而 nums = [2,2,3,3] 或 nums = [2,2,0,0],也会被视作正确答案。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2 输出:5, nums = [0,1,3,0,4] 解释:函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。注意这五个元素可为任意顺序。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 500 <= val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(nums[i] != val) {
nums[j++] = nums[i]; // 不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素
}
}
return j;
}
};
int main() {
int val;
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n') {
break;
}
}
cin>>val;
Solution solution;
int len = solution.removeElement(nums, val);
cout << len;
return 0;
} 28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad" 输出:0 解释:"sad" 在下标 0 和 6 处匹配。 第一个匹配项的下标是 0 ,所以返回 0 。
示例 2:
输入:haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto" 输出:-1 解释:"leeto" 没有在 "leetcode" 中出现,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 10^4haystack和needle仅由小写英文字符组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
return haystack.find(needle);
}
};
int main() {
string haystack, needle;
cin >> haystack >> needle;
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.strStr(haystack, needle);
return 0;
}注:在C++中,string类的find()函数用于在一个字符串中查找子字符串,并返回第一次出现的位置。find()函数有多种重载形式,常用的形式包括:
size_t find(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找子字符串str,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找C风格字符串s,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const: 在当前字符串中从指定位置pos开始查找字符c,返回第一次出现的位置。如果未找到则返回string::npos。
示例用法:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str = "Hello, World!";
// 查找子字符串
size_t found = str.find("World");
if (found != string::npos) {
cout << "Found at position: " << found << endl;
} else {
cout << "Not found" << endl;
}
// 查找字符
size_t foundChar = str.find(',');
if (foundChar != string::npos) {
cout << "Found character at position: " << foundChar << endl;
} else {
cout << "Character not found" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
29. 两数相除
给你两个整数,被除数 dividend 和除数 divisor。将两数相除,要求 不使用 乘法、除法和取余运算。
整数除法应该向零截断,也就是截去(truncate)其小数部分。例如,8.345 将被截断为 8 ,-2.7335 将被截断至 -2 。
返回被除数 dividend 除以除数 divisor 得到的 商 。
注意:假设我们的环境只能存储 32 位 有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−231, 231 − 1] 。本题中,如果商 严格大于 231 − 1 ,则返回 231 − 1 ;如果商 严格小于 -231 ,则返回 -231 。
示例 1:
输入: dividend = 10, divisor = 3 输出: 3 解释: 10/3 = 3.33333.. ,向零截断后得到 3 。
示例 2:
输入: dividend = 7, divisor = -3 输出: -2 解释: 7/-3 = -2.33333.. ,向零截断后得到 -2 。
提示:
-2^31 <= dividend, divisor <= 2^31 - 1divisor != 0
#include<iostream>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
if(dividend == INT_MIN && divisor == -1) {
return INT_MAX;
}
long dvd = labs(dividend);
long dvs = labs(divisor);
int sign = (dividend > 0) ^ (divisor > 0) ? -1 : 1;
long res = 0;
while(dvd >= dvs) {
long temp = dvs, m = 1;
while(temp<<1 <= dvd) {
temp <<= 1;
m <<= 1; // 左移一位
}
dvd = -= temp;
res += m;
}
return sign * res;
}
};
int main() {
int dividend, divisor;
cin >> dividend >> divisor;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.divide(dividend, divisor);
return 0;
}30. 串联所有单词的子串
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。 words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
- 例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", 和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。
返回所有串联子串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9] 解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。 子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。 输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"]
输出:[]
解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。
s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。
所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"] 输出:[6,9,12] 解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。 子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1041 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
解法一:超时版
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
vector<int> result;
if(s.empty() || words.empty()) {
return result;
}
int wordLen = words[0].length();
int wordCount = words.size();
int totalLen = wordLen * wordCount;
unordered_map<string, int> wordFreq;
for(const string& word : words) {
wordFreq[word]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= (int)s.length() - totalLen; ++i) {
unordered_map<string, int> seen;
int j = 0;
for(; j < wordCount; ++j) {
string word = s.substr(i + j * wordLen, wordLen);
if(wordFreq.find(word) == wordFreq.end()) {
break;
}
seen[word]++;
if(seen[word] > wordFreq[word]) {
break;
}
}
if(j == wordCount) {
result.push_back(i);
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
string s;
vector<string> words;
string tmp;
cin >> s;
while(cin >> tmp) {
words.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.findSubstring(s, words);
for(auto num : result) {
cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}解法二:在每个可能的位置只遍历一次,使用滑动窗口来优化时间复杂度。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
vector<int> result;
if(s.empty() || words.empty()) {
return result;
}
int wordLen = words[0].length();
int wordCount = words.size();
int totalLen = wordLen * wordCount;
unordered_map<string, int> wordFreq;
for(const string& word : words) {
wordFreq[word]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < wordLen; i++) {
int left = i, count = 0;
unordered_map<string, int> seen;
for(int j = i; j <= (int)s.length() - totalLen; j += wordLen) {
string word = s.substr(j, wordLen);
if(wordFreq.find(word) != wordFreq.end()) {
seen[word]++;
count++;
while(seen[word] > wordFreq[word]) {
string temp = s.substr(left, wordLen);
seen[temp]--;
count--;
left += wordLen;
}
if(count == wordCount) {
result.push_back(left);
string temp = s.substr(left, wordLen);
seen[temp]--;
count--;
left += wordLen;
}
} else {
seen.clear();
count = 0;
left = j + wordLen;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
string s;
vector<string> words;
string tmp;
cin >> s;
while(cin >> tmp) {
words.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.findSubstring(s, words);
for(auto num : result) {
cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}31. 下一个排列
整数数组的一个 排列 就是将其所有成员以序列或线性顺序排列。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3],以下这些都可以视作arr的排列:[1,2,3]、[1,3,2]、[3,1,2]、[2,3,1]。
整数数组的 下一个排列 是指其整数的下一个字典序更大的排列。更正式地,如果数组的所有排列根据其字典顺序从小到大排列在一个容器中,那么数组的 下一个排列 就是在这个有序容器中排在它后面的那个排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,那么这个数组必须重排为字典序最小的排列(即,其元素按升序排列)。
- 例如,
arr = [1,2,3]的下一个排列是[1,3,2]。 - 类似地,
arr = [2,3,1]的下一个排列是[3,1,2]。 - 而
arr = [3,2,1]的下一个排列是[1,2,3],因为[3,2,1]不存在一个字典序更大的排列。
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出 nums 的下一个排列。
必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,1] 输出:[1,2,3]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,1,5] 输出:[1,5,1]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int i = n - 2;
while(i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1]) {
// 找到第一个满足nums[i] < nums[i + 1]的位置i
i--;
}
if(i >= 0) {
int j = n - 1;
while(j >= 0 && nums[j] <= nums[i]) {
// 从的数组末尾开始向前遍历,找到第一个大于nums[i]的元素的位置j
j--;
}
swap(nums[i], nums[j]); // 交换位置
}
// 将位置 i 后面的元素进行翻转,使其变为升序排列,这样就得到了下一个排列
reverse(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end());
}
};
int main() {
int tmp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
solution.nextPermutation(nums);
for(auto num : nums) {
cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}32. 最长有效括号
给你一个只包含 '(' 和 ')' 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。
示例 1:
输入:s = "(()" 输出:2 解释:最长有效括号子串是 "()"
示例 2:
输入:s = ")()())" 输出:4 解释:最长有效括号子串是 "()()"
示例 3:
输入:s = "" 输出:0
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 3 * 10^4s[i]为'('或')'
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(-1);
int maxLen = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(s[i] == '(') {
// 左括号
stk.push(i);
} else {
// 右括号
stk.pop();
if(stk.empty()) {
stk.push(i);
} else {
maxLen = max(maxLen, i - stk.top());
}
}
}
return maxLen;
}
};
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.longestValidParentheses(s);
return 0;
}33. 搜索选择排序数组
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
你必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0 输出:4
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3 输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1], target = 0 输出:-1
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4nums中的每个值都 独一无二- 题目数据保证
nums在预先未知的某个下标上进行了旋转 -10^4 <= target <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if(nums[left] <= nums[mid]) { // 小于等于
if(nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else { // 大于
if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
int tmp, target;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
cout << solution.search(nums, target) << endl;
return 0;
}34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
给你一个按照非递减顺序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。请你找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
如果数组中不存在目标值 target,返回 [-1, -1]。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8 输出:[3,4]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6 输出:[-1,-1]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [], target = 0 输出:[-1,-1]
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9nums是一个非递减数组-10^9 <= target <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
int start = -1, end = -1;
// 寻找开始位置
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) {
start = mid;
right = mid - 1; // 区别在这里
} else if(nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// 寻找结束位置
left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) {
end = mid;
left = mid + 1; // 区别在这里
} else if(nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return {start, end};
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int target, tmp;
Solution solution;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
vector<int> result = solution.searchRange(nums, target);
for(auto num : result) {
cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}35. 搜索插入位置
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5 输出: 2
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2 输出: 1
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 7 输出: 4
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4nums为 无重复元素 的 升序 排列数组-10^4 <= target <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right) { // 二分查找法
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int target, temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin>>target;
Solution solution;
cout<<solution.searchInsert(nums, target);
return 0;
}36. 有效的数独
请你判断一个 9 x 9 的数独是否有效。只需要 根据以下规则 ,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
注意:
- 一个有效的数独(部分已被填充)不一定是可解的。
- 只需要根据以上规则,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。
- 空白格用
'.'表示。
示例 1:
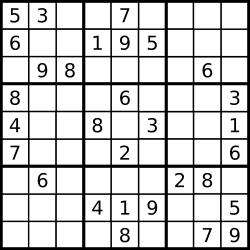
输入:board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."] ,["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."] ,[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."] ,["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"] ,["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"] ,["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"] ,[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."] ,[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"] ,[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:board = [["8","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."] ,["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."] ,[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."] ,["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"] ,["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"] ,["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"] ,[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."] ,[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"] ,[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] 输出:false 解释:除了第一行的第一个数字从 5 改为 8 以外,空格内其他数字均与 示例1 相同。 但由于位于左上角的 3x3 宫内有两个 8 存在, 因此这个数独是无效的。
提示:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]是一位数字(1-9)或者'.'
