lib和dll
lib和dll文件的区别和联系
.dll是在你的程序运行的时候才连接的文件,因此它是一种比较小的可执行文件格式,.dll还有其他的文件格式如.ocx等,所有的.dll文件都是可执行。
.lib是在你的程序编译连接的时候就连接的文件,因此你必须告知编译器连接的lib文件在那里。
一般来说,与动态连接文件相对比,lib文件也被称为是静态连接库。当你把代码编译成这几种格式的文件时,在以后他们就不可能再被更改。如果你想使用lib文件,就必须:
1 包含一个对应的头文件告知编译器lib文件里面的具体内容
2 设置lib文件允许编译器去查找已经编译好的二进制代码
实例:用Dev C++制作DLL文件
首先,新建一个DLL工程
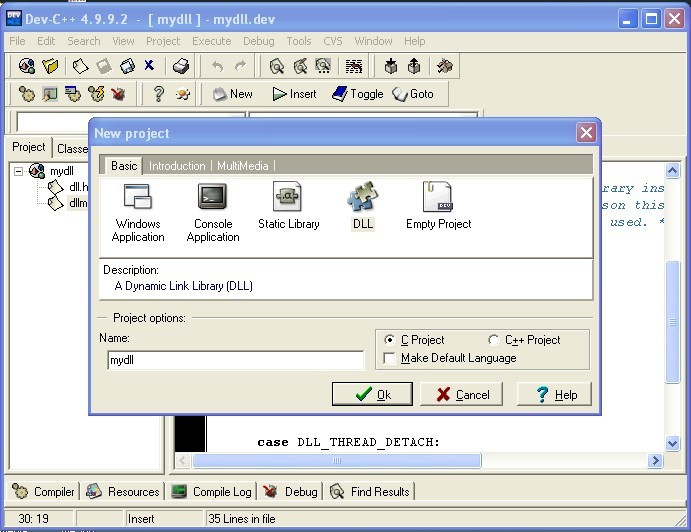
然后里面生成的文件如下
dll.h头文件
#ifndef _DLL_H_
#define _DLL_H_
#if BUILDING_DLL
# define DLLIMPORT __declspec (dllexport)
#else /* Not BUILDING_DLL */
# define DLLIMPORT __declspec (dllimport)
#endif /* Not BUILDING_DLL */
DLLIMPORT void HelloWorld (void);
#endif /* _DLL_H_ */
dllmain.c 源文件
/* Replace "dll.h" with the name of your header */
#include "dll.h"
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
DLLIMPORT void HelloWorld ()
{
MessageBox (0, "Hello World from DLL!/n", "Hi", MB_ICONINFORMATION);
}
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain (HINSTANCE hInst /* Library instance handle. */ ,
DWORD reason /* Reason this function is being called. */ ,
LPVOID reserved /* Not used. */ )
{
switch (reason)
{
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
break;
case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
break;
case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
break;
case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
break;
}
/* Returns TRUE on success, FALSE on failure */
return TRUE;
}
编译后生成功生成 mydll.dll 文件
使用部分:
新建工程Console Application: C Project
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//windows head file
#include <windows.h>
typedef void (*DLLFunc)(int);
int main()
{
DLLFunc dllFunc;
HINSTANCE hInstLibrary = LoadLibrary("mydll.dll");
if (hInstLibrary == NULL)
{
FreeLibrary(hInstLibrary);
}
dllFunc = (DLLFunc)GetProcAddress(hInstLibrary, "HelloWorld");
if (dllFunc == NULL)
{
FreeLibrary(hInstLibrary);
}
dllFunc(1);
FreeLibrary(hInstLibrary);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
编译运行:
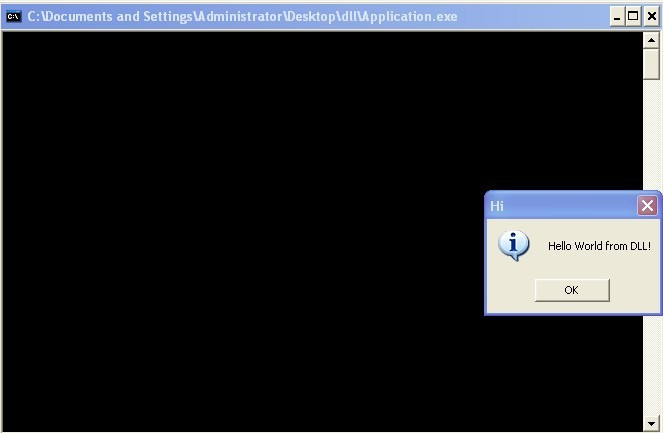




 本文详细解释了lib和dll文件的区别及联系。lib用于程序编译链接阶段,需告知编译器其位置;而dll则在程序运行时动态链接。文章还通过DevC++示例展示了如何创建和使用dll。
本文详细解释了lib和dll文件的区别及联系。lib用于程序编译链接阶段,需告知编译器其位置;而dll则在程序运行时动态链接。文章还通过DevC++示例展示了如何创建和使用dll。

















 6685
6685

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








