| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 11333 | Accepted: 4818 |
Description
- Choose any one of the 16 pieces.
- Flip the chosen piece and also all adjacent pieces to the left, to the right, to the top, and to the bottom of the chosen piece (if there are any).
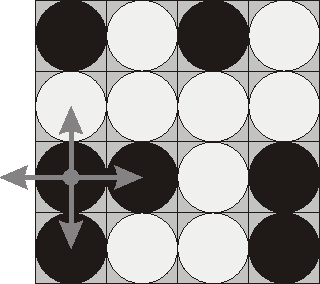 Consider the following position as an example:
Consider the following position as an example:
bwbw
wwww
bbwb
bwwb
Here "b" denotes pieces lying their black side up and "w" denotes pieces lying their white side up. If we choose to flip the 1st piece from the 3rd row (this choice is shown at the picture), then the field will become:
bwbw
bwww
wwwb
wwwb
The goal of the game is to flip either all pieces white side up or all pieces black side up. You are to write a program that will search for the minimum number of rounds needed to achieve this goal.
Input
Output
Sample Input
bwwb bbwb bwwb bwww
Sample Output
4
这是原题。
本题如果定义一个数组的话,遍历并判断状态 将是一件费时的事,此时可以想到用位来操作。
先讲一些位操作的基本知识:
int test = 0;
C中,int 有2个字节,C++/Java等语言中有4个字节,而一个字节有8位。
要使test的第一位变成1,则可做一个或运算:test | 1, 第二位变成1,则可这样:test | (1 << 1), 第三位变1,则:test | (1 << 2)。把某位变成0可以用与、非运算,如把第三位变成0,则test & ~(1 << 2) 。可以写一个程序试试:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 7; //7用2进制表示是111
b &= ~(a <<2);
cout<<b<<endl; //输出结果为3,用2进制表示是11
return 0;
}
要把两个数的各个位合并(就是有1即1),可用或运算,给一个示例:
int a = 5, b = 3;
a |= b;
cout<<a<<endl; //答案7把两个数的各个位相减,用抑或或运算,示例:
int a = 5, b = 3;
a ^= b;
cout<<a<<endl; //答案:6……之后还遇到什么位运算再补充。。。
本题 可用16位来表示各个状态,两位一个,用1来表示black,0表示white。则65536是全black的情况,0是全白的情况,这样的话,要判断是否已经得出结果时,就不用遍历16个元素了!!!
如本题:
bwwb
bbwb
bwwb
bwww
状态值为6585,计算方法为
1*2^0+0*2^1+0*2^2..1*2^12+0*2^13..=6585
下面是网上摘取的一段代码,呵呵,写得比我的好,转此来学习。
在此基础上进行BFS搜索,首先理解一点,先点(0,0)再点(0,1)与先点(0,1)再点(0,0)对结果不造成任何影响.因此遍历棋盘的16个位置,将每次点击后的状态id利用树状结构保存.如:
6585
/ | \ ...
(0,0) (0,1) (0,2)
/ | \ ...
6568 6553 6646
...............................
对此树进行BFS搜索,将id为0(全白)或65535(全黑)的时候则搜索成功,输出树的高度,否则输出"Impossible".
为了提高搜索效率,采用位运算,如果想将整数的二进制某一位翻转可采用id^=(1<<x)(x代表要翻转的位置)
#include "assert.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_STATE = 65536;
const int ALL_WHILE_STATE = 0;
const int ALL_BLACK_STATE = 65535;
const int WIDTH_OF_BOARD = 4;
const int SIZE_OF_BOARD = WIDTH_OF_BOARD * WIDTH_OF_BOARD; // 4 * 4
int ConvertPieceColorToInt(char color)
{
switch(color)
{
case 'b':
return 1;
case 'w':
return 0;
}
}
int FlipPiece(int state_id, int position)
{
state_id ^= (1 << position);
// up
if(position - 4 >= 0)
state_id ^= (1 << (position - 4));
// down
if(position + 4 < SIZE_OF_BOARD)
state_id ^= (1 << (position + 4));
// left
if(position % 4 != 0)
state_id ^= (1 << (position - 1));
// right
if(position % 4 != 3)
state_id ^= (1 << (position + 1));
return state_id;
}
int main()
{
int current_state_id = 0;
int state[MAX_STATE];
queue<int> search_queue;
memset(state, -1, sizeof(state));
char color;
for(int i = 0; i < SIZE_OF_BOARD; ++i)
{
cin >> color;
current_state_id += ConvertPieceColorToInt(color) << i;
}
if(current_state_id == ALL_WHILE_STATE
|| current_state_id == ALL_BLACK_STATE)
{
cout << "0" << endl;
return 0;
}
state[current_state_id] = 0;
search_queue.push(current_state_id);
int next_state_id;
while(!search_queue.empty())
{
current_state_id = search_queue.front();
search_queue.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < SIZE_OF_BOARD; ++i)
{
next_state_id = FlipPiece(current_state_id, i);
if(next_state_id == ALL_WHILE_STATE
|| next_state_id == ALL_BLACK_STATE)
{
cout << state[current_state_id] + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
assert(next_state_id < MAX_STATE);
if(state[next_state_id] == -1 /* not visited */)
{
state[next_state_id] = state[current_state_id] + 1;
search_queue.push(next_state_id);
}
}
}
cout << "Impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}























 829
829

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