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
unordered_set<string> seen;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
char num = board[i][j];
if(num != '.') {
string row = "row" + to_string(i) + num; // 行
string col = "col" + to_string(j) + num; // 列
string box = "box" + to_string(i / 3) + to_string(j / 3) + num; // 3×3宫
if(seen.count(row) || seen.count(col) || seen.count(box)) {
return false;
}
seen.insert(row);
seen.insert(col);
seen.insert(box);
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
vector<vector<char>> board(9, vector<char>(9));
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
cin >> board[i][j];
}
}
cout << boolalpha << solution.isValidSudoku(board) << endl;
return 0;
}
/*5 3 . . 7 . . . .
6 . . 1 9 5 . . .
. 9 8 . . . . 6 .
8 . . . 6 . . . 3
4 . . 8 . 3 . . 1
7 . . . 2 . . . 6
. 6 . . . . 2 8 .
. . . 4 1 9 . . 5
. . . . 8 . . 7 9*/37. 解数独
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
示例 1:

输入:board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] 输出:[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]] 解释:输入的数独如上图所示,唯一有效的解决方案如下所示:
提示:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]是一位数字或者'.'- 题目数据 保证 输入数独仅有一个解
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if(board.empty() || board.size() != 9 || board[0].size() != 9) {
return;
}
solve(board);
}
bool solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == '.') {
for(char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
if(isValid(board, i, j, c)) { // 判断填入数字是否破坏规则
board[i][j] = c;
if(solve(board)) { // 递归调用
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool isValid(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int col, char c) {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if(board[i][col] == c || board[row][i] == c || board[3 * (row / 3) + i / 3][3 * (col / 3) + i % 3] == c) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
vector<vector<char>> board(9, vector<char>(9));
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
cin >> board[i][j];
}
}
solution.solveSudoku(board);
for(const auto& row : board) {
for(char c : row) {
cout << c << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*5 3 . . 7 . . . .
6 . . 1 9 5 . . .
. 9 8 . . . . 6 .
8 . . . 6 . . . 3
4 . . 8 . 3 . . 1
7 . . . 2 . . . 6
. 6 . . . . 2 8 .
. . . 4 1 9 . . 5
. . . . 8 . . 7 9*/38. 外观数列
给定一个正整数 n ,输出外观数列的第 n 项。
「外观数列」是一个整数序列,从数字 1 开始,序列中的每一项都是对前一项的描述。
你可以将其视作是由递归公式定义的数字字符串序列:
countAndSay(1) = "1"countAndSay(n)是对countAndSay(n-1)的描述,然后转换成另一个数字字符串。
前五项如下:
1. 1 2. 11 3. 21 4. 1211 5. 111221 第一项是数字 1 描述前一项,这个数是 1 即 “ 一 个 1 ”,记作 "11" 描述前一项,这个数是 11 即 “ 二 个 1 ” ,记作 "21" 描述前一项,这个数是 21 即 “ 一 个 2 + 一 个 1 ” ,记作 "1211" 描述前一项,这个数是 1211 即 “ 一 个 1 + 一 个 2 + 二 个 1 ” ,记作 "111221"
要 描述 一个数字字符串,首先要将字符串分割为 最小 数量的组,每个组都由连续的最多 相同字符 组成。然后对于每个组,先描述字符的数量,然后描述字符,形成一个描述组。要将描述转换为数字字符串,先将每组中的字符数量用数字替换,再将所有描述组连接起来。
例如,数字字符串 "3322251" 的描述如下图:

示例 1:
输入:n = 1 输出:"1" 解释:这是一个基本样例。
示例 2:
输入:n = 4 输出:"1211" 解释: countAndSay(1) = "1" countAndSay(2) = 读 "1" = 一 个 1 = "11" countAndSay(3) = 读 "11" = 二 个 1 = "21" countAndSay(4) = 读 "21" = 一 个 2 + 一 个 1 = "12" + "11" = "1211"
提示:
1 <= n <= 30
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
if(n == 1) {
return "1";
}
string prev = countAndSay(n - 1); // 递归调用,获得前一项的外观数列
string result = ""; // 存储当前的外观数列
int count = 1; // 记录连续相同数字的个数
for(int i = 0; i < prev.size(); i++) {
if(i + 1 < prev.size() && prev[i] == prev[i + 1]) { // 如1211
count++; // 如果当前数字与下一个数字相同,计数加1
} else {
result += to_string(count) + prev[i]; // 将当前数字的计数和数字本身添加到结果当中
count = 1; // 重置计数
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.countAndSay(n) << endl;
return 0;
}39. 组合总和
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7 输出:[[2,2,3],[7]] 解释: 2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。 7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。 仅有这两种组合。
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8 输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
示例 3:
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1 输出: []
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 302 <= candidates[i] <= 40candidates的所有元素 互不相同1 <= target <= 40
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> current; // 存储当前组合
backtrack(candidates, target, 0, current, result); // 回溯搜索不同组合
return result;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int start, vector<int>& current, vector<vector<int>>& result) {
if(target < 0) {
return; // 如果目标值小于0,说明当前组合不符合要求
}
if(target == 0) {
result.push_back(current); // 如果目标值等于0,说明当前组合符合要求
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); i++) {
current.push_back(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i, current, result);
current.pop_back(); // 回溯,将当前数字从当前组合中溢出
}
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> candidates;
int tmp, target;
while(cin >> tmp) {
candidates.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int>> result = solution.combinationSum(candidates, target);
// for(vector<int> combo : result) {
// cout << "[";
// for(int num : combo) {
// cout << num << " ";
// }
// cout << "]" << endl;
// }
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << "[";
for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {
if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {
cout << result[i][j];
} else {
cout << result[i][j] << ", ";
}
}
if(i == result.size() - 1) {
cout << "]";
} else {
cout << "], ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}40. 组合总和Ⅱ
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 输出: [ [1,1,6], [1,2,5], [1,7], [2,6] ]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, 输出: [ [1,2,2], [5] ]
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 1001 <= candidates[i] <= 501 <= target <= 30
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> current; // 存储当前组合
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
backtrack(candidates, target, 0, current, result); // 回溯搜索不同组合
return result;
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int start, vector<int>& current, vector<vector<int>>& result) {
if(target < 0) {
return; // 如果目标值小于0,说明当前组合不符合要求
}
if(target == 0) {
result.push_back(current); // 如果目标值等于0,说明当前组合符合要求
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.size(); i++) {
if(i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue; // 避免重复组合,如果当前数字与前一个数字相同,则跳过
}
current.push_back(candidates[i]); // 将当前数字加入到当前组合
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1, current, result); // 从i + 1开始回溯
current.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> candidates;
int tmp, target;
while(cin >> tmp) {
candidates.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> target;
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int>> result = solution.combinationSum2(candidates, target);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << "[";
for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {
if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {
cout << result[i][j];
} else {
cout << result[i][j] << ", ";
}
}
if(i == result.size() - 1) {
cout << "]";
} else {
cout << "], ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}58. 最后一个单词的长度
给你一个字符串 s,由若干单词组成,单词前后用一些空格字符隔开。返回字符串中 最后一个 单词的长度。
单词 是指仅由字母组成、不包含任何空格字符的最大子字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "Hello World" 输出:5 解释:最后一个单词是“World”,长度为5。
示例 2:
输入:s = " fly me to the moon " 输出:4 解释:最后一个单词是“moon”,长度为4。
示例 3:
输入:s = "luffy is still joyboy" 输出:6 解释:最后一个单词是长度为6的“joyboy”。
提示
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅有英文字母和空格' '组成s中至少存在一个单词
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int lengthOfLastWord(const string& s) {
int length = 0;
int i = s.length() - 1;
// 从字符串末尾开始向前遍历
while (i >= 0 && s[i] == ' ') {
i--; // 跳过末尾的空格
}
// 统计最后一个单词的长度
while (i >= 0 && s[i] != ' ') {
length++;
i--;
}
return length;
}
int main() {
string s1;
cin >> s1;
cout << lengthOfLastWord(s1);
return 0;
}
66. 加一
给定一个由 整数 组成的 非空 数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。
你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
示例 1:
输入:digits = [1,2,3] 输出:[1,2,4] 解释:输入数组表示数字 123。
示例 2:
输入:digits = [4,3,2,1] 输出:[4,3,2,2] 解释:输入数组表示数字 4321。
示例 3:
输入:digits = [0] 输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= digits.length <= 1000 <= digits[i] <= 9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {
int n = digits.size();
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if(digits[i] < 9) {
digits[i]++;
return digits;
}
digits[i] = 0; // 进1
}
digits.insert(digits.begin(), 1); // 增加一位,如9999
return digits;
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> digits;
while(cin >> temp) {
digits.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
solution.plusOne(digits);
for(int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++)
cout << digits[i] << " ";
return 0;
} 67. 二进制求和
给你两个二进制字符串 a 和 b ,以二进制字符串的形式返回它们的和。
示例 1:
输入:a = "11", b = "1" 输出:"100"
示例 2:
输入:a = "1010", b = "1011" 输出:"10101"
提示:
1 <= a.length, b.length <= 104a和b仅由字符'0'或'1'组成- 字符串如果不是
"0",就不含前导零
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string addBinary(string a, string b) {
int i = a.size(), j = b.size();
while(i < j) { // 两个字符不等长时
a = '0' + a;
++i;
}
while(i > j) {
b = '0' + b;
++j;
}
for(int n = a.size() - 1; n > 0; --n) { // 从后到前遍历所有的位数(第0位除外),同位相加
a[n] = a[n] - '0' + b[n];
if(a[n] >= '2') { // 若大于等于字符'2',进一
a[n] = (a[n] - '0') % 2 + '0';
a[n - 1] = a[n - 1] + 1;
}
}
a[0] = a[0] - '0' + b[0]; // 将a b的第0位相加
if(a[0] >= '2') { // 第一位大于等于2, 进一
a[0] = (a[0] - '0') % 2 + '0';
a = '1' + a;
}
return a;
}
};
int main() {
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
Solution solution;
string result = solution.addBinary(a, b);
cout << result;
return 0;
} 69. x的平方根
给你一个非负整数 x ,计算并返回 x 的 算术平方根 。
由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留 整数部分 ,小数部分将被 舍去 。
注意:不允许使用任何内置指数函数和算符,例如 pow(x, 0.5) 或者 x ** 0.5 。
示例 1:
输入:x = 4 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:x = 8 输出:2 解释:8 的算术平方根是 2.82842..., 由于返回类型是整数,小数部分将被舍去。
提示:
0 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x == 1)
return 1;
int min = 0;
int max = x;
while(max - min > 1) {
int m = (max + min) / 2; // 二分查找法
if(x / m < m) // 平方根落在m的左侧,更新max
max = m;
else // 平方根落在m的右侧,更新min
min = m;
}
return min;
}
};
int main() {
int x;
cin >> x;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.mySqrt(x);
return 0;
} 70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
示例 1:
输入:n = 2 输出:2 解释:有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入:n = 3 输出:3 解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 1 阶 + 2 阶 3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
提示:
1 <= n <= 45
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n == 1)
return 1;
if(n == 2)
return 2;
int prev = 1;
int current = 2;
for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { // 保存前两个台阶的爬楼方式数
int temp = current;
current = prev + current;
prev = temp;
}
return current;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.climbStairs(n);
return 0;
} 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,1,2] 输出:[1,2]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序 排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL && current->next != NULL) {
if(current->val == current->next->val) {
ListNode* temp = current->next;
current->next = current->next->next;
delete temp;
} else {
current = current->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
void printList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = createList();
Solution solution;
head = solution.deleteDuplicates(head);
printList(head);
return 0;
}88. 合并两个有序数组
给你两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。
请你 合并 nums2 到 nums1 中,使合并后的数组同样按 非递减顺序 排列。
注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组 nums1 中。为了应对这种情况,nums1 的初始长度为 m + n,其中前 m 个元素表示应合并的元素,后 n 个元素为 0 ,应忽略。nums2 的长度为 n 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3 输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6] 解释:需要合并 [1,2,3] 和 [2,5,6] 。 合并结果是 [1,2,2,3,5,6] ,其中斜体加粗标注的为 nums1 中的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0 输出:[1] 解释:需要合并 [1] 和 [] 。 合并结果是 [1] 。
示例 3:
输入:nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1 输出:[1] 解释:需要合并的数组是 [] 和 [1] 。 合并结果是 [1] 。 注意,因为 m = 0 ,所以 nums1 中没有元素。nums1 中仅存的 0 仅仅是为了确保合并结果可以顺利存放到 nums1 中。
提示:
nums1.length == m + nnums2.length == n0 <= m, n <= 2001 <= m + n <= 200-10^9 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>&nums2, int n) {
int i = m + n - 1;
m--;
n--;
while(n >= 0) {
if(m >= 0 && nums1[m] > nums2[n]) { // 从后往前比较大小
swap(nums1[i--], nums1[m--]);
} else {
swap(nums1[i--], nums2[n--]);
}
}
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums1, nums2;
int m, n;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums1.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> m;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums2.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
solution.merge(nums1, m, nums2, n);
for(int i = 0; i < m + n; i++)
cout << nums1[i] << " ";
return 0;
}94. 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> s;
vector<int> v;
TreeNode* rt = root;
while(rt || s.size()) {
while(rt) {
s.push(rt);
rt = rt->left;
}
rt = s.top();
s.pop();
v.push_back(rt->val);
rt = rt->right;
}
return v;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.inorderTraversal(root);
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}100. 相同的树
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] 输出:false
提示:
- 两棵树上的节点数目都在范围
[0, 100]内 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;
if(p == NULL || q == NULL) return false;
if(p->val != q->val) return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* p = createBinaryTree();
TreeNode* q = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
int result = solution.isSameTree(p, q);
if(result)
cout << "true";
else
cout << "false";
return 0;
}2024-03
101. 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return true;
else {
return dfs(root->left, root->right);
}
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if(left == NULL && right == NULL)
return true;
if(left == NULL || right == NULL)
return false;
return (left->val == right->val) && dfs(left->left, right->right) && dfs(left->right, right->left);
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
int result = solution.isSymmetric(root);
if(result)
cout << "true";
else
cout << "false";
return 0;
}104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 10^4]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 递归
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
} else {
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
cout << solution.maxDepth(root);
return 0;
}解法二:迭代
#include<iostream>
//#include<math.h>
#include <queue>
#include<stack>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 递归
// if(root == NULL) {
// return 0;
// } else {
// return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
// }
// }
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 迭代
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int> > s;
s.push(make_pair(root, 1));
int maxDepth = 0;
while(!s.empty()) {
pair<TreeNode*, int> current = s.top();
s.pop();
TreeNode* node = current.first;
int depth = current.second;
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, depth);
if(node->left != NULL) {
s.push(make_pair(node->left, depth + 1));
}
if(node->right != NULL) {
s.push(make_pair(node->right, depth + 1));
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
cout << solution.maxDepth(root);
return 0;
}108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。
高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,3] 输出:[3,1] 解释:[1,null,3] 和 [3,1] 都是高度平衡二叉搜索树。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104nums按 严格递增 顺序排列
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) {
return NULL;
}
return helper(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
TreeNode* helper(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end) {
if(start > end) {
return NULL;
}
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = helper(nums, start, mid - 1);
root->right = helper(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
};
// 层序遍历
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
cout << "null ";
return;
}
cout << root->val << " ";
if(root->left != NULL || root->right != NULL) {
printTree(root->left);
printTree(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
TreeNode* root = solution.sortedArrayToBST(nums);
printTree(root);
return 0;
}110. 平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:true
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return true;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(root->right);
if(abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if(node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
int result = solution.isBalanced(root);
if(result)
cout << "true";
else
cout << "false";
return 0;
}111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 10^5]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int depth = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) // 根节点
return depth;
if(node->left != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right != NULL) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
depth++; // 不符合第一个if的条件时
}
return depth;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
cout << solution.minDepth(root);
return 0;
}112. 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == NULL) {
return false;
}
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && (root->val - targetSum == 0)) {
return true;
}
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
int targetSum;
cin >> targetSum;
Solution solution;
int result = solution.hasPathSum(root, targetSum);
if(result)
cout << "true";
else
cout << "false";
return 0;
}解法二:迭代
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == NULL)
return false;
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int> > nodes;
nodes.push(make_pair(root, targetSum - root->val));
while(!nodes.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = nodes.top().first;
int currentSum = nodes.top().second;
nodes.pop();
if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL && currentSum == 0) {
return true;
}
if(node->right != NULL) {
nodes.push(make_pair(node->right, currentSum - node->right->val));
}
if(node->left != NULL) {
nodes.push(make_pair(node->left, currentSum - node->left->val));
}
}
return false;
}118. 杨辉三角
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
示例 1:
输入: numRows = 5 输出: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]
示例 2:
输入: numRows = 1 输出: [[1]]
提示:
1 <= numRows <= 30
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > generate(int numRows) {
vector<vector<int> > triangle(numRows);
for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
triangle[i].resize(i + 1);
triangle[i][0] = 1;
triangle[i][i] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
triangle[i][j] = triangle[i - 1][j - 1] + triangle[i - 1][j];
}
}
return triangle;
}
};
int main() {
int numRows;
cin >> numRows;
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int> > result = solution.generate(numRows);
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << "[";
for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size() - 1; j++) {
cout << result[i][j] << ", ";
}
cout<<result[i][result[i].size() - 1];
cout << "]" << endl;
}
return 0;
}119. 杨辉三角Ⅱ
给定一个非负索引 rowIndex,返回「杨辉三角」的第 rowIndex 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
示例 1:
输入: rowIndex = 3 输出: [1,3,3,1]
示例 2:
输入: rowIndex = 0 输出: [1]
示例 3:
输入: rowIndex = 1 输出: [1,1]
提示:
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
进阶:
你可以优化你的算法到 O(rowIndex) 空间复杂度吗?
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {
vector<int> row(rowIndex + 1, 1);
for(int i = 2; i <= rowIndex; i++) {
for(int j = i - 1; j > 0; j--) { // 从行 后 往 前
row[j] = row[j] + row[j - 1];
}
}
return row;
}
};
int main() {
int rowIndex;
cin >> rowIndex;
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.getRow(rowIndex);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size() - 1; i++) {
cout << result[i] << ", ";
}
cout << result[result.size() - 1] << "]";
return 0;
} 解法二:
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {
vector<int> result;
long long cur = 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; i++) {
result.push_back(cur);
cur = cur * (rowIndex - i) / (i + 1);
}
return result;
}121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] 输出:0 解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
提示:
1 <= prices.length <= 1050 <= prices[i] <= 104
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int minPrice = INT_MAX;
int maxProfit = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++) {
if(prices[i] < minPrice) {
minPrice = prices[i];
} else if(prices[i] - minPrice > maxProfit) {
maxProfit = prices[i] - minPrice;
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> prices;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
prices.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.maxProfit(prices);
return 0;
}125. 验证回文串
如果在将所有大写字符转换为小写字符、并移除所有非字母数字字符之后,短语正着读和反着读都一样。则可以认为该短语是一个 回文串 。
字母和数字都属于字母数字字符。
给你一个字符串 s,如果它是 回文串 ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" 输出:true 解释:"amanaplanacanalpanama" 是回文串。
示例 2:
输入:s = "race a car" 输出:false 解释:"raceacar" 不是回文串。
示例 3:
输入:s = " " 输出:true 解释:在移除非字母数字字符之后,s 是一个空字符串 "" 。 由于空字符串正着反着读都一样,所以是回文串。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 2 * 105s仅由可打印的 ASCII 字符组成
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
string processedStr = "";
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(isalnum(s[i])) {
processedStr += tolower(s[i]);
}
}
int left = 0, right = processedStr.length() - 1;
while(left < right) {
if(processedStr[left] != processedStr[right]) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
string str;
cin >> str;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isPalindrome(str);
return 0;
}136. 只出现一次的数字
给你一个 非空 整数数组 nums ,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
你必须设计并实现线性时间复杂度的算法来解决此问题,且该算法只使用常量额外空间。
示例 1 :
输入:nums = [2,2,1] 输出:1
示例 2 :
输入:nums = [4,1,2,1,2] 输出:4
示例 3 :
输入:nums = [1] 输出:1
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-3 * 10^4 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 10^4- 除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
result ^= nums[i]; // 相同为0,相异为1
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.singleNumber(nums);
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
return accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0,bit_xor<int>());
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.singleNumber(nums);
return 0;
}141. 环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
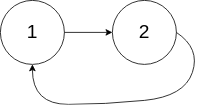
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:false 解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 104] -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { // 快慢指针法
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = buildLinkedList();;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.hasCycle(head);
return 0;
}142. 环形链表Ⅱ
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:返回 null 解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
进阶:你是否可以使用 O(1) 空间解决此题?
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast) {
ListNode *slow2 = head;
while(slow2 != slow) {
slow = slow->next;
slow2 = slow2->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = buildLinkedList();;
Solution solution;
ListNode *cycleStart = solution.detectCycle(head);
if(cycleStart != NULL)
cout << cycleStart->val;
else
cout << "null";
return 0;
}143. 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
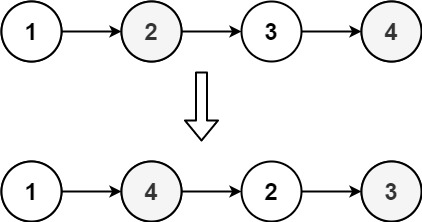
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[1,4,2,3]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[1,5,2,4,3]
提示:
- 链表的长度范围为
[1, 5 * 10^4] 1 <= node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
vector<ListNode*> nodes;
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
nodes.push_back(current);
current = current->next;
}
int left = 0;
int right = nodes.size() - 1;
while(left < right) {
nodes[left]->next = nodes[right];
left++;
if(left == right)
break;
nodes[right]->next = nodes[left];
right--;
}
nodes[left]->next = NULL;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = buildLinkedList();;
Solution solution;
solution.reorderList(head);
ListNode *current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
return 0;
}144. 二叉树的前序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
示例 4:

输入:root = [1,2] 输出:[1,2]
示例 5:

输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
//Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == NULL)
return result;
vector<int> left = preorderTraversal(root->left);
vector<int> right = preorderTraversal(root->right);
result.push_back(root->val);
result.insert(result.end(), left.begin(), left.end());
result.insert(result.end(), right.begin(), right.end());
return result;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.preorderTraversal(root);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size() - 1; i++) {
cout << result[i] << ", ";
}
cout << result[result.size() - 1];
cout << "]";
return 0;
}解法二:迭代
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == NULL)
return result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(curr->val);
if(curr->right != NULL) { // 后进先出
st.push(curr->right);
}
if(curr->left != NULL) {
st.push(curr->left);
}
}
return result;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.preorderTraversal(root);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size() - 1; i++) {
cout << result[i] << ", ";
}
cout << result[result.size() - 1];
cout << "]";
return 0;
}145. 二叉树的后序遍历
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == NULL)
return result;
vector<int> left = postorderTraversal(root->left);
vector<int> right = postorderTraversal(root->right);
result.insert(result.end(), left.begin(), left.end());
result.insert(result.end(), right.begin(), right.end());
result.push_back(root->val);
return result;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.postorderTraversal(root);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if(i == result.size() - 1) {
cout << result[i];
} else{
cout << result[i] << ", ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}解法二:迭代
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == NULL)
return result;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
st.push(root);
stack<int> output; // 用于存储后序遍历的结果
while(!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = st.top();
st.pop();
output.push(curr->val); // 将节点值存入output栈
if(curr->left != NULL) {
st.push(curr->left);
}
if(curr->right != NULL) {
st.push(curr->right);
}
}
// 从output栈中将结果取出,即为后序遍历的倒序结果
while(!output.empty()) {
result.push_back(output.top());
output.pop();
}
return result;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.postorderTraversal(root);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if(i == result.size() - 1) {
cout << result[i];
} else{
cout << result[i] << ", ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}160. 相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0listA- 第一个链表listB- 第二个链表skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
— 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^41 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
进阶:你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list.
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode *pA = headA;
ListNode *pB = headB;
while(pA != pB) {
pA = (pA == NULL) ? headB : pA->next;
pB = (pB == NULL) ? headA : pB->next;
}
return pA;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode *headA = buildLinkedList();
ListNode *headB = buildLinkedList();
Solution solution;
ListNode *result = solution.getIntersectionNode(headA, headB);
if(result != NULL) {
cout << result->val;
} else {
cout << "null";
}
return 0;
}168. Excel表列名称
给你一个整数 columnNumber ,返回它在 Excel 表中相对应的列名称。
例如:
A -> 1 B -> 2 C -> 3 ... Z -> 26 AA -> 27 AB -> 28 ...
示例 1:
输入:columnNumber = 1 输出:"A"
示例 2:
输入:columnNumber = 28 输出:"AB"
示例 3:
输入:columnNumber = 701 输出:"ZY"
示例 4:
输入:columnNumber = 2147483647 输出:"FXSHRXW"
提示:
1 <= columnNumber <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string convertToTitle(int columnNumber) {
string result = "";
while(columnNumber > 0) {
int remainder = (columnNumber - 1) % 26;
result = char('A' + remainder) + result;
columnNumber = (columnNumber - 1) / 26;
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int columnNumber;
cin >> columnNumber;
Solution solution;
string columnName = solution.convertToTitle(columnNumber);
cout << columnName;
return 0;
}169. 多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组 nums ,返回其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数 大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,2,3] 输出:3
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,2,1,1,1,2,2] 输出:2
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 5 * 10^4-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
进阶:尝试设计时间复杂度为 O(n)、空间复杂度为 O(1) 的算法解决此问题。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> countMap;
int majority = 0;
int maxCount = 0;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = nums.begin(); it != nums.end(); ++it) {
int num = *it;
countMap[num]++;
if (countMap[num] > maxCount) {
majority = num;
maxCount = countMap[num];
}
}
return majority;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> nums(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> nums[i];
}
Solution solution;
int result = solution.majorityElement(nums);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
class Solution {
public:
int majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int x = 0, votes = 0;
for(vector<int>::iterator it = nums.begin(); it != nums.end(); ++it) {
int num = *it;
if(votes == 0)
x = num;
votes += (num == x) ? 1 : -1;
}
return x;
}
};171. Excel表列序号
给你一个字符串 columnTitle ,表示 Excel 表格中的列名称。返回 该列名称对应的列序号 。
例如:
A -> 1 B -> 2 C -> 3 ... Z -> 26 AA -> 27 AB -> 28 ...
示例 1:
输入: columnTitle = "A" 输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: columnTitle = "AB" 输出: 28
示例 3:
输入: columnTitle = "ZY" 输出: 701
提示:
1 <= columnTitle.length <= 7columnTitle仅由大写英文组成columnTitle在范围["A", "FXSHRXW"]内
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int titleToNumber(string columnTitle) {
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < columnTitle.length(); i++) {
result = result * 26 + (columnTitle[i] - 'A' + 1); // 将每个字母视为26进制数,从右到左计算每个字母对应的值
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
string columnTitle;
cin >> columnTitle;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.titleToNumber(columnTitle);
return 0;
}
172. 阶乘后的零
给定一个整数 n ,返回 n! 结果中尾随零的数量。
提示 n! = n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) * ... * 3 * 2 * 1
示例 1:
输入:n = 3 输出:0 解释:3! = 6 ,不含尾随 0
示例 2:
输入:n = 5 输出:1 解释:5! = 120 ,有一个尾随 0
示例 3:
输入:n = 0 输出:0
提示:
0 <= n <= 10^4
进阶:你可以设计并实现对数时间复杂度的算法来解决此问题吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int trailingZeroes(int n) {
// 计算阶乘结果中包含的5的个数,因为每个5和2相乘可以产生一个0。因此,只需要计算n中包含多少个5的因子,就可以确定尾随0的数量
int count = 0;
for(int i = 5; n / i >= 1; i *= 5) {
count += n / i;
}
return count;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.trailingZeroes(n);
return 0;
}int trailingZeroes(int n) {
// 每次迭代,将n除以5,并将商加到计数器中。
int count = 0;
while(n > 0) {
count += n / 5;
n /= 5;
}
return count;
}173. 二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)初始化BSTIterator类的一个对象。BST 的根节点root会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。boolean hasNext()如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回true;否则返回false。int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:

输入 ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] 输出 [null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false] 解释 BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]); bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3 bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 105]内 0 <= Node.val <= 106- 最多调用
105次hasNext和next操作
进阶:
- 你可以设计一个满足下述条件的解决方案吗?
next()和hasNext()操作均摊时间复杂度为O(1),并使用O(h)内存。其中h是树的高度。
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<cctype>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class BSTIterator {
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
pushLeftNodes(root);
}
int next() {
TreeNode* node = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
pushLeftNodes(node->right);
return node->val;
}
bool hasNext() {
return !nodes.empty();
}
private:
stack<TreeNode*> nodes;
void pushLeftNodes(TreeNode* root) {
while(root != NULL) {
nodes.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
BSTIterator bSTIterator(root);
cout << bSTIterator.next() << endl;
cout << bSTIterator.next() << endl;
cout << boolalpha << bSTIterator.hasNext() << endl;
cout << bSTIterator.next() << endl;
cout << boolalpha << bSTIterator.hasNext() << endl;
cout << bSTIterator.next() << endl;
cout << boolalpha << bSTIterator.hasNext() << endl;
cout << bSTIterator.next() << endl;
cout << boolalpha << bSTIterator.hasNext() << endl;
return 0;
}
175. 组合两个表
表: Person
+-------------+---------+ | 列名 | 类型 | +-------------+---------+ | PersonId | int | | FirstName | varchar | | LastName | varchar | +-------------+---------+ personId 是该表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。 该表包含一些人的 ID 和他们的姓和名的信息。
表: Address
+-------------+---------+ | 列名 | 类型 | +-------------+---------+ | AddressId | int | | PersonId | int | | City | varchar | | State | varchar | +-------------+---------+ addressId 是该表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。 该表的每一行都包含一个 ID = PersonId 的人的城市和州的信息。
编写解决方案,报告 Person 表中每个人的姓、名、城市和州。如果 personId 的地址不在 Address 表中,则报告为 null 。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入: Person表: +----------+----------+-----------+ | personId | lastName | firstName | +----------+----------+-----------+ | 1 | Wang | Allen | | 2 | Alice | Bob | +----------+----------+-----------+ Address表: +-----------+----------+---------------+------------+ | addressId | personId | city | state | +-----------+----------+---------------+------------+ | 1 | 2 | New York City | New York | | 2 | 3 | Leetcode | California | +-----------+----------+---------------+------------+ 输出: +-----------+----------+---------------+----------+ | firstName | lastName | city | state | +-----------+----------+---------------+----------+ | Allen | Wang | Null | Null | | Bob | Alice | New York City | New York | +-----------+----------+---------------+----------+ 解释: 地址表中没有 personId = 1 的地址,所以它们的城市和州返回 null。 addressId = 1 包含了 personId = 2 的地址信息。
# Write your MySQL query statement below
SELECT p.FirstName, p.LastName, a.City, a.State
FROM Person p
LEFT JOIN Address a
ON p.PersonId = a.PersonId;176. 第二高的薪水
Employee 表:
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | id | int | | salary | int | +-------------+------+ 在 SQL 中,id 是这个表的主键。 表的每一行包含员工的工资信息。
查询并返回 Employee 表中第二高的薪水 。如果不存在第二高的薪水,查询应该返回 null(Pandas 则返回 None) 。
查询结果如下例所示。
示例 1:
输入: Employee 表: +----+--------+ | id | salary | +----+--------+ | 1 | 100 | | 2 | 200 | | 3 | 300 | +----+--------+ 输出: +---------------------+ | SecondHighestSalary | +---------------------+ | 200 | +---------------------+
示例 2:
输入: Employee 表: +----+--------+ | id | salary | +----+--------+ | 1 | 100 | +----+--------+ 输出: +---------------------+ | SecondHighestSalary | +---------------------+ | null | +---------------------+
# Write your MySQL query statement below
SELECT
(SELECT DISTINCT Salary
FROM Employee
ORDER BY Salary DESC
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1) AS SecondHighestSalary179. 最大数
给定一组非负整数 nums,重新排列每个数的顺序(每个数不可拆分)使之组成一个最大的整数。
注意:输出结果可能非常大,所以你需要返回一个字符串而不是整数。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [10,2]输出:"210"
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,30,34,5,9]输出:"9534330"
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
解题思路:①将整数数组转换为字符串数组;②自定义一个比较函数,用于比较两个字符串的连接结果的大小。比如,对于字符串a和b,如果ab大于ba,则认为a大于b;③对字符串数组进行排序;④将排序后的字符串数组连接起来,得到最大的整数。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
static bool compare(string a, string b) {
return a + b > b + a;
}
string largestNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
string result = "";
vector<string> nums_str;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
nums_str.push_back(to_string(nums[i]));
}
sort(nums_str.begin(), nums_str.end(), compare);
if(nums_str[0] == "0") {
return "0";
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums_str.size(); i++) {
result += nums_str[i];
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.largestNumber(nums);
return 0;
}187. 重复的DNA序列
DNA序列 由一系列核苷酸组成,缩写为 'A', 'C', 'G' 和 'T'.。
- 例如,
"ACGAATTCCG"是一个 DNA序列 。
在研究 DNA 时,识别 DNA 中的重复序列非常有用。
给定一个表示 DNA序列 的字符串 s ,返回所有在 DNA 分子中出现不止一次的 长度为 10 的序列(子字符串)。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT" 输出:["AAAAACCCCC","CCCCCAAAAA"]
示例 2:
输入:s = "AAAAAAAAAAAAA" 输出:["AAAAAAAAAA"]
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 10^5s[i]=='A'、'C'、'G'or'T'
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findRepeatedDnaSequences(string s) {
vector<string> result;
if(s.length() <= 10) {
return result;
}
map<string, int> sequenceCount;
for(int i = 0; i <= s.length() - 10; ++i) {
string sequence = s.substr(i, 10); // 截取从i开始的10个字符
sequenceCount[sequence]++;
if(sequenceCount[sequence] == 2) { // 出现不止一次的长度为10的序列
result.push_back(sequence);
}
}
return result;
}
};#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findRepeatedDnaSequences(string s) {
vector<string> result;
if(s.length() <= 10) {
return result;
}
unordered_map<string, int> sequenceCount;
for(int i = 0; i <= s.length() - 10; i++) {
string sequence = s.substr(i, 10); // 截取从i开始的10个字符
sequenceCount[sequence]++;
}
for(unordered_map<string, int>::iterator it = sequenceCount.begin(); it != sequenceCount.end(); ++it) {
string f = it->first;
int v = it->second;
if(v > 1) {
result.push_back(f);
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
Solution solution;
vector<string> result = solution.findRepeatedDnaSequences(s);
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}188. 买卖股票的最佳时机IV
给你一个整数数组 prices 和一个整数 k ,其中 prices[i] 是某支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。
设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 k 笔交易。也就是说,你最多可以买 k 次,卖 k 次。
注意:你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
示例 1:
输入:k = 2, prices = [2,4,1] 输出:2 解释:在第 1 天 (股票价格 = 2) 的时候买入,在第 2 天 (股票价格 = 4) 的时候卖出,这笔交易所能获得利润 = 4-2 = 2 。
示例 2:
输入:k = 2, prices = [3,2,6,5,0,3]
输出:7
解释:在第 2 天 (股票价格 = 2) 的时候买入,在第 3 天 (股票价格 = 6) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-2 = 4 。
随后,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 0) 的时候买入,在第 6 天 (股票价格 = 3) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3
提示:
1 <= k <= 1001 <= prices.length <= 10000 <= prices[i] <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(int k, vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if(n <= 1 || k == 0) {
return 0;
}
if(k >= n / 2) {
int maxProfit = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if(prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
vector<int> buy(k, INT_MIN);
vector<int> sell(k, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
buy[j] = max(buy[j], (j == 0) ? -prices[i] : sell[j - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[j] = max(sell[j], buy[j] + prices[i]);
}
}
return sell[k - 1];
}
};
int main() {
int k;
cin >> k;
vector<int> prices;
int tmp;
while(cin >> tmp) {
prices.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.maxProfit(k, prices);
return 0;
}189. 轮转数组
给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3 输出:[5,6,7,1,2,3,4]解释: 向右轮转 1 步:[7,1,2,3,4,5,6]向右轮转 2 步:[6,7,1,2,3,4,5]向右轮转 3 步:[5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2 输出:[3,99,-1,-100] 解释: 向右轮转 1 步: [99,-1,-100,3] 向右轮转 2 步: [3,99,-1,-100]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 10 <= k <= 10^5
进阶:
- 尽可能想出更多的解决方案,至少有 三种 不同的方法可以解决这个问题。
- 你可以使用空间复杂度为
O(1)的 原地 算法解决这个问题吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
k = k % n;
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + k);
reverse(nums.begin() + k, nums.end());
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int tmp;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
int k;
cin >> k;
Solution solution;
solution.rotate(nums, k);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}190. 颠倒二进制位
颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
提示:
- 请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不应影响您的实现,因为无论整数是有符号的还是无符号的,其内部的二进制表示形式都是相同的。
- 在 Java 中,编译器使用二进制补码记法来表示有符号整数。因此,在 示例 2 中,输入表示有符号整数
-3,输出表示有符号整数-1073741825。
示例 1:
输入:n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
输出:964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
解释:输入的二进制串 00000010100101000001111010011100 表示无符号整数 43261596,
因此返回 964176192,其二进制表示形式为 00111001011110000010100101000000。
示例 2:
输入:n = 11111111111111111111111111111101 输出:3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111) 解释:输入的二进制串 11111111111111111111111111111101 表示无符号整数 4294967293, 因此返回 3221225471 其二进制表示形式为 10111111111111111111111111111111 。
提示:
- 输入是一个长度为
32的二进制字符串
进阶: 如果多次调用这个函数,你将如何优化你的算法?
#include<iostream>
#include<bitset>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
result = (result << 1) | (n & 1); // 将result左移1为,低位补n的最低位
n >>= 1; // 右移一位,高位补0
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
uint32_t n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.reverseBits(n);
return 0;
}191. 位1的个数
编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数(以二进制串的形式),返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 '1' 的个数(也被称为汉明重量)。
提示:
- 请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不应影响您的实现,因为无论整数是有符号的还是无符号的,其内部的二进制表示形式都是相同的。
- 在 Java 中,编译器使用二进制补码记法来表示有符号整数。因此,在 示例 3 中,输入表示有符号整数
-3。
示例 1:
输入:n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
输出:3
解释:输入的二进制串 00000000000000000000000000001011 中,共有三位为 '1'。
示例 2:
输入:n = 00000000000000000000000010000000 输出:1 解释:输入的二进制串 00000000000000000000000010000000 中,共有一位为 '1'。
示例 3:
输入:n = 11111111111111111111111111111101 输出:31 解释:输入的二进制串 11111111111111111111111111111101 中,共有 31 位为 '1'。
提示:
- 输入必须是长度为
32的 二进制串 。
进阶:
- 如果多次调用这个函数,你将如何优化你的算法?
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<bitset>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
count += n & 1;
n >>= 1;
}
return count;
}
};
int main() {
uint32_t n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.hammingWeight(n);
return 0;
}class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0) {
count += n & 1; // 取n的最后一位
n >>= 1; // 右移一位
}
return count;
}
}; 198. 打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入:[1,2,3,1] 输出:4 解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。 偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:
输入:[2,7,9,3,1] 输出:12 解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。 偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 400
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums){
if(nums.empty()){
return 0;
}
int size = nums.size();
if(size == 1){
return nums[0];
}
vector<int> dp(size, 0);
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for(int i = 2; i < size; i++){
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]);
// ①若偷窃第k间房屋,就不能偷窃第k-1间房屋,偷窃金额为前k-2间房屋的最高总金额与第k间房屋的金额;
// ②若不偷窃第k间房屋,偷窃金额为前k-1间房屋的最高总金额。
}
return dp[size - 1];
}
};
int main(){
vector<int> nums;
int a;
while(cin >> a){
nums.push_back(a);
if(cin.get() == '\n') break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.rob(nums);
return 0;
}202. 快乐数
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
「快乐数」 定义为:
- 对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。
- 然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。
- 如果这个过程 结果为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
如果 n 是 快乐数 就返回 true ;不是,则返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 19 输出:true 解释: 12 + 92 = 82 82 + 22 = 68 62 + 82 = 100 12 + 02 + 02 = 1
示例 2:
输入:n = 2 输出:false
提示:
1 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_set<int> seen; // 存储已经出现过的数字,直到出现循环或者得到1为止
while(n != 1 && !seen.count(n)) {
seen.insert(n);
n = getNext(n);
}
return n == 1;
}
int getNext(int n) {
int totalSum = 0;
while(n > 0) {
int digit = n % 10;
totalSum += digit * digit;
n /= 10;
}
return totalSum;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isHappy(n);
return 0;
}203. 移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
提示:
- 列表中的节点数目在范围
[0, 10^4]内 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head; // 头指针
ListNode* prev = dummy;
ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr != NULL) {
if(curr->val == val) {
prev->next = curr->next;
delete curr;
curr = prev->next;
} else {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
ListNode * newHead = dummy->next;
delete dummy;
return newHead;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = buildLinkedList();
int val;
cin >> val;
Solution solution;
solution.removeElements(head, val);
ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
return 0;
}205. 同构字符串
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,判断它们是否是同构的。
如果 s 中的字符可以按某种映射关系替换得到 t ,那么这两个字符串是同构的。
每个出现的字符都应当映射到另一个字符,同时不改变字符的顺序。不同字符不能映射到同一个字符上,相同字符只能映射到同一个字符上,字符可以映射到自己本身。
示例 1:
输入:s = "egg", t = "add" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "foo", t = "bar" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s = "paper", t = "title" 输出:true
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 10^4t.length == s.lengths和t由任意有效的 ASCII 字符组成
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if(s.size() != t.size())
return false;
unordered_map<char, char> s2t, t2s;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
char cs = s[i];
char ct = t[i];
if((s2t.count(cs) && s2t[cs] != ct) || (t2s.count(ct) && t2s[ct] != cs)) { // 一一对应
return false;
}
s2t[cs] = ct;
t2s[ct] = cs;
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
string s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isIsomorphic(s, t);
}206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// 迭代
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = NULL;
ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr != NULL) {
ListNode* nextTemp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev; // 当前节点的指针指向前一个节点
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
// 递归
ListNode* reverseList2(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) // 递归终止条件
return head;
ListNode* reversedHead = reverseList2(head->next); // 得到以下一个节点为起点的反转后的链表头节点
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return reversedHead;
}
};
ListNode* buildLinkedList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
if(head == NULL) {
head = new ListNode(val);
current = head;
} else{
current->next = new ListNode(val);
current = current->next;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = buildLinkedList();
Solution solution;
ListNode* current = solution.reverseList2(head);
while(current != NULL) {
cout << current->val << " ";
current = current->next;
}
return 0;
} 217. 存在重复元素
给你一个整数数组 nums 。如果任一值在数组中出现 至少两次 ,返回 true ;如果数组中每个元素互不相同,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,1] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4] 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2] 输出:true
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> seen;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(seen.count(nums[i])) {
return true;
}
seen.insert(nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
bool containsDuplicate2(vector<int>& nums) {
map<int, int> count;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
count[nums[i]]++;
if(count[nums[i]] == 2){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.containsDuplicate2(nums);
return 0;
}219. 存在重复元素Ⅱ
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,判断数组中是否存在两个 不同的索引 i 和 j ,满足 nums[i] == nums[j] 且 abs(i - j) <= k 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1 输出:true
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2 输出:false
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^90 <= k <= 10^5
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int, int> numIndexMap;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(numIndexMap.find(nums[i]) != numIndexMap.end() && i - numIndexMap[nums[i]] <= k) {
return true;
}
numIndexMap[nums[i]] = i;
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums;
int temp;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
int k;
cin >> k;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.containsNearbyDuplicate(nums, k);
return 0;
}222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 10^4] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
进阶:遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* current = q.front();
q.pop();
count++;
if(current->left) {
q.push(current->left);
}
if(current->right) {
q.push(current->right);
}
}
return count;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
cout << solution.countNodes(root);
return 0;
}225. 用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的标准操作 —— 也就是
push to back、peek/pop from front、size和is empty这些操作。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入: ["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 2, 2, false] 解释: MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // 返回 2 myStack.pop(); // 返回 2 myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
提示:
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、top和empty - 每次调用
pop和top都保证栈不为空
进阶:你能否仅用一个队列来实现栈。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class MyStack {
private:
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
int topElement;
public:
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
q1.push(x);
topElement = x;
}
int pop() {
while(q1.size() > 1) {
topElement = q1.front();
q2.push(topElement);
q1.pop();
}
int result = q1.front();
q1.pop();
swap(q1, q2);
return result;
}
int top() {
return topElement;
}
bool empty() {
return q1.empty();
}
};
int main() {
MyStack myStack;
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
cout << myStack.top() << " ";
cout << myStack.pop() << " ";
cout << boolalpha << myStack.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}226. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] 输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,1,3] 输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// 递归翻转左右子树
TreeNode* left = invertTree(root->left);
TreeNode* right = invertTree(root->right);
// 交换左右子树
root->left = right;
root->right = left;
return root;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
return;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << curr->val << " ";
if(curr->left) {
q.push(curr->left);
}
if(curr->right) {
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
TreeNode* result = solution.invertTree(root);
printTree(result);
return 0;
}228. 汇总区间
给定一个 无重复元素 的 有序 整数数组 nums 。
返回 恰好覆盖数组中所有数字 的 最小有序 区间范围列表 。也就是说,nums 的每个元素都恰好被某个区间范围所覆盖,并且不存在属于某个范围但不属于 nums 的数字 x 。
列表中的每个区间范围 [a,b] 应该按如下格式输出:
"a->b",如果a != b"a",如果a == b
示例 1:
输入:nums = [0,1,2,4,5,7] 输出:["0->2","4->5","7"] 解释:区间范围是: [0,2] --> "0->2" [4,5] --> "4->5" [7,7] --> "7"
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,2,3,4,6,8,9] 输出:["0","2->4","6","8->9"] 解释:区间范围是: [0,0] --> "0" [2,4] --> "2->4" [6,6] --> "6" [8,9] --> "8->9"
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 20-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 1nums中的所有值都 互不相同nums按升序排列
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> summaryRanges(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<string> result;
if(nums.empty()) {
return result;
}
int start = nums[0];
int end = nums[0]; // 区间
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(nums[i] == end + 1) { // 连续
end = nums[i];
} else { // 非连续
if(start == end) {
result.push_back(to_string(start));
} else {
result.push_back(to_string(start) + "->" + to_string(end));
}
start = end = nums[i];
}
}
if(start == end) {
result.push_back(to_string(start));
} else {
result.push_back(to_string(start) + "->" + to_string(end));
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int tmp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
vector<string> result = solution.summaryRanges(nums);
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if(i == result.size() - 1) {
cout << '"' + result[i] + '"';
} else {
cout << '"' + result[i] + '"' << ", ";
}
}
cout << "]";
return 0;
}231. 2的幂
给你一个整数 n,请你判断该整数是否是 2 的幂次方。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
如果存在一个整数 x 使得 n == 2^x ,则认为 n 是 2 的幂次方。
示例 1:
输入:n = 1 输出:true 解释:20 = 1
示例 2:
输入:n = 16 输出:true 解释:24 = 16
示例 3:
输入:n = 3 输出:false
示例 4:
输入:n = 4 输出:true
示例 5:
输入:n = 5 输出:false
提示:
-2^31 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
进阶:你能够不使用循环/递归解决此问题吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfTwo(int n) {
/*
要判断一个整数是否是2的幂次方,可以利用2的幂次方性质:二进制表示中,
2的幂次方只有最高位为1,其余位为0。根据这个性质,我们可以通过位运算
来判断一个数是否是2的幂次方。
*/
if(n <= 0) {
return false;
}
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isPowerOfTwo(n);
return 0;
}232. 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
说明:
- 你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, 和is empty操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例 1:
输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false] 解释: MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、peek和empty - 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用
pop或者peek操作)
进阶:
- 你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为
O(1)的队列?换句话说,执行n个操作的总时间复杂度为O(n),即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> inStack;
stack<int> outStack;
void transferStacks() {
while(!inStack.empty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.top());
inStack.pop();
}
}
public:
MyQueue() {
cout << "null, ";
}
void push(int x) { // 入栈
inStack.push(x);
cout << "null, ";
}
// 先把inStack的元素转移到outStack,再对outStack的元素出栈,
// 从而用两个栈实现队列先进先出的效果
int pop() { // 出栈
if(outStack.empty()) {
transferStacks();
}
int front = outStack.top();
outStack.pop();
return front;
}
int peek() { // 获取栈顶
if(outStack.empty()) {
transferStacks();
}
return outStack.top();
}
bool empty() {
return inStack.empty() && outStack.empty();
}
};
int main() {
cout << "[";
MyQueue myQueue;
myQueue.push(1);
myQueue.push(2);
cout << myQueue.peek() << ", ";
cout << myQueue.pop() << ", ";
cout << boolalpha << myQueue.empty();
cout << "]";
return 0;
}234. 回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为
回文链表
。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,2,1] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:false
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[1, 105]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9
进阶:你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Definition for single-linked list
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return true;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
// find the middle of the linked list(快慢指针法)
while(fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next; // 循环结束后slow所在位置即为middle
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// 反转后半部分单链表
ListNode* secondHalf = reverseList(slow->next);
// 比较前部分和反转后的后半部分链表值
while(secondHalf != NULL) {
if(head->val != secondHalf->val) {
return false;
}
head = head->next;
secondHalf = secondHalf->next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = NULL;
ListNode* curr = head;
while(curr != NULL) {
ListNode* nextTemp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
};
// 创建单链表
ListNode* createList() {
ListNode* head = NULL;
ListNode* current = NULL;
int val;
while(cin >> val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
current = newNode;
} else {
current->next = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
ListNode* head = createList();
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isPalindrome(head);
return 0;
} 242. 有效的字母异位词
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
示例 1:
输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" 输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = "rat", t = "car" 输出: false
提示:
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 5 * 104s和t仅包含小写字母
进阶: 如果输入字符串包含 unicode 字符怎么办?你能否调整你的解法来应对这种情况?
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) { // 长度不等
return false;
}
unordered_map<char, int> count;
for(char c : s) { // 统计每个字符出现的次数
count[c]++;
}
for(char c : t) {
if(count.find(c) == count.end() || count[c] == 0) { // 找不到对应字符或字符出现次数不等
return false;
}
count[c]--;
}
return true;
}
// 或
bool isAnagram2(string s, string t) {
int record[26] = {0};
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
record[s[i] - 'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) {
record[t[i] - 'a']--;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if(record[i] != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
string s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isAnagram2(s, t);
return 0;
}257. 二叉树的所有路径
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5] 输出:["1->2->5","1->3"]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:["1"]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void binaryTreePathsHelper(TreeNode* root, string path, vector<string>& result) {
if(root == NULL) {
return;
}
path += to_string(root->val);
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
result.push_back(path);
} else {
path += "->";
binaryTreePathsHelper(root->left, path, result);
binaryTreePathsHelper(root->right, path, result);
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> result;
if(root == NULL) {
return result;
}
binaryTreePathsHelper(root, "", result);
return result;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Solution solution;
vector<string> paths = solution.binaryTreePaths(root);
for(string path : paths) {
cout << path << endl;
}
return 0;
}258. 各位相加
给定一个非负整数 num,反复将各个位上的数字相加,直到结果为一位数。返回这个结果。
示例 1:
输入: num = 38 输出: 2 解释: 各位相加的过程为: 38 --> 3 + 8 --> 11 11 --> 1 + 1 --> 2 由于 2是一位数,所以返回 2。
示例 2:
输入: num = 0 输出: 0
提示:
0 <= num <= 2^31 - 1
进阶:你可以不使用循环或者递归,在 O(1) 时间复杂度内解决这个问题吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int addDigits(int num) {
while(num >= 10) { // 直到结果为1位数
int sum = 0;
while(num > 0) {
sum += num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
num = sum;
}
return num;
}
};
int main() {
int num;
cin >> num;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.addDigits(num);
return 0;
}263. 丑数
丑数 就是只包含质因数 2、3 和 5 的正整数。
给你一个整数 n ,请你判断 n 是否为 丑数 。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 6 输出:true 解释:6 = 2 × 3
示例 2:
输入:n = 1
输出:true
解释:1 没有质因数,因此它的全部质因数是 {2, 3, 5} 的空集。习惯上将其视作第一个丑数。
示例 3:
输入:n = 14 输出:false 解释:14 不是丑数,因为它包含了另外一个质因数 7 。
提示:
-2^31 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isUgly(int n) {
if(n <= 0) {
return false;
}
while(n != 1 && n % 2 == 0) {
n /= 2;
}
while(n != 1 && n % 3 == 0) {
n /= 3;
}
while(n != 1 && n % 5 == 0) {
n /= 5;
}
return n == 1;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.isUgly(n);
return 0;
}268. 丢失的数字
给定一个包含 [0, n] 中 n 个数的数组 nums ,找出 [0, n] 这个范围内没有出现在数组中的那个数。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,0,1] 输出:2 解释:n = 3,因为有 3 个数字,所以所有的数字都在范围 [0,3] 内。2 是丢失的数字,因为它没有出现在 nums 中。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1] 输出:2 解释:n = 2,因为有 2 个数字,所以所有的数字都在范围 [0,2] 内。2 是丢失的数字,因为它没有出现在 nums 中。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1] 输出:8 解释:n = 9,因为有 9 个数字,所以所有的数字都在范围 [0,9] 内。8 是丢失的数字,因为它没有出现在 nums 中。
示例 4:
输入:nums = [0] 输出:1 解释:n = 1,因为有 1 个数字,所以所有的数字都在范围 [0,1] 内。1 是丢失的数字,因为它没有出现在 nums 中。
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 10^40 <= nums[i] <= nnums中的所有数字都 独一无二
进阶:你能否实现线性时间复杂度、仅使用额外常数空间的算法解决此问题?
解法一:通过计算期望和实际的和之间的差来找出丢失的数字
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
// 通过计算期望和实际的和之间的差来找出丢失的数字
int n = nums.size();
int expectedSum = n * (n + 1) / 2;
int actualSum = 0;
for(int num : nums) {
actualSum += num;
}
return expectedSum - actualSum;
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.missingNumber(nums);
return 0;
}解法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
// 利用异或运算的性质:相同为0,相异为1
int result = nums.size();
int n= nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result ^= i ^ nums[i];
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.missingNumber(nums);
return 0;
}278. 第一个错误的版本
你是产品经理,目前正在带领一个团队开发新的产品。不幸的是,你的产品的最新版本没有通过质量检测。由于每个版本都是基于之前的版本开发的,所以错误的版本之后的所有版本都是错的。
假设你有 n 个版本 [1, 2, ..., n],你想找出导致之后所有版本出错的第一个错误的版本。
你可以通过调用 bool isBadVersion(version) 接口来判断版本号 version 是否在单元测试中出错。实现一个函数来查找第一个错误的版本。你应该尽量减少对调用 API 的次数。
示例 1:
输入:n = 5, bad = 4 输出:4 解释:调用 isBadVersion(3) -> false 调用 isBadVersion(5) -> true 调用 isBadVersion(4) -> true所以,4 是第一个错误的版本。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1, bad = 1 输出:1
提示:
1 <= bad <= n <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// The API isBadVersion is defined for you
// bool isBadVersion(int version)
class Solution {
public:
int firstBadVersion(int n) {
// 二分查找法
int left = 0, right = n;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(isBadVersion(mid)) { // 是错误版本
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
};
int main() {
int n, bad;
cin >> n >> bad;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.firstBadVersion(n);
return 0;
}283. 移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
示例 2:
输入: nums = [0] 输出: [0]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 1
进阶:你能尽量减少完成的操作次数吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
// 双指针法
// 在循环中,右指针right向右移动,如果当前元素不为0,
// 则将其与左指针指向的元素交换,并且左指针向右移动。
int n = nums.size();
int left = 0, right = 0;
while(right < n) {
if(nums[right] != 0) {
swap(nums[left], nums[right]);
left++;
}
right++;
}
}
};
int main() {
int temp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> temp) {
nums.push_back(temp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
solution.moveZeroes(nums);
for(int num : nums) {
cout << num << " ";
}
return 0;
}290. 单词规律
给定一种规律 pattern 和一个字符串 s ,判断 s 是否遵循相同的规律。
这里的 遵循 指完全匹配,例如, pattern 里的每个字母和字符串 s 中的每个非空单词之间存在着双向连接的对应规律。
示例1:
输入: pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat dog" 输出: true
示例 2:
输入:pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat fish" 输出: false
示例 3:
输入: pattern = "aaaa", s = "dog cat cat dog" 输出: false
提示:
1 <= pattern.length <= 300pattern只包含小写英文字母1 <= s.length <= 3000s只包含小写英文字母和' 's不包含 任何前导或尾随对空格s中每个单词都被 单个空格 分隔
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool wordPattern(string pattern, string s) {
// 1. 首先将字符串s按空格分割成单词,并存储在一个vector中
vector<string> words;
stringstream ss(s);
string word;
while(ss >> word) {
words.push_back(word);
}
// 2. 判断pattern和单词数目是否相同,如果不同则直接返回false
if(pattern.size() != words.size()) {
return false;
}
// 3. 分别建立两个映射表,一个用来存储字符到单词的映射,另一个用来存储单词到字符的映射
unordered_map<char, string> charToWord;
unordered_map<string, char> wordToChar;
// 4. 遍历pattern和单词数组,依次建立字符到单词、单词到字符的映射关系
for(int i = 0; i < pattern.size(); ++i) {
char c = pattern[i];
string w = words[i];
if(charToWord.find(c) == charToWord.end() && wordToChar.find(w) == wordToChar.end()) {
charToWord[c] = w;
wordToChar[w] = c;
} else {
// 5. 在建立映射的过程中,如果发现当前字符对应的单词与之前存储的不一致,直接返回false
if(charToWord[c] != w || wordToChar[w] != c) {
return false;
}
}
}
// 6. 如果遍历结束后没有发现不一致的情况,则返回true
return true;
}
};
int main() {
string pattern, s;
cin >> pattern;
getline(cin >> ws, s);
Solution solution;
cout << boolalpha << solution.wordPattern(pattern, s);
return 0;
}292. Nim游戏
你和你的朋友,两个人一起玩 Nim 游戏:
- 桌子上有一堆石头。
- 你们轮流进行自己的回合, 你作为先手 。
- 每一回合,轮到的人拿掉 1 - 3 块石头。
- 拿掉最后一块石头的人就是获胜者。
假设你们每一步都是最优解。请编写一个函数,来判断你是否可以在给定石头数量为 n 的情况下赢得游戏。如果可以赢,返回 true;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4 输出:false 解释:以下是可能的结果: 1. 移除1颗石头。你的朋友移走了3块石头,包括最后一块。你的朋友赢了。 2. 移除2个石子。你的朋友移走2块石头,包括最后一块。你的朋友赢了。 3.你移走3颗石子。你的朋友移走了最后一块石头。你的朋友赢了。 在所有结果中,你的朋友是赢家。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:true
示例 3:
输入:n = 2 输出:true
提示:
1 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool canWinNim(int n) {
/*
如果石头数量 n 为 4 的倍数,那么无论你拿走多少块石头,
最后都会留给你的朋友 4 的倍数块石头,从而使得你的朋友获胜。
如果石头数量 n 不是 4 的倍数,那么你可以通过控制每一步的石头数量,
确保最终留给你的朋友的石头数量是 4 的倍数,从而你获胜
*/
return n % 4 != 0;
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << boolalpha << solution.canWinNim(n);
return 0;
}295. 数据流的中位数
中位数是有序整数列表中的中间值。如果列表的大小是偶数,则没有中间值,中位数是两个中间值的平均值。
- 例如
arr = [2,3,4]的中位数是3。 - 例如
arr = [2,3]的中位数是(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5。
实现 MedianFinder 类:
-
MedianFinder()初始化MedianFinder对象。 -
void addNum(int num)将数据流中的整数num添加到数据结构中。 -
double findMedian()返回到目前为止所有元素的中位数。与实际答案相差10-5以内的答案将被接受。
示例 1:
输入 ["MedianFinder", "addNum", "addNum", "findMedian", "addNum", "findMedian"] [[], [1], [2], [], [3], []] 输出 [null, null, null, 1.5, null, 2.0] 解释 MedianFinder medianFinder = new MedianFinder(); medianFinder.addNum(1); // arr = [1] medianFinder.addNum(2); // arr = [1, 2] medianFinder.findMedian(); // 返回 1.5 ((1 + 2) / 2) medianFinder.addNum(3); // arr[1, 2, 3] medianFinder.findMedian(); // return 2.0
提示:
-10^5 <= num <= 10^5- 在调用
findMedian之前,数据结构中至少有一个元素 - 最多
5 * 104次调用addNum和findMedian
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class MedianFinder {
/*
最大堆用于存储数据流中较小的一半元素,最小堆用于存储数据流中较大的一半元素。
这样可以保证最大堆的堆顶元素是较小一半的最大值,
最小堆的堆顶元素是较大一半的最小值,从而方便计算中位数。
*/
private:
priority_queue<int> maxHeap; // 最大堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > minHeap; // 最小堆
public:
// 初始化MedianFinder对象
MedianFinder() {
}
// 将数据流中的整数num添加到数据结构中
void addNum(int num) {
if(maxHeap.empty() || num <= maxHeap.top()) {
maxHeap.push(num);
} else {
minHeap.push(num);
}
if(maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size() + 1) {
minHeap.push(maxHeap.top());
maxHeap.pop();
} else if(minHeap.size() > maxHeap.size()) {
maxHeap.push(minHeap.top());
minHeap.pop();
}
}
// 返回到目前为止所有元素的中位数
double findMedian() {
if(maxHeap.size() == minHeap.size()) {
return (maxHeap.top() + minHeap.top()) / 2.0;
} else {
return maxHeap.top();
}
}
};
int main() {
MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder();
obj->addNum(1);
obj->addNum(2);
cout << obj->findMedian() << endl;
obj->addNum(3);
cout << obj->findMedian();
return 0;
}297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
序列化是将一个数据结构或者对象转换为连续的比特位的操作,进而可以将转换后的数据存储在一个文件或者内存中,同时也可以通过网络传输到另一个计算机环境,采取相反方式重构得到原数据。
请设计一个算法来实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。这里不限定你的序列 / 反序列化算法执行逻辑,你只需要保证一个二叉树可以被序列化为一个字符串并且将这个字符串反序列化为原始的树结构。
提示: 输入输出格式与 LeetCode 目前使用的方式一致,详情请参阅 LeetCode 序列化二叉树的格式。你并非必须采取这种方式,你也可以采用其他的方法解决这个问题。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] 输出:[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
示例 4:
输入:root = [1,2] 输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中结点数在范围
[0, 10^4]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// Definition for a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out; // 序列化
serializeHelper(root, out);
return out.str();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream in(data); // 从字符串中读取数据
return deserializeHelper(in);
}
private:
void serializeHelper(TreeNode* root, ostringstream& out) {
if(root) {
out << root->val << ' '; // 先序遍历
serializeHelper(root->left, out);
serializeHelper(root->right, out);
} else {
out << "# ";
}
}
TreeNode* deserializeHelper(istringstream& in) {
string val;
in >> val;
if(val == "#") {
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val)); // 根据先序遍历的顺序构建二叉树
root->left = deserializeHelper(in);
root->right = deserializeHelper(in);
return root;
}
};
// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {
cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";
int rootVal;
cin >> rootVal;
if(rootVal == -1)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int leftVal;
cin >> leftVal;
if (leftVal != -1) {
curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);
q.push(curr->left);
}
cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";
int rightVal;
cin >> rightVal;
if (rightVal != -1) {
curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
return root;
}
// 1 2 3 4 5
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) {
cout << "null ";
return;
}
cout << root->val << " ";
if(root->left != NULL || root->right != NULL) {
printTree(root->left);
printTree(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();
Codec ser, deser;
TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));
printTree(ans);
return 0;
}299. 猜数字游戏
你在和朋友一起玩 猜数字(Bulls and Cows)游戏,该游戏规则如下:
写出一个秘密数字,并请朋友猜这个数字是多少。朋友每猜测一次,你就会给他一个包含下述信息的提示:
- 猜测数字中有多少位属于数字和确切位置都猜对了(称为 "Bulls",公牛),
- 有多少位属于数字猜对了但是位置不对(称为 "Cows",奶牛)。也就是说,这次猜测中有多少位非公牛数字可以通过重新排列转换成公牛数字。
给你一个秘密数字 secret 和朋友猜测的数字 guess ,请你返回对朋友这次猜测的提示。
提示的格式为 "xAyB" ,x 是公牛个数, y 是奶牛个数,A 表示公牛,B 表示奶牛。
请注意秘密数字和朋友猜测的数字都可能含有重复数字。
示例 1:
输入:secret = "1807", guess = "7810" 输出:"1A3B" 解释:数字和位置都对(公牛)用 '|' 连接,数字猜对位置不对(奶牛)的采用斜体加粗标识。 "1807" | "7810"
示例 2:
输入:secret = "1123", guess = "0111" 输出:"1A1B" 解释:数字和位置都对(公牛)用 '|' 连接,数字猜对位置不对(奶牛)的采用斜体加粗标识。 "1123" "1123" | or | "0111" "0111" 注意,两个不匹配的 1 中,只有一个会算作奶牛(数字猜对位置不对)。通过重新排列非公牛数字,其中仅有一个 1 可以成为公牛数字。
提示:
1 <= secret.length, guess.length <= 1000secret.length == guess.lengthsecret和guess仅由数字组成
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string getHint(string secret, string guess) {
// 公牛表示数字和位置都猜对了,奶牛表示数字猜对了但位置不对
/*
首先遍历秘密数字和猜测数字,计算公牛的数量。
然后使用两个哈希表分别记录秘密数字和猜测数字中每个数字的出现次数。
接着再次遍历哈希表,计算奶牛的数量。
*/
int bulls = 0, cows = 0;
unordered_map<char, int> secretCount;
unordered_map<char, int> guessCount;
for(int i = 0; i < secret.size(); ++i) {
if(secret[i] == guess[i]) {
bulls++;
} else {
secretCount[secret[i]]++;
guessCount[guess[i]]++;
}
}
for(auto& pair : secretCount) {
char digit = pair.first;
cows += min(pair.second, guessCount[digit]);
}
return to_string(bulls) + "A" + to_string(cows) + "B";
}
};
int main() {
string secret, guess;
cin >> secret >> guess;
Solution solution;
cout << solution.getHint(secret, guess);
return 0;
}
300. 最长递增子序列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。
子序列 是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] 输出:4 解释:最长递增子序列是 [2,3,7,101],因此长度为 4 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3] 输出:4
示例 3:
输入:nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7] 输出:1
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 2500-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
进阶:
- 你能将算法的时间复杂度降低到
O(n log(n))吗?
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
/*
动态规划法
定义一个dp数组来保存 以每个元素结尾 的最长递增子序列的长度。
然后遍历数组,对于每个元素,再次遍历之前的元素,如果当前元素大于之前的元素,
则更新当前元素结尾的最长递增子序列长度 。
最终,返回dp数组中的最大值即为最长递增子序列长度
*/
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0) {
return 0;
}
vector<int> dp(n, 1);
int maxLength = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { // 从第二个元素开始
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if(nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
maxLength = max(maxLength, dp[i]);
}
return maxLength;
}
};
int main() {
int tmp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.lengthOfLIS(nums);
return 0;
}解法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
/*
使用二分查找法优化动态规划以将时间复杂度降低到O(nlog(n))时,
我们可以使用Patience Sorting算法。该算法的思想是模拟纸牌游戏”patience sorting",
在这个游戏中,我们需要将纸牌按照一定规则堆放,使得堆的数量最小。
*/
vector<int> tails;
for(int num : nums) {
auto it = lower_bound(tails.begin(), tails.end(), num);
if(it == tails.end()) {
// 如果 num 大于 tails 数组中的最后一个元素,将 num 加入 tails 数组的末尾。
tails.push_back(num);
} else {
// 否则,在 tails 数组中找到第一个大于等于 num 的元素,将其更新为 num
*it = num;
}
}
return tails.size();
}
};
int main() {
int tmp;
vector<int> nums;
while(cin >> tmp) {
nums.push_back(tmp);
if(cin.get() == '\n')
break;
}
Solution solution;
cout << solution.lengthOfLIS(nums);
return 0;
}





















 655
655

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








